|
Anthozoa
Anthozoa is a subphylum of marine invertebrates which includes the sea anemones, stony corals and soft corals. Adult anthozoans are almost all attached to the seabed, while their larvae can disperse as part of the plankton. The basic unit of the adult is the polyp; this consists of a cylindrical column topped by a disc with a central mouth surrounded by tentacles. Sea anemones are mostly solitary, but the majority of corals are colonial, being formed by the budding of new polyps from an original, founding individual. Colonies are strengthened by calcium carbonate and other materials and take various massive, plate-like, bushy or leafy forms. Anthozoa is included within the phylum Cnidaria, which also includes the jellyfish, box jellies and parasitic Myxozoa and Polypodiozoa. The two main subclasses of Anthozoa are the Hexacorallia, members of which have six-fold symmetry and includes the stony corals, sea anemones, tube anemones and zoanthids; and the Octocorallia, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Anemone
Sea anemones are a group of predatory marine invertebrates of the order Actiniaria. Because of their colourful appearance, they are named after the '' Anemone'', a terrestrial flowering plant. Sea anemones are classified in the phylum Cnidaria, class Anthozoa, subclass Hexacorallia. As cnidarians, sea anemones are related to corals, jellyfish, tube-dwelling anemones, and '' Hydra''. Unlike jellyfish, sea anemones do not have a medusa stage in their life cycle. A typical sea anemone is a single polyp attached to a hard surface by its base, but some species live in soft sediment, and a few float near the surface of the water. The polyp has a columnar trunk topped by an oral disc with a ring of tentacles and a central mouth. The tentacles can be retracted inside the body cavity or expanded to catch passing prey. They are armed with cnidocytes (stinging cells). In many species, additional nourishment comes from a symbiotic relationship with single-celled dinoflagellates, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoantharia
Zoanthids ( order Zoantharia also called Zoanthidea or Zoanthiniaria) are an order of cnidarians commonly found in coral reefs, the deep sea and many other marine environments around the world. These animals come in a variety of different colonizing formations and in numerous different colors. They can be found as individual polyps, attached by a fleshy stolon or a mat that can be created from small pieces of sediment, sand and rock. The term "zoanthid" refers to all animals within this order Zoantharia, and should not be confused with "'' Zoanthus''", which is one genus within Zoantharia. These are among the most commonly collected corals in reef aquaria, easily propagating and very durable in many water conditions. Nomenclature controversy The name of the order is controversial. Non-specialists often use the term Zoanthidea whereas most taxonomists use Zoantharia. The term Zoantharia in turn is used temporarily instead of Hexacorallia. However, major taxonomic papers publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyp (zoology)
A polyp in zoology is one of two forms found in the phylum Cnidaria, the other being the medusa. Polyps are roughly cylindrical in shape and elongated at the axis of the vase-shaped body. In solitary polyps, the aboral (opposite to oral) end is attached to the substrate by means of a disc-like holdfast called a pedal disc, while in colonies of polyps it is connected to other polyps, either directly or indirectly. The oral end contains the mouth, and is surrounded by a circlet of tentacles. Classes In the class Anthozoa, comprising the sea anemones and corals, the individual is always a polyp; in the class Hydrozoa, however, the individual may be either a polyp or a medusa, with most species undergoing a life cycle with both a polyp stage and a medusa stage. In class Scyphozoa, the medusa stage is dominant, and the polyp stage may or may not be present, depending on the family. In those scyphozoans that have the larval planula metamorphose into a polyp, the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octocorallia
Octocorallia (also known as Alcyonaria) is a class of Anthozoa comprising around 3,000 species of water-based organisms formed of colonial polyps with 8-fold symmetry. It includes the blue coral, soft corals, sea pens, and gorgonians (sea fans and sea whips) within three orders: Alcyonacea, Helioporacea, and Pennatulacea. These organisms have an internal skeleton secreted by mesoglea and polyps with eight tentacles and eight mesentaries. As with all Cnidarians these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile phase when they are considered plankton and later characteristic sessile phase. Octocorals have existed at least since the Ordovician period, as shown by Maurits Lindström's findings in the 1970s, however recent work has shown a possible Cambrian origin. Biology Octocorals resemble the stony corals in general appearance and in the size of their polyps, but lack the distinctive stony skeleton. Also unlike the stony corals, each polyp has only eight tentacles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexacorallia
Hexacorallia is a class of Anthozoa comprising approximately 4,300 species of aquatic organisms formed of polyps, generally with 6-fold symmetry. It includes all of the stony corals, most of which are colonial and reef-forming, as well as all sea anemones, and zoanthids, arranged within five extant orders. The hexacorallia are distinguished from another class of Anthozoa, Octocorallia, in having six or fewer axes of symmetry in their body structure; the tentacles are simple and unbranched and normally number more than eight. These organisms are formed of individual soft polyps which in some species live in colonies and can secrete a calcite skeleton. As with all Cnidarians, these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile planktonic phase and a later characteristic sessile phase. Hexacorallia also include the significant extinct order of rugose corals. Phylogeny Hexacorallia is considered to be monophyletic, that is all contained species are descended from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella-shaped bells and trailing tentacles, although a few are anchored to the seabed by stalks rather than being mobile. The bell can pulsate to provide propulsion for highly efficient locomotion. The tentacles are armed with stinging cells and may be used to capture prey and defend against predators. Jellyfish have a complex life cycle; the medusa is normally the sexual phase, which produces planula larvae that disperse widely and enter a sedentary polyp phase before reaching sexual maturity. Jellyfish are found all over the world, from surface waters to the deep sea. Scyphozoans (the "true jellyfish") are exclusively marine, but some hydrozoans with a similar appearance live in freshwater. Large, often colorful, jellyfish are common in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriantharia
Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different class of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Within the tubes of these ceriantharians, more than one polyp is present, which is an exceptional trait because species that create tube systems usually contain only one polyp per tube. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own subclass, Ceriantharia. Ceriantharians have a crown of tentacles that are composed of two whorls of distinctly different sized tentacles. The outer whorl consists of large tentacles that extend outwards. These tentacles taper to points and are mostly used in food capture and defence. The smaller in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incertae Sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty at specific taxonomic levels is indicated by ' (of uncertain family), ' (of uncertain suborder), ' (of uncertain order) and similar terms. Examples *The fossil plant '' Paradinandra suecica'' could not be assigned to any family, but was placed ''incertae sedis'' within the order Ericales when described in 2001. * The fossil '' Gluteus minimus'', described in 1975, could not be assigned to any known animal phylum. The genus is therefore ''incertae sedis'' within the kingdom Animalia. * While it was unclear to which order the New World vultures (family Cathartidae) should be assigned, they were placed in Aves ''incertae sedis''. It was later agreed to place them in a separate order, Cathartiformes. * Bocage's longbill, ''Motacilla boca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Pansy
The sea pansy, ''Renilla reniformis,'' is a species of colonial cnidarian in the family Renillidae, part of an octocoral subclass of Anthozoa that inhabit an expansive range of environments. It is native to warm continental shelf waters of the Western Hemisphere. It is frequently found washed ashore on North East Florida beaches following northeasterly winds or rough surf conditions. It also can often be found living intertidally completely buried in the sand. Its predator is the striped sea slug, '' Armina tigrina''. The sea pansy is a collection of polyps with different forms and functions. A single, giant polyp up to two inches in diameter forms the anchoring stem (peduncle). This peduncle can be distended to better anchor the colony in the substrate. The pansy-like body bears many small, anemone-like feeding polyps. A cluster of tentacleless polyps form an outlet valve that releases water to deflate the colony. If the colony is on a sand bar at low tide, it usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry In Biology
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, take the face of a human being which has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone with a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
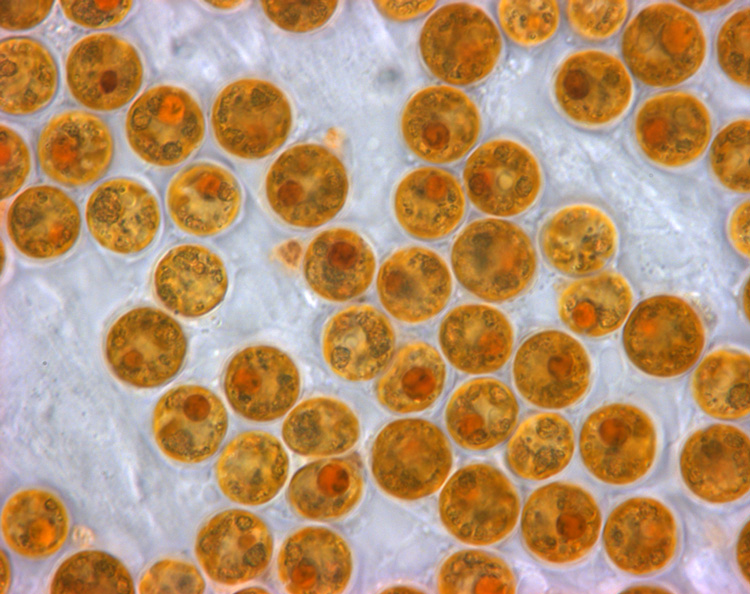
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus ''Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |