|
Apparent Polar Wander
Apparent polar wander (APW) is the perceived movement of the Earth's paleo- magnetic poles relative to a continent while regarding the continent being studied as fixed in position. It is frequently displayed on the present latitude-longitude map as a path connecting the locations of geomagnetic poles, inferred at distinct times using paleomagnetic techniques. In reality, the relative polar movement can be either real polar wander or continental drift (or a combination of both). Data from around the globe are needed in order to isolate or distinguish between the two. Nevertheless, the magnetic poles rarely stray far from the geographic poles of the planet; rather they tend to follow true polar wander. Therefore, the concept of apparent polar wander is very useful in plate tectonics, since it can retrace the relative motion of continents, as well as the formation and break-up of supercontinents. History It has been known for a long time that the geomagnetic field varies through tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleomagnetism
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.'' Certain magnetic minerals in rocks can record the direction and intensity of Earth's magnetic field at the time they formed. This record provides information on the past behavior of the geomagnetic field and the past location of tectonic plates. The record of geomagnetic reversals preserved in volcanic and sedimentary rock sequences ( magnetostratigraphy) provides a time-scale that is used as a geochronologic tool. Evidence from paleomagnetism led to the revival of the continental drift hypothesis and its transformation into the modern theory of plate tectonics. Apparent polar wander paths provided the first clear geophysical evidence for continental drift, while marine magnetic anomalies did the same for seafloor spreading. Paleomagnetic data continues to extend t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poles Of Astronomical Bodies
The poles of astronomical bodies are determined based on their axis of rotation in relation to the celestial poles of the celestial sphere. Astronomical bodies include stars, planets, dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies such as comets and minor planets (e.g., asteroids), as well as natural satellites and minor-planet moons. Poles of rotation The International Astronomical Union (IAU) defines the north pole of a planet or any of its satellites in the Solar System as the planetary pole that is in the same celestial hemisphere, relative to the invariable plane of the Solar System, as Earth's north pole. This definition is independent of the object's direction of rotation about its axis. This implies that an object's direction of rotation, when viewed from above its north pole, may be either clockwise or counterclockwise. The direction of rotation exhibited by most objects in the solar system (including Sun and Earth) is counterclockwise. Venus rotates clockwise, and Uranu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
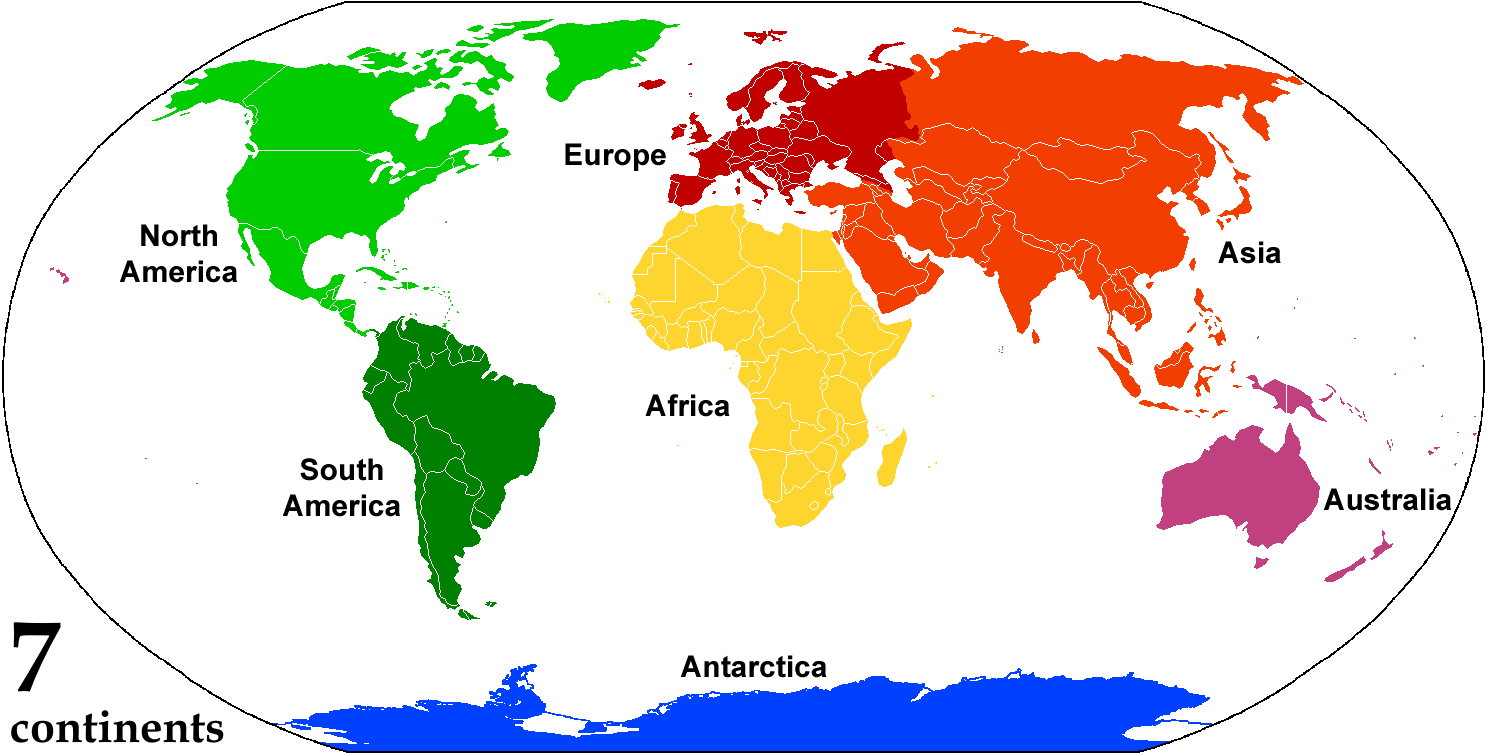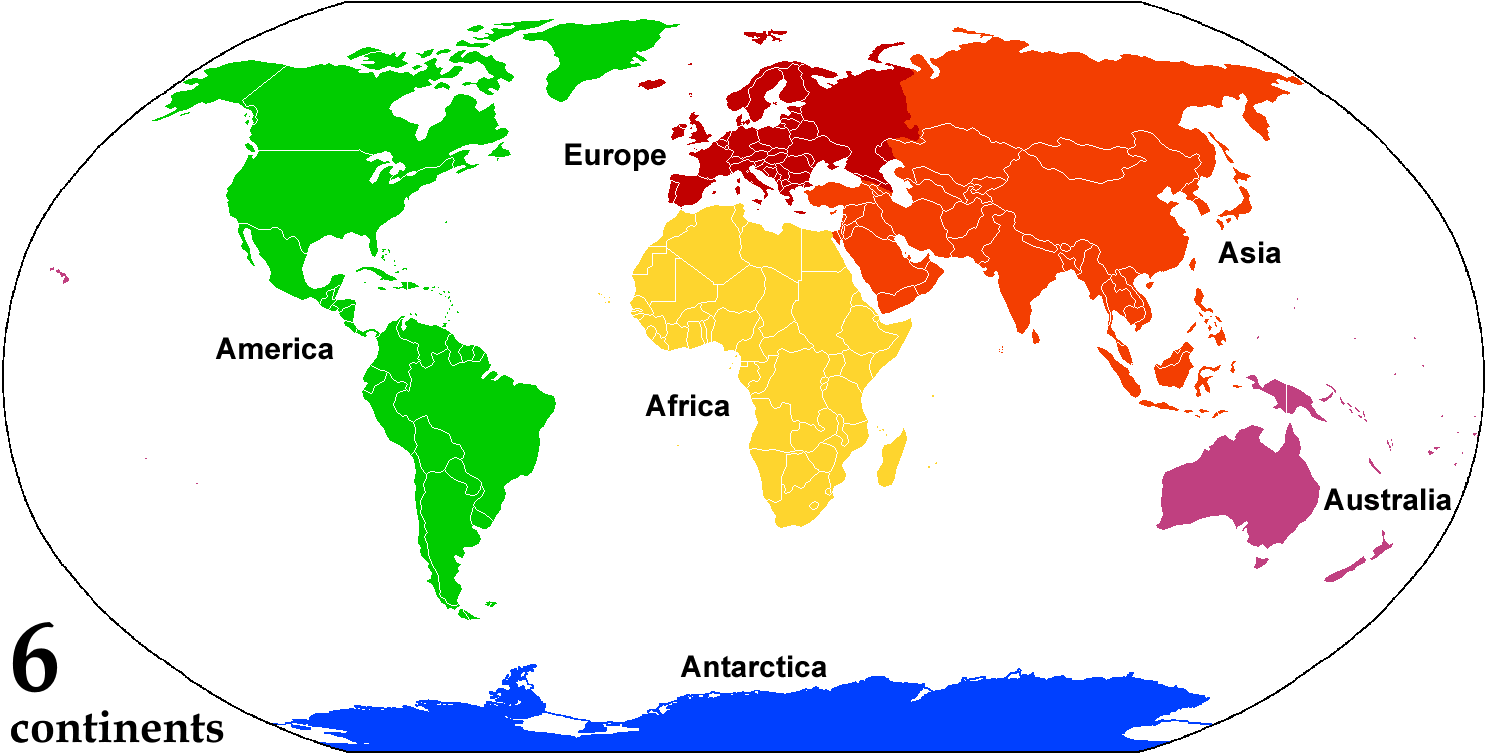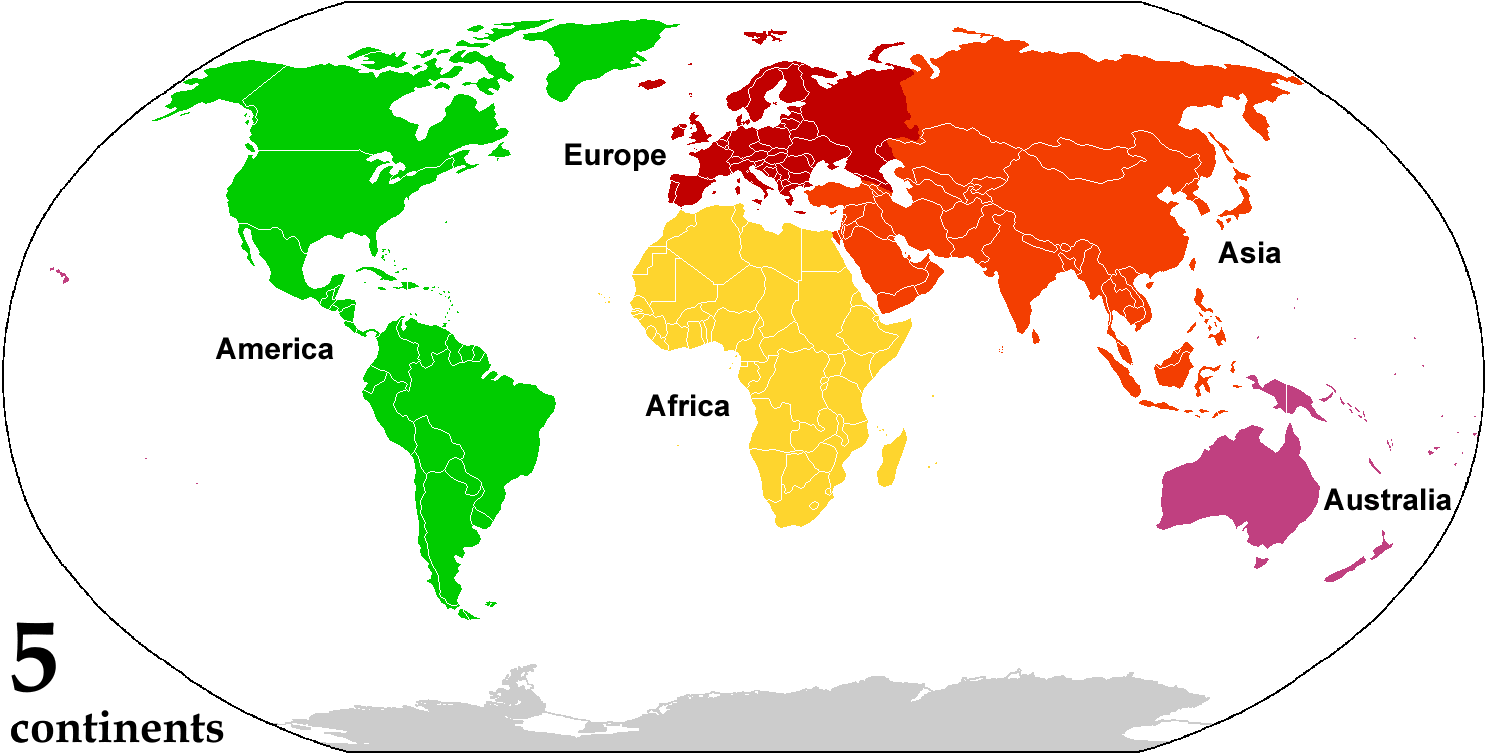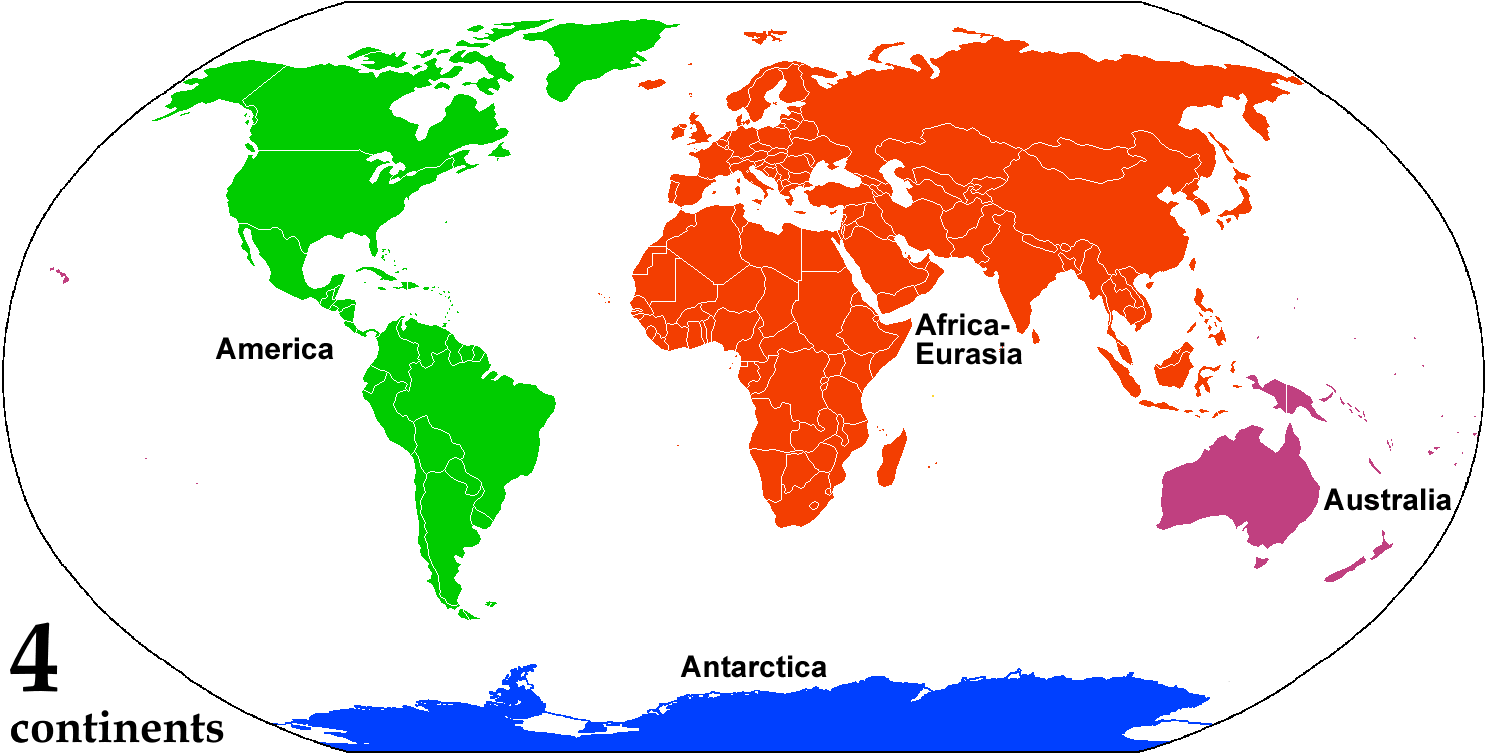
Continent
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ... are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia (continent), Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example Americas, America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single contin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomagnetic Pole
The geomagnetic poles are antipodal points where the axis of a best-fitting dipole intersects the surface of Earth. This ''theoretical'' dipole is equivalent to a powerful bar magnet at the center of Earth, and comes closer than any other point dipole model to describing the magnetic field observed at Earth's surface. In contrast, the magnetic poles of the actual Earth are not antipodal; that is, the line on which they lie does not pass through Earth's center. Owing to motion of fluid in the Earth's outer core, the actual magnetic poles are constantly moving (secular variation). However, over thousands of years, their direction averages to the Earth's rotation axis. On the order of once every half a million years, the poles reverse (i.e., north switches place with south) although the time frame of this switching can be anywhere from every 10 thousand years to every 50 million years. The poles also swing in an oval of around in diameter daily due to solar wind deflectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Wander
Polar wander is the motion of a pole in relation to some reference frame. It can be used, for example, to measure the degree to which Earth's magnetic poles have been observed to move relative to the Earth's rotation axis. It is also possible to use continents as reference and observe the relative motion of the magnetic pole relative to the different continents; by doing so, the relative motion of those two continents to each other can be observed over geologic time as paleomagnetism. Apparent polar wander The magnetic poles are relatively stationary in position over time and because of this, researchers often use magnetic minerals, like magnetite, in order to find at what latitude the continent was positioned relative to the magnetic poles of that time. Since the continents have been moving relative to the pole; it is as if they were immobile and the magnetic pole was moving instead. If enough data is collected, it is then possible to reconstruct the motion of the continents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Polar Wander
True polar wander is a solid-body rotation of a planet or moon with respect to its spin axis, causing the geographic locations of the north and south poles to change, or "wander". Unless the body is totally rigid (which the Earth is not) its stable state rotation has the largest moment of inertia axis aligned with the spin axis, with the smaller two moments of inertia axes lying in the plane of the equator. If the body is not in this steady state, true polar wander will occur: the planet or moon will rotate as a rigid body to realign the largest moment of inertia axis with the spin axis. (See .) If the body is near the steady state but with the angular momentum not exactly lined up with the largest moment of inertia axis, the pole position will oscillate. Weather and water movements can also induce small changes. These subjects are covered in the article ''Polar motion''. Description in the context of Earth The mass distribution of the Earth is not spherically symmetric, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure Temperature
In radiometric dating, closure temperature or blocking temperature refers to the temperature of a system, such as a mineral, at the time given by its radiometric date. In physical terms, the closure temperature is the temperature at which a system has cooled so that there is no longer any significant diffusion of the parent or daughter isotopes out of the system and into the external environment. The concept's initial mathematical formulation was presented in a seminal paper by Martin H. Dodson, "Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems" in the journal '' Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology'', 1973, with refinements to a usable experimental formulation by other scientists in later years. This temperature varies broadly among different minerals and also differs depending on the parent and daughter atoms being considered.''Earth: a Portrait of a Planet'Glossary W.W. Norton & Company It is specific to a particular material and isotopic system.R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler's Rotation Theorem
In geometry, Euler's rotation theorem states that, in three-dimensional space, any displacement of a rigid body such that a point on the rigid body remains fixed, is equivalent to a single rotation about some axis that runs through the fixed point. It also means that the composition of two rotations is also a rotation. Therefore the set of rotations has a group structure, known as a '' rotation group''. The theorem is named after Leonhard Euler, who proved it in 1775 by means of spherical geometry. The axis of rotation is known as an Euler axis, typically represented by a unit vector . Its product by the rotation angle is known as an axis-angle vector. The extension of the theorem to kinematics yields the concept of instant axis of rotation, a line of fixed points. In linear algebra terms, the theorem states that, in 3D space, any two Cartesian coordinate systems with a common origin are related by a rotation about some fixed axis. This also means that the product of two ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of ''continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or ''transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |