|
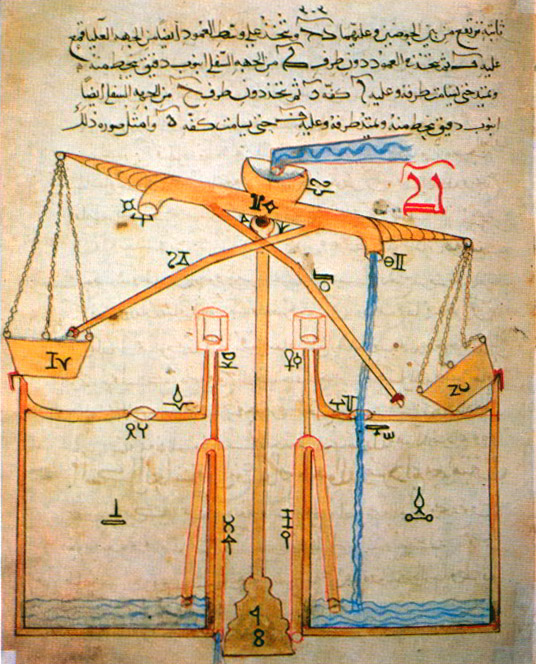
Al-Jazari
BadД«Кї az-Zaman Abu l-КїIzz ibn IsmДЃКїД«l ibn ar-RazДЃz al-JazarД« (1136–1206, ar, ШЁШЇЩЉШ№ Ш§Щ„ШІЩ…Ш§Щ† ШЈЩЋШЁЩЏ Ш§ЩЋЩ„Щ’Ш№ЩђШІЩђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ ШҐШіЩ’Щ…Ш§Ш№ЩђЩЉЩ„Щђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ Ш§Щ„Ш±ЩђЩ‘ШІШ§ШІ Ш§Щ„Ш¬ШІШ±ЩЉ, ) was a polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan, artist and mathematician from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing '' The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' ( ar, ЩѓШЄШ§ШЁ ЩЃЩЉ Щ…Ш№Ш±ЩЃШ© Ш§Щ„ШЩЉЩ„ Ш§Щ„Щ‡Щ†ШЇШіЩЉШ©, lit=Book in knowledge of engineering tricks, translit=Kitab fi ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiya) in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. He is credited with the invention of the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-jazari Water Device
BadД«Кї az-Zaman Abu l-КїIzz ibn IsmДЃКїД«l ibn ar-RazДЃz al-JazarД« (1136–1206, ar, ШЁШЇЩЉШ№ Ш§Щ„ШІЩ…Ш§Щ† ШЈЩЋШЁЩЏ Ш§ЩЋЩ„Щ’Ш№ЩђШІЩђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ ШҐШіЩ’Щ…Ш§Ш№ЩђЩЉЩ„Щђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ Ш§Щ„Ш±ЩђЩ‘ШІШ§ШІ Ш§Щ„Ш¬ШІШ±ЩЉ, ) was a polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan, artist and mathematician from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing '' The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' ( ar, ЩѓШЄШ§ШЁ ЩЃЩЉ Щ…Ш№Ш±ЩЃШ© Ш§Щ„ШЩЉЩ„ Ш§Щ„Щ‡Щ†ШЇШіЩЉШ©, lit=Book in knowledge of engineering tricks, translit=Kitab fi ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiya) in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. He is credited with the invention of the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-jazari Elephant Clock
BadД«Кї az-Zaman Abu l-КїIzz ibn IsmДЃКїД«l ibn ar-RazДЃz al-JazarД« (1136–1206, ar, ШЁШЇЩЉШ№ Ш§Щ„ШІЩ…Ш§Щ† ШЈЩЋШЁЩЏ Ш§ЩЋЩ„Щ’Ш№ЩђШІЩђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ ШҐШіЩ’Щ…Ш§Ш№ЩђЩЉЩ„Щђ ШҐШЁЩ’Щ†ЩЏ Ш§Щ„Ш±ЩђЩ‘ШІШ§ШІ Ш§Щ„Ш¬ШІШ±ЩЉ, ) was a polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan, artist and mathematician from the Artuqid Dynasty of Jazira in Mesopotamia. He is best known for writing '' The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' ( ar, ЩѓШЄШ§ШЁ ЩЃЩЉ Щ…Ш№Ш±ЩЃШ© Ш§Щ„ШЩЉЩ„ Ш§Щ„Щ‡Щ†ШЇШіЩЉШ©, lit=Book in knowledge of engineering tricks, translit=Kitab fi ma'rifat al-hiyal al-handasiya) in 1206, where he described 50 mechanical devices, along with instructions on how to construct them. He is credited with the invention of the elephant clock. He has been described as the "father of robotics" and modern day engineering. Biography Al-Jazari was born in the area of Upper Mesopotamia in 1136. Sources state his exact location is unknown, but they speculate he could have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Inventions In The Medieval Islamic World
The following is a list of inventions made in the medieval Islamic world, especially during the Islamic Golden Age,George Saliba (1994), ''A History of Arabic Astronomy: Planetary Theories During the Golden Age of Islam'', pp. 245, 250, 256–57. New York University Press, . as well as in later states of the Age of the Islamic Gunpowders such as the Ottoman and Mughal empires. The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the eighth century to the fourteenth century, with several contemporary scholars dating the end of the era to the fifteenth or sixteenth century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, where scholars from various parts of the world with different cultural backgrounds were mandated to gather and translate all of the world's classical k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Ingenious Devices
The ''Book of Ingenious Devices'' (Arabic: ЩѓШЄШ§ШЁ Ш§Щ„ШЩЉЩ„ ''Kitab al-Hiyal'', Persian: ЩѓШЄШ§ШЁ ШЄШ±ЩЃЩ†ШЇЩ‡Ш§ ''Ketab tarfandha'', literally: "The Book of Tricks") is a large illustrated work on mechanical devices, including automata, published in 850 by the three brothers of Persian descent, known as the Banu Musa (Ahmad, Muhammad and Hasan bin Musa ibn Shakir) working at the House of Wisdom (''Bayt al-Hikma'') in Baghdad, Iraq, under the Abbasid Caliphate. The book described about one hundred devices and how to use them. Overview The book was commissioned by the Abbasid Caliph of Baghdad, also made by Al-Jazari, Abu Jafar al-Ma'mun ibn Harun (786–833), who instructed the Banu Musa to acquire all of the Hellenistic texts that had been preserved by monasteries and by scholars during the decline and fall of Roman civilization. The BanЕ« MЕ«sДЃ brothers invented a number of automata (automatic machines) and mechanical devices, and they described a hundred such devices i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artuklu Palace
The Artuklu Palace or Artukid Palace or Artuqid Palace ( tr, Artuklu Sarayı) was the seat of the Diyarbakır branch of the Artuqid dynasty, a Turkish Beylik that ruled eastern Anatolia and Al-Jazira in the 12th and 13th centuries. The palace was situated in the present-day İçkale neighborhood, inside the Diyarbakır City Walls. Built during the reign of Nasir al-Din Mahmud ( tr, Salih Nasreddin Muhammed) (1200–1222) and partially excavated in the 1960s, the main body of the palace is today still buried under a mound. This palace was also where, as his father before him, the groundbreaking Muslim scholar, inventor, and mechanical engineer Al-Jazari had worked for 30 years and was the place, inspiration and context of many of this inventions and devices. Surrounded by gardens, rich in amenities as well as in decorative and artistic elements (''such as statues, with a number of scholars defining a period of less strict observance of ban on human representation in the early cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant Clock
The elephant clock was a model of water clock invented by the medieval Islamic engineer Ismail al-Jazari (1136–1206). Its design was detailed in his book, ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices.'' Representation of multiculturality Upon finishing the development and construction of his elephant clock, Al-Jazari wrote: "The elephant represents the Indian and African cultures, the two dragons represent Chinese culture, the phoenix represents Persian culture, the water work represents Greek culture, and the turban represents Islamic culture," expressing his multicultural mentality. Mechanism The timing mechanism is based on a water-filled basin hidden inside the elephant. In the bucket is a deep bowl floating in the water, but with a small hole in the centre. The bowl takes half an hour to fill through this hole. In the process of sinking, the bowl pulls a string attached to a see-saw mechanism in the tower on top of the elephant. This releases a ball that dro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Hill
Donald Routledge Hill (6 August 1922 – 30 May 1994)D. A. King, “In Memoriam: Donald Routledge Hill (1922-1994)”, ''Arabic Sciences and Philosophy,'' Volume 5 / Issue 02 / September 1995, pp 297-302 was a British engineer and historian of science and technology best known for his translation of ''The Book of Knowledge of Ingenious Mechanical Devices'' of the Muslim engineer Ismail al-Jazari.Hill Donald(1993) Life and work Born in London, after secondary school Hill served in the British army, in the Royal Engineers from 1941 to 1946. Two years he served in the Eighth Army in North Africa until he was wounded in action in Italy. Back in England he studied Engineering at the London University, obtaining his engineering degree in 1949. In 1964 he obtained his M.Litt in Islamic History at the University of Durham, and in 1970 his PhD from the University of London. Late 1940s Hill started his career working for the Iraq Petroleum Company in Lebanon, Syria and Qatar. Back in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, but some are made to resemble humans in appearance. This is claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, Ш№ЩЋШ±ЩЋШЁЩђЩЉЩЊЩ‘, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, Ш№ЩЋШ±ЩЋШЁ, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found in nearly every automobile manufactured. Current issues inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial And Error
Trial and error is a fundamental method of problem-solving characterized by repeated, varied attempts which are continued until success, or until the practicer stops trying. According to W.H. Thorpe, the term was devised by C. Lloyd Morgan (1852–1936) after trying out similar phrases "trial and failure" and "trial and practice". Under Morgan's Canon, animal behaviour should be explained in the simplest possible way. Where behavior seems to imply higher mental processes, it might be explained by trial-and-error learning. An example is a skillful way in which his terrier Tony opened the garden gate, easily misunderstood as an insightful act by someone seeing the final behavior. Lloyd Morgan, however, had watched and recorded the series of approximations by which the dog had gradually learned the response, and could demonstrate that no insight was required to explain it. Edward Lee Thorndike was the initiator of the theory of trial and error learning based on the findings he sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سه‌لاШه‌دین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, he spearheaded the Muslim military effort against the Crusader states in the Levant. At the height of his power, Ayyubid territorial control spanned Egypt, Syria, Upper Mesopotamia, the Hejaz, Yemen, the Maghreb, and Nubia. Alongside his uncle Shirkuh, a military general of the Zengid dynasty, Saladin was sent to Egypt under the Fatimid Caliphate in 1164, on the orders of Nur ad-Din. With their original purpose being to help restore Shawar as the to the teenage Fatimid caliph al-Adid, a power struggle ensued between Shirkuh and Shawar after the latter was reinstated. Saladin, meanwhile, climbed the ranks of the Fatimid government by virtue of his military successes against Crus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |