|
Alfisols
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron (Fe). Because of their productivity and abundance, Alfisols represent one of the more important soil orders for food and fiber production. They are widely used both in agriculture and forestry, and are generally easier to keep fertile than other humid-climate soils, though those in Australia and Africa are still very deficient in nitrogen and available phosphorus. Those in monsoonal tropical regions, however, have a tendency to acidify when heavily cultivated, especially when nitrogenous fertilizers are used. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), most Alfisols are classified as Luvisols or Lixisols, but some are classed as Retisols or Nitisols. Aqualfs are mainly Stagnosols or Planosols. Alfisols with a natric hori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitisol
A nitisol in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is a deep, red, well-drained soil with a clay content of more than 30% and a blocky structure. Nitisols correlate with the kandic alfisols, ultisols and inceptisols of the USDA soil taxonomy. These soils are found in the tropics and subtropics; there are extensive areas of them in the tropical highlands of Ethiopia, Kenya, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Cameroon. Nitisols form from fine-textured material weathered from intermediate to basic parent rock and kaolinite, halloysite and iron oxides dominate their clay mineralogy. The natural vegetation on nitisols includes tropical rain forest and savannah. Limitations frequently include low phosphorus availability and low base status, but once ameliorated, these deep, stable soils have high agricultural potential, and are often planted to crops. See also *Pedogenesis *Pedology *Soil classification Soil classification deals with the systematic categoriza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxisol
Oxisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy, best known for their occurrence in tropical rain forest within 25 degrees north and south of the Equator. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), they belong mainly to the ferralsols, but some are plinthosols or nitisols. Some oxisols have been previously classified as laterite soils. Formation The main processes of soil formation of oxisols are weathering, humification and pedoturbation due to animals. These processes produce the characteristic soil profile. They are defined as soils containing ''at all depths'' no more than ten percent weatherable minerals, and low cation exchange capacity. Oxisols are always a red or yellowish color, due to the high concentration of iron(III) and aluminium oxides and hydroxides. They also contain quartz and kaolin, plus small amounts of other clay minerals and organic matter. Etymology The word "oxisol" comes from ''"oxide"'' in reference to the dominance of oxide minerals such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USDA Soil Taxonomy
USDA soil taxonomy (ST) developed by the United States Department of Agriculture and the National Cooperative Soil Survey provides an elaborate classification of soil types according to several parameters (most commonly their properties) and in several levels: ''Order'', ''Suborder'', ''Great Group'', ''Subgroup'', ''Family'', and '' Series''. The classification was originally developed by Guy Donald Smith, former director of the U.S. Department of Agriculture's soil survey investigations. Discussion A taxonomy is an arrangement in a systematic manner; the USDA soil taxonomy has six levels of classification. They are, from most general to specific: order, suborder, great group, subgroup, family and series. Soil properties that can be measured quantitatively are used in this classification system – they include: depth, moisture, temperature, texture, structure, cation exchange capacity, base saturation, clay mineralogy, organic matter content and salt content. There are 12 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
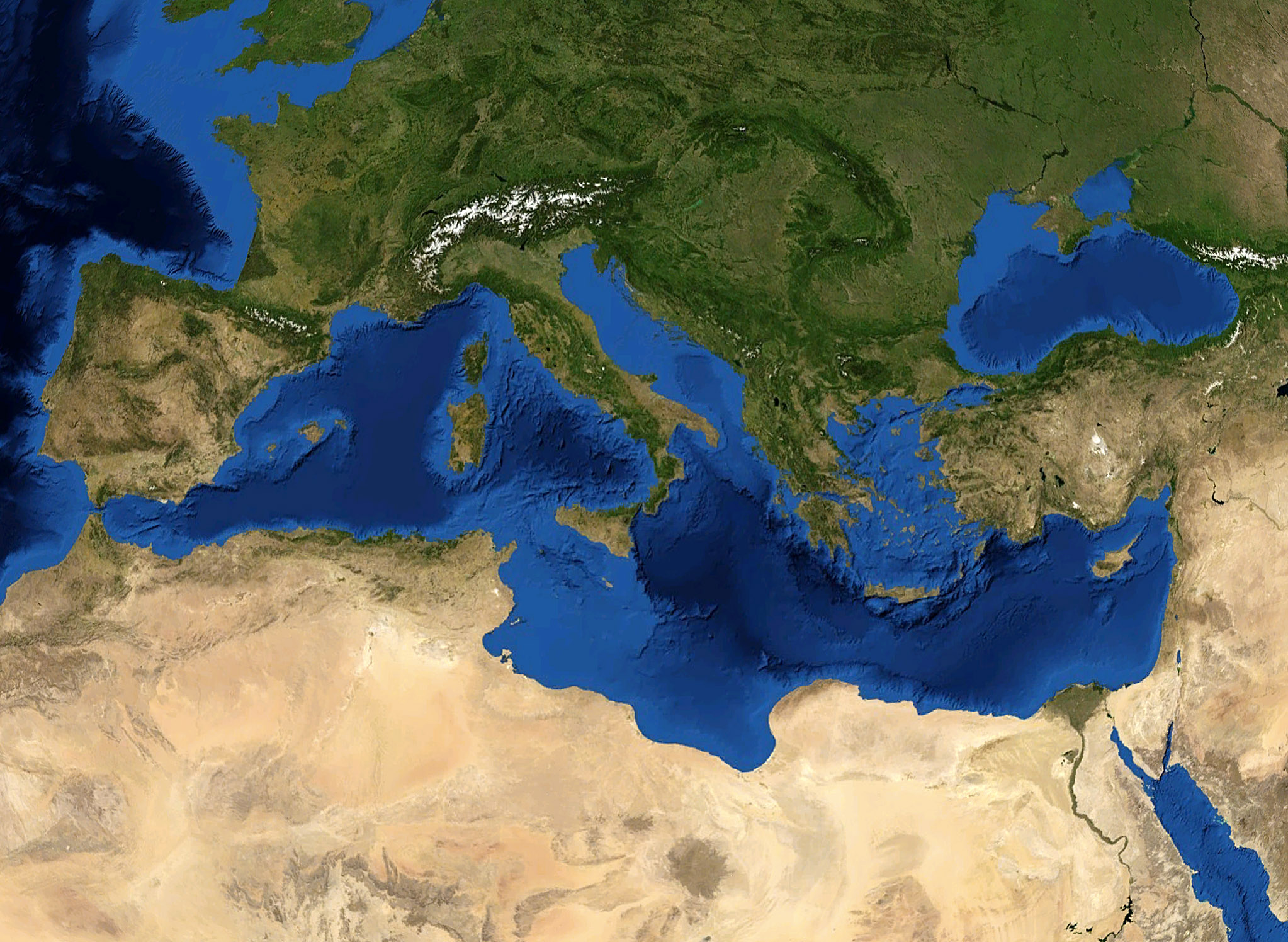
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, East Thrace, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Moldova, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, Southern France, Spain, and Vatican City (the Holy See). Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Apennine Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
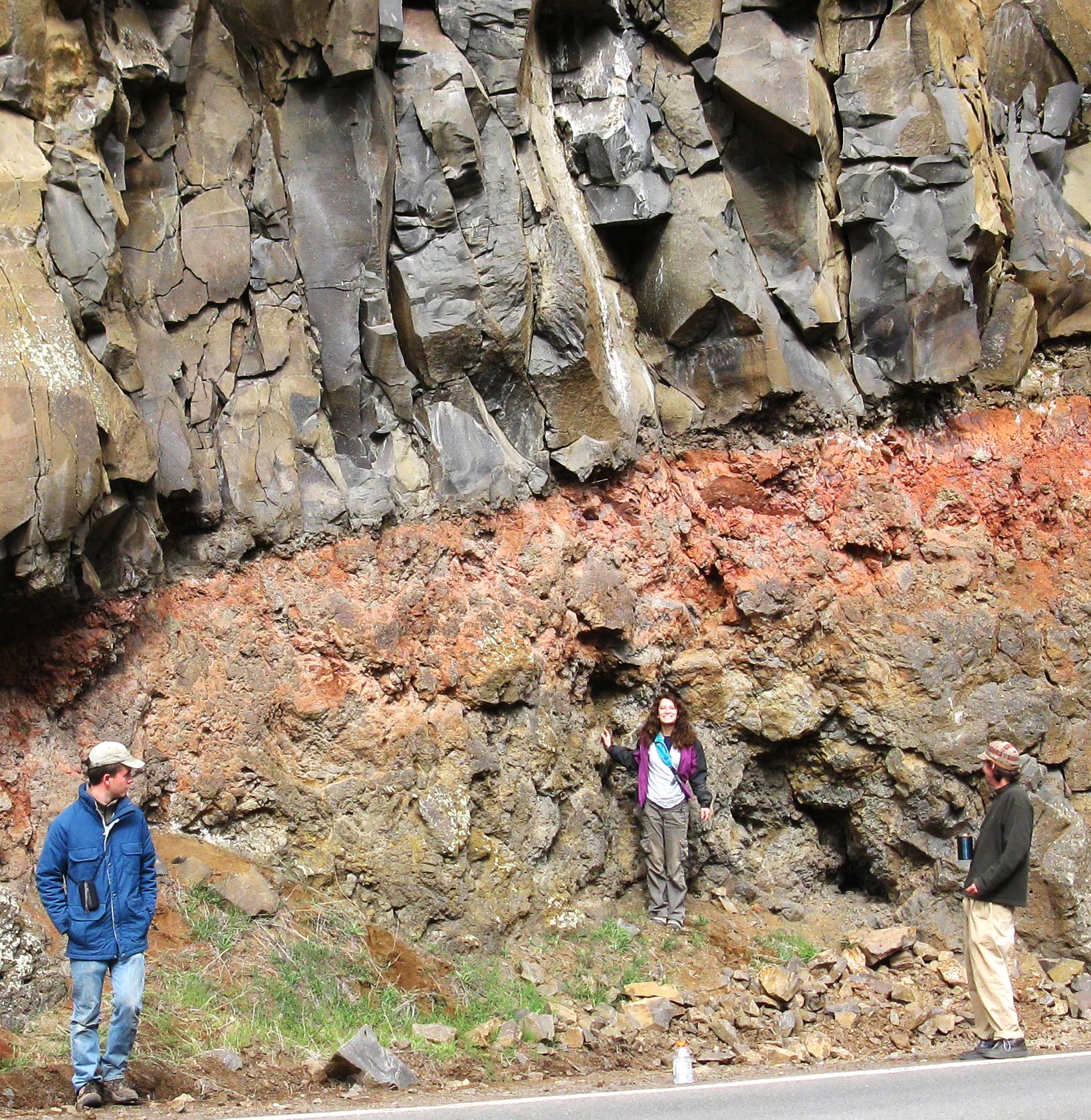
Paleopedological Record
{{inline citations, date=June 2013 The paleopedological record is, essentially, the fossil record of soils. The paleopedological record consists chiefly of paleosols buried by flood sediments, or preserved at geological unconformities, especially plateau escarpments or sides of river valleys. Other fossil soils occur in areas where volcanic activity has covered the ancient soils. Problems of recognition After burial, soil fossils tend to be altered by various chemical and physical processes. These include: * Decomposition of organic matter that was once present in the old soil. This hinders the recognition of vegetation that was in the soil when it was present. * Oxidation of iron from Fe2+ to Fe3+ by O2 as the former soil becomes dry and more oxygen enters the soil. * Drying out of hydrous ferric oxides to anhydrous oxides - again due to the presence of more available O2 in the dry environment. The keys to recognising fossils of various soils include: * Tubular structures tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultisols
Ultisols, commonly known as red clay soils, are one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continuous weathering of minerals in a humid, temperate climate without new soil formation via glaciation. They are defined as mineral soils which contain no calcareous ( calcium carbonate containing) material anywhere within the soil, have less than 10% weatherable minerals in the extreme top layer of soil, and have less than 35% base saturation throughout the soil. Ultisols occur in humid temperate or tropical regions. While the term is usually applied to the red clay soils of the Southern United States, Ultisols are also found in regions of Africa, Asia, and South America. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), most Ultisols are known as Acrisols and Alisols. Some belong to the Retisols or to the Nitisols. Aquults are typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

