|
Apalachee
The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River,Bobby G. McEwan, "Apalachee and Neighboring Groups," 669. at the head of Apalachee Bay, an area known as the Apalachee Province. They spoke a Muskogean language called Apalachee, which is now extinct. The Apalachee occupied the site of Velda Mound starting about 1450 CE, they but had mostly abandoned it when Spanish started settlements in the 17th century. They first encountered Spanish explorers in 1528, when the Narváez expedition arrived. Their tribal enemies, European diseases, and European encroachment severely reduced their population. Warfare from 1701 to 1704 devastated the Apalachee, and they abandoned their homelands by 1704, fleeing north to the Carolinas, Georgia, and Alabama. Language The Apalachee language was a Musk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachicola People
Apalachicola (sometimes Palachacola) was the name of a Native American town and chiefdom, and of the people living in it, and of a group of towns associated with it, located along the lower part of the Chattahoochee River in present-day Alabama and Georgia. The Spanish called the association of towns the Apalachicola Province. It is believed that before the 17th century, the residents of all the Apalachicola towns spoke the Hitchiti language, although other towns whose people spoke Muscogee relocated among the Apalachicolas along the Chattahoochee River in the middle- to later- 17th century. All of the Apalachicola towns moved to central Georgia at the end of the 17th century, where the English called them "Ochese Creek Indians". They moved back to the Chattahoochee River after 1715, with the English then calling them "Lower Creeks" ("Lower Towns of the Muscogee Confederacy"), while the Spanish called them "Ochese". Origins In the first half of the 17th century, a number of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachee Province
Apalachee Province was the area in the Panhandle of the present-day U.S. state of Florida inhabited by the Native American peoples known as the Apalachee at the time of European contact. The southernmost extent of the Mississippian culture, the Apalachee lived in what is now Leon County, Wakulla County and Jefferson County. The name was in use during the early period of European exploration. During Spanish colonization, the Apalachee Province became one of the four major provinces in the Spanish mission system, the others being the Timucua Province, (between the St. Johns and Suwanee Rivers), the Mocama Province (along the Atlantic coast of what is now northern Florida and southern Georgia) and the Guale Province (along the Georgia coast north of the Altamaha River). History Around 12,000 years ago, bands of indigenous peoples roamed the hilltops and lake shores of what are now Leon County and Jefferson County. They lived by hunting, fishing and gathering. Eventually th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous People Of Florida
The indigenous peoples of Florida lived in what is now known as Florida for more than 12,000 years before the time of first contact with Europeans. However, the indigenous Floridians living east of the Apalachicola River had largely died out by the early 18th century. Some Apalachees migrated to Louisiana, where their descendants now live; some were taken to Cuba and Mexico by the Spanish in the 18th century, and a few may have been absorbed into the Seminole and Miccosukee tribes. Paleoindians The first people arrived in Florida before the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. Human remains and/or artifacts have been found in association with the remains of Pleistocene animals at a number of Florida locations. A carved bone depicting a mammoth found near the site of Vero man has been dated to 13,000 to 20,000 years ago. Artifacts recovered at the Page-Ladson site date to 12,500 to 14,500 years ago. Evidence that a giant tortoise was cooked in its shell at Little Salt Spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
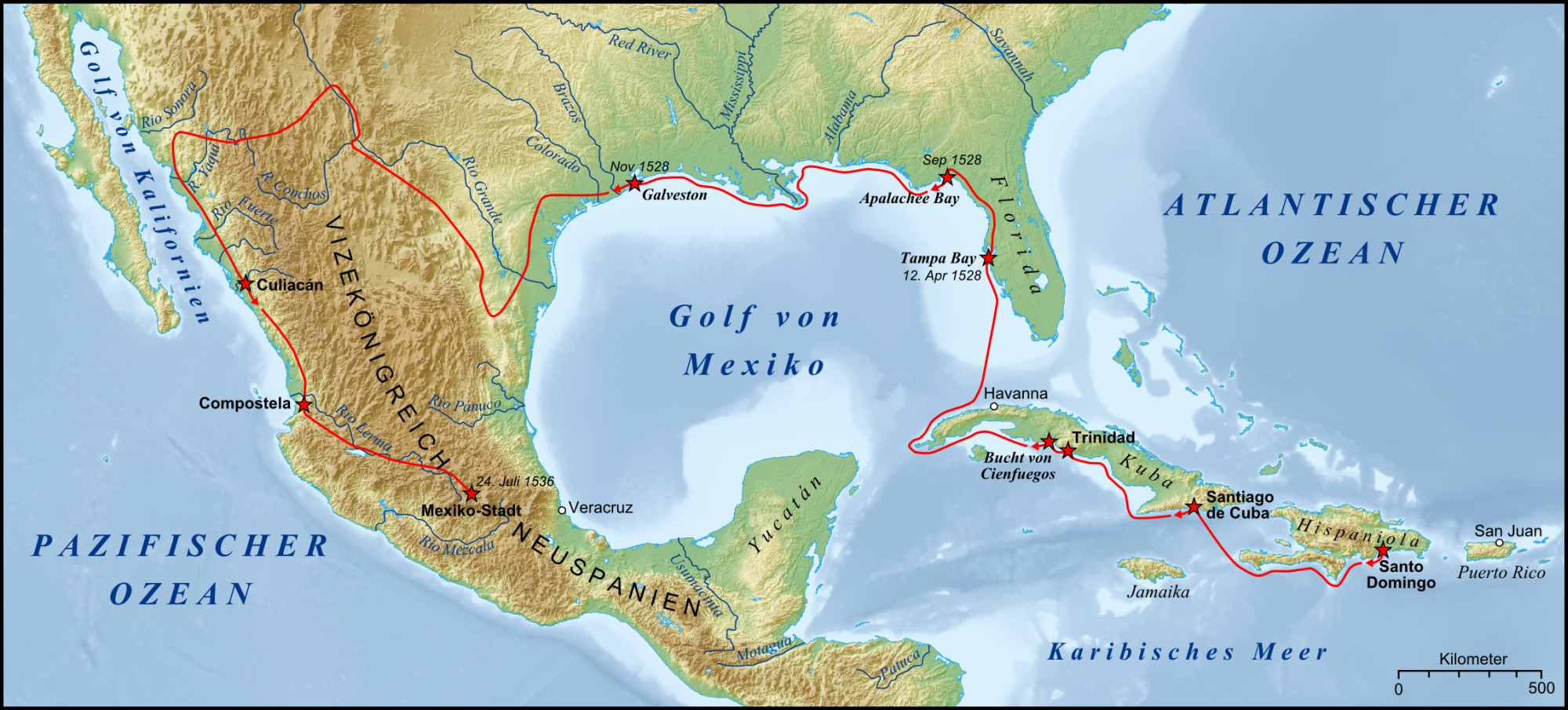
Narváez Expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish journey of exploration and colonization started in 1527 that intended to establish colonial settlements and garrisons in Florida. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. Many more people died as the expedition traveled west along the explored Gulf Coast of the present-day United States and into the American Southwest. Only four of the expedition's original members survived, reaching Mexico City in 1536. These survivors were the first known non-Native Americans to see the Mississippi River, and to cross the Gulf of Mexico and Texas. Narváez's crew initially numbered about 600, including men from Spain, Portugal, Greece, and Italy. The expedition met with disaster almost immediately. Making stops at Hispaniola and Cuba on the way to La Florida, the fleet was devastated by a hurricane, among other storms, and lost two ships. They left Cuba in February 1528. Their intended destination was the Rio de las Palma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallahassee, Florida
Tallahassee ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat and only incorporated municipality in Leon County. Tallahassee became the capital of Florida, then the Florida Territory, in 1824. In 2020, the population was 196,169, making it the 8th-largest city in the U.S state of Florida, and the 126th-largest city in the United States. The population of the Tallahassee metropolitan area was 385,145 . Tallahassee is the largest city in the Florida Big Bend and Florida Panhandle region, and the main center for trade and agriculture in the Florida Big Bend and Southwest Georgia regions. With a student population exceeding 70,000, Tallahassee is a college town, home to Florida State University, ranked the nation's 19th-best public university by '' U.S. News & World Report;'' Florida A&M University, ranked the nation's best public historically black university by '' U.S. News & World Report''; and Tallahassee Community College, a large state col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachee Bay
Apalachee Bay is a bay in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico occupying an indentation of the Florida coast to the west of where the Florida peninsula joins the United States mainland. It is bordered by Taylor, Jefferson, Wakulla, and Franklin counties. The Aucilla, Econfina, St. Marks, and Ochlockonee rivers drain into the bay. In 1528 five boats were constructed by Pánfilo de Narváez in the bay. It is named for the Apalachee tribe which lived between the Aucilla and Ochlockonee rivers until the 18th century. Most of the bay's coast is the St. Marks National Wildlife Refuge. Underwater archaeological sites Beginning in the 1980s submerged archaeological sites have been identified and examined on the seabed of Apalachee Bay. During the height of the last glacial period, global sea levels were at least lower than in the 20th Century. All of the Florida Platform would have been above sea level, with the west coast of the Florida peninsula being about west of the curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskogean Languages
Muskogean (also Muskhogean, Muskogee) is a Native American language family spoken in different areas of the Southeastern United States. Though the debate concerning their interrelationships is ongoing, the Muskogean languages are generally divided into two branches, Eastern Muskogean and Western Muskogean. Typologically, Muskogean languages are agglutinative. One documented language, Apalachee, is extinct and the remaining languages are critically endangered. Genetic relationships Family division The Muskogean family consists of six languages that are still spoken: Alabama, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek-Seminole, Koasati, and Mikasuki, as well as the now-extinct Apalachee, Houma, and Hitchiti (the last is generally considered a dialect of Mikasuki). "Seminole" is listed as one of the Muskogean languages in Hardy's list, but it is generally considered a dialect of Creek rather than a separate language, as she comments. The major subdivisions of the family have long been con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochlockonee River
The Ochlockonee River ( ) is a fast running river, except where it has been dammed to form Lake Talquin in Florida, originating in Georgia and flowing for before terminating in Florida. Background The name is from the Hitchiti language words for yellow river. The Ochlockonee originates south of the town of Sylvester in Worth County in southwest Georgia and empties into Ochlockonee Bay and then Apalachee Bay in Florida. The river forms the western boundaries of Leon County and Wakulla County and eastern boundaries of Gadsden County, Liberty County, and Franklin County in Florida. It flows through the Red Hills, the Jackson Bluff Dam, Talquin State Forest, Lake Talquin State Park and the Apalachicola National Forest, and past Ochlockonee River State Park, where it is tidally influenced and a mixture of fresh, brackish, and salt water, on the way to its terminus in Ochlockonee Bay, which then empties into Apalachee Bay, with tidal influences extending upstream over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachee Language
Apalachee was a Muskogean language of Florida. It was closely related to Koasati and Alabama. The language is known primarily from one document, a letter written in 1688 to Charles II of Spain. Geoffrey Kimball has produced a grammatical sketch and a vocabulary of the language based on the contents of the letter. Apalachee was found to belong to the same branch of the Muskogean family as Koasati, Alabama, and Hitchiti The Hitchiti ( ) were a historic indigenous tribe in the Southeast United States. They formerly resided chiefly in a town of the same name on the east bank of the Chattahoochee River, four miles below Chiaha, in western present-day Georgia. The n .... Phonology Consonants Orthography is only shown where it differs from the IPA. Vowels Vowels may also be elongated. References External links Apalachee Language Guide Apalachee Muskogean languages Languages extinct in the 18th century 18th-century disestablishments in North America Extinct languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhaica
Anhaica (also known as Iviahica, Yniahico, and pueblo of Apalache) was the principal town of the Apalachee people, located in what is now Tallahassee, Florida. In the early period of Spanish colonization, it was the capital of the Apalachee Province. The site, now known as Martin Archaeological Site, was rediscovered in 1988. History In the late pre-invasion era the site became the capital of the Apalachee after the abandonment of the former capital, the Lake Jackson Mounds Site, in approximately 1500. The fact that no platform mounds are found at Anhaica may indicate a political change. Either Anhiaca was not occupied long enough for the construction of mounds to begin, or mounds were no longer being built. Also, disease could have been introduced from the Pánfilo de Narváez expedition through Apalachee in 1528 reducing population, changing village location and/or mound-building activities. Anhaica had 250 buildings when Hernando de Soto set up camp there on October 6, 1539, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velda Mound
Velda Mound ( 8LE44) is a Native American archaeological site located in northern Tallahassee, Leon County, Florida, United States. The site was first occupied by peoples of the Fort Walton Culture (a regional variation of the Mississippian culture) in the late prehistoric period and during the protohistoric period was part of the extensive Apalachee Province of the panhandle. The site is now owned by the State of Florida and managed as a park. History and use Velda Mound was built in approximately 1450 by Fort Walton peoples and occupied by their descendants the Apalachee until about 1625. The Spanish explorers called this area Apalachee Province in recognition of the tribe's power, a territory which also included the Lake Jackson Mounds and major center of ''Anhaica''. The platform mound is believed to have served as a residence for a village leader, with a village surrounding the mound. The village inhabitants cultivated vegetables in small family plots and farmed large c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Soto (explorer)
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States (through Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and most likely Arkansas). He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River. De Soto's North American expedition was a vast undertaking. It ranged throughout what is now the southeastern United States, both searching for gold, which had been reported by various Native American tribes and earlier coastal explorers, and for a passage to China or the Pacific coast. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River; different sources disagree on the exact location, whether it was what is now Lake Village, Arkansas, or Ferriday, Louisia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |