|
Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
Ammonium sulfate precipitation is one of the most commonly used methods for large and laboratory scale protein purification and fractionation that can be used to separate proteins by altering their solubility in the presence of a high salt concentration. Properties Ammonium sulfate is an inorganic salt with a high solubility that disassociates into ammonium () and sulfate () in aqueous solutions. Ammonium sulfate is especially useful as a precipitant because it is highly soluble, stabilizes protein structure, has a relatively low density, is readily available, and is relatively inexpensive. Mechanism Ammonium sulfate, as well as other neutral salts, will stabilize proteins by preferential solvation. Proteins are usually stored in ammonium sulfate because it inhibits bacterial growth. With the addition of ammonium sulfate, proteins unfolded by denaturants can be pushed into their native conformations. This can be seen with the folding of recombinant proteins. The solubility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be " miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur. Uses The primary use of ammonium sulfate is as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil the ammonium ion is released and forms a small amount of acid, lowering the pH balance of the soil, while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth. The main disadvantage to the use of ammonium sulfate is its low nitrogen content relative to ammonium nitrate, which elevates transportation costs.Karl-Heinz Zapp "Ammonium Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It is also used as an agricultural spray adjuvant for water-soluble insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. There, it functions to bind iron and calcium cations that are present in both well water and plant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent Effects
In chemistry, solvent effects are the influence of a solvent on chemical reactivity or molecular associations. Solvents can have an effect on solubility, stability and reaction rates and choosing the appropriate solvent allows for thermodynamic and kinetic control over a chemical reaction. A solute dissolves in a solvent when solvent-solute interactions are more favorable than solute-solute interaction. Effects on stability Different solvents can affect the equilibrium constant of a reaction by differential stabilization of the reactant or product. The equilibrium is shifted in the direction of the substance that is preferentially stabilized. Stabilization of the reactant or product can occur through any of the different non-covalent interactions with the solvent such as H-bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, van der Waals interactions etc. Acid-base equilibria The ionization equilibrium of an acid or a base is affected by a solvent change. The effect of the solvent is not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
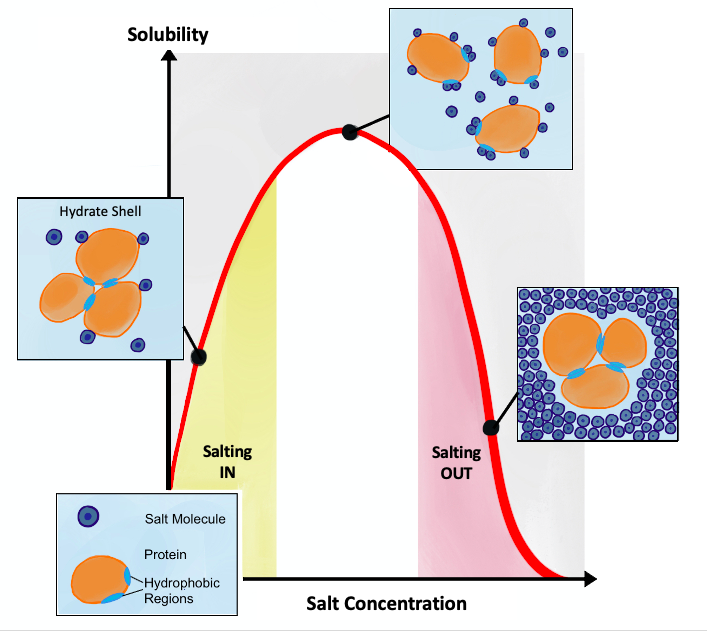
Salting In
Salting in refers to the effect where increasing the ionic strength of a solution increases the solubility of a solute, such as a protein. This effect tends to be observed at lower ionic strengths. Protein solubility is a complex function of physicochemical nature of the protein, pH, temperature, and the concentration of the salt used. It also depends on whether the salt is kosmotropic, whereby the salt will stabilize water. The solubility of proteins usually increases slightly in the presence of salt, referred to as "salting in". However, at high concentrations of salt, the solubility of the proteins drop sharply and proteins can precipitate out, referred to as "salting out". Anionic interactions Initial salting in at low concentrations is explained by the Debye–Huckel theory. Proteins are surrounded by the salt counterions (ions of opposite net charge) and this screening results in decreasing electrostatic free energy of the protein and increasing activity of the solvent, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salting Out
Salting out (also known as salt-induced precipitation, salt fractionation, anti-solvent crystallization, precipitation crystallization, or drowning out) is a purification technique that utilizes the reduced solubility of certain molecules in a solution of very high ionic strength. Salting out is typically used to precipitate large biomolecules, such as proteins or DNA. Because the salt concentration needed for a given protein to precipitate out of the solution differs from protein to protein, a specific salt concentration can be used to precipitate a target protein. This process is also used to concentrate dilute solutions of proteins. Dialysis can be used to remove the salt if needed. Principle Salt compounds dissociate in aqueous solutions. This property is exploited in the process of salting out. When the salt concentration is increased, some of the water molecules are attracted by the salt ions, which decreases the number of water molecules available to interact with the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofmeister Series
The Hofmeister series or lyotropic series is a classification of ions in order of their lyotrophic properties, which is the ability to salt out or salt in proteins. The effects of these changes were first worked out by Franz Hofmeister, who studied the effects of cations and anions on the solubility of proteins. Hofmeister discovered a series of salts that have consistent effects on the solubility of proteins and (it was discovered later) on the stability of their secondary and tertiary structure. Anions appear to have a larger effect than cations, and are usually ordered : \mathrm (This is a partial listing; many more salts have been studied.) The order of cations is usually given as : \mathrm The mechanism of the Hofmeister series is not entirely clear, but does not seem to result from changes in general water structure, instead more specific interactions between ions and proteins and ions and the water molecules directly contacting the proteins may be more important. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugation
Centrifugation is a mechanical process which involves the use of the centrifugal force to separate particles from a solution according to their size, shape, density, medium viscosity and rotor speed. The denser components of the mixture migrate away from the axis of the centrifuge, while the less dense components of the mixture migrate towards the axis. Chemists and biologists may increase the effective gravitational force of the test tube so that the precipitate (pellet) will travel quickly and fully to the bottom of the tube. The remaining liquid that lies above the precipitate is called a supernatant or supernate. There is a correlation between the size and density of a particle and the rate that the particle separates from a heterogeneous mixture, when the only force applied is that of gravity. The larger the size and the larger the density of the particles, the faster they separate from the mixture. By applying a larger effective gravitational force to the mixture, like a ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Filtration
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), also known as molecular sieve chromatography, is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. The chromatography column is packed with fine, porous beads which are commonly composed of dextran, agarose, or polyacrylamide polymers. The pore sizes of these beads are used to estimate the dimensions of macromolecules. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers. Applications The main application of gel-filtration chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Chromatography
Ion chromatography (or ion-exchange chromatography) separates ions and polar molecules based on their affinity to the ion exchanger. It works on almost any kind of charged molecule—including large proteins, small nucleotides, and amino acids. However, ion chromatography must be done in conditions that are one unit away from the isoelectric point of a protein. The two types of ion chromatography are anion-exchange and cation-exchange. Cation-exchange chromatography is used when the molecule of interest is positively charged. The molecule is positively charged because the pH for chromatography is less than the pI (a/k/a pH(I)). In this type of chromatography, the stationary phase is negatively charged and positively charged molecules are loaded to be attracted to it. Anion-exchange chromatography is when the stationary phase is positively charged and negatively charged molecules (meaning that pH for chromatography is greater than the pI) are loaded to be attracted to it. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size-exclusion Chromatography
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), also known as molecular sieve chromatography, is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. The chromatography column is packed with fine, porous beads which are commonly composed of dextran, agarose, or polyacrylamide polymers. The pore sizes of these beads are used to estimate the dimensions of macromolecules. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers. Applications The main application of gel-filtration chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |