|
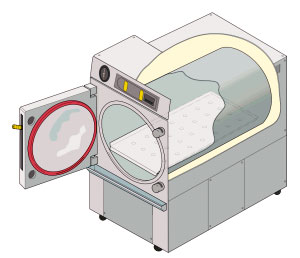
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoclave (industrial)
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for around 30-60 minutes at a pressure of 15 psi (103 kPa or 1.02 atm) depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Autoclave
A waste autoclave is a form of solid waste treatment that uses heat, steam and pressure of an industrial autoclave in the processing of waste. Waste autoclaves process waste either in batches or in continuous-flow processes. In batch processes, saturated steam is pumped into the autoclave at temperatures around 160 °C. Environment Agency Waste Technology Data Centre Evaluation of Estech Fibrecycle Process The steam pressure in the vessel is maintained up to 6 bar (gauge) for a period of up to 45 minutes to allow the process to fully 'cook' the waste. The autoclave process gives a very high and |
Hydrothermal Synthesis
Hydrothermal synthesis includes the various techniques of crystallizing substances from high-temperature aqueous solutions at high vapor pressures; also termed "hydrothermal method". The term " hydrothermal" is of geologic origin. Geochemists and mineralogists have studied hydrothermal phase equilibria since the beginning of the twentieth century. George W. Morey at the Carnegie Institution and later, Percy W. Bridgman at Harvard University did much of the work to lay the foundations necessary to containment of reactive media in the temperature and pressure range where most of the hydrothermal work is conducted. Hydrothermal synthesis can be defined as a method of synthesis of single crystals that depends on the solubility of minerals in hot water under high pressure. The crystal growth is performed in an apparatus consisting of a steel pressure vessel called an autoclave, in which a nutrient is supplied along with water. A temperature gradient is maintained between the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer time than was typical. Canning of foods is an extension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Waste
Biomedical waste or hospital waste is any kind of waste containing infectious (or potentially infectious) materials. It may also include waste associated with the generation of biomedical waste that visually appears to be of medical or laboratory origin (e.g. packaging, unused bandages, infusion kits etc.), as well research laboratory waste containing biomolecules or organisms that are mainly restricted from environmental release. As detailed below, discarded sharps are considered biomedical waste whether they are contaminated or not, due to the possibility of being contaminated with blood and their propensity to cause injury when not properly contained and disposed. Biomedical waste is a type of biowaste. Biomedical waste may be solid or liquid. Examples of infectious waste include discarded blood, sharps, unwanted microbiological cultures and stocks, identifiable body parts (including those as a result of amputation), other human or animal tissue, used bandages and dressings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterilization (microbiology)
Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life (particularly microorganisms such as fungi, bacteria, spores, and unicellular eukaryotic organisms) and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic. Applications Foods One of the first steps toward modernized sterilization was made by Nicolas Appert, who discovered that application of heat over a suitable period slowed the decay of foods and various liquids, preserving them for safe consumption for a longer time than was typical. Canning of foods is an extension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Crystals
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Piercing
Body piercing, which is a form of body modification, is the practice of puncturing or cutting a part of the human body, creating an opening in which jewelry may be worn, or where an implant could be inserted. The word ''piercing'' can refer to the act or practice of body piercing, or to an opening in the body created by this act or practice. It can also, by metonymy, refer to the resulting decoration, or to the decorative jewelry used. Piercing implants alter body and/or skin profile and appearance (e.g. golden threads installed subdermal, platinum, titanium or medical grade steel subdermal implants). Although the history of body piercing is obscured by popular misinformation and by a lack of scholarly reference, ample evidence exists to document that it has been practiced in various forms by multiple sexes since ancient times throughout the world.Body piercing can be performed on people of all ages, although most minors are only permitted to have earlobe piercings. Ear pierc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Digester
The steam digester or bone digester (also known as Papin’s digester) is a high-pressure cooker invented by French physicist Denis Papin in 1679. It is a device for extracting fats from bones in a high-pressure steam environment, which also renders them brittle enough to be easily ground into bone meal. It is the forerunner of the autoclave and the domestic pressure cooker. The steam-release valve, which was invented for Papin's digester following various explosions of the earlier models, inspired the development of the piston-and-cylinder steam engine. History The artificial vacuum was first produced in 1643 by Italian scientist Evangelista Torricelli and further developed by German scientist Otto von Guericke with his Magdeburg hemispheres. Guerike's demonstration was documented by Gaspar Schott, in a book that was read by Robert Boyle. Boyle and his assistant Robert Hooke improved Guericke's air pump design and built their own. From this, through various experiments, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
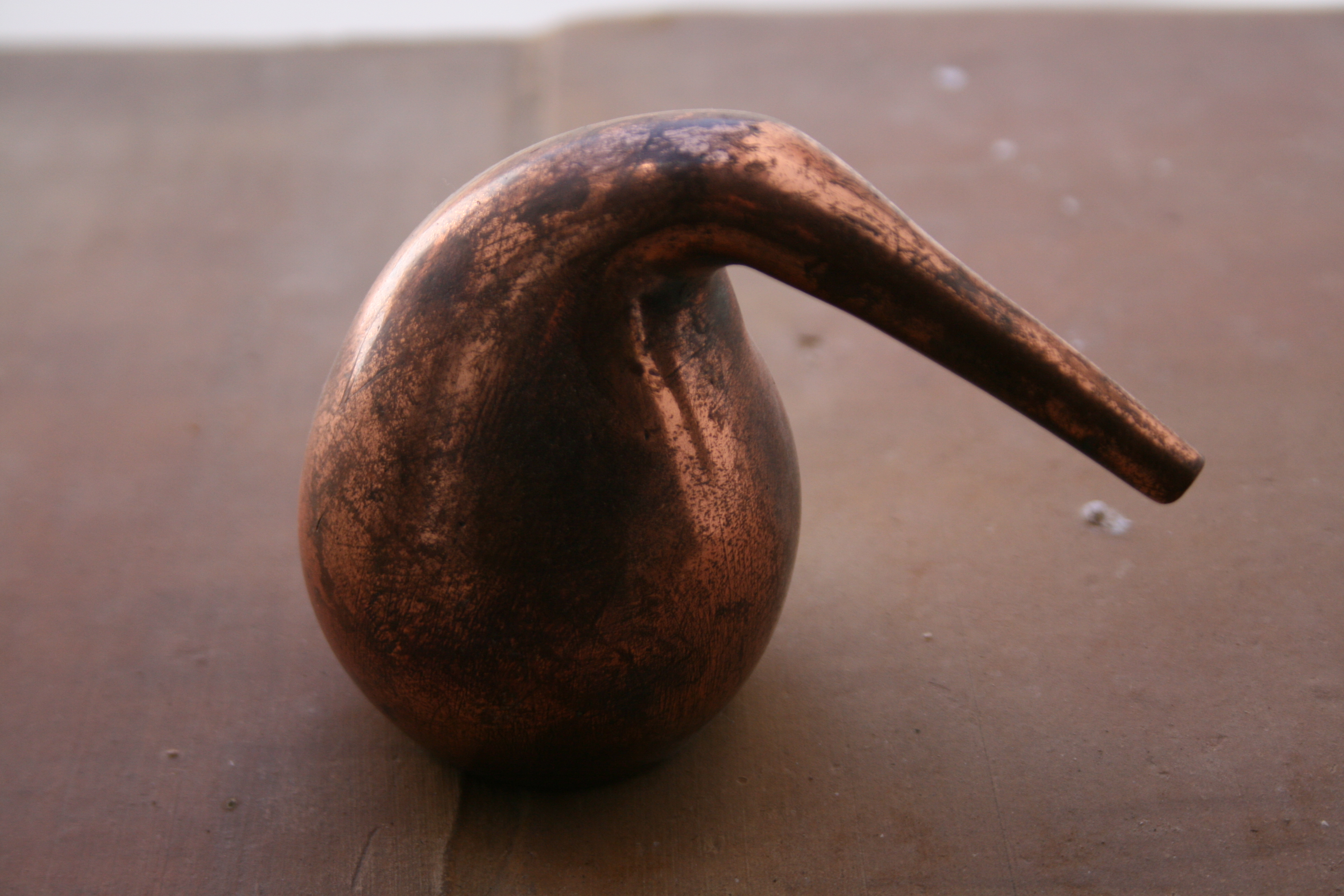
Retort
In a chemistry laboratory, a retort is a device used for distillation or dry distillation of substances. It consists of a spherical vessel with a long downward-pointing neck. The liquid to be distilled is placed in the vessel and heated. The neck acts as a condenser, allowing the vapors to condense and flow along the neck to a collection vessel placed underneath. In the chemical industry, a retort is an airtight vessel in which substances are heated for a chemical reaction producing gaseous products to be collected in a collection vessel or for further processing. Such industrial-scale retorts are used in shale oil extraction, the production of charcoal and in the recovery of mercury in gold mining processes and hazardous waste. A process of heating oil shale to produce shale oil, oil shale gas, and spent shale is commonly called retorting. Airtight vessels to apply pressure as well as heat are called autoclaves. In the food industry, pressure cookers are often referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattooing
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, and/or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern tattoo machines. The history of tattooing goes back to Neolithic times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), or pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item). Many tattoos serve as rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of fertility, pledges of love, amulets and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves and convicts. Extensive decorative tattooing has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Chamberland
Charles Chamberland (; 12 March 1851 – 2 May 1908) was a French microbiologist from Chilly-le-Vignoble in the department of Jura who worked with Louis Pasteur. In 1884 he developed a type of filtration known today as the Chamberland filter or Chamberland-Pasteur filter, a device that made use of an unglazed porcelain bar. The filter had pores that were smaller than bacteria, thus making it possible to pass a solution containing bacteria through the filter, and having the bacteria completely removed from the solution. Chamberland was also credited for starting a research project that led to the invention of the autoclave An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilizati ... device in 1879. References External links * Charles Edouard Chamberland and Louis Pasteur PasteurBrewi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |