|
Asamanja
Asamanjasa (), also rendered Asamanja, is the eldest son of King King Sagara, Sagara and one of his two queens, Keshini, in Hindu Literature, Hindu literature. Legend Ramayana The birth of Asamanjasa is described in the Ramayana. King Sagara of the Solar dynasty, Suryavamsha dynasty married Keshini and Sumati, but still lacked heirs for several years. Thus, accompanied by his two queens, he set forth towards the mountain Bhṛguprasravaṇa in the Himalayas, and performed a long Tapas (Indian religions), tapas. Pleased, the sage Bhrigu offered the king a boon: One of his queens would give birth to one son, but one who would further the dynasty's line, and his other queen would produce 60,000 sons. After a few years, Keshini gave birth to Asamanjasa, and Sumati gave birth to the 60,000 sons. According the text, the prince was a wild and wicked young man. He used to throw young boys playing in Sarayu river into great depths, and see them drown. Thus, his father Sagara (Vedic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Sagara
Sagara () is a king of the Suryavamsha dynasty in Hinduism. The son of Bahuka, he ruled the city of Ayodhya, with two wives, and 60,001 sons. Legend Birth Sagara was born to Bāhuka, and his wife, Yadavi, at the ashrama of Sage Aurva, while seeking refuge in the hermitage from the attacks of Tālajaṅgha, the king of Hehaya. While Yadavi was in the seventh month of her pregnancy, her co-wife administered a poison to her, due to which she remained pregnant for seven years. When Bahuka passed away in the hermitage, Yadavi was ready to follow him in his funeral pyre, but was prevented by Aurva, who promised her that her child would grow up to become a great and fortunate emperor. Yadavi delivered shortly. As the poison (''gara'') given to her by her co-wife had immobilised her pregnancy, Aurva named her son Sagara (Sa-with, gara-poison). Reign Sage Aurva conducted the Upanayana ceremony of Sagara, and taught him the Vedas. Once, Yadavi wept to hear the boy address ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amshuman
Anshuman () is a king of the Suryavamsha dynasty in Hinduism. The son of Asamanjasa, Anshuman becomes the king of Ayodhya after the death of his grandfather, King Sagara. Anshuman's grandson, Bhagiratha, brings the flow of the Ganges down from heaven. Legend Quest When King Sagara performs the ashvamedha yajna, Indra steals the sacrificial horse. Sagara asks his 60,000 sons, including Amshuman's father, Asamanjasa, to go and fetch it. The sons venture to the netherworld, and find the horse tied beside the meditating Sage Kapila. The sons create a great din upon their discovery, disturbing the penance of the sage. As a consequence, Kapila burns them to ashes with his fiery eyes. When Sagara's sons do not return, he requests his grandson, Amshuman, to go and look for them. Discovery Amshuman follows the path that his father and uncles took to Patala In Indian religions, Patala ( Sanskrit: पाताल, IAST: pātāla, lit. ''that which is below the feet''), de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagara (Vedic King)
Sagara () is a king of the Suryavamsha dynasty in Hinduism. The son of Bahuka, he ruled the city of Ayodhya, with two wives, and 60,001 sons. Legend Birth Sagara was born to Bāhuka, and his wife, Yadavi, at the ashrama of Sage Aurva, while seeking refuge in the hermitage from the attacks of Tālajaṅgha, the king of Hehaya. While Yadavi was in the seventh month of her pregnancy, her co-wife administered a poison to her, due to which she remained pregnant for seven years. When Bahuka passed away in the hermitage, Yadavi was ready to follow him in his funeral pyre, but was prevented by Aurva, who promised her that her child would grow up to become a great and fortunate emperor. Yadavi delivered shortly. As the poison (''gara'') given to her by her co-wife had immobilised her pregnancy, Aurva named her son Sagara (Sa-with, gara-poison). Reign Sage Aurva conducted the Upanayana ceremony of Sagara, and taught him the Vedas. Once, Yadavi wept to hear the boy address the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayodhya
Ayodhya (; ) is a city situated on the banks of holy river Saryu in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Ayodhya, also known as Saketa, is an ancient city of India, the birthplace of Rama and setting of the great epic Ramayana. Ayodhya was once the capital of the ancient Kosala Kingdom. It has an average elevation of 93 meters (305 feet). Owing to the belief as the birthplace of Rama, Ayodhya (Awadhpuri) has been regarded as first one of the seven most important pilgrimage sites (Mokshdayini Sapt Puris) for Hindus. The early Buddhist and Jain canonical texts mention that the religious leaders Gautama Buddha and Mahavira visited and lived in the city. The Jain texts also describe it as the birthplace of five tirthankaras namely, Rishabhanatha, Ajitanatha, Abhinandananatha, Sumatinath and Anantnath, and associate it with the legendary Bharata Chakravarti. From the Gupta period onwards, several sources mention Ayodhya and Saketa as the name of the same city. Owing to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashvamedha
The Ashvamedha ( sa, अश्वमेध, aśvamedha, translit-std=IAST) was a horse sacrifice ritual followed by the Śrauta tradition of Vedic religion. It was used by ancient Indian kings to prove their imperial sovereignty: a horse accompanied by the king's warriors would be released to wander for a year. In the territory traversed by the horse, any rival could dispute the king's authority by challenging the warriors accompanying it. After one year, if no enemy had managed to kill or capture the horse, the animal would be guided back to the king's capital. It would be then sacrificed, and the king would be declared as an undisputed sovereign. The best-known text describing the sacrifice is the '' Ashvamedhika Parva'' ( sa, अश्वमेध पर्व), or the "Book of Horse Sacrifice," the fourteenth of eighteen books of the Indian epic poem ''Mahabharata''. Krishna and Vyasa advise King Yudhishthira to perform the sacrifice, which is described at great length. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harivamsa
The ''Harivamsa'' ( , literally "the genealogy of Hari") is an important work of Sanskrit literature, containing 16,374 shlokas, mostly in the '' anustubh'' metre. The text is also known as the ''Harivamsa Purana.'' This text is believed to be a ''khila'' (appendix or supplement) to the MahabharataThe Mahabharata in Sanskrit: Book I: Chapter 2 in sacred-texts.com website and is traditionally ascribed to . The most celebrated commentary of the ''Mahabharata'' by Neelakantha Chaturdhara, the ''Bharata Bhava Deepa'' also covers the ''Harivamsa''. According to a tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
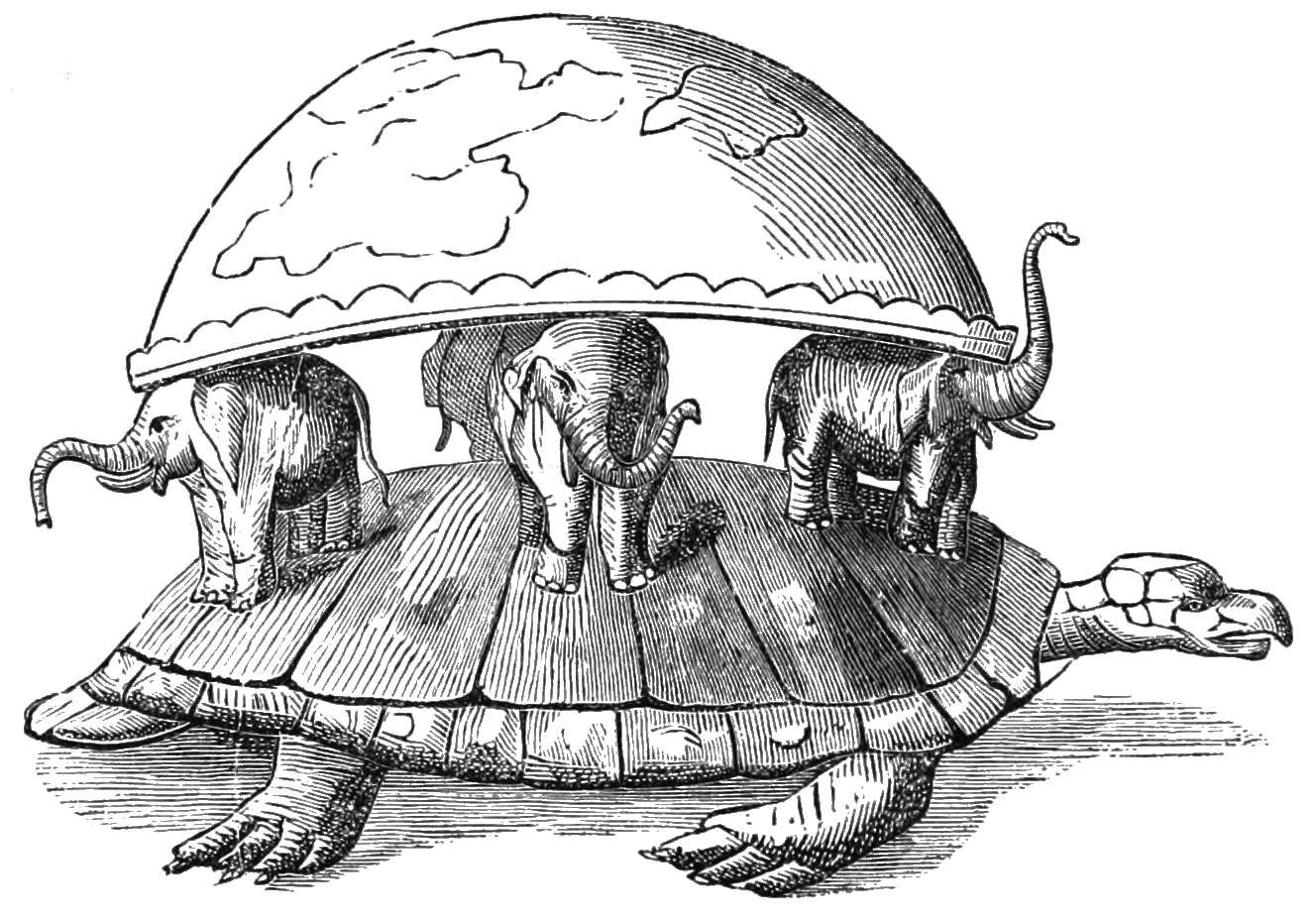
World Elephant
The Ashtadiggajas () is a group of eight legendary elephants that appear in Hindu cosmology, serving as the guardians of the eight zones of the universe. There are also eight female elephants that stand beside the Ashtadiggajas, referred to as the Ashtadikkarinis. List There are a total of eight Ashtadiggjas and Ashtadikkarinis that stand guard over the eight zones: Literature Besides the Ashtadiggajas, there are four elephants who support the earth from the four directions from the netherworld, whose names are given in the Ramayana: Virūpākṣa (east), Mahāpadmasama (south), Saumanasa (west), and Bhadra (north). In popular culture The popular rendition of the World Turtle supporting one or several World Elephants is recorded in 1599 in a letter by Emanual de Veiga. Wilhelm von Humboldt claimed, without any proof, that the idea of a world-elephant maybe due to a confusion, caused by the Sanskrit noun Nāga having the dual meaning of "serpent" and "elephant" (named for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapila
Kapila ( sa, कपिल), also referred to as Cakradhanus, is a sage in Hindu tradition. According to Bhagavata Purana, he is the son of the sage Kardama and Devahuti, the daughter of the Svayambhuva Manu. Kardama had nine daughters, who were very learned and went ahead to marry Marici, as well as other great sages. When he came of age, Kapila is most well-known as the founder of the Samkhya school of Hindu philosophy., Quote:"Kapila (fl. 550 BC), Vedic sage and founder of the system of Samkhya, one of the six schools of Vedic philosophy." Kapila of Samkhya fame is considered a Vedic sage, estimated to have lived in the 6th-century BCE, or the 7th-century BCE. His home was in Mithila. His influence by Buddha and Buddhism have long been the subject of scholarly studies. According to the Brahmanda Purana, Kapila is described to be an incarnation of Vishnu: "Bhagavān Nārāyaṇa will protect us all. The Lord of the universe has now been born in the world as Kapilācārya." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patala
In Indian religions, Patala (Sanskrit: पाताल, IAST: pātāla, lit. ''that which is below the feet''), denotes the subterranean realms of the universe – which are located under the earthly dimension. Patala is often translated as underworld or netherworld. Patala is described as more beautiful than Svarga (subtle dimensions, loosely translated as heaven). Patala is described as filled with splendid jewels, beautiful groves and lakes. In Vajrayana Buddhism, caves inhabited by asuras are entrances to Patala; these asuras, particularly female asuras, are often "tamed" (converted to Buddhism) as dharmapala or dakinis by famous Buddhist figures such as Padmasambhava. In Hindu cosmology, the universe is divided into the three worlds: Svarga, Prithvi or Martya (earth/mortal plane) and Patala (gross dimensions, the underworld). Patala is composed of seven realms/dimensions or lokas, the seventh and lowest of them is also called Patala or Naga-loka, the region of the Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deva (Hinduism)
''Deva'' (; Sanskrit: , ) means "shiny", "exalted", "heavenly being", "divine being", "anything of excellence", and is also one of the Sanskrit terms used to indicate a deity in Hinduism.Monier Monier-Williams, A Sanskrit-English Dictionary” Etymologically and Philologically Arranged to cognate Indo-European Languages, Motilal Banarsidass, page 492 ''Deva'' is a masculine term; the feminine equivalent is '' Devi''. In the earliest Vedic literature, all supernatural beings are called ''Devas''George Williams (2008), A Handbook of Hindu Mythology, Oxford University Press, , pages 90, 112 and '' Asuras''. The concepts and legends evolved in ancient Indian literature, and by the late Vedic period, benevolent supernatural beings are referred to as ''Deva-Asuras''. In post-Vedic Hindu texts, such as the Puranas and the Itihasas of Hinduism, the ''Devas'' represent the good, and the ''Asuras'' the bad. In some medieval works of Indian literature, ''Devas'' are also referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indra
Indra (; Sanskrit: इन्द्र) is the king of the devas (god-like deities) and Svarga (heaven) in Hindu mythology. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes/ref> Indra's myths and powers are similar to other Indo-European deities such as Jupiter, Perun, Perkūnas, Zalmoxis, Taranis, Zeus, and Thor, part of the greater Proto-Indo-European mythology. Indra is the most referred deity in the ''Rigveda''. He is celebrated for his powers, and as the one who killed the great evil (a malevolent type of asura) named Vritra, who obstructed human prosperity and happiness. Indra destroys Vritra and his "deceiving forces", and thereby brings rains and sunshine as the saviour of mankind. He is also an important deity worshipped by the Kalash people, indicating his prominence in ancient Hinduism. Indra's significance diminishes in the post-Vedic Indian literature, but he still plays an important role in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yajna
Yajna ( sa, यज्ञ, yajña, translit-std=IAST, sacrifice, devotion, worship, offering) refers in Hinduism to any ritual done in front of a sacred fire, often with mantras.SG Nigal (1986), Axiological Approach to the Vedas, Northern Book, , pages 80–81 Yajna has been a Vedic tradition, described in a layer of Vedic literature called Brahmanas, as well as Yajurveda. The tradition has evolved from offering oblations and libations into sacred fire to symbolic offerings in the presence of sacred fire ( Agni). Yajna rituals-related texts have been called the ''Karma-kanda'' (ritual works) portion of the Vedic literature, in contrast to ''Jnana-kanda'' (knowledge) portion contained in the Vedic Upanishads. The proper completion of Yajna-like rituals was the focus of Mimansa school of Hindu philosophy. Yajna have continued to play a central role in a Hindu's rites of passage, such as weddings. Modern major Hindu temple ceremonies, Hindu community celebrations, or monastic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
.jpg)
