|
Andreas Von Bechtolsheim
Andreas Maria Maximilian Freiherr von Mauchenheim genannt Bechtolsheim (born 30 September 1955) is a German electrical engineer, entrepreneur and investor. He co-founded Sun Microsystems in 1982 and was its chief hardware designer. His net worth reached $7 billion in September 2018.Andreas von Bechtolsheim profile forbes.com, 14 February 2018. Early life Bechtolsheim was born at Hängeberg am Ammersee, located in Finning, Landsberg, |
German People
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. One of its predecessors was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools; it became the Carnegie Institute of Technology in 1912 and began granting four-year degrees in the same year. In 1967, the Carnegie Institute of Technology merged with the Mellon Institute of Industrial Research, founded in 1913 by Andrew Mellon and Richard B. Mellon and formerly a part of the University of Pittsburgh. Carnegie Mellon University has operated as a single institution since the merger. The university consists of seven colleges and independent schools: The College of Engineering, College of Fine Arts, Dietrich College of Humanities and Social Sciences, Mellon College of Science, Tepper School of Business, Heinz College of Information Systems and Public Policy, and the School of Computer Science. The university has its main campus located 5 miles (8 km) from Dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaughan Pratt
Vaughan Pratt (born April 12, 1944) is a Professor Emeritus at Stanford University, who was an early pioneer in the field of computer science. Since 1969, Pratt has made several contributions to foundational areas such as search algorithms, sorting algorithms, and primality testing. More recently, his research has focused on formal modeling of concurrent systems and Chu spaces. Career Raised in Australia and educated at Knox Grammar School, where he was dux in 1961, Pratt attended Sydney University, where he completed his masters thesis in 1970, related to what is now known as natural language processing. He then went to the United States, where he completed a Ph.D. thesis at Stanford University in only 20 months under the supervision of advisor Donald Knuth. His thesis focused on analysis of the Shellsort sorting algorithm and sorting networks. Pratt was an assistant professor at MIT (1972 to 1976) and then associate professor (1976 to 1982). In 1974, working in collaborati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Baskett
Forest Baskett (born May 11, 1943) is an American venture capitalist, computer scientist and former professor of electrical engineering at Stanford University. He is a venture capitalist at New Enterprise Associates. Baskett designed the operating system for the original Cray-1 super-computer and was an original pioneer of Very Large Scale Integration. Baskett received a BA in Mathematics from Rice University, a Ph.D. in Computer Science from the University of Texas at Austin. He became a member of the National Academy of Engineering The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of ... in 1994 for his vision and leadership in the development of hardware and software for high-performance workstations. Baskett was the doctoral advisor of computer scientist Andy Bechtolsheim while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-large-scale Integration
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) chips were developed and then widely adopted, enabling complex semiconductor and telecommunication technologies. The microprocessor and memory chips are VLSI devices. Before the introduction of VLSI technology, most ICs had a limited set of functions they could perform. An electronic circuit might consist of a CPU, ROM, RAM and other glue logic. VLSI enables IC designers to add all of these into one chip. History Background The history of the transistor dates to the 1920s when several inventors attempted devices that were intended to control current in solid-state diodes and convert them into triodes. Success came after World War II, when the use of silicon and germanium crystals as radar detectors led to improvements in fabric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynn Conway
Lynn Ann Conway (born January 2, 1938) is an American computer scientist, electrical engineer and transgender activist. She worked at IBM in the 1960s and invented generalized dynamic instruction handling, a key advance used in out-of-order execution, used by most modern computer processors to improve performance. She initiated the Mead-Conway VLSI chip design revolution in very large scale integrated (VLSI) microchip design. That revolution spread rapidly through the research universities and computing industries during the 1980s, incubating an emerging electronic design automation industry, spawning the modern 'foundry' infrastructure for chip design and production, and triggering a rush of impactful high-tech startups in the 1980s and 1990s."Lynn Conway: 2009 Computer Pioneer Award R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARC (company)
PARC (Palo Alto Research Center; formerly Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. Founded in 1969 by Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, the company was originally a division of Xerox, tasked with creating computer technology-related products and hardware systems. Xerox PARC has been at the heart of numerous revolutionary computer developments, including laser printing, Ethernet, the modern personal computer, GUI (graphical user interface) and desktop paradigm, object-oriented programming, ubiquitous computing, electronic paper, a-Si (amorphous silicon) applications, the computer mouse, and VLSI (very-large-scale integration) for semiconductors. Unlike Xerox's existing research laboratory in Rochester, New York, which focused on refining and expanding the company's copier business, Goldman's “Advanced Scientific & Systems Laboratory” aimed to pioneer new technologies in advanced physics, materials science, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerox Alto
The Xerox Alto is a computer designed from its inception to support an operating system based on a graphical user interface (GUI), later using the desktop metaphor. The first machines were introduced on 1 March 1973, a decade before mass-market GUI machines became available. The Alto is contained in a relatively small cabinet and uses a custom central processing unit (CPU) built from multiple SSI and MSI integrated circuits. Each machine cost tens of thousands of dollars despite its status as a personal computer. Only small numbers were built initially, but by the late 1970s, about 1,000 were in use at various Xerox laboratories, and about another 500 in several universities. Total production was about 2,000 systems. The Alto became well known in Silicon Valley and its GUI was increasingly seen as the future of computing. In 1979, Steve Jobs arranged a visit to Xerox PARC, during which Apple Computer personnel would receive demonstrations of Xerox technology in exchange for Xer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University Network
The Stanford University Network, also known as SUN, SUNet or SU-Net is the campus computer network for Stanford University. History Stanford Research Institute, formerly part of Stanford but on a separate campus, was the site of one of the four original ARPANET nodes. Later ARPANET nodes were located in the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, the Computer Science Department, and the Stanford University Medical Center. In late 1979, the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center donated equipment including Xerox Alto computers, a laser printer, and file server connected by Ethernet local area network technology. CSL Technical Report 229 (First author name is misspelled on cover) A router based on the PDP-11 computer from Digital Equipment Corporation with software from MIT was used to connect the Ethernet to the ARPANET. The PARC Universal Packet protocol was initially used on the local parts of the network, which was the experimental version of Ethernet with a data rate und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUN Workstation
The SUN workstation was a modular computer system designed at Stanford University in the early 1980s. It became the seed technology for many commercial products, including the original workstations from Sun Microsystems. History In 1979 Xerox donated some Alto computers, developed at their Palo Alto Research Center, to Stanford's Computer Science Department, as well as other universities that were developing the early Internet. The Altos were connected using Ethernet to form several local area networks. The SUN's design was inspired by that of the Alto, but used lower-cost modular components. (Many words are spelled phonetically) The project name was derived from the initials of the campus' Stanford University Network. CSL Technical Report 229 (First author name is misspelled on cover) Professor Forest Baskett suggested the best-known configuration: a relatively low-cost personal workstation for computer-aided logic design work. The design created a 3M computer: a 1 million instr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstation'' has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s. Workstations offer higher performance than mainstream personal computers, especially in CPU, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the visualization and manipulation of different types of complex data such as 3D mechanical design, engineering simulations like computational fluid dynamics, animation, medical imaging, image render ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
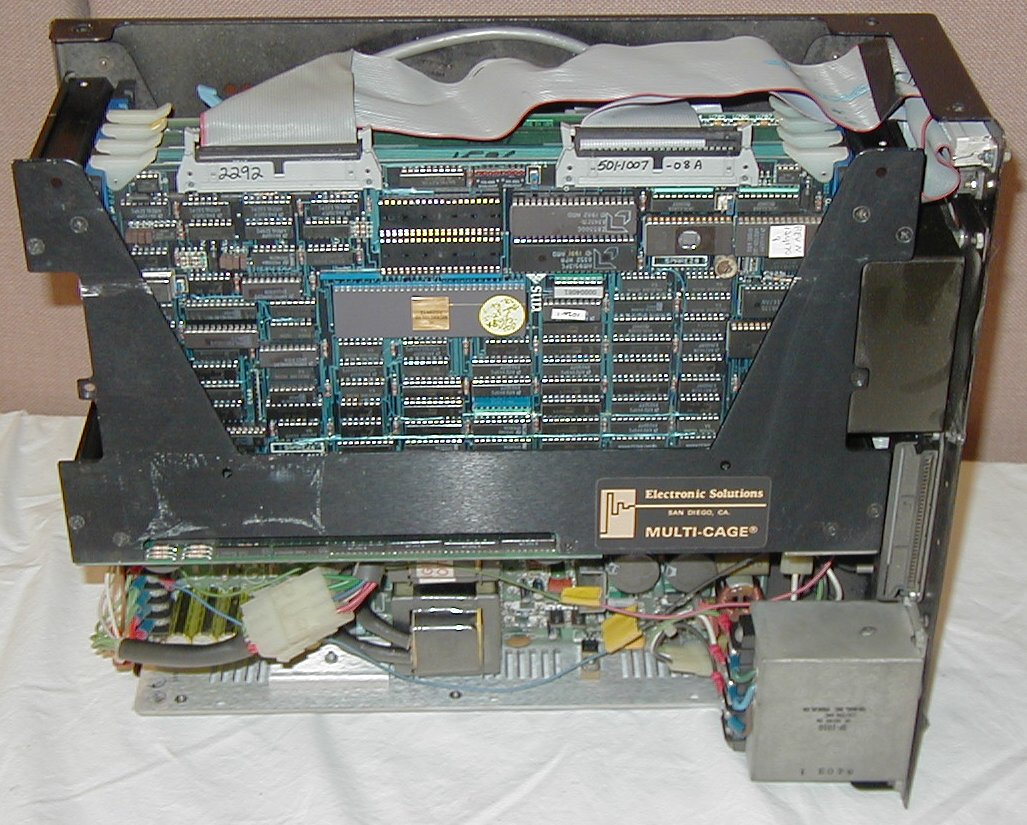
Sun100U Cardcage
Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University and funded by DARPA. The Sun-1 systems ran SunOS 0.9, a port of UniSoft's UniPlus V7 port of Seventh Edition UNIX to the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, with no window system. Early Sun-1 workstations and servers used the original Sun logo, a series of red "U"s laid out in a square, rather than the more familiar purple diamond shape used later. The first Sun-1 workstation was sold to Solo Systems in May 1982. The Sun-1/100 was used in the original Lucasfilm EditDroid non-linear editing system. Models Hardware The Sun-1 workstation was based on the Stanford University SUN workstation designed by Andy Bechtolsheim (advised by Vaughan Pratt and Forest Baskett), a graduate student and co-founder of Sun Microsystems. At the heart of this d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
