|
Archeocyatha
Archaeocyatha (or archaeocyathids 'ancient cups') is a taxon of extinct, sessile, reef-building marine sponges that lived in warm tropical and subtropical waters during the Cambrian Period. It is believed that the centre of the Archaeocyatha origin is now located in East Siberia, where they are first known from the beginning of the Tommotian Age of the Cambrian, 525 million years ago ( mya). In other regions of the world, they appeared much later, during the Atdabanian, and quickly diversified into over a hundred families. They became the planet's very first reef-building animals and are an index fossil for the Lower Cambrian worldwide. Preservation The remains of Archaeocyatha are mostly preserved as carbonate structures in a limestone matrix. This means that the fossils cannot be chemically or mechanically isolated, save for some specimens that have already eroded out of their matrices, and their morphology has to be determined from thin cuts of the stone in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Sponge
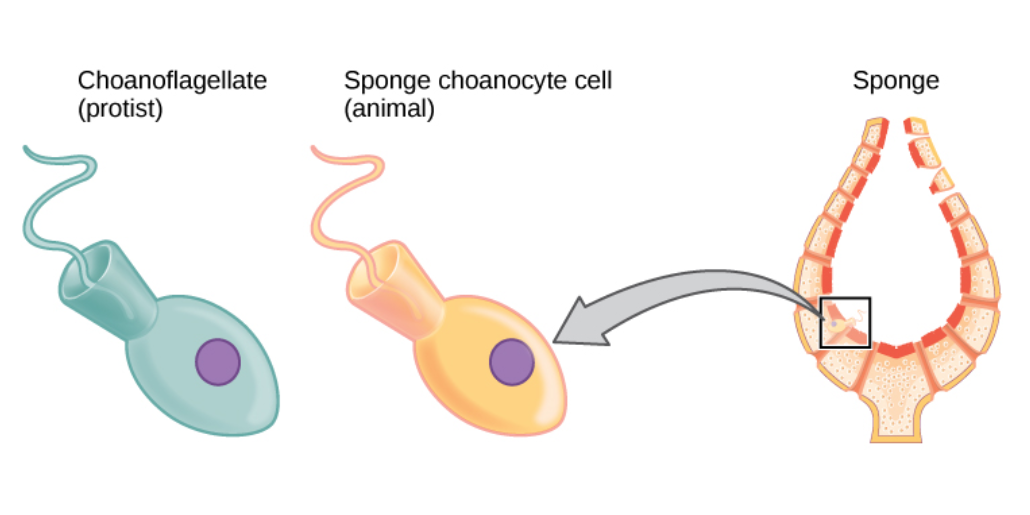
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, het ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (zoology)
Sessility is the biological property of an organism describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile organisms for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile organisms can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other sessile organisms grow from a solid such as a rock, dead tree trunk, or a man-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyonian
Cambrian Stage 4 is the still unnamed fourth stage of the Cambrian and the upper stage of Cambrian Series 2. It follows Cambrian Stage 3 and lies below the Wuliuan. The lower boundary has not been formally defined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy. One proposal is the first appearance of two trilobite genera, ''Olenellus'' or '' Redlichia''. Another proposal is the first appearance of the trilobite species '' Arthricocephalus chauveaui''. Both proposals will set the lower boundary close to million years ago. The upper boundary corresponds to the beginning of the Wuliuan. Naming The International Commission on Stratigraphy The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), sometimes referred to unofficially as the "International Stratigraphic Commission", is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigr ... has not named the fourth stage of the Cambrian yet. In the widely used Siberian nomenclature stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holdfast (biology)
A holdfast is a root-like structure that anchors aquatic sessile organisms, such as seaweed, other sessile algae, stalked crinoids, benthic cnidarians, and sponges, to the substrate. Holdfasts vary in shape and form depending on both the species and the substrate type. The holdfasts of organisms that live in muddy substrates often have complex tangles of root-like growths. These projections are called haptera and similar structures of the same name are found on lichens. The holdfasts of organisms that live in sandy substrates are bulb-like and very flexible, such as those of sea pens, thus permitting the organism to pull the entire body into the substrate when the holdfast is contracted. The holdfasts of organisms that live on smooth surfaces (such as the surface of a boulder) have flattened bases which adhere to the surface. The organism derives no nutrition from this intimate contact with the substrate, as the process of liberating nutrients from the substrate requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (marine Biology)
Stream substrate (sediment) is the material that rests at the bottom of a stream. There are several classification guides. One is: * Mud – silt and clay. *Sand – Particles between 0.06 and 2 mm in diameter. * Granule – Between 2 and 4 mm in diameter. *Pebble – Between 4 – 64 mm in diameter. * Cobble – between 6.4 and 25.6 cm in diameter *Boulder – more than 25.6 cm in diameter. Stream substrate can affect the life found within the stream habitat. Muddy streams generally have more sediment in the water, reducing clarity. Clarity is one guide to stream health. Marine substrate can be classified geologically as well. See Green et al., 1999 for a reference. Mollusks and clams that live in areas with substrate, and need them to survive, use their silky byssal threads to cling to it. See Cteniodes Ales for reference. See also * Grain size * Substrate (biology) In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cream Cone
An ice cream cone, poke (Ireland/Scotland) or cornet (England) is a brittle, cone-shaped pastry, usually made of a wafer similar in texture to a waffle, made so ice cream can be carried and eaten without a bowl or spoon, for example, the Hong Kong-style bubble cone. Many styles of cones are made, including pretzel cones and chocolate-coated cones (coated on the inside). The term ''ice cream cone'' can also refer, informally, to the cone with one or more scoops of ice cream on top. There are two techniques for making cones: one is by baking them flat then quickly rolling them into shape (before they harden), the other is by baking them inside a cone-shaped mold. History 19th century Cones, in the form of wafers rolled and baked hard, date back to Ancient Rome and Greece. When exactly they transitioned to being used for desserts, and ice cream in particular, is not clear. Some historians point to France in the early 19th century as the birthplace of the ice cream cone; an 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeologists and stone trade professionals, the term alabaster is used not just as in geology and mineralogy, where it is res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Coral
The rugosa, also called the tetracorallia or horn coral, are an extinct order of solitary and colonial corals that were abundant in Middle Ordovician to Late Permian seas. Solitary rugosans (e.g., '' Caninia'', '' Lophophyllidium'', '' Neozaphrentis'', '' Streptelasma'') are often referred to as horn corals because of a unique horn-shaped chamber with a wrinkled, or rugose, wall. Some solitary rugosans reached nearly a meter in length. However, some species of rugose corals could form large colonies (e.g., ''Lithostrotion''). When radiating septa were present, they were usually in multiples of four, hence ''Tetracoralla'' in contrast to modern ''Hexacoralla'', colonial polyps generally with sixfold symmetry. Rugose corals have a skeleton made of calcite that is often fossilized. Like modern corals (Scleractinia), rugose corals were invariably benthic, living on the sea floor or in a reef-framework. Some symbiotic rugose corals were endobionts of Stromatoporoidea, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeocyatha
Archaeocyatha (or archaeocyathids 'ancient cups') is a taxon of extinct, sessile, reef-building marine sponges that lived in warm tropical and subtropical waters during the Cambrian Period. It is believed that the centre of the Archaeocyatha origin is now located in East Siberia, where they are first known from the beginning of the Tommotian Age of the Cambrian, 525 million years ago ( mya). In other regions of the world, they appeared much later, during the Atdabanian, and quickly diversified into over a hundred families. They became the planet's very first reef-building animals and are an index fossil for the Lower Cambrian worldwide. Preservation The remains of Archaeocyatha are mostly preserved as carbonate structures in a limestone matrix. This means that the fossils cannot be chemically or mechanically isolated, save for some specimens that have already eroded out of their matrices, and their morphology has to be determined from thin cuts of the stone in which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_holdfast.jpg)
.jpg)


