|
Ablaut
In linguistics, the Indo-European ablaut (, from German '' Ablaut'' ) is a system of apophony (regular vowel variations) in the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). An example of ablaut in English is the strong verb ''sing, sang, sung'' and its related noun ''song'', a paradigm inherited directly from the Proto-Indo-European stage of the language. Traces of ablaut are found in all modern Indo-European languages, though its prevalence varies greatly. History of the concept The phenomenon of Indo-European ablaut was first recorded by Sanskrit grammarians in the later Vedic period (roughly 8th century BCE), and was codified by Pāṇini in his ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' (4th century BCE), where the terms ' and '' '' were used to describe the phenomena now known respectively as the ''full grade'' and ''lengthened grade''.Burrow, §2.1. In the context of European languages, the phenomenon was first described in the early 18th century by the Dutch linguist Lambert ten Kate, in his boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablaut
In linguistics, the Indo-European ablaut (, from German '' Ablaut'' ) is a system of apophony (regular vowel variations) in the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). An example of ablaut in English is the strong verb ''sing, sang, sung'' and its related noun ''song'', a paradigm inherited directly from the Proto-Indo-European stage of the language. Traces of ablaut are found in all modern Indo-European languages, though its prevalence varies greatly. History of the concept The phenomenon of Indo-European ablaut was first recorded by Sanskrit grammarians in the later Vedic period (roughly 8th century BCE), and was codified by Pāṇini in his ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' (4th century BCE), where the terms ' and '' '' were used to describe the phenomena now known respectively as the ''full grade'' and ''lengthened grade''.Burrow, §2.1. In the context of European languages, the phenomenon was first described in the early 18th century by the Dutch linguist Lambert ten Kate, in his boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Strong Verb
In the Germanic languages, a strong verb is a verb that marks its past tense by means of changes to the stem vowel ( ablaut). The majority of the remaining verbs form the past tense by means of a dental suffix (e.g. ''-ed'' in English), and are known as '' weak verbs''. In modern English, strong verbs include ''sing'' (present ''I sing'', past ''I sang'', past participle ''I have sung'') and ''drive'' (present ''I drive'', past ''I drove'', past participle ''I have driven''), as opposed to weak verbs such as ''open'' (present ''I open'', past ''I opened'', past participle ''I have opened''). Not all verbs with a change in the stem vowel are strong verbs, however; they may also be irregular weak verbs such as ''bring, brought, brought'' or ''keep, kept, kept''. The key distinction is that most strong verbs have their origin in the earliest sound system of Proto-Indo-European, whereas weak verbs use a dental ending (in English usually ''-ed'' or ''-t'') that developed later with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophony
In linguistics, apophony (also known as ablaut, (vowel) gradation, (vowel) mutation, alternation, internal modification, stem modification, stem alternation, replacive morphology, stem mutation, internal inflection etc.) is any alternation within a word that indicates grammatical information (often inflectional). Description Apophony is exemplified in English as the ''internal'' vowel alternations that produce such related words as * sng, sng, sng, sng * bnd, bnd * bld, bld * brd, brd * dm, dm * fd, fd * l, l * rse, rse, rsen * wve, wve * ft, ft * gse, gse * tth, tth The difference in these vowels marks variously a difference in tense or aspect (e.g. ''sing/sang/sung''), transitivity (''rise/raise''), part of speech (''sing/song''), or grammatical number (''goose/geese''). That these sound alternations function grammatically can be seen as they are often equivalent to grammatical suffixes (an ''external modification''). Compare the following: The vowel alternation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narten Present
Narten present is a proposed inflectional class of the Proto-Indo-European verb, named after the Indo-Iranianist Johanna Narten who posited its existence in 1968. It is characterized by accent on the root in all of the person-number forms. Roots having Narten presents always possess a surface accent, having a lengthened grade R(ḗ) in the singular active, and a full-grade R(é) in the rest of the active forms, as well as the mediopassive. The proposed examples of roots having such ''acrostatic presents'' include the following: These forms are best reflected in Indo-Iranian and Hittite, with relics surviving in other languages, particularly in the root "to eat". Narten roots In 1994 Jochem Schindler suggested the existence of what is called ''Narten roots'' – roots exhibiting a systematic *R(ḗ) ~ *R(é) ablaut in both nominal and verbal derivations, as opposed to the more common R(e) ~ R(Ø) pattern. These roots always carried a surface accent, and such ablaut is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
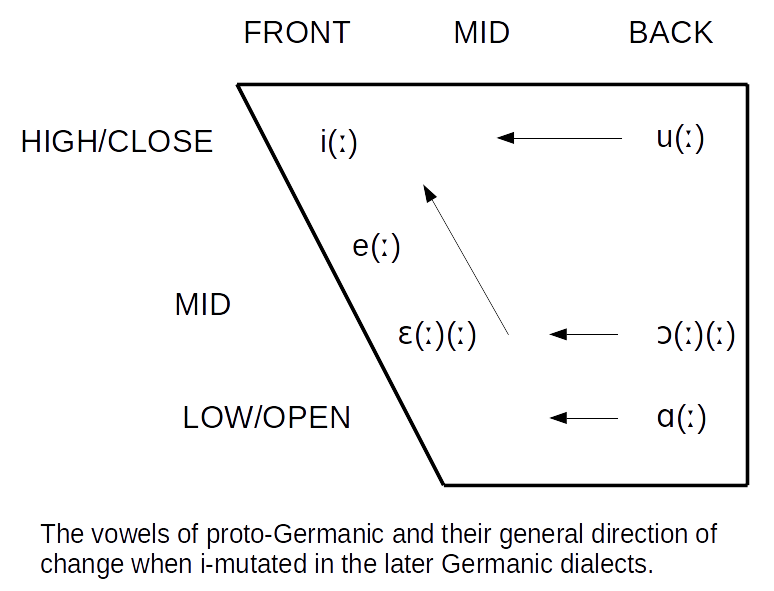
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel ( fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to ( raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Grammar
The grammar of the Sanskrit language has a complex verbal system, rich nominal declension, and extensive use of compound nouns. It was studied and codified by Sanskrit grammarians from the later Vedic period (roughly 8th century BCE), culminating in the Pāṇinian grammar of the 4th century BCE. Grammatical tradition Origins Sanskrit grammatical tradition (''vyākaraṇa'', one of the six Vedanga disciplines) began in late Vedic India and culminated in the ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' of Pāṇini. The oldest attested form of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language as it had evolved in the Indian subcontinent after its introduction with the arrival of the Indo-Aryans is called Vedic. By 1000 BCE, the end of the early Vedic period, a large body of Vedic hymns had been consolidated into the Ṛg·Veda, which formed the canonical basis of the Vedic religion, and was transmitted from generation to generation entirely orally. In the course of the following centuries, as the popular speech evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aṣṭādhyāyī
The (Devanagari अष्टाध्यायी) is a grammar that describes a form of an early Indo-Aryan language: Sanskrit. Authored by Sanskrit philologist and scholar Pāṇini and dated to around 500 BCE, it describes the language as current in his time, specifically the dialect and register of an élite of model speakers, referred to by Pāṇini himself as ''śiṣṭa''. The work also accounts both for some features specific to the older Vedic form of the language, as well as certain dialectal features current in the author's time. The ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' employs a derivational system to describe the language, where real speech is derived from posited abstract utterances formed by means of affixes added to bases under certain conditions. The Aṣṭādhyāyī is supplemented by three ancillary texts: ''akṣarasamāmnāya'', ''dhātupāṭha'' and ''gaṇapāṭha''. Etymology ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'' is made of two words ''aṣṭa-'', 'eight' and ''adhyāya-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vṛddhi
Vṛddhi (also rendered vr̥ddhi) is a technical term in morphophonology given to the strongest grade in the vowel gradation system of Sanskrit. The term is derived from Sanskrit ''vṛddhi'', , 'growth', from . Origins Vṛddhi itself has its origins in proto-vṛddhi, a process in the early stage of the Proto-Indo-European language originally for forming possessive derivatives of ablauting noun stems, with the meaning "of, belonging to, descended from".Clackson, §3.3. To form a vṛddhi-derivative, one takes the zero-grade of the ablauting stem (i.e. removes the vowel), inserts the vowel *''e'' in a position which does not necessarily match that of the original vowel, and appends an accented thematic vowel (or accents any existing final thematic vowel). For example: However, in a later stage of the language this appears to have extended to non-ablauting noun stems that already contained ''*e'', which would contract with the inserted vowel to form a lengthened ''*ē'': ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Verb
A regular verb is any verb whose conjugation follows the typical pattern, or one of the typical patterns, of the language to which it belongs. A verb whose conjugation follows a different pattern is called an irregular verb. This is one instance of the distinction between regular and irregular inflection, which can also apply to other word classes, such as nouns and adjectives. In English, for example, verbs such as ''play'', ''enter'', and ''like'' are regular since they form their inflected parts by adding the typical endings ''-s'', ''-ing'' and ''-ed'' to give forms such as ''plays'', ''entering'', and ''liked''. On the other hand, verbs such as ''drink'', ''hit'' and ''have'' are irregular since some of their parts are not made according to the typical pattern: ''drank'' and ''drunk'' (not "drinked"); ''hit'' (as past tense and past participle, not "hitted") and ''has'' and ''had'' (not "haves" and "haved"). The classification of verbs as regular or irregular is to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Language
Gothic is an extinct East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the ''Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian and Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other languages such as Portuguese, Spanish, and French. As a Germanic language, Gothic is a part of the Indo-European language family. It is the earliest Germanic language that is attested in any sizable texts, but it lacks any modern descendants. The oldest documents in Gothic date back to the fourth century. The language was in decline by the mid-sixth century, partly because of the military defeat of the Goths at the hands of the Franks, the elimination of the Goths in Italy, and geographic isolation (in Spain, the Gothic language lost its last and probably already declining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |