|
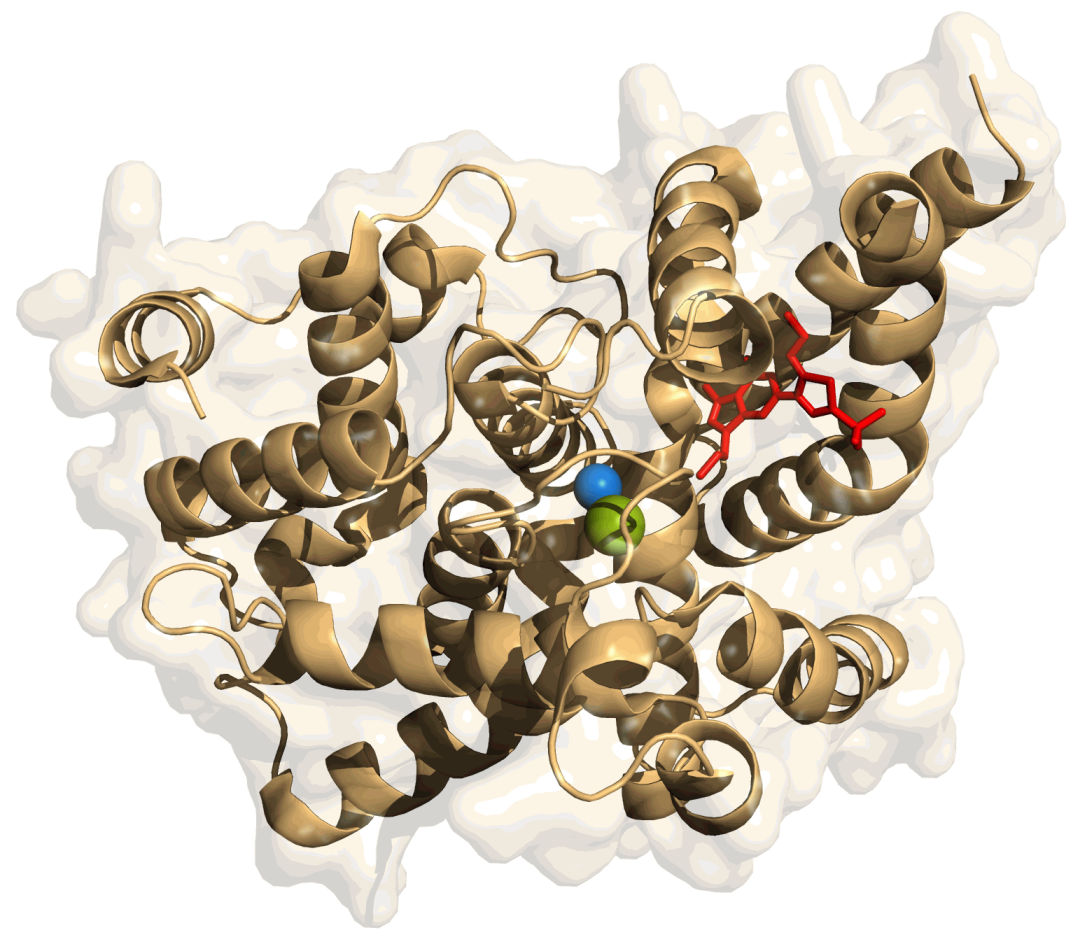
Aminophylline
Aminophylline is a compound of the bronchodilator theophylline with ethylenediamine in 2:1 ratio. The ethylenediamine improves solubility, and the aminophylline is usually found as a dihydrate. Aminophylline is less potent and shorter-acting than theophylline. Its most common use is in the treatment of airway obstruction from asthma or COPD. Aminophylline is a nonselective adenosine receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Medical uses Intravenous aminophylline can be used for acute exacerbation of symptoms and reversible airway obstruction in asthma and other chronic lung disease such as COPD, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is used as an adjunct to inhaled beta-2 selective agonists and systemically administered corticosteroids. Aminophylline is used to reverse regadenoson, dipyridamole or adenosine based infusions during nuclear cardiology stress testing. Aminophylline has also been reported to be effective in preventing slow heart rates during complex cardio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), thereby preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) by the respective PDE subtype(s). The ubiquitous presence of this enzyme means that non-specific inhibitors have a wide range of actions, the actions in the heart, and lungs being some of the first to find a therapeutic use. History The different forms or subtypes of phosphodiesterase were initially isolated from rat brains in the early 1970s and were soon afterward shown to be selectively inhibited in the brain and in other tissues by a variety of drugs. The potential for selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors as therapeutic agents was predicted as early as 1977 by Weiss and Hait. This prediction meanwhile has proved to be true in a variety of fields. Classification Nonselective PDE inhibitors Methy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthine
Xanthine ( or ; archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms. Several stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Xanthine is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. * It is created from guanine by guanine deaminase. * It is created from hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidoreductase. * It is also created from xanthosine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the xanthine oxidase enzyme. Use and manufacturing Xanthine is used as a drug precursor for human and animal medications, and is manufactured as a pesticide ingredient. Clinical significance Derivatives of xanthine (known collectively as xanthines) are a group of alkaloids commonly used for their effects as mild stimulants and as bronchodilators, notably in the treatment of asthma or infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a phosphodiesterase inhibiting drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma under a variety of brand names. As a member of the xanthine family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to theobromine and caffeine, and is readily found in nature, being present in tea (''Camellia sinensis'') and cocoa (''Theobroma cacao''). A small amount of theophylline is one of the products of caffeine metabolic processing in the liver. Medical uses The main actions of theophylline involve: * relaxing bronchial smooth muscle * increasing heart muscle contractility and efficiency (positive inotrope) * increasing heart rate (positive chronotropic) * increasing blood pressure * increasing renal blood flow * anti-inflammatory effects * central nervous system stimulatory effect mainly on the medullary respiratory center. The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylenediamine
Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998.Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke "Amines, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005 Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim. Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines. Synthesis Ethylenediamine is produced industrially by treating 1,2-dichloroethane with ammonia under pressure at 180 °C in an aqueous medium:Hans-Jürgen Arpe, Industrielle Organische Chemie, 6. Auflage (2007), Seite 245, Wiley VCH : In this reaction hydrogen chloride is generated, which forms a salt with the amine. The amine is liberated by addition of sodium hydroxide and can then be recovered by . Diethylenetriamine (DETA) and triethylenetetramine (TETA) ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipyridamole
Dipyridamole (trademarked as Persantine and others) is a nucleoside transport inhibitor and a PDE3 inhibitor medication that inhibits blood clot formation when given chronically and causes blood vessel dilation when given at high doses over a short time. Medical uses * Dipyridamole is used to dilate blood vessels in people with peripheral arterial disease and coronary artery disease * Dipyridamole has been shown to lower pulmonary hypertension without significant drop of systemic blood pressure * It inhibits formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines ( MCP-1, MMP-9) in vitro and results in reduction of hsCRP in patients. * It inhibits proliferation of smooth muscle cells in vivo and modestly increases unassisted patency of synthetic arteriovenous hemodialysis grafts. * It increases the release of tissue plasminogen activator from brain microvascular endothelial cells. * It results in an increase of 13-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid and decrease of 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) alleviate pain by counteracting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. On its own, COX enzyme synthesizes prostaglandins, creating inflammation. In whole, the NSAIDs prevent the prostaglandins from ever being synthesized, reducing or eliminating the inflammation and resulting pain. Some common examples of NSAIDs are aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. The newer specific COX-inhibitors are not classified together with the traditional NSAIDs, even though they presumably share the same mode of action. On the other hand, there are analgesics that are commonly associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Immunity
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms (see Beyond vertebrates).. The major functions of the innate immune system are to: * recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines * activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells * identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells * activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation * act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Receptor
The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene. The adenosine receptors are commonly known for their antagonists caffeine and theophylline, whose action on the receptors produces the stimulating effects of coffee, tea and chocolate. Pharmacology Each type of adenosine receptor has different functions, although with some overlap. For instance, both A1 receptors and A2A play roles in the heart, regulating myocardial oxygen consumption and coronary blood flow, while the A2A receptor also has broader anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body. These two receptors also have important roles in the brain, regulating the release of other neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate, while the A2B and A3 receptors are located mainly peripherally and are involved in proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in fat adipocytes. The most important regulatory hormone in lipolysis is insulin; lipolysis can only occur when insulin action falls to low levels, as occurs during fasting. Other hormones that affect lipolysis include glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine, growth hormone, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, and cortisol. Mechanisms In the body, stores of fat are referred to as adipose tissue. In these areas, intracellular triglycerides are stored in cytoplasmic lipid droplets. When lipase enzymes are phosphorylated, they can access lipid droplets and through multiple steps of hydrolysis, breakdown triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. Each step of hydrolysis leads to the removal of one fatty acid. The first step and the rate-limiting step of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at various locations in the interior of the cell. Adenylate cyclase is ''activated'' by a range of signaling molecules through the activation of adenylate cyclase stimulatory G ( Gs)-protein-coupled receptors. Adenylate cyclase is ''inhibited'' by agonists of adenyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catecholamine
A catecholamine (; abbreviated CA) is a monoamine neurotransmitter, an organic compound that has a catechol (benzene with two hydroxyl side groups next to each other) and a side-chain amine. Catechol can be either a free molecule or a substituent of a larger molecule, where it represents a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene group. Catecholamines are derived from the amino acid tyrosine, which is derived from dietary sources as well as synthesis from phenylalanine. Catecholamines are water-soluble and are 50% bound to plasma proteins in circulation. Included among catecholamines are epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and dopamine. Release of the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine from the adrenal medulla of the adrenal glands is part of the fight-or-flight response. Tyrosine is created from phenylalanine by hydroxylation by the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Tyrosine is also ingested directly from dietary protein. Catecholamine-secreting cells u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |