|
Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the border between Israel to the west and Jordan to the east. The old meaning, which was in use up to the early 20th century, covered almost the entire length of what today is called the Jordan Rift Valley, running in a north–south orientation between the southern end of the Sea of Galilee and the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba of the Red Sea at Aqaba– Eilat. This included the Jordan River Valley between the Sea of Galilee and the Dead Sea, the Dead Sea itself, and what today is commonly called the Arava Valley. The contemporary use of the term is restricted to this southern section alone. Geography The Arabah is in length, from the Gulf of Aqaba to the southern shore of the Dead Sea. Topographically, the region is divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan Valley (Middle East)
The Jordan Valley ( ar, غور الأردن, ''Ghor al-Urdun''; he, עֵמֶק הַיַרְדֵּן, ''Emek HaYarden'') forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. Unlike most other river valleys, the term "Jordan Valley" often applies just to the lower course of the Jordan River, from the spot where it exits the Sea of Galilee in the north, to the end of its course where it flows into the Dead Sea in the south. In a wider sense, the term may also cover the Dead Sea basin and the Arabah valley, which is the rift valley segment beyond the Dead Sea and ending at Aqaba/Eilat, farther south. The valley, in the common, narrow sense, is a long and narrow trough, long if measured " as the crow flies", with a width averaging with some points narrowing to over most of the course, before widening out to a delta when reaching the Dead Sea. Due to meandering, the length of the river itself is . This is the valley with the lowest elevation in the world, beginning at below sea level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank to the west. It lies in the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River. As of 2019, the lake's surface is below sea level, making its shores the lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the world's saltiest bodies of water – 9.6 times as salty as the ocean – and has a density of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point. The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around the Mediterranean Basin fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ''Bīrʿāt haYardēn'', ar, الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr),, date=November 2022 also called the Syro-African Depression, is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, and Jordan. This geographic region includes the entire length of the Jordan River – from its sources, through the Hula Valley, the Korazim block, the Sea of Galilee, the (Lower) Jordan Valley, all the way to the Dead Sea, the lowest land elevation on Earth – and then continues through the Arabah depression, the Gulf of Aqaba whose shorelines it incorporates, until finally reaching the Red Sea proper at the Straits of Tiran. History and physical features The Jordan Rift Valley was formed many millions of years ago in the Miocene epoch (23.8 – 5.3 Myr ago) when the Arabian Plate moved northward and then eastward away from Africa. One million years later, the land between the Mediterranean and the Jordan Rift Valley rose so that the sea water stopped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eilat
Eilat ( , ; he, אֵילַת ; ar, إِيلَات, Īlāt) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jordan as the Gulf of Aqaba. The city is considered a tourist destination for domestic and international tourists heading to Israel. Eilat is part of the Southern Negev Desert, at the southern end of the Arabah, adjacent to the Egyptian resort city of Taba to the south, the Jordanian port city of Aqaba to the east, and within sight of Haql, Saudi Arabia, across the gulf to the southeast. Eilat's arid desert climate and low humidity are moderated by proximity to a warm sea. Temperatures often exceed in summer, and in winter, while water temperatures range between . Eilat averages 360 sunny days a year. Name The name ''Eilat'' was given to ''Umm al-Rashrāsh'' () in 1949 by the Committee for the Designation of Place-Names in the Negev. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Stork
The black stork (''Ciconia nigra'') is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. Measuring on average from beak tip to end of tail with a wingspan, the adult black stork has mainly black plumage, with white underparts, long red legs and a long pointed red beak. A widespread but uncommon species, it breeds in scattered locations across Europe (predominantly in Portugal and Spain, and central and eastern parts), and east across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent. When migrating between Europe and Africa, it avoids crossing the Mediterranean Sea and detours via the Levant in the east or the Strait of Gibraltar in the west. An isolated, non-migratory, population occurs in Southern Africa. Unlike the closely related white stork, the black stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Partridge
The sand partridge (''Ammoperdix heyi'') is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. This partridge has its main native range from Egypt and Israel east to south Arabia. It is closely related and similar to its counterpart in southeast Turkey and east to Pakistan, the see-see partridge, ''Ammoperdix griseogularis''. This 22–25 cm bird Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ... is a resident breeder in dry, open and often hilly country. It nests in a scantily lined ground scrape laying 5-7 eggs. The sand partridge takes a wide variety of seeds and some insect food. Description The sand partridge is a rotund bird, mainly sandy-brown with wavy white and brown flank stripes. The male has a grey head with a white st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garganey
The garganey (''Spatula querquedula'') is a small dabbling duck. It breeds in much of Europe and across the Palearctic, but is strictly migratory, with the entire population moving to southern Africa, India (in particular Santragachi), Bangladesh (in the natural reservoirs of Sylhet district) and Australasia during the winter of the Northern hemisphere, where large flocks can occur. This species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. Like other small ducks such as the Eurasian teal, this species rises easily from the water with a fast twisting wader-like flight. Their breeding habitat is grassland adjacent to shallow marshes and steppe lakes. Taxonomy The first formal description of the garganey was by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. He introduced the binomial name ''Anas querquedula''. A molecular phylogentic study comparing mitochondrial DNA sequences publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
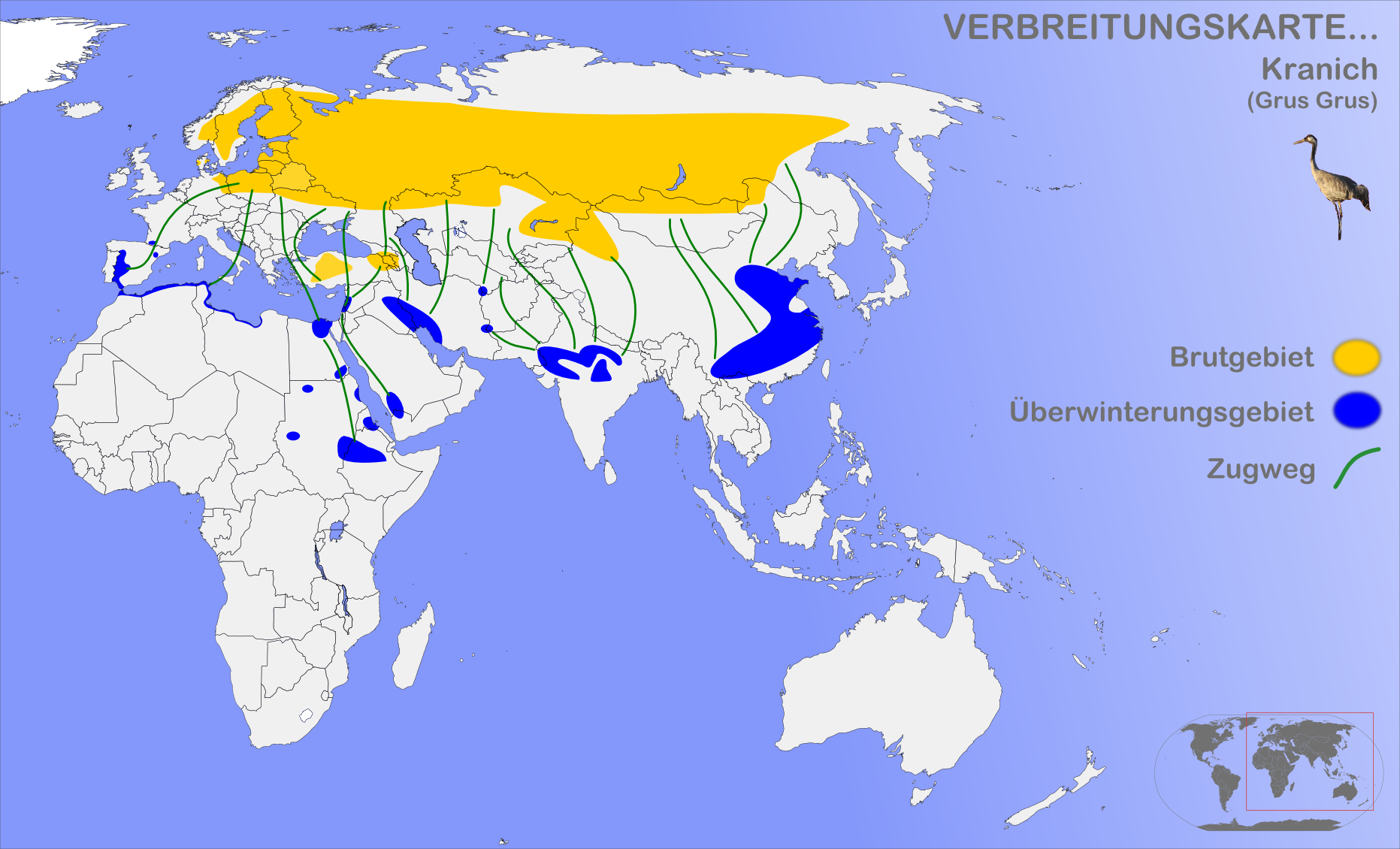
Common Crane
The common crane (''Grus grus''), also known as the Eurasian crane, is a bird of the family Gruidae, the cranes. A medium-sized species, it is the only crane commonly found in Europe besides the demoiselle crane (''Grus virgo'') and the Siberian crane (''Leucogeranus leucogeranus''). Along with the sandhill (''Antigone canadensis'') and demoiselle cranes and the brolga (''Antigone rubicunda''), it is one of only four crane species not currently classified as threatened with extinction or conservation dependent on the species level. Despite the species' large numbers, local extinctions and extirpations have taken place in part of its range, and an ongoing reintroduction project is underway in the United Kingdom. Taxonomy The first formal description of the common crane was by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Ardea grus''. The current genus ''Grus'' was erected by the French zoologist Mathurin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Spoonbill
The Eurasian spoonbill (''Platalea leucorodia''), or common spoonbill, is a wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae. The genus name ''Platalea'' is from Latin and means "broad", referring to the distinctive shape of the bill, and ''leucorodia'' is from Ancient Greek ''leukerodios'' "spoonbill", itself derived from ''leukos'', "white" and ''erodios'' "heron". In England it was traditionally known as the "shovelard", a name later used for the Northern Shoveller. Taxonomy and systematics A study of mitochondrial DNA of the spoonbills found that the Eurasian spoonbill is sister taxon to a clade containing the royal and black-faced spoonbills. The Eurasian spoonbill has three subspecies: * ''P. l. leucorodia'' – Linnaeus, 1758: nominate, occupies all the range except as below. * ''P. l. balsaci'' – Naurois & Roux, 1974: found on the islands off the Banc d'Arguin, Mauritania. * ''P. l. archeri'' – Neumann, 1928: found on the coasts of the Red Sea and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Stork
The white stork (''Ciconia ciconia'') is a large bird in the stork family, Ciconiidae. Its plumage is mainly white, with black on the bird's wings. Adults have long red legs and long pointed red beaks, and measure on average from beak tip to end of tail, with a wingspan. The two subspecies, which differ slightly in size, breed in Europe (north to Finland), northwestern Africa, southwestern Asia (east to southern Kazakhstan) and southern Africa. The white stork is a long-distance migrant, wintering in Africa from tropical Sub-Saharan Africa to as far south as South Africa, or on the Indian subcontinent. When migrating between Europe and Africa, it avoids crossing the Mediterranean Sea and detours via the Levant in the east or the Strait of Gibraltar in the west, because the air thermals on which it depends for soaring do not form over water. A carnivore, the white stork eats a wide range of animal prey, including insects, fish, amphibians, reptiles, small mammals and small bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_in_AP_W_IMG_2844.jpg)