|
Abanico Formation
Abanico Formation ( es, Formación Abanico) is a thick sedimentary formation exposed in the Andes of Central Chile. The formation has been deposited in a timespan from the Eocene to the Miocene. Abanico Formation's contact with the overlying Miocene Farellones Formation has been the subject of differing interpretations since the 1960s.Godoy, 2012 A small part of the formation crops out in the Mendoza Province of western Argentina.Muñoz et al., 2006 Description The sediments accumulated in the Abanico Extensional Basin within a context of the Andean orogeny. The basin had a north-south elongated shape that spanned the latitudes of 29–38° S. Tectonic inversion from 21 to 16 million years ago made the basin collapse and the sediments to be incorporated to the Andean ranges.Charrier et al., 2006, pp.93-94 The northern part of the basin inverted before the southern part. Parts of the formation are known to have experienced Prehnite-pumpellyite facies metamorphism.Muñoz et a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Chile
Central Chile (''Zona central'') is one of the five natural regions into which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. It is home to a majority of the Chilean population and includes the three largest metropolitan areas—Santiago, Valparaíso, and Concepción. It extends from 32° south latitude to 37° south latitude. Geography Central Chile is one of the five main geographical zones in which Chile is divided. The Chilean Central Valley lies between the coastal range ("Cordillera de la Costa") and the Andes Mountains. To the north is the semi-desert region known as El Norte Chico, (the "little north"), which lies between 28° and 32° south latitude. To the south lies the cooler and wetter Valdivian temperate rain forests ecoregion, in Los Lagos Region; (the latter includes most of South America's temperate rain forests). The Central valley is a fertile region and the agricultural heartland of Chile. Climate The climate is of the temperate Mediterranean type, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colhuehuapian
The Colhuehuapian age is a period of geologic time (21.0–17.5 Ma) within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Deseadan and precedes the Santacrucian age. Etymology The age is named after the Colhué Huapí Member of the Sarmiento Formation in the Golfo San Jorge Basin, Patagonia, Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th .... Formations Fossils References Bibliography ;Colhué Huapí Member * * ;Abanico Formation * * * * * * ;Biblián Formation * ;Castillo Formation * * * * * ;Cerro Bandera Formation * * ;Chichinales Formation * * ;Chilcatay Formation * * * * * * * * * * ;Cura-Mallín Group * * * ;Gaiman Formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aysén Region
The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region ( es, Región de Aysén, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's official meteorological agency refers to the region as "Región de Aisén".3 Chilean government official website refers of Pilar Cuevas Mardones as intendant of "Región de Aysén" .4 Chile's Ministry of Public Works calls the region "Región de Aysén" in the title of their 2011 report on that region.5, Corporación Nacional Forestal, a government agency refers to the region as "Región de Aysén" in their homepage. Here is some evidence of the short name use in English:I '' The Guardian'' reports on the 2012 Aysén protest.II ''Santiago Times'', a local English language newspaper use "Aysén Region" in a note referring to the same protest.III''Santiago Times'' again. *Vscientific paper in ''Journal of Hospital Infection'' referring to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Frías Formation
Río Frías Formation ( es, Formación Río Frías) is a Middle Miocene geologic formation made up sedimentary rock located in Aysén Region, western Patagonia. The formation crops out along the upper couse of Cisnes River ( es, Río Cisnes).Marshall & Salinas, 1990 Marsupial fossils have been found in the formation.Marshall, 1990 The Friasian period in the South American Land Mammal Ages is named after the formation. Description Río Frías Formation was discovered by Santiago Roth in the summer of 1897–98. Roth was a Swiss immigrant who had been sent to survey the area by Francisco Moreno. Moreno was director of La Plata Museum and was involved in the Cordillera of the Andes Boundary Case between Chile and Argentina, thus there was both a political and scientific motivation behind the exploration of Patagonia. Santiago Roth called the upper course of Río Cisnes for Río Frías being unaware that it was the same river. Further he thought this unexplored area to be in Argent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friasian
The Friasian age is a period of geologic time (16.3–15.5 Ma) within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Santacrucian and precedes the Colloncuran age. Etymology The age is named after the Río Frías Formation in the Aysén Basin, Patagonia, Chile Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas .... Formations Fossils References Bibliography ;Río Frías Formation * * * * * ;Castilletes Formation * * * * * * * * ;Cerdas Beds * ;Chilcatay Formation * * * * ;Cura-Mallín Group * * * ;Gran Bajo del Gualicho Formation * ;Parángula Formation * ;Pebas Formation * * ;Río Foyel Formation * * ;Río Yuca Formation * {{SALMA Miocene Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South American Land Mammal Age
The South American land mammal ages (SALMA) establish a geologic timescale for prehistoric South American fauna beginning 64.5 Ma during the Paleocene and continuing through to the Late Pleistocene (0.011 Ma). These periods are referred to as ages, stages, or intervals and were established using geographic place names where fossil materials where obtained.Flynn & Swisher, 1995 The basic unit of measure is the first/last boundary statement. This shows that the first appearance event of one taxon is known to predate the last appearance event of another. If two taxa are found in the same fossil quarry or at the same stratigraphic horizon, then their age-range zones overlap. Background South America was an island continent for much of the Cenozoic, or the "Age of Mammals". As a result, its mammals evolved in their own unique directions, as Australia and Madagascar still have today. Paleogeographic timeline A simplified paleogeographic timeline of South America: * 66 Ma – Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinguiririca River
Tinguiririca River is a river of Chile located in the Libertador General Bernardo O'Higgins Region. It rises in the Andes, at the confluence In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ... of the rivers ''Las Damas'' and ''Del Azufre''. From its source, it flows northwest for about 56 km to the vicinity of the city of San Fernando. In this portion of its course, the river receives the waters of the tributaries ''Clarillo'' and ''Claro''. Then the river flows southwest and then turns northwest to empty into Rapel Lake. See also * Tinguiririca Volcano References Cuenca del río Rapel Rivers of O'Higgins Region Rivers of Chile {{Chile-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
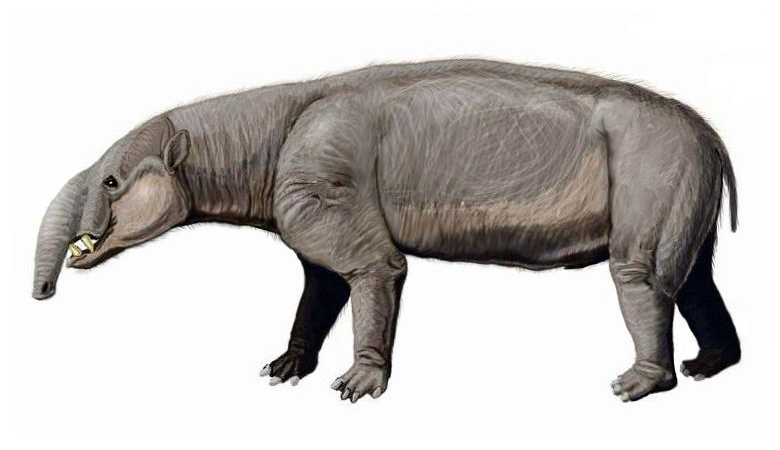
Tinguiririca Fauna
The fossil Tinguiririca fauna, entombed in volcanic mudflows and ash layers at the onset of the Oligocene, about 33-31.5 million years ago, represents a unique snapshot of the history of South America's endemic fauna, which was extinguished when the former island continent was joined to North America by the rising Isthmus of Panama. The fossil-bearing sedimentary layers of the Abanico Formation were first discovered in the valley of the Tinguiririca River, high in the Andes of central Chile. The faunal assemblage lends its name to the Tinguirirican stage in the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. Description The endemic fauna bridges a massive gap in the history of those mammals that were unique to South America. Paleontologists knew the earlier sloth and anteater forebears of 40 mya, but no fossils from this previously poorly sampled transitional age had been seen. Fossils of the Tinguiririca fauna include the chinchilla-like earliest rodents discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including regional, contact, hydrothermal, shock, and dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasing temperature and pressure characterize ''retrograde metamorphism''. Metamorphic petrology is the study of metamorphism. Metamorphic petrologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehnite-pumpellyite Facies
The prehnite-pumpellyite facies is a metamorphic facies typical of subseafloor alteration of the oceanic crust around mid-ocean ridge spreading centres. It is a metamorphic grade transitional between zeolite facies and greenschist facies representing a temperature range of 250 to 350 °C and a pressure range of approximately two to seven kilobars. The mineral assemblage is dependent on host composition. *In mafic rocks the assemblage is chlorite, prehnite, albite, pumpellyite and epidote. *In ultramafic rocks the assemblage is serpentine, talc, forsterite, tremolite and chlorite. *In argillaceous sedimentary rocks the assemblage is quartz, illite, albite, and stilpnomelane chlorite. *In carbonate sediments the assemblage is calcite, dolomite, quartz, clays, talc, and muscovite Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula K Al2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Inversion
In structural geology inversion or basin inversion relates to the relative uplift of a sedimentary basin or similar structure as a result of crustal shortening. This normally excludes uplift developed in the footwalls of later extensional faults, or uplift caused by mantle plumes. "Inversion" can also refer to individual faults, where an extensional fault is reactivated in the opposite direction to its original movement. The term ''negative inversion'' is also occasionally used to describe the reactivation of reverse faults and thrusts during extension. The term "inversion" simply refers to the fact that a relatively low-lying area is uplifted – the rock sequence itself is not normally inverted. Formation Many inversion structures are caused by the direct reactivation of pre-existing extensional faults. In some cases only the deeper parts of the fault are reactivated and the shortening is accommodated over a much broader area in the shallow part of the section. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |