|
Albion
Albion is an alternative name for Great Britain. The oldest attestation of the toponym comes from the Greek language. It is sometimes used poetically and generally to refer to the island, but is less common than 'Britain' today. The name for Scotland in most of the Celtic languages is related to Albion: ''Alba'' in Scottish Gaelic, ''Albain'' (genitive ''Alban'') in Irish, ''Nalbin'' in Manx and ''Alban'' in Welsh and Cornish. These names were later Latinised as ''Albania'' and Anglicised as ''Albany'', which were once alternative names for Scotland. ''New Albion'' and ''Albionoria'' ("Albion of the North") were briefly suggested as names of Canada during the period of the Canadian Confederation. Sir Francis Drake gave the name New Albion to what is now California when he landed there in 1579. Etymology The toponym is thought to derive from the Greek word , Latinised as ( genitive ). It was seen in the Proto-Celtic nasal stem * ( oblique *) and survived in Old Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Albion
New Albion, also known as ''Nova Albion'' (in reference to an archaic name for Britain), was the name of the continental area north of Mexico claimed by Sir Francis Drake for England when he landed on the North American west coast in 1579. This claim became the justification for English charters across America to the Atlantic coast and soon influenced further national expansion projects on the continent. Drake's landing site has been identified as Drake's Cove, which is part of Point Reyes National Seashore. Drake, after successfully sacking Spanish towns and plundering Spanish ships along their eastern Pacific coast colonies, sought safe harbour to prepare his ship, '' Golden Hind'', for circumnavigation back to England. He found it on 17 June 1579, when he and his crew landed on the Pacific coast at Drakes Bay in Northern California. While encamped there, he had friendly relations with the Coast Miwok people who inhabited the area near his landing. Naming the area ''Nova Alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The 60% smaller island of Ireland is to the west—these islands, along with over 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, form the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a landbridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's third-most-populous island after Java in Indonesia and Honshu in Japan. The term "Great Britain" is often used to refer to England, Scotland and Wales, including their component adjoining islands. Great Britain and Northern Ireland now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (the first English circumnavigation, the second carried out in a single expedition, and third circumnavigation overall). This included his incursion into the Pacific Ocean, until then an area of exclusive Spanish interest, and his claim to New Albion for England, an area in what is now the U.S. state of California. His expedition inaugurated an era of conflict with the Spanish on the western coast of the Americas, an area that had previously been largely unexplored by Western shipping. He was Member of Parliament (MP) for three constituencies; Camelford in 1581, Bossiney in 1584, and Plymouth in 1593. Elizabeth I awarded Drake a knighthood in 1581 which he received on the ''Golden Hind'' in Deptford. In the same year, he was appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
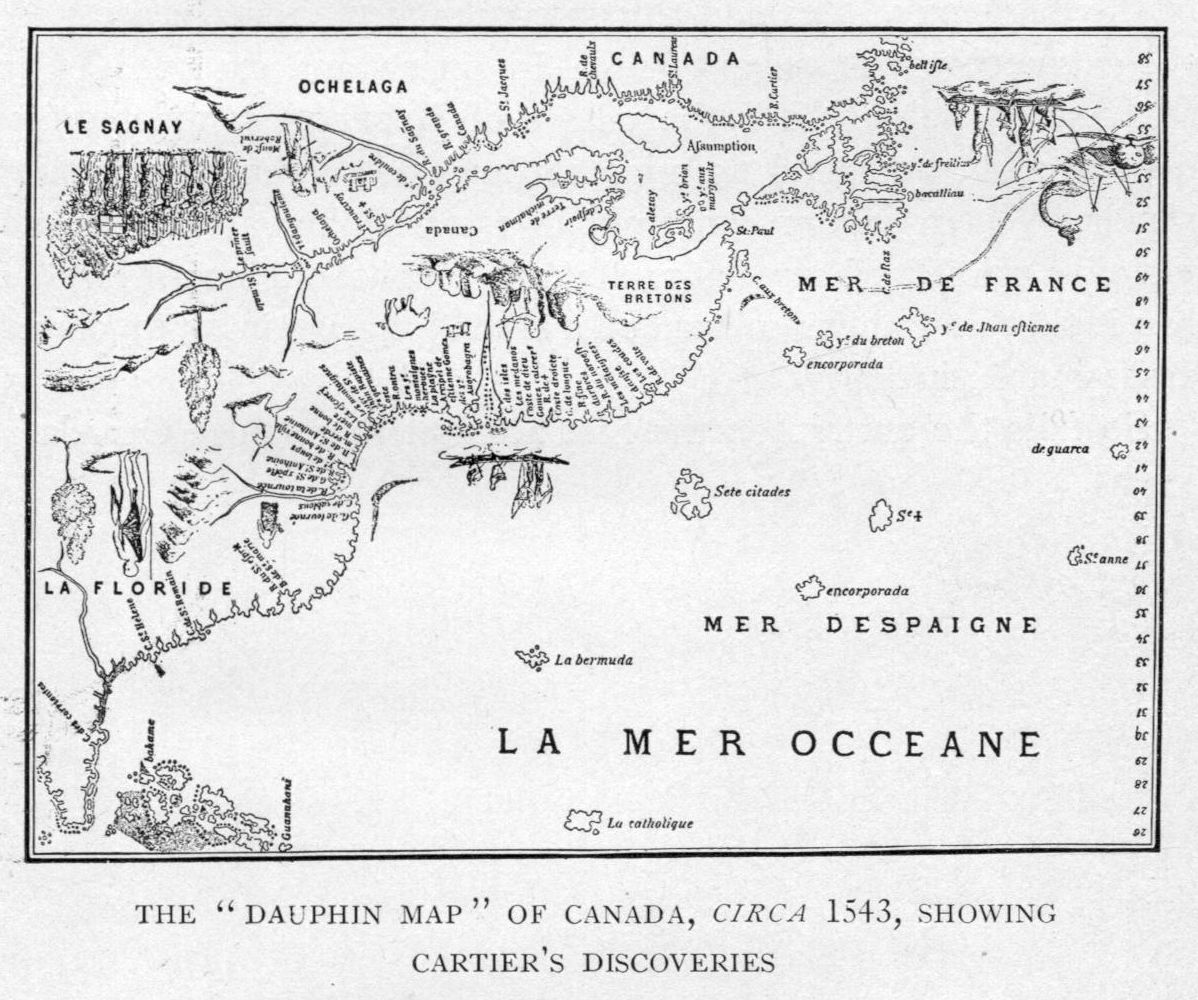
Name Of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec City region used the word to direct French explorer Jacques Cartier to the village of Stadacona. Cartier later used the word ''Canada'' to refer not only to that particular village but to the entire area subject to Donnacona (the chief at Stadacona); by 1545, European books and maps had begun referring to this small region along the Saint Lawrence River as ''Canada''. From the 16th to the early 18th century, ''Canada'' referred to the part of New France that lay along the Saint Lawrence River. In 1791, the area became two British colonies called Upper Canada and Lower Canada. These two colonies were collectively named the Canadas until their union as the British Province of Canada in 1841. Upon Confederation in 1867, ''Canada'' was ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonia
Caledonia (; ) was the Latin name used by the Roman Empire to refer to the part of Great Britain () that lies north of the River Forth, which includes most of the land area of Scotland. Today, it is used as a romantic or poetic name for all of Scotland. During the Roman Empire's occupation of Scotland, the area they called Caledonia was physically separated from the rest of the island by the Antonine Wall. The Romans several times invaded and occupied it, but unlike the rest of the island, it remained outside the administration of Roman Britain. Latin historians, including Tacitus and Cassius Dio, referred to the territory north of the River Forth as "Caledonia", and described it as inhabited by the Maeatae and the Caledonians (). Other ancient authors, however, used the adjective "Caledonian" more generally to describe anything pertaining to inland or northern Britain. The name is probably derived from a word in one of the Gallo-Brittonic languages. History Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Cliffs Of Dover 09 2004
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, with the advent of neoclassical architecture, white became the most common color of new churches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The main contemporary texts are dated 700–850; by 900 the language had already transitioned into early Middle Irish. Some Old Irish texts date from the 10th century, although these are presumably copies of texts written at an earlier time. Old Irish is thus forebear to Modern Irish, Manx, and Scottish Gaelic. Old Irish is known for having a particularly complex system of morphology and especially of allomorphy (more or less unpredictable variations in stems and suffixes in differing circumstances) as well as a complex sound system involving grammatically significant consonant mutations to the initial consonant of a word. Apparently,It is difficult to know for sure, given how little Primitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatian Language
Galatian is an extinct Celtic language once spoken by the Galatians in Galatia, in central Anatolia ( Asian part of modern Turkey), from the 3rd century BC up to at least the 4th century AD. Some sources suggest that it was still spoken in the 6th century. Galatian was contemporary with, and closely related to, Gaulish. History Emergence The Galatian language, based on onomastic evidence (as no texts written in Galatian have yet been discovered), seems to have closely resembled Gaulish of western and central Europe. The language was introduced to Anatolia in the 3rd century BC, when Celtic tribes – notably the Tectosages, Trocmii, and Tolistobogii – migrated south from the Balkans. According to the Greek historian Strabo, the Tectosages of Anatolia were related to the Volcae Tectosages of Gaul; the parent tribe of both branches, the Volcae, originally lived in central Europe. Contemporary Roman sources Sometime in AD 48–55, the Apostle Paul wrote his Epistle to the Gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaulish Language
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switzerland, Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the west bank of the Rhine). In a wider sense, it also comprises varieties of Celtic that were spoken across much of central Europe (" Noric"), parts of the Balkans, and Anatolia (" Galatian"), which are thought to have been closely related. The more divergent Lepontic of Northern Italy has also sometimes been subsumed under Gaulish. Together with Lepontic and the Celtiberian spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, Gaulish helps form the geographic group of Continental Celtic languages. The precise linguistic relationships among them, as well as between them and the modern Insular Celtic languages, are uncertain and a matter of ongoing debate because of their sparse a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Celtic Language
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celtic is generally thought to have been spoken between 1300 and 800 BC, after which it began to split into different languages. Proto-Celtic is often associated with the Urnfield culture and particularly with the Hallstatt culture. Celtic languages share common features with Italic languages that are not found in other branches of Indo-European, suggesting the possibility of an earlier Italo-Celtic linguistic unity. Proto-Celtic is currently being reconstructed through the comparative method by relying on later Celtic languages. Though Continental Celtic presents much substantiation for Proto-Celtic phonology, and some for its morphology, recorded material is too scanty to allow a secure reconstruction of syntax, though some complete sente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |