|
Atlatl Cave
Atlatl Cave is an important archaeological site that contains organic evidence of occupation by Archaic North Americans . It is located at the west end of the Chaco Culture National Historical Park in San Juan County, New Mexico, at an elevation of 1910 meters. History During the 1970s, archaeologists discovered corn, beans, squash, a yucca fiber sandal, a variety of different kinds of miniature beads made from juniper, basketry, juniperus monoserma and juniperus scopulorum twigs, p''seudotsuga'' ''menziesii'' wood fragments, and fabric made from rabbit fur in the cave. The breaths of the Archaic-age maize pollen grains are significantly larger than Puebloan and present maize pollen. They also found part of an atlatl, or spear-thrower A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Period In North America
In the classification of the archaeological cultures of North America, the Archaic period in North America, taken to last from around 8000 to 1000 BC in the sequence of North American pre-Columbian cultural stages, is a period defined by the ''archaic stage'' of cultural development. The Archaic stage is characterized by subsistence economies supported through the exploitation of nuts, seeds, and shellfish. As its ending is defined by the adoption of sedentary farming, this date can vary significantly across the Americas. The rest of the Americas also have an Archaic Period. Classifications This classification system was first proposed by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in the widely accepted 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology''. In the organization of the system, the Archaic period followed the Lithic stage and is superseded by the Formative stage. # The Lithic stage # The Archaic stage # The Formative stage # The Classic stage # The Post-Classic stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Culture National Historical Park
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important pre-Columbian cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major center of culture for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requiring generations of astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan County, New Mexico
San Juan County is located in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the population was 121,661 making it the fifth-most populous county in New Mexico. Its county seat is Aztec. The county was created in 1887. San Juan County is part of the Farmington, New Mexico, Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is in the state's northwest corner and includes the New Mexico portion of the Four Corners. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (0.5%) is water. Indian reservations (and off-reservation trust lands) comprise 63.4 percent of the county's land area: The Navajo Nation takes up 60.45% and the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe Reservation another 2.93%. The physical features include three rivers: the San Juan, Animas, and La Plata rivers; also, the Chuska Mountains and Shiprock Pinnacle to the west, volcanic structures, buttes, mesas, badlands, and fertile river valleys. Adjacent counties * Rio Arriba County - eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish flowers. They are native to the hot and dry (arid) parts of the Americas and the Caribbean. Early reports of the species were confused with the cassava (''Manihot esculenta''). Consequently, Linnaeus mistakenly derived the generic name from the Taíno word for the latter, ''yuca''. The Aztecs living in Mexico since before the Spanish arrival, in Nahuatl, call the local yucca species (''Yucca gigantea'') , which gave the Spanish . is also used for ''Yucca filifera''. Distribution The natural distribution range of the genus ''Yucca'' (49 species and 24 subspecies) covers a vast area of the Americas. The genus is represented throughout Mexico and extends into Guatemala (''Yucca guatemalensis''). It also extends to the north through Baja Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a bearing surface which allows the user to store energy during the throw. It may consist of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the spear. It's usually about as long as the user's arm or forearm. The user holds the spear-thrower in one hand, gripping near the end farthest from the cup. The user puts the butt end of the spear, or dart, in the cup, or grabs the spur with the end of the spear. The spear is much longer than the thrower. The user holds the spear parallel to the spear-thrower and going in the other direction. The user can hold the spear, with the index and thumb, with the same hand as the thrower, with the other fingers. The user reaches back with the spear pointed at the target. Then they make an overhand throwing motion with the thrower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In New Mexico
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
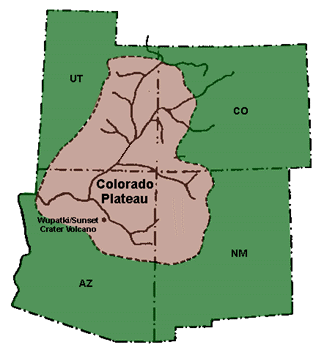
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The people and their archaeological culture are often referred to as ''Anasazi'', meaning "ancient enemies", as they were called by Navajo. Contemporary Puebloans object to the use of this term, with some viewing it as derogatory. The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)