|
Albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino. Varied use and interpretation of the terms mean that written reports of albinistic animals can be difficult to verify. Albinism can reduce the survivability of an animal; for example, it has been suggested that albino alligators have an average survival span of only 24 hours due to the lack of protection from UV radiation and their lack of camouflage to avoid predators. It is a common misconception that all albino animals have characteristic pink or red eyes (resulting from the lack of pigment in the iris allowing the blood vessels of the retina to be visible), however this is not the case for some forms of albinism. Familiar albino animals include in-bred strains of laboratory animals (rats, mice and rabbits), but populations of naturally occurring albino animals exist in the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculocutaneous Albinism
Oculocutaneous albinism is a form of albinism involving the eyes ('' oculo-''), the skin (''-cutaneous''), and the hair. Overall, an estimated 1 in 20,000 people worldwide are born with oculocutaneous albinism. OCA is caused by mutations in several genes that control the synthesis of melanin within the melanocytes. Seven types of oculocutaneous albinism have been described, all caused by a disruption of melanin synthesis and all autosomal recessive disorders. Oculocutaneous albinism is also found in non-human animals. Types The following types of oculocutaneous albinism have been identified in humans. See also * Piebaldism * List of skin conditions * List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer There are several conditions of or affecting the human integumentary system that are associated with an increased risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancer (i.e. squamous-cell carcinoma and basal-cell carcinoma). See also * List of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oculocutaneous Albinism
Oculocutaneous albinism is a form of albinism involving the eyes ('' oculo-''), the skin (''-cutaneous''), and the hair. Overall, an estimated 1 in 20,000 people worldwide are born with oculocutaneous albinism. OCA is caused by mutations in several genes that control the synthesis of melanin within the melanocytes. Seven types of oculocutaneous albinism have been described, all caused by a disruption of melanin synthesis and all autosomal recessive disorders. Oculocutaneous albinism is also found in non-human animals. Types The following types of oculocutaneous albinism have been identified in humans. See also * Piebaldism * List of skin conditions * List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer There are several conditions of or affecting the human integumentary system that are associated with an increased risk of developing nonmelanoma skin cancer (i.e. squamous-cell carcinoma and basal-cell carcinoma). See also * List of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. Functionally, eumelanin serves as protection against Ultraviolet, UV radiation. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. The most common type is eumelanin, of which there are two types— brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Pheomelanin, which is produced when melanocytes are malfunctioning due to derivation of the gene to its recessive format is a cysteine-derivative that contains polybenzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the of red yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheomelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. Functionally, eumelanin serves as protection against UV radiation. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. The most common type is eumelanin, of which there are two types— brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Pheomelanin, which is produced when melanocytes are malfunctioning due to derivation of the gene to its recessive format is a cysteine-derivative that contains poly benzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the of red yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumelanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. Functionally, eumelanin serves as protection against UV radiation. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. The most common type is eumelanin, of which there are two types— brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Pheomelanin, which is produced when melanocytes are malfunctioning due to derivation of the gene to its recessive format is a cysteine-derivative that contains poly benzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the of red yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
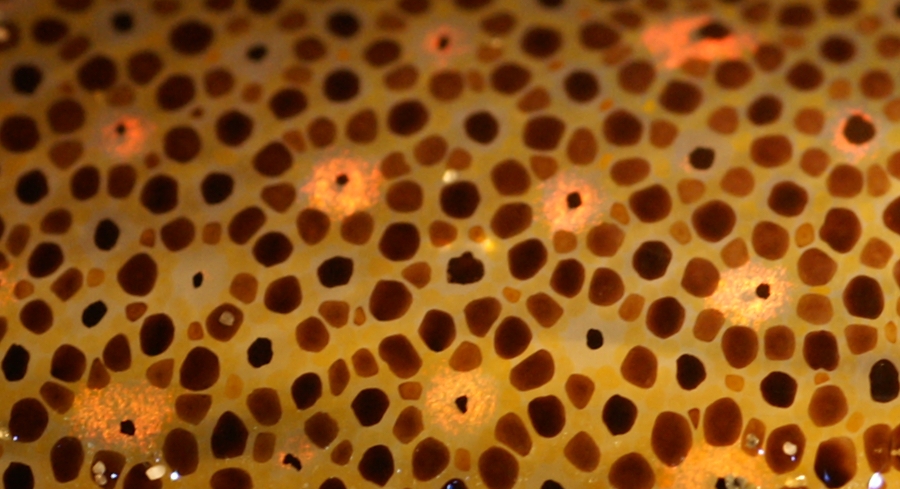
Claude (alligator)
Claude is an albino alligator ('' Alligator mississippiensis'') at the California Academy of Sciences. Claude lacks the pigment melanin, resulting in colorless skin, and he has poor eyesight associated with his albinism. Background Claude was hatched on 15 September 1995 in Louisiana weighing . He weighs and is long. He has 76 teeth. He was in danger in the wilderness owing to albinism which did not allow him to camouflage into his surroundings like other alligators. There are only a couple of dozen known albino alligators in the world, all in captivity. Claude was taken to the California Academy of Sciences The California Academy of Sciences is a research institute and natural history museum in San Francisco, California, that is among the largest museums of natural history in the world, housing over 46 million specimens. The Academy began in 1853 ... in 2008. In 2009, a finger on Claude's right claw was amputated after developing an infection from being bitten by another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly " hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. Some species can rapidly change colour throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes to induce pigmentation. Thus darker skin tones have more melanosomes present than lighter skin tones. Functionally, melanin serves as protection against UV radiation. Melanocytes also have a role in the immune system. Function Through a process called melanogenesis, melanocytes produce melanin, which is a pigment found in the skin, eyes, hair, nasal cavity, and inner ear. This melanogenesis leads to a long-lasting pigmentation, which is in contrast to the pigmentation that originates from oxidation of already-existing melanin. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pigments
Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments. Many biological structures, such as skin, eyes, feathers, fur and hair contain pigments such as melanin in specialized cells called chromatophores. In some species, pigments accrue over very long periods during an individual's lifespan. Pigment color differs from structural color in that it is the same for all viewing angles, whereas structural color is the result of selective reflection or iridescence, usually because of multilayer structures. For example, butterfly wings typically contain structural color, although many butterflies have cells that contain pigment as well. Biological pigments See conjugated systems for electron bond chemistry that causes these molecules to have pigment. * Heme/porphyrin-based: chlorophyll, bilirubin, hemocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris (anatomy)
In humans and most mammals and birds, the iris (plural: ''irides'' or ''irises'') is a thin, annular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm. Structure The iris consists of two layers: the front pigmented fibrovascular layer known as a stroma and, beneath the stroma, pigmented epithelial cells. The stroma is connected to a sphincter muscle ( sphincter pupillae), which contracts the pupil in a circular motion, and a set of dilator muscles ( dilator pupillae), which pull the iris radially to enlarge the pupil, pulling it in folds. The sphincter pupillae is the opposing muscle of the dilator pupillae. The pupil's diameter, and thus the inner border of the iris, changes size when constricting or dilating. The outer border of the iris does not change size. The constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pigments
Biological pigments, also known simply as pigments or biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption. Biological pigments include plant pigments and flower pigments. Many biological structures, such as skin, eyes, feathers, fur and hair contain pigments such as melanin in specialized cells called chromatophores. In some species, pigments accrue over very long periods during an individual's lifespan. Pigment color differs from structural color in that it is the same for all viewing angles, whereas structural color is the result of selective reflection or iridescence, usually because of multilayer structures. For example, butterfly wings typically contain structural color, although many butterflies have cells that contain pigment as well. Biological pigments See conjugated systems for electron bond chemistry that causes these molecules to have pigment. * Heme/porphyrin-based: chlorophyll, bilirubin, hemoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Alligator
The American alligator (''Alligator mississippiensis''), sometimes referred to colloquially as a gator or common alligator, is a large crocodilian reptile native to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the two extant species in the genus ''Alligator'', and is larger than the only other living alligator species, the Chinese alligator. Adult male American alligators measure in length, and can weigh up to , with unverified sizes of up to and weights of making it one of the largest members of the family Alligatoridae, alongside the black caiman. Females are smaller, measuring in length. The American alligator inhabits subtropical and tropical freshwater wetlands, such as marshes and cypress swamps, from southern Texas to North Carolina. It is distinguished from the sympatric American crocodile by its broader snout, with overlapping jaws and darker coloration, and is less tolerant of saltwater but more tolerant of cooler climates than the American crocodile, which is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |