|
Anomaluromorpha
Anomaluromorpha is a clade that unites the anomalures, springhares, and zenkerella. It has alternately been designated as either a suborder or infraorder. Most recently, recognized it as one of five suborders of rodents. Characteristics The suborder Anomaluromorpha was erected to unite sciurognathous rodents with a hystricomorphous zygomasseteric system restricted to sub-Saharan Africa. Many authors have suggested that the two extant families may be only distantly related, and that they belong to separate suborders or infraorders. For example, the Pedetidae are the only family of rodents with multiserial enamel except for the Hystricognathi. This characteristic, the hystricomorphous zygomatic region, and a common distribution in southern continents has led many researchers to suggest that the springhares (but not anomalures) may be allied with hystricognaths. generated some support for Anomaluromorpha in a molecular phylogeny using 12S rRNA and cytochrome b. Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomaluromorpha
Anomaluromorpha is a clade that unites the anomalures, springhares, and zenkerella. It has alternately been designated as either a suborder or infraorder. Most recently, recognized it as one of five suborders of rodents. Characteristics The suborder Anomaluromorpha was erected to unite sciurognathous rodents with a hystricomorphous zygomasseteric system restricted to sub-Saharan Africa. Many authors have suggested that the two extant families may be only distantly related, and that they belong to separate suborders or infraorders. For example, the Pedetidae are the only family of rodents with multiserial enamel except for the Hystricognathi. This characteristic, the hystricomorphous zygomatic region, and a common distribution in southern continents has led many researchers to suggest that the springhares (but not anomalures) may be allied with hystricognaths. generated some support for Anomaluromorpha in a molecular phylogeny using 12S rRNA and cytochrome b. Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent Taxonomy
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose incisors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
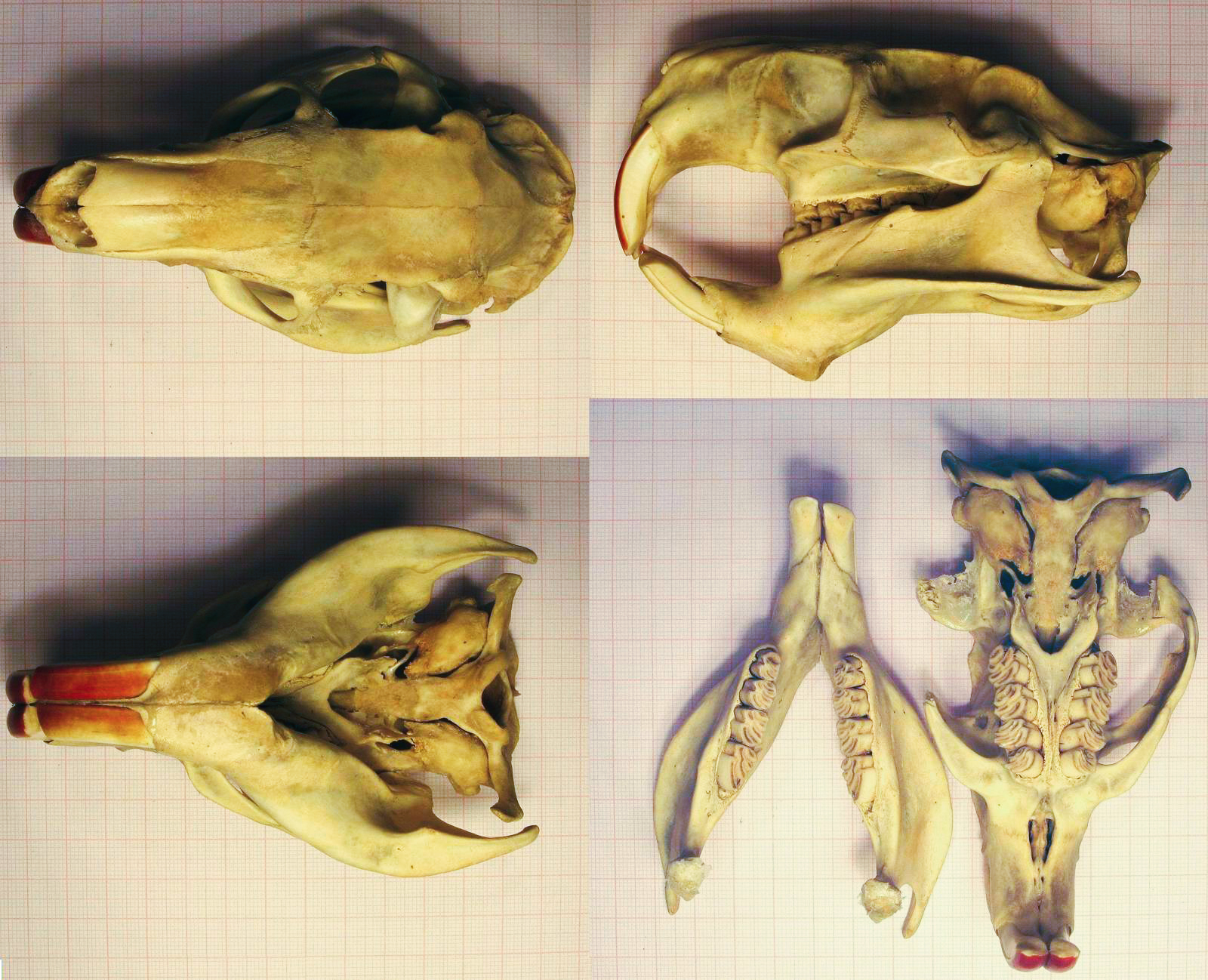
Pedetidae
The Pedetidae are a family of mammals from the rodent order. The two living species, the springhares, are distributed throughout much of southern Africa and also around Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Fossils have been found as far north as Turkey.McKenna, M.C. and Bell, S.K. 1997. Classification of Mammals: Above the species level. New York: Columbia University Press, 631 pp. (p. 185) Together with the anomalures and zenkerella, Pedetidae forms the suborder Anomaluromorpha. The fossil genus '' Parapedetes'' is also related. Taxonomy The family includes one living genus and three extinct genera. The Asian fossil ''Diatomys'' was previously included, but is now classified in the family Diatomyidae with the Laotian rock rat. *Family Pedetidae **Genus '' Pedetes'' *** South African springhare, ''P. capensis'' ***†''Pedetes gracilis'' ***†''Pedetes hagenstadti'' *** East African springhare, ''P. surdaster'' **Genus †''Megapedetes ''Megapedetes'' is a genus of fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon Scaly-tail
The Cameroon scaly-tail (''Zenkerella insignis''), also referred to as the Cameroon anomalure, flightless anomalure or flightless scaly-tail, is a rodent species endemic to West Central Africa. The scientific literature has never (or possibly only obscurely) reported observations of live individuals. The taxonomic classification of the species has been subject to recent revision. Phylogeny Previous common names for this species included ''flightless scaly-tail ‘squirrel’'', but this is a misnomer as anomalures are very distantly related to the true squirrels of the rodent family Sciuridae and only superficially resemble them. ''Z. insignis'' is the only extant species in the genus ''Zenkerella'' and family Zenkerellidae and is the only surviving species of a lineage that diverged from the other extant anomalures (genera '' Idiurus'' and ''Anomalurus'') ~49 million years ago (Ma). Among mammals, very few species are the sole survivors of such ancient lineages, some other examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciurognathi
Sciurognathi is a suborder of rodents that includes squirrels, chipmunks, beavers, and many types of mice. The group is characterized by a specific shape to the lower jaw. In sciurognaths, the angular process of the jaw is in the same plane as the root of the incisors. This is in contrast to the suborder Hystricognathi where the angular process is outside the plane formed at the root of the incisor due to the presence of a shelf for muscle attachment. The sciurognathous condition is considered to be the primitive condition in rodents, and is therefore not a good character for cladistic analysis. Although hystricognaths are almost universally accepted as representing a real evolutionary grouping, most researchers do not consider Sciurognathi as an equally valid group. In particular, gundis are thought to be more closely related to the hystricognathous rodents than to other sciurognaths. In spite of this, most texts continue to use these two suborders due primarily to a lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenkerella (rodent)
''Zenkerella'' is a genus of rodent, the only member of the family Zenkerellidae. It was formerly classified in Anomaluridae until phylogenetic studies made its distinctiveness clear. While the Anomalurus of the family Anomaluridae has gliding membranes between its forelimb and hindlimb, the Zenkerella has no such adaptation. It is estimated from fossil records that this divergence might have occurred in the middle of the Eocene. There is a single extant and a single fossil representative. The fossil species '' Zenkerella wintoni'' is known from a single mandible from Songhor, Kenya dated to the Early Miocene The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages: the Aquitanian age, Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 annum, Ma to .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q19717489 Rodent genera Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by Paul Mats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenkerellinae
''Zenkerella'' is a genus of rodent, the only member of the family Zenkerellidae. It was formerly classified in Anomaluridae until phylogenetic studies made its distinctiveness clear. While the Anomalurus of the family Anomaluridae has gliding membranes between its forelimb and hindlimb, the Zenkerella has no such adaptation. It is estimated from fossil records that this divergence might have occurred in the middle of the Eocene. There is a single extant and a single fossil representative. The fossil species '' Zenkerella wintoni'' is known from a single mandible from Songhor, Kenya dated to the Early Miocene The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages: the Aquitanian age, Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 annum, Ma to .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q19717489 Rodent genera Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by Paul Matsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hystricomorphy
The zygomasseteric system (or zygomasseteric structure) in rodents is the anatomical arrangement of the masseter muscle of the jaw and the zygomatic arch of the skull. The anteroposterior or propalinal (front-to-back) motion of the rodent jaw is enabled by an extension of the zygomatic arch and the division of the masseter into a superficial, lateral and medial muscle. The four main types are described as protrogomorphous, sciuromorphous, hystricomorphous, and myomorphous.{* Protrogomorphy The members of this grade include nearly all of the pre-Oligocene rodents of North America and Asia and some of those of Europe. Several lineages survive into the Oligocene or early Miocene, with only one species still alive today, the mountain beaver ('' Aplodontia rufa''). The molerats (family Bathyergidae) are considered secondarily protrogomorphous since their zygomatic condition is clearly derived from a hystricomorphous ancestor. The rostrum of protrogomorph rodents is unmodified an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomasseteric System
The zygomasseteric system (or zygomasseteric structure) in rodents is the anatomical arrangement of the masseter muscle of the jaw and the zygomatic arch of the skull. The anteroposterior or propalinal (front-to-back) motion of the rodent jaw is enabled by an extension of the zygomatic arch and the division of the masseter into a superficial, lateral and medial muscle. The four main types are described as protrogomorphous, sciuromorphous, hystricomorphous, and myomorphous.{* Protrogomorphy The members of this grade include nearly all of the pre-Oligocene rodents of North America and Asia and some of those of Europe. Several lineages survive into the Oligocene or early Miocene, with only one species still alive today, the mountain beaver ('' Aplodontia rufa''). The molerats (family Bathyergidae) are considered secondarily protrogomorphous since their zygomatic condition is clearly derived from a hystricomorphous ancestor. The rostrum of protrogomorph rodents is unmodified an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B
Cytochrome b within both molecular and cell biology, is a protein found in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It functions as part of the electron transport chain and is the main subunit of transmembrane cytochrome bc1 and b6f complexes. Function In the mitochondrion of eukaryotes and in aerobic prokaryotes, cytochrome b is a component of respiratory chain complex III () — also known as the bc1 complex or ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. In plant chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, there is an analogous protein, cytochrome b6, a component of the plastoquinone-plastocyanin reductase (), also known as the b6f complex. These complexes are involved in electron transport, the pumping of protons to create a proton-motive force ( PMF). This proton gradient is used for the generation of ATP. These complexes play a vital role in cells. Structure Cytochrome b/b6 is an integral membrane protein of approximately 400 amino acid residues that probably has 8 transmembrane segments. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |