|
Army Group
An army group is a military organization consisting of several field armies, which is self-sufficient for indefinite periods. It is usually responsible for a particular geographic area. An army group is the largest field organization handled by a single commander – usually a full general or field marshal – and it generally includes between 400,000 and 1,000,000 soldiers. In the Polish Armed Forces and former Soviet Red Army an army group was known as a Front. The equivalent of an army group in the Imperial Japanese Army was a "general army" (). Army groups may be multi-national formations. For example, during World War II, the Southern Group of Armies (also known as the U.S. 6th Army Group) comprised the U.S. Seventh Army and the French First Army; the 21st Army Group comprised the British Second Army, the Canadian First Army and the US Ninth Army. In both Commonwealth and U.S. usage, the number of an army group is expressed in Arabic numerals (e.g., "12th Army Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO Joint Military Symbology
NATO Joint Military Symbology is the NATO standard for military map symbols. Originally published in 1986 as Allied Procedural Publication 6 (APP-6), NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems, the standard has evolved over the years and is currently in its fifth version (APP-6D). The symbols are designed to enhance NATO's joint interoperability by providing a standard set of common symbols. APP-6 constituted a single system of joint military symbology for land, air, space and sea-based formations and units, which can be displayed for either automated map display systems or for manual map marking. It covers all of the joint services and can be used by them. History The first basic military map symbols began to be used by western armies in the decades following the end of the Napoleonic Wars. During World War I, there was a degree of harmonisation between the British and French systems, including the adoption of the colour red for enemy forces and blue for allies; the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (United Kingdom)
The British Second Army was a field army active during the First and Second World Wars. During the First World War the army was active on the Western Front throughout most of the war and later active in Italy. During the Second World War the army was the main British contribution to the Normandy landings on 6 June 1944 and advance across Europe. First World War The Second Army was part of the British Army formed on 26 December 1914, when the British Expeditionary Force was split in two due to becoming too big to control its subordinate formations. The army controlled both III Corps and IV Corps. Second Army spent most of the war positioned around the Ypres salient, but was redeployed to Italy as part of the Italian Expeditionary Force between November 1917 and March 1918. In 1919 it was reconstituted as the British Army of the Rhine.Edmonds (1987) Commanders * 1914–1915 General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien * 1915–1917 General Sir Herbert Plumer * 1917–1918 General Sir Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm, German Crown Prince
Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince of Prussia (Friedrich Wilhelm Victor August Ernst; 6 May 1882 – 20 July 1951) was the eldest child of the last ''Kaiser'', the German Emperor, Wilhelm II, and his consort Augusta Victoria of Schleswig-Holstein. As Emperor Wilhelm's heir, he was the last Crown Prince of the German Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. Wilhelm became crown prince at the age of six in 1888, when his grandfather Frederick III died and his father became emperor. He was crown prince for 30 years until the fall of the empire on 9 November 1918. During World War I, he commanded the 5th Army from 1914 to 1916 and was commander of the Army Group German Crown Prince for the remainder of the war. After his return to Germany in 1923, he fought the Weimar Republic and campaigned for the reintroduction of the monarchy in Germany. After his plans to become president had been blocked by his father, Wilhelm supported Adolf Hitler's rise to power, but when Wilhelm rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (German Empire)
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (german: Deutsches Heer), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia, and was dissolved in 1919, after the defeat of the German Empire in World War I (1914–1918). In the Federal Republic of Germany, the term ' identifies the German Army, the land component of the '. Formation and name The states that made up the German Empire contributed their armies; within the German Confederation, formed after the Napoleonic Wars, each state was responsible for maintaining certain units to be put at the disposal of the Confederation in case of conflict. When operating together, the units were known as the Federal Army ('). The Federal Army system functioned during various conflicts of the 19th century, such as the First Schleswig War from 1848–50 but by the time of the Second Schleswig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
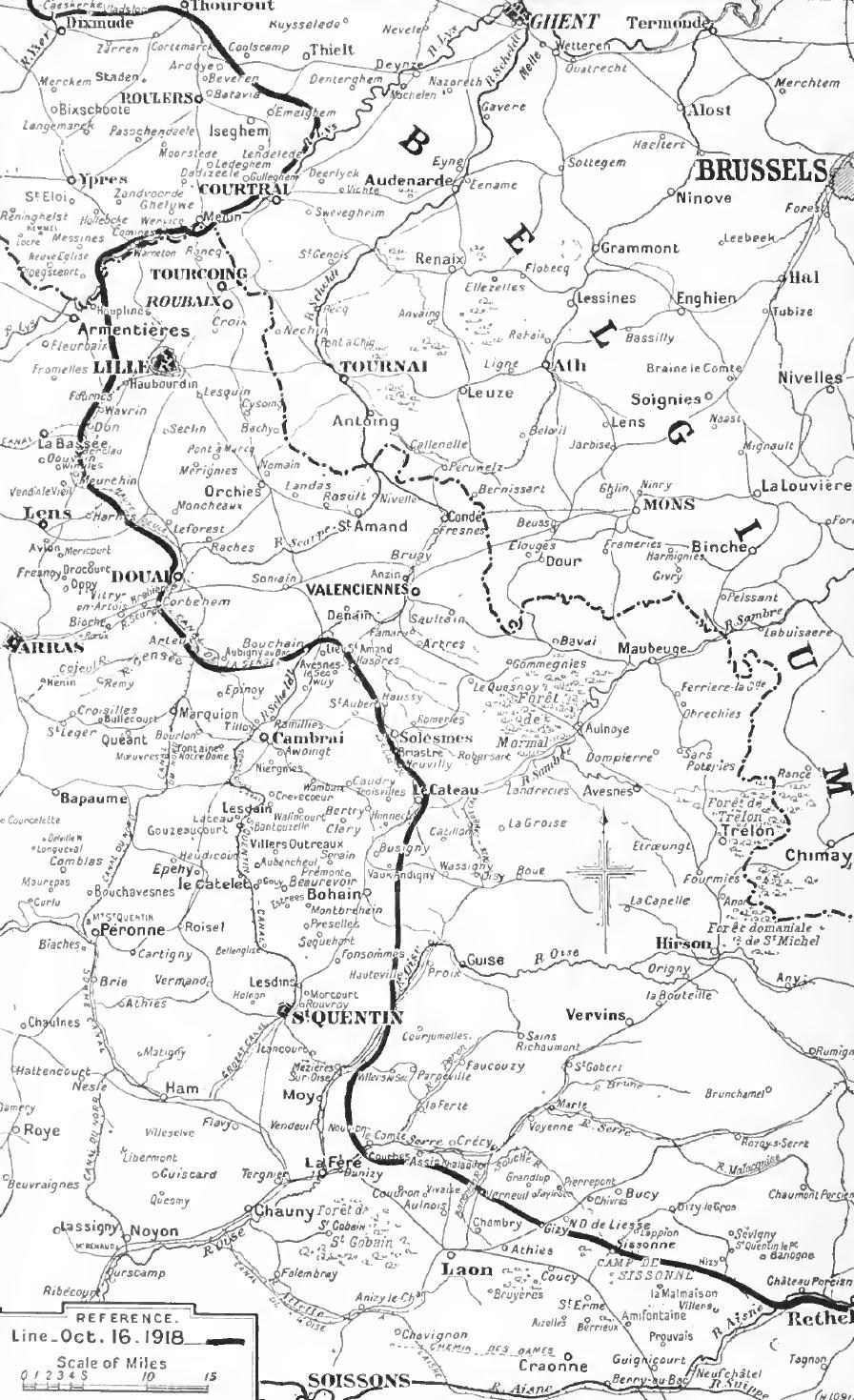
Hundred Days Offensive
The Hundred Days Offensive (8 August to 11 November 1918) was a series of massive Allies of World War I, Allied offensives that ended the First World War. Beginning with the Battle of Amiens (1918), Battle of Amiens (8–12 August) on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, the Allies pushed the Central Powers back, undoing their gains from the German spring offensive. The Germans retreated to the Hindenburg Line, but the Allies broke through the line with a series of victories, starting with the Battle of St Quentin Canal on 29 September. The offensive, together with a German Revolution of 1918–19, revolution breaking out in Germany, led to the Armistice of 11 November 1918 which ended the war with an Allied victory. The term "Hundred Days Offensive" does not refer to a battle or strategy, but rather the rapid series of Allied victories against which the German Army (German Empire), German Army had no reply. Background The German spring offensive of the German Army (Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Belgium
The Battle of Courtrai (also known as the Second Battle of Belgium (french: 2ème Bataille de Belgique) and the Battle of Roulers (french: Bataille de Roulers)) was one of a series of offensives in northern France and southern Belgium that took place in late September and October 1918. Background The (GAF) comprising twelve Belgian divisions, ten divisions of the British Second Army and six divisions of the French Sixth Army, under the command of King Albert I of Belgium, with the French General Jean Degoutte as Chief of Staff, defeated the German 4th Army in the Fifth Battle of Ypres The breaking of the Hindenburg Line further south, led the Allies to follow a strategy of pursuing the Germans for as long as possible, before movement was stopped by the winter rains. Mud and a collapse of the supply-system, had stopped the advance in early October but by the middle of the month, the GAF was ready to resume the offensive. Battle The offensive began at on 14 October, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I Of Belgium
Albert I (8 April 1875 – 17 February 1934) was King of the Belgians from 23 December 1909 until his death in 1934. Born in Brussels as the fifth child and second son of Prince Philippe, Count of Flanders and Princess Marie of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, Albert succeeded his uncle, Leopold II, to the Belgian throne in 1909. He married Elisabeth of Bavaria, with whom he had three children. Albert ruled during an eventful period in the history of Belgium, which included the period of World War I (1914–1918), when most of Belgium was occupied by German forces. Other crucial events of his reign included the adoption of the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919, the ruling of the Belgian Congo as an overseas possession of Belgium along with the League of Nations mandate of Ruanda-Urundi, the reconstruction of Belgium following the war, and the first five years of the Great Depression (1929–1934). Albert died in a mountaineering accident in eastern Belgium in 1934, at the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Flanders
The Fifth Battle of Ypres, also called the Advance in Flanders and the Battle of the Peaks of Flanders (french: Bataille des Crêtes de Flandres) is an informal name used to identify a series of World War I battles in northern France and southern Belgium (Flanders) from late September to October 1918. Background After the German spring offensive of 1918 failed to achieve a decisive victory, German morale waned and the increasing numbers of American soldiers arriving on the Western Front gave the Allies a growing numerical advantage over the western armies of the German Empire. To take advantage of this Marshal of France Ferdinand Foch developed a strategy which became known as the Grand Offensive, in which attacks were made on the German lines over as wide a front as possible. Belgian, British and French forces around the Ypres Salient were to form the northern pincer of an offensive towards the Belgian city of Liège. The British Second Army had followed up some minor wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Reserve (France)
Army Group Reserve (french: Groupe d'armées de réserve) or Army Group Rupture (french: Groupe d'armées de rupture), G. A. R.) was a grouping of French field armies during World War I, which was created on January 1, 1917 to fight in the Offensive of Chemin des Dames. The Army group was dissolved on May 8, 1917 after the failure of the Offensive. The Army Group was recreated after the German spring offensive of 1918. Composition April 15, 1917 * 6th Army (général Charles Mangin) * 10th Army (général Denis Auguste Duchêne) * 5th Army (général Olivier Mazel) March 23, 1918 * 1st Army (général Marie-Eugène Debeney) * 3rd Army (général Georges Louis Humbert) July 1, 1918 * 6th Army (général Jean Degoutte) * 10th Army (général Charles Mangin) Commanders * Général Joseph Alfred Micheler (January 1, 1917 – May 8, 1917) * Général Émile Fayolle Marie Émile Fayolle (14 May 1852 – 27 August 1928) was a French general during World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre (France)
Army Group Centre (french: Groupe d'armées du Centre, G. A. C.) was a grouping of French field armies during World War I, which was created on June 22, 1915. The army group covered the Western Front roughly between Rheims and Verdun. Composition July 1, 1915 from North to South : * 6th Army (général Pierre Joseph Dubois) * 5th Army (général Louis Franchet d'Espèrey) * 4th Army (général Fernand de Langle de Cary) February 15, 1917 From West to East : * 4th Army (général Pierre Roques) * 2nd Army (général Adolphe Guillaumat) Commanders * Général Édouard de Castelnau (June 22, 1915 – December 12, 1915) * Général Fernand de Langle de Cary (December 12, 1915 – May 2, 1916) * Général Philippe Pétain (May 2, 1916 – May 4, 1917) * Général Émile Fayolle Marie Émile Fayolle (14 May 1852 – 27 August 1928) was a French general during World War I and a diplomat, elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France. Early life Marie Émile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group East (France)
Army Group East (french: Groupe d'armées de l'Est, G. A. E.) was a grouping of French field armies during World War I, which was created on June 22, 1915 from the (G. P. E.) which had been formed in January 1915. The army group covered the Western Front from the Swiss border to roughly east of Verdun. Composition July 1, 1915 from North to South : * 3rd Army (général Maurice Sarrail) * Détachement d'armée de Lorraine (DAL) (général George Humbert) * 7th Army (général Louis de Maud'huy) February 15, 1917 From West to East : * 8th Army (général Augustin Gérard) * 7th Army (général Marie-Eugène Debeney) May 25, 1918 From West to East : * 2nd Army (général Auguste Hirschauer) * 8th Army (général Augustin Gérard) * 7th Army (général Antoine de Boissoudy) Commanders * Général Augustin Dubail (July 1, 1915 – March 31, 1916) * Général Louis Franchet d'Espèrey Louis Félix Marie François Franchet d'Espèrey (25 May 1856 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group North (France)
Army Group North (french: Groupe d'armées du Nord, GAN) was a grouping of French field armies during the First World War, which was created on June 13, 1915 from french: Groupe Provisoire du Nord (GPN) which had been formed on October 4, 1914. On July 6, 1918, GAN was renamed '' Groupe d'armées du Centre'' (GAC). Composition October 1914 * 2nd Army (général Philippe Pétain) * 10th Army (général Louis de Maud'huy) * Détachement d'Armée de Belgique (DAB) (général Victor d'Urbal) July 1, 1915 from North to South : * Belgian Army (general Félix Wielemans) * 36th French Army Corps (général de division Alexis Hély d'Oissel) * 2nd British Army (general Horace Smith-Dorrien) * 1st British Army (general Douglas Haig) * 10th French Army (général Victor d'Urbal) * 2nd French Army (général Philippe Pétain) July 1, 1916 from North to South : * 6th Army (général Émile Fayolle) * 10th Army (général Victor d'Urbal) February 15, 1917 from North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |