|
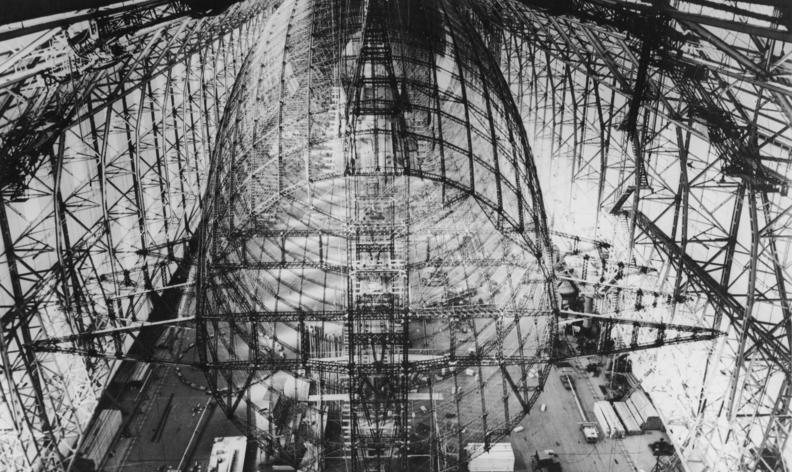
Airship
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air. In early dirigibles, the lifting gas used was hydrogen, due to its high lifting capacity and ready availability. Helium gas has almost the same lifting capacity and is not flammable, unlike hydrogen, but is rare and relatively expensive. Significant amounts were first discovered in the United States and for a while helium was only available for airships in that country. Most airships built since the 1960s have used helium, though some have used hot air.A few airships after World War II used hydrogen. The first British airship to use helium was the ''Chitty Bang Bang'' of 1967. The envelope of an airship may form the gasbag, or it may contain a number of gas-filled cells. An airship also has engines, crew, and optionally also payload accommodatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airship Gondola
An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air. In early dirigibles, the lifting gas used was hydrogen, due to its high lifting capacity and ready availability. Helium gas has almost the same lifting capacity and is not flammable, unlike hydrogen, but is rare and relatively expensive. Significant amounts were first discovered in the United States and for a while helium was only available for airships in that country. Most airships built since the 1960s have used helium, though some have used hot air.A few airships after World War II used hydrogen. The first British airship to use helium was the ''Chitty Bang Bang'' of 1967. The envelope of an airship may form the gasbag, or it may contain a number of gas-filled cells. An airship also has engines, crew, and optionally also payload accommodatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R101
R101 was one of a pair of British rigid airships completed in 1929 as part of a British government programme to develop civil airships capable of service on long-distance routes within the British Empire. It was designed and built by an Air Ministry–appointed team and was effectively in competition with the government-funded but privately designed and built R100. When built, it was the world's largest flying craft at in length, and it was not surpassed by another hydrogen-filled rigid airship until the LZ 129 ''Hindenburg'' was launched seven years later. After trial flights and subsequent modifications to increase lifting capacity, which included lengthening the ship by to add another gasbag,"R101". Airship Heritage Trust via Airshipsonline.com. Retrieved: 23 July 2008. the R101 crashed in France during its maiden overseas voy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppellin NT Amk
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155–157. and developed in detail in 1893.Dooley 2004, p. A.187. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word ''zeppelin'' came to be commonly used to refer to all rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and as scouts, resulting in over 500 deaths in bombing raids in Britain. The defeat of Germany in 1918 temporarily slowed the airship business. Although DELAG establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155–157. and developed in detail in 1893.Dooley 2004, p. A.187. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word ''zeppelin'' came to be commonly used to refer to all rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and as scouts, resulting in over 500 deaths in bombing raids in Britain. The defeat of Germany in 1918 temporarily slowed the airship business. Although DELAG establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezekiel Airship
The Ezekiel Airship was an early experimental aircraft conceived, designed, and built by the Baptist minister Burrell Cannon, an experienced sawmill operator born in 1848 in Coffeeville, Mississippi. Inspired by and named after the Book of Ezekiel, the craft's design featured four "wheel within a wheel" paddle wheels powered by a four-cylinder gasoline engine. There are unverified claims that it was flown in 1902 in Pittsburg, Texas, a year before the Wright Flyer flew at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. On an unspecified Sunday in 1902, the aircraft is alleged to have flown approximately at a height of between and in the presence of only a handful of witnesses; there is, however, no physical evidence that such a flight ever took place. Historians have generally discounted claims that the airship ever flew, although some believe that it may have achieved uncontrolled flight. The original aircraft was destroyed in a storm near Texarkana, en route to St. Louis for the 1904 World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LZ 129 Hindenburg
LZ 129 ''Hindenburg'' (; Registration: D-LZ 129) was a German commercial passenger-carrying rigid airship, the lead ship of the ''Hindenburg'' class, the longest class of flying machine and the largest airship by envelope volume. It was designed and built by the Zeppelin Company ( ''Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH'') on the shores of Lake Constance in Friedrichshafen, Germany, and was operated by the German Zeppelin Airline Company ('' Deutsche Zeppelin-Reederei''). It was named after Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, who was President of Germany from 1925 until his death in 1934. The airship flew from March 1936 until it was destroyed by fire 14 months later on May 6, 1937, while attempting to land at Lakehurst Naval Air Station in Manchester Township, New Jersey, at the end of the first North American transatlantic journey of its second season of service. This was the last of the great airship disasters; it was preceded by the crashes of the British R38, the US airship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigid Airship
A rigid airship is a type of airship (or dirigible) in which the Aerostat, envelope is supported by an internal framework rather than by being kept in shape by the pressure of the lifting gas within the envelope, as in blimps (also called pressure airships) and semi-rigid airships. Rigid airships are often commonly called Zeppelins, though this technically refers only to airships built by the Luftschiffbau Zeppelin company. In 1900, Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin successfully performed the maiden flight of his first airship; further models quickly followed. Prior to the First World War, Germany was a world leader in the field, largely attributable to the work of von Zeppelin and his Luftschiffbau Zeppelin company. During the conflict, rigid airships were tasked with various military duties, which included their participation in German strategic bombing during World War I, Germany's strategic bombing campaign. Numerous rigid airships were produced and employed with relative commer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Macon (ZRS-5)
USS ''Macon'' (ZRS-5) was a rigid airship built and operated by the United States Navy for scouting and served as a "flying aircraft carrier", designed to carry biplane parasite aircraft, five single-seat Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk for scouting or two-seat Fleet N2Y-1 for training. In service for less than two years, in 1935 the ''Macon'' was damaged in a storm and lost off California's Big Sur coast, though most of the crew were saved. The wreckage is listed as the USS ''Macon'' Airship Remains on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. Less than shorter than ''Hindenburg'', both ''Macon'' and her sister ship were among the largest flying objects in the world in terms of length and volume. Although both of the hydrogen-filled, Zeppelin-built ''Hindenburg'' and LZ 130 ''Graf Zeppelin II'' were longer, the two American-built sister naval airships still hold the world record for helium-filled rigid airships. Construction USS ''Macon'' was built at the Goodyear Aird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-rigid Airship
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships (e.g. Zeppelins), blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas (usually helium, rather than hydrogen) inside the envelope and the strength of the envelope itself to maintain their shape. Principle Since blimps keep their shape with internal overpressure, typically the only solid parts are the passenger car (gondola) and the tail fins. A non-rigid airship that uses heated air instead of a light gas (such as helium) as a lifting medium is called a hot-air airship (sometimes there are battens near the bow, which assist with higher forces there from a mooring attachment or from the greater aerodynamic pressures there). Volume changes of the lifting gas due to temperature changes or to changes of altitude are compensated for by pumping air into internal ballonets (air bags) to maintain the overpressure. Without sufficient overpressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
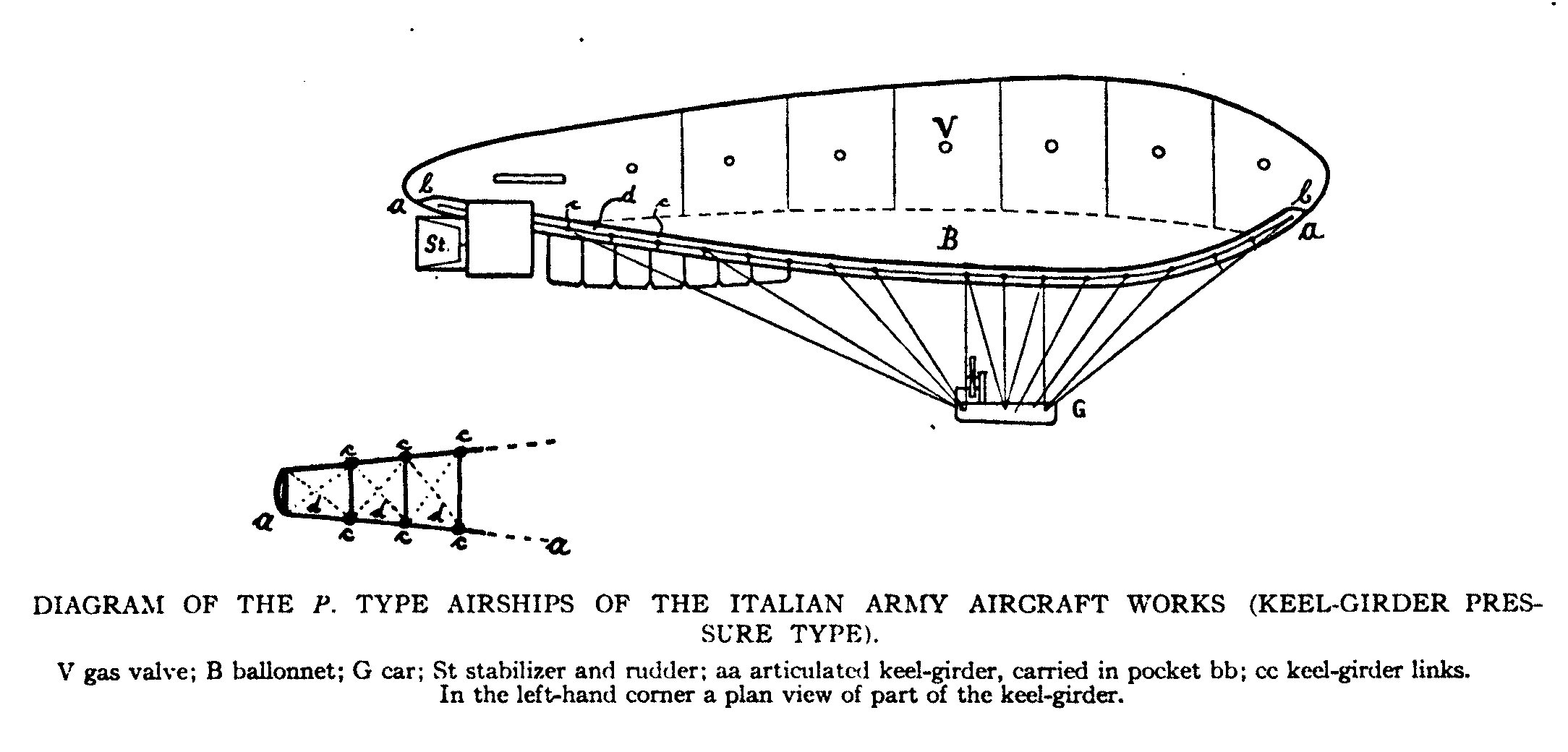
Semi-rigid Airship
A semi-rigid airship is an airship which has a stiff keel or truss supporting the main envelope along its length. The keel may be partially flexible or articulated and may be located inside or outside the main envelope. The outer shape of the airship is maintained by gas pressure, as with the non-rigid "blimp". Semi-rigid dirigibles were built in significant quantity from the late 19th century but in the late 1930s they fell out of favour along with rigid airships. No more were constructed until the semi-rigid design was revived by the Zeppelin NT in 1997. Semi-rigid construction is lighter-weight than the outer framework of a rigid airship, while it allows greater loading than a non-rigid type. Principle More or less integrally attached to the hull are the gondola, engines and sometimes the empennage (tail). The framework has the task of distributing the suspension loads of these attachments and the lifting gas loads evenly throughout the whole hull's surface and may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airborne Aircraft Carrier
An airborne aircraft carrier is a type of mother ship aircraft which can carry, launch, retrieve and support other smaller parasite aircraft. The only dedicated examples to have been built were airships, although existing heavier-than-air aircraft have been modified for use in similar roles, and airborne aircraft carriers of various types appear in fiction, such as ''Cloudbase'' in Gerry Anderson's ''Captain Scarlet and the Mysterons'', the Helicarrier from Marvel Comics, the ''Valiant'' from series 3 of ''Doctor Who,'' and an unnamed one in ''Sky Captain and the World of Tomorrow''. Airship projects In July 1917, experiments were made with aircraft slung under HM Airship No. 23, in hopes that they could defend the airship. First an unmanned, then a manned, Sopwith Camel fighters were launched successfully. The experiment was successfully completed with two other manned Camels. The British Imperial Airship Scheme of 1924 initially envisaged an airship that could carry fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitty Bang Bang (airship)
''Chitty Bang Bang'' was an airship built for the 1968 film '' Chitty Chitty Bang Bang''. It was intended to represent the airship of Baron Bomburst of Vulgaria. Although fictional in inspiration, it was a fully functional flying airship. Appearance Vulgaria, and the airship, is drawn from Roald Dahl's screenplay for the film, rather than Ian Fleming's original book. The semi-rigid airship, whose appearance was designed by Ken Adam, was an approximate replica of a 1904 Lebaudy airship. The envelope was symmetrical fore-and-aft and short and deep compared to typical rigid airships, with pointed ends above the centre of the envelope that gave it the distinctive Lebaudy "hooked" appearance. Jane's, Airship Development, p. 29 The gondola was a long open truss structure beneath this and a crew basket beneath, with the typical Lebaudy feature of cruciform control surfaces at the rear of the gondola. The ends of the airship envelope were coloured with bands of the Vulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |