|
4-bit
In computer architecture, 4-bit integers, or other data units are those that are 4 bits wide. Also, 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, or data buses of that size. Memory addresses (and thus address buses) for 4-bit CPUs are generally much larger than 4-bit (since only 16 memory locations would be very restrictive), such as 12-bit or more, while they could in theory be 8-bit. A group of four bits is also called a nibble and has 24 = 16 possible values. Some of the first microprocessors had a 4-bit word length and were developed around 1970. Traditional (non-quantum) 4-bit computers are by now obsolete, while recent quantum computers are 4-bit, but also based on qubits, such as the IBM Q Experience. See also: Bit slicing#Bit-sliced quantum computers. The first commercial microprocessor was the binary-coded decimal (BCD-based) Intel 4004, developed for calculator applications in 1971; it had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs. The 4004 was the first significant example of large scale integration, showcasing the superiority of the MOS silicon gate technology (SGT). Compared to the incumbent technology, the SGT integrated on the same chip area twice the number of transistors with five times the operating speed. This step-function increase in performance made possible a single-chip CPU, replacing the existing multi-chip CPUs. The innovative 4004 chip design served as a model on how to use the SGT for complex logic and memory circuits, thus accelerating the adoption of the SGT by the world’s semiconductor industry. The developer of the original SGT at Fairchild was Federico Faggin who designed the first commercial integrated circuit (IC) that used the new technology, proving its superiority for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
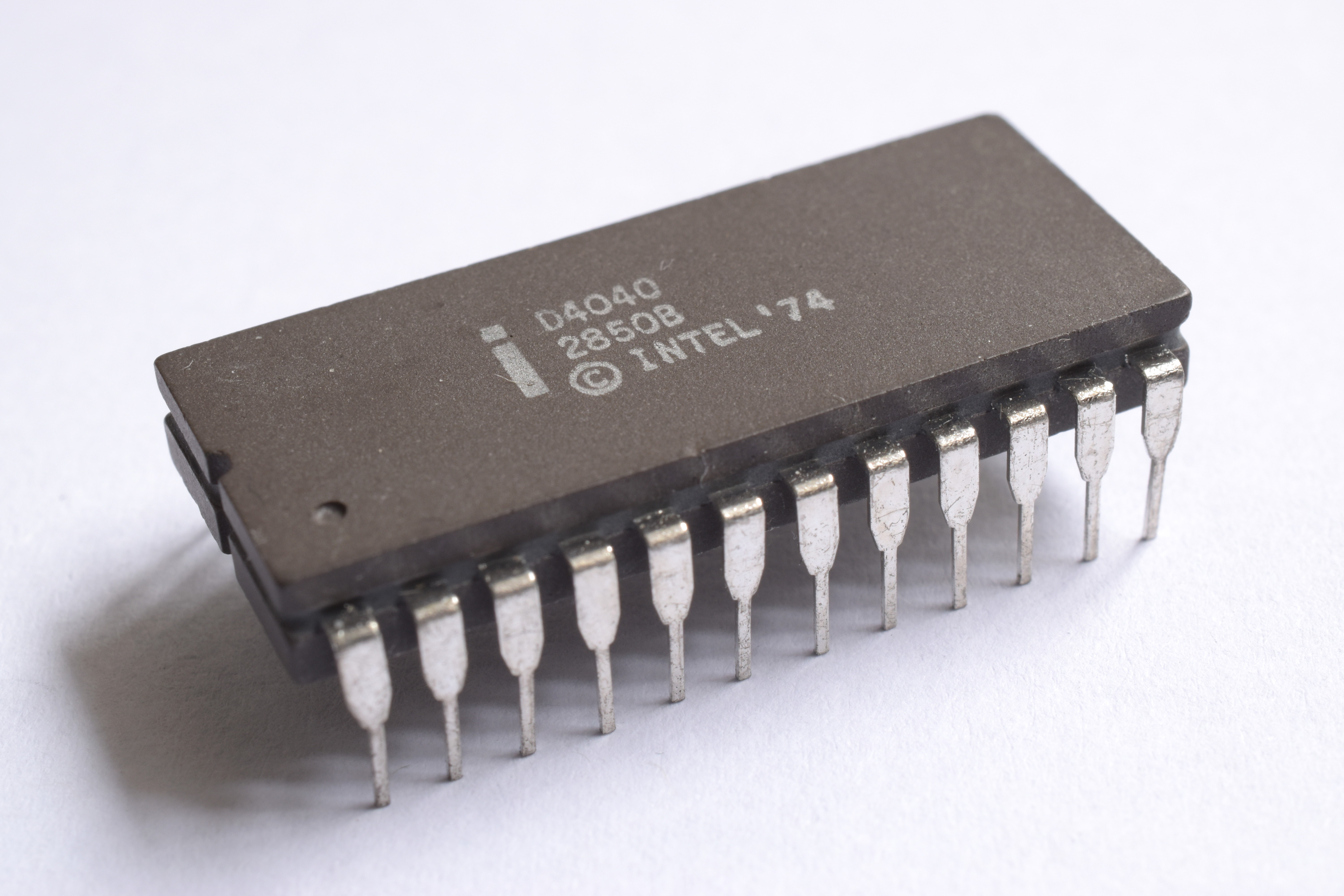
Intel 4040
The Intel 4040 microprocessor was the successor to the Intel 4004. It was introduced in 1974. The 4040 employed a 10 μm silicon gate enhancement load PMOS technology, was made up of 3,000 transistors and could execute approximately 62,000 instructions per second. General performance, bus layout and instruction set was identical to the 4004, with the main improvements being in the addition of extra lines and instructions to recognise and service interrupts and hardware Halt/Stop commands (the latter allowing operator-controlled single-stepping for debugging purposes), an extended internal stack and general-purpose "Index" register space to handle nesting of several subroutines and/or interrupts, plus a doubling of program ROM address range. New features *Interrupts *Single Stepping plus both hardware and software HALTing. *Low-power standbyEssentially a side function of Halt/Single Step; all internal processing would be suspended, and most of the chip hardware put into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary-coded Decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise 4-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (for the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named , ''pseudo-decimals'' or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in comparison to binary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMD Am2900
Am2900 is a family of integrated circuits (ICs) created in 1975 by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). They were constructed with bipolar devices, in a bit-slice topology, and were designed to be used as modular components each representing a different aspect of a computer control unit (CCU). By using the bit slicing technique, the Am2900 family was able to implement a CCU with data, addresses, and instructions to be any multiple of 4 bits by multiplying the number of ICs. One major problem with this modular technique was that it required a larger number of ICs to implement what could be done on a single CPU IC. The Am2901 chip was the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and the "core" of the series. It could count using 4 bits and implement binary operations as well as various bit-shifting operations. The 2901 and some other chips in the family were second sourced by an unusually large number of other manufacturers, starting with Motorola and then Raytheon both in 1975 and also Cyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Slicing
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full word-length of a given software design. Bit slicing more or less died out due to the advent of the microprocessor. Recently it has been used in arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for quantum computers and as a software technique, e.g. for cryptography in x86 CPUs. Operational details Bit-slice processors (BSPs) usually include 1-, 2-, 4-, 8- or 16-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control lines (including carry or overflow signals that are internal to the processor in non-bitsliced CPU designs). For example, two 4-bit ALU chips could be arranged side by side, with control lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontrollers
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs ( processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash or OTP ROM is also often included on chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). An SoC may connect the external microcontroller chips as the motherboard components, but an SoC usually integrates the advanced peripherals like graphics processing unit (GPU) and Wi-Fi interface controller as its internal microcontroller unit circuits. Microcontrollers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Slicing
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary ''n''-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full word-length of a given software design. Bit slicing more or less died out due to the advent of the microprocessor. Recently it has been used in arithmetic logic units (ALUs) for quantum computers and as a software technique, e.g. for cryptography in x86 CPUs. Operational details Bit-slice processors (BSPs) usually include 1-, 2-, 4-, 8- or 16-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control lines (including carry or overflow signals that are internal to the processor in non-bitsliced CPU designs). For example, two 4-bit ALU chips could be arranged side by side, with control lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
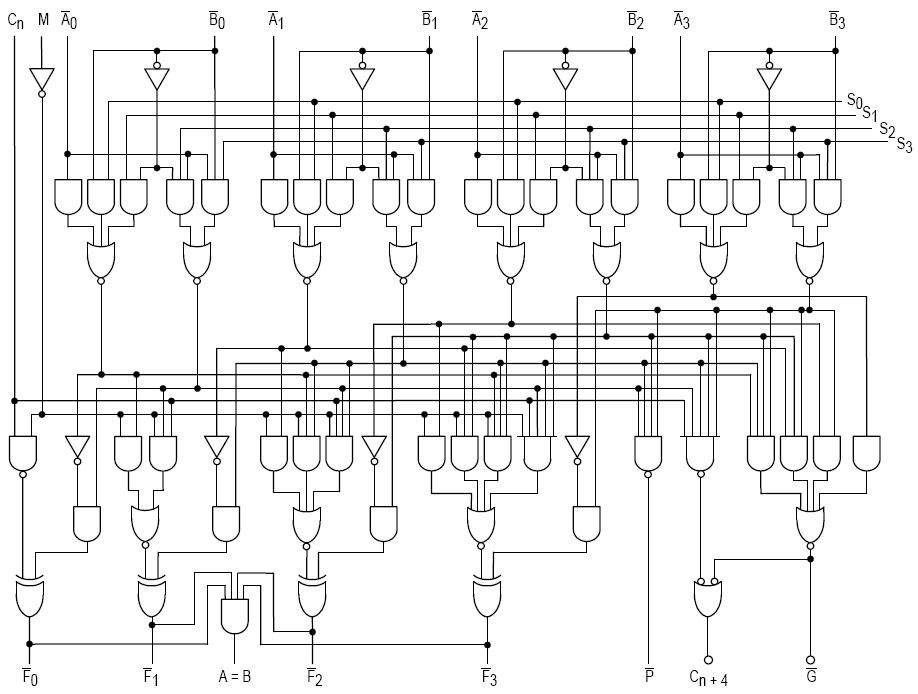
74181
The 74181 is a 4-bit slice arithmetic logic unit (ALU), implemented as a 7400 series TTL integrated circuit. The first complete ALU on a single chip, it was used as the arithmetic/logic core in the CPUs of many historically significant minicomputers and other devices. The 74181 represents an evolutionary step between the CPUs of the 1960s, which were constructed using discrete logic gates, and today's single-chip microprocessor CPUs. Although no longer used in commercial products, the 74181 is still referenced in computer organization textbooks and technical papers. It is also sometimes used in "hands-on" college courses to train future computer architects. Specifications The 74181 is a 7400 series medium-scale integration (MSI) TTL integrated circuit, containing the equivalent of 75 logic gates and most commonly packaged as a 24-pin DIP. The 4-bit wide ALU can perform all the traditional add / subtract / decrement operations with or without carry, as well as AND / NAND ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer (computer Science)
In computer science, an integer is a datum of integral data type, a data type that represents some range of mathematical integers. Integral data types may be of different sizes and may or may not be allowed to contain negative values. Integers are commonly represented in a computer as a group of binary digits (bits). The size of the grouping varies so the set of integer sizes available varies between different types of computers. Computer hardware nearly always provides a way to represent a processor register or memory address as an integer. Value and representation The ''value'' of an item with an integral type is the mathematical integer that it corresponds to. Integral types may be ''unsigned'' (capable of representing only non-negative integers) or ''signed'' (capable of representing negative integers as well). An integer value is typically specified in the source code of a program as a sequence of digits optionally prefixed with + or −. Some programming languages allow ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were delivered in March 1976, and it was officially introduced on the market in July 1976. With the revenue from the Z80, the company built its own chip factories and grew to over a thousand employees over the following two years. The Zilog Z80 is a software-compatible extension and enhancement of the Intel 8080 and, like it, was mainly aimed at embedded systems. Although used in that role, the Z80 also became one of the most widely used CPUs in desktop computers and home computers from the 1970s to the mid-1980s. It was also common in military applications, musical equipment such as synthesizers (like the Roland Jupiter-8), and coin-operated arcade games of the late 1970s and early 1980s, including ''Pac-Man''. Zilog licensed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processor Register
A processor register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's processor. Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage, although some registers have specific hardware functions, and may be read-only or write-only. In computer architecture, registers are typically addressed by mechanisms other than main memory, but may in some cases be assigned a memory address e.g. DEC PDP-10, ICT 1900. Almost all computers, whether load/store architecture or not, load data from a larger memory into registers where it is used for arithmetic operations and is manipulated or tested by machine instructions. Manipulated data is then often stored back to main memory, either by the same instruction or by a subsequent one. Modern processors use either static or dynamic RAM as main memory, with the latter usually accessed via one or more cache levels. Processor registers are normally at the top of the memory hierarchy, and provide the fastest way to access data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |