|
Analatos Painter
The Analatos Painter was an Attica, Attic vase painter of the Early Proto-Attic vase painting, Proto-Attic style. The name of the Analatos Painter is derived from the central Attic area of Analatos (today Nea Smyrni), where several of his works have been excavated. His name vase is a ''hydria''. His period of activity is estimated to be similar to that of the Mesogeia Painter, between c. 700 and 675 BC. It is possible that the Analatos Painter was also a potter. The Analatos Painter belongs to the transition from Geometric Art, Late Geometric to Early Proto-Attic vase painting. He is thought to have been a pupil of the Late Geometric Statathou Painter. The earliest works ascribed to him are still within a clear Late Geometric tradition. For example, one of his Geometric ''hydriai'' depicts a ''Lying in repose, prothesis'' (laying-out of a body), showing Egyptian influences. The adoption of eastern influences was a key feature of the subsequent Orientalizing Period, Orient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loutrophoros Analatos Louvre CA2985 N2
A loutrophoros (Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: λουτροφόρος; Greek etymology: λουτρόν/loutron and φέρω/pherō, English language, English translation: "bathwater" and "carry") is a distinctive type of Pottery of Ancient Greece, Greek pottery Packaging and labelling, vessel characterized by an elongated neck with two Handle (grip), handles. The loutrophoros was used to carry water for a bride's pre-nuptial ritual bath, and in funeral rituals, and was placed in the tombs of the unmarried.Richter, p. 57. The loutrophoros itself is a motif for Greek tombstones, either as a relief (for instance, the lekythos on the Stele of Panaetius) or as a stone vessel. There are many in the funeral area at the Kerameikos in Athens, some of which are now preserved in the National Archaeological Museum of Athens. File:Antikensammlung Kiel 367.JPG, Attic black-figure loutrophoros-hydria; late 6th century BC File:Antikensammlung Berlin 431.JPG, Attic black-figure loutrophoros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashmolean Museum
The Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology () on Beaumont Street, Oxford, England, is Britain's first public museum. Its first building was erected in 1678–1683 to house the cabinet of curiosities that Elias Ashmole gave to the University of Oxford in 1677. It is also the world's second university museum, after the establishment of the Kunstmuseum Basel in 1661 by the University of Basel. The present building was built between 1841 and 1845. The museum reopened in 2009 after a major redevelopment, and in November 2011, new galleries focusing on Egypt and Nubia were unveiled. In May 2016, the museum also opened redisplayed galleries of 19th-century art. History Broad Street The museum opened on 24 May 1683, with naturalist Robert Plot as the first keeper. The building on Broad Street (later known as the Old Ashmolean) is sometimes attributed to Sir Christopher Wren or Thomas Wood. Elias Ashmole had acquired the collection from the gardeners, travellers, and collecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Vase Painters
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century BC Greek People
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery Of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek pottery, due to its relative durability, comprises a large part of the archaeological record of ancient Greece, and since there is so much of it (over 100,000 painted vases are recorded in the Corpus vasorum antiquorum), it has exerted a disproportionately large influence on our understanding of Greek society. The shards of pots discarded or buried in the 1st millennium BC are still the best guide available to understand the customary life and mind of the ancient Greeks. There were several vessels produced locally for everyday and kitchen use, yet finer pottery from regions such as Attica was imported by other civilizations throughout the Mediterranean, such as the Etruscans in Italy.John H. Oakley (2012). "Greek Art and Architecture, Classical: Classical Greek Pottery," in Neil Asher Silberman et al. (eds), ''The Oxford Companion to Archaeology, Vol 1: Ache-Hoho'', Second Edition, 641–644. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press. , p. 641. There were a multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Greek Vase Painters
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Mannack
Thomas Mannack (born in 1958) is a German classical archaeologist. Mannack obtained his Doctorate in 1992 with at the University of Kiel. The thema of his dissertation was ''Beazleys spätere und späteste Manieristen''. He is a specialist in the field of ancient ceramics. He is in charge of the Beazley Archive database and teaches classical iconography at the University of Oxford , mottoeng = The Lord is my light , established = , endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019) , budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20) , chancellor .... Writings * ''The Late Mannerists in Athenian Vase Painting''. Oxford University Press, Oxford 2001 (English version of the dissertation) * ''Griechische Vasenmalerei. Eine Einführung''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Boardman (art Historian)
Sir John Boardman, (; born 20 August 1927) is a classical archaeologist and art historian. He has been described as "Britain's most distinguished historian of ancient Greek art." Biography John Boardman was educated at Chigwell School (1938–1945); then Magdalene College, Cambridge, where he read Classics beginning in 1945. After completing two years' national service in the Intelligence Corps he spent three years in Greece, from 1952 to 1955, as the Assistant Director of the British School at Athens. He married Sheila Stanford in 1952 (d. 2005), and has two children, Julia and Mark. On his return to England in 1955, Boardman took up the post of Assistant Keeper at the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, thus beginning his lifelong affiliation with it. In 1959 he was appointed Reader in Classical Archaeology in the University of Oxford, and in 1963 was appointed a Fellow of Merton College. Here he remained until his appointment as Lincoln Professor of Classical Art and Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Language
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
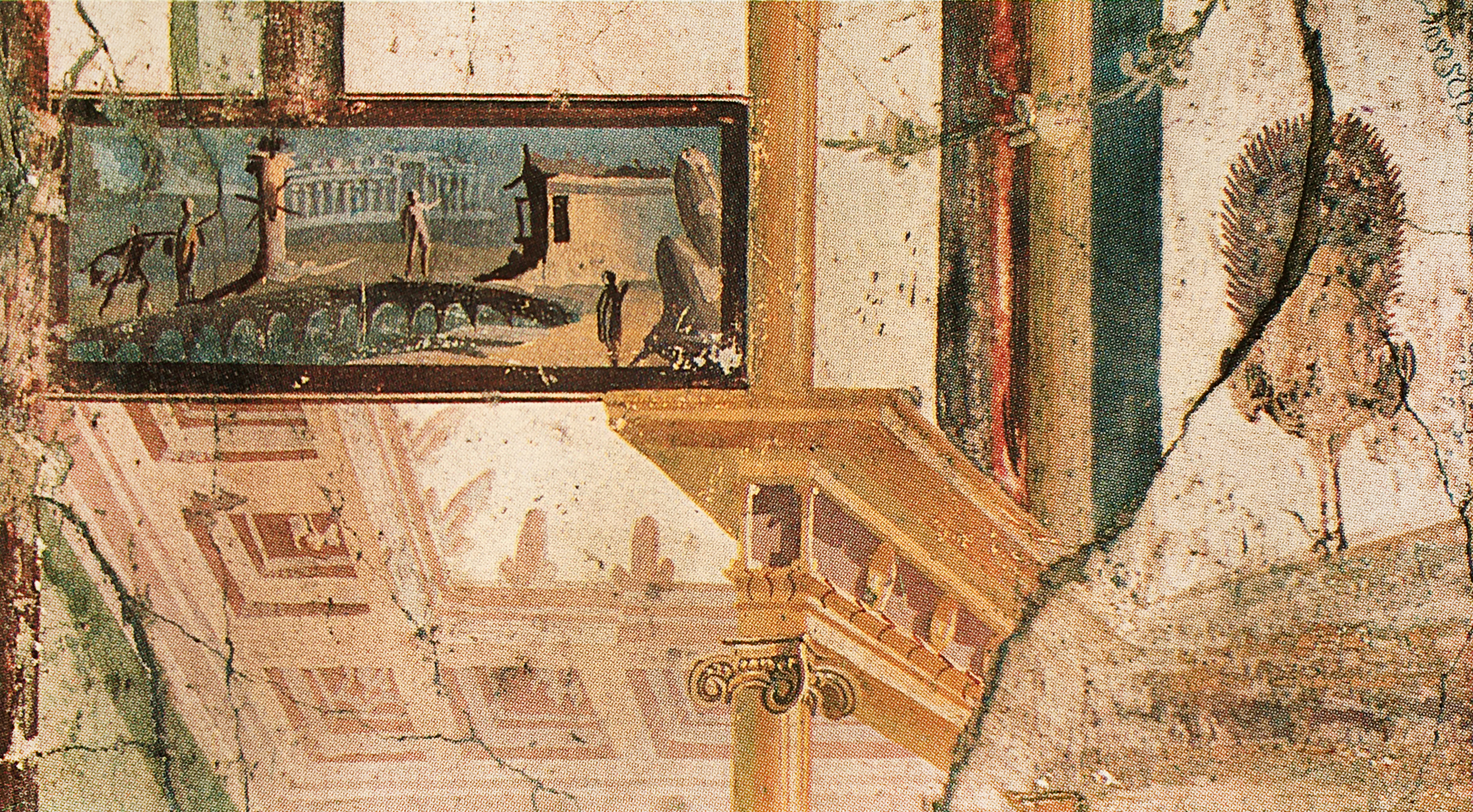
Pinax
In the modern study of the culture of ancient Greece and Magna Graecia, a ''pinax'' (πίναξ) (plural ''pinakes'' - πίνακες), meaning "board", is a votive tablet of painted wood, or terracotta, marble or bronze relief that served as a votive object deposited in a sanctuary or as a memorial affixed within a burial chamber. Such ''pinakes'' feature in the classical collections of most comprehensive museums. In the Third and Fourth Style of ancient Roman mural painting, a pinax was a painted framed picture usually in the main zone of the wall surface. Other uses To the ancient Greeks ''pinax'' seems also to have been a general term for a plate, but this is generally not followed in modern archaeological usage. In daily life ''pinax'' might equally denote a wax-covered writing tablet. In Christian contexts, painted icons ("images") are ''pinakes''. In the theatre of ancient Greece, they were images probably usually painted on cloth, but also carved either in stone o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krater
A krater or crater ( grc-gre, , ''kratēr'', literally "mixing vessel") was a large two-handled shape of vase in Ancient Greek pottery and metalwork, mostly used for the mixing of wine with water. Form and function At a Greek symposium, kraters were placed in the center of the room. They were quite large, so they were not easily portable when filled. Thus, the wine-water mixture would be withdrawn from the krater with other vessels, such as a ''kyathos'' (pl. ''kyathoi''), an ''amphora'' (pl. ''amphorai''), or a ''kylix'' (pl. ''kylikes''). In fact, Homer's ''Odyssey'' describes a steward drawing wine from a krater at a banquet and then running to and fro pouring the wine into guests' drinking cups. The modern Greek word now used for undiluted wine, ''krasi'' ( κρασί), originates from the ''krasis'' (''κράσις'', i.e., mixing) of wine and water in kraters. Pottery kraters were glazed on the interior to make the surface of the clay more impervious for holding wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |