|
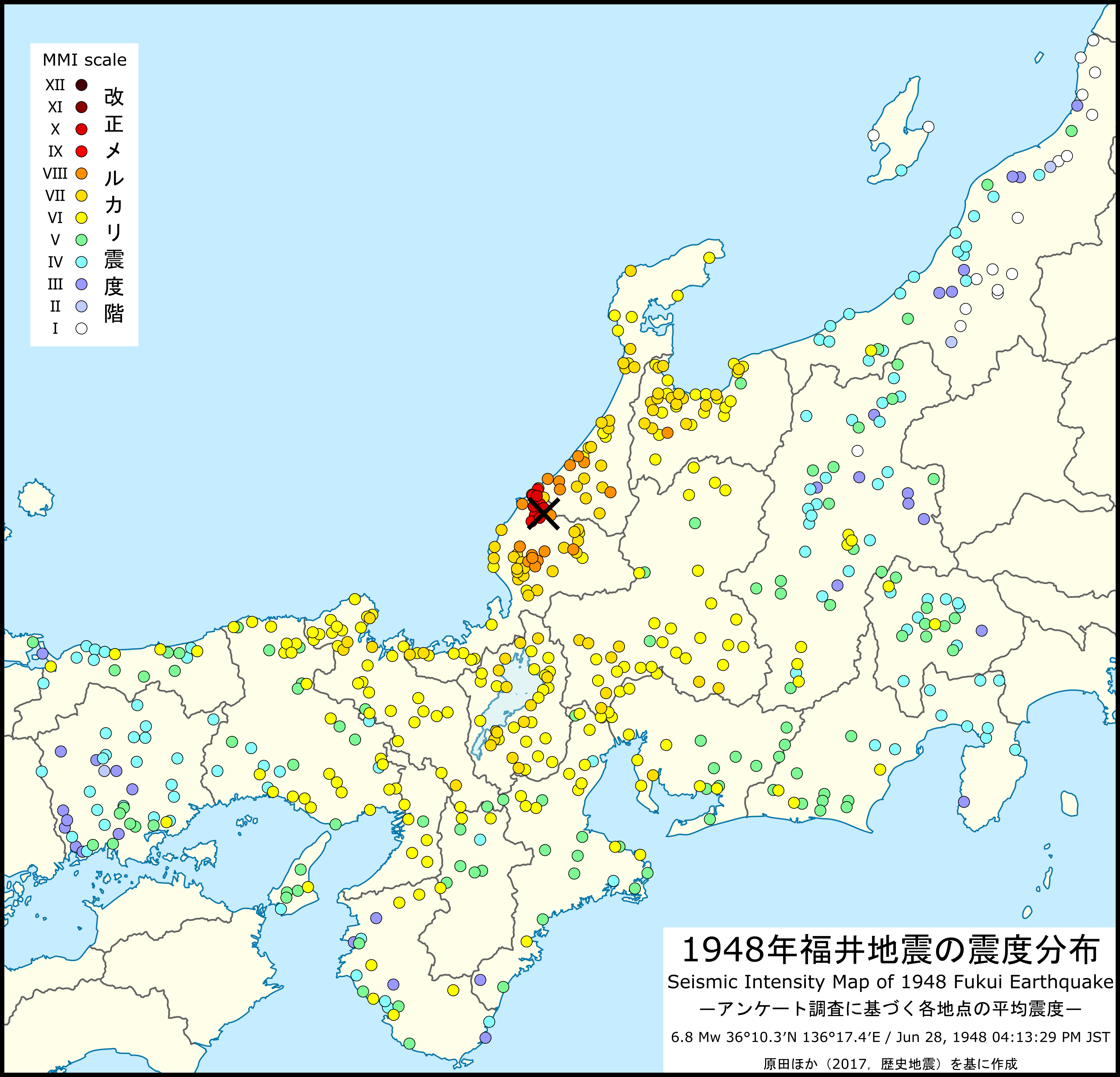
1948 Fukui Earthquake
The occurred in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. The magnitude 6.8 quake struck at 5:13:31 p.m.( JDT) on June 28, 1948. The quake's hypocenter was approximately 10 km north-northeast of Fukui, in the present-day neighborhood of Maruoka, Sakai City. The strongest shaking occurred in the city of Fukui, where it was recorded as 6 (equivalent to the current 7) on the Japan Meteorological Agency seismic intensity scale. Overview The earthquake devastated Fukui, which was still recovering from damage sustained during WWII air raids in July 1945. Damage across the entire Fukuiheiya flood plain into neighboring Ishikawa prefecture. Official casualty estimates totaled 3,769 dead and 22,000 wounded, with more than 36,000 buildings completely destroyed. In the Kanazugocho district (modern-day eastern Arawa); Maruoka and Harue; and Yoshida District, nearly every building was leveled. In central Fukui city, which was adjacent to the epicenter, approximately 79% of structures were compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Standard Time
, or , is the standard time zone in Japan, 9 hours ahead of UTC ( UTC+09:00). Japan does not observe daylight saving time, though its introduction has been debated on several occasions. During World War II, the time zone was often referred to as Tokyo Standard Time. Japan Standard Time is equivalent to Korean Standard Time, Pyongyang Time ( North Korea), Eastern Indonesia Standard Time, East-Timorese Standard Time and Yakutsk Time (Russia). History Before the Meiji era (1868–1912), each local region had its own time zone in which noon was when the sun was exactly at its culmination. As modern transportation methods, such as trains, were adopted, this practice became a source of confusion. For example, there is a difference of about 5 degrees longitude between Tokyo and Osaka and because of this, a train that departed from Tokyo would arrive at Osaka 20 minutes behind the time in Tokyo. In 1886, Ordinance 51 was issued in response to this problem, which stated: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuzuryū River
The is a river flowing through Fukui Prefecture, Japan. It has its source at the Aburasaka Pass (油坂峠 ''Aburasaka-tōge'') in the city of Ōno and empties into the Sea of Japan near the city of Sakai. River system Some of the main rivers that flow into the Kuzuryū River include: the Itoshiro River, the Hino River The is a major river in the western part of Tottori Prefecture. The river flows east-northeast for , and is the longest river in the prefecture. The Hino River emerges from the Chūgoku Mountains. The source of the river is at an elevation of ..., the Asuwa River and the Takeda River River communities The river passes through or forms the boundary of the communities listed below. ;Fukui Prefecture: : Ōno, Katsuyama, Eiheiji, Fukui, Sakai References External links * (confluence with Ibi River) Rivers of Fukui Prefecture Rivers of Japan {{Japan-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Hanshin Earthquake
The , or Kobe earthquake, occurred on January 17, 1995, at 05:46:53 JST (January 16 at 20:46:53 UTC) in the southern part of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, including the region known as Hanshin. It measured 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum intensity of 7 on the JMA Seismic Intensity Scale (XI on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale). The tremors lasted for approximately 20 seconds. The focus of the earthquake was located 17 km beneath its epicenter, on the northern end of Awaji Island, 20 km away from the center of the city of Kobe. Approximately 6,434 people died as a result of this earthquake; about 4,600 of them were from Kobe. Among major cities, Kobe, with its population of 1.5 million, was the closest to the epicenter and hit by the strongest tremors. This was Japan's deadliest earthquake in the 20th century after the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923, which claimed more than 105,000 lives. Earthquake Most of the largest earthquakes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishikawa Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshu island. Ishikawa Prefecture has a population of 1,140,573 (31 October 2019) and has a geographic area of 4,186 km2 (1,616 sq mi). Ishikawa Prefecture borders Toyama Prefecture to the east, Gifu Prefecture to the southeast, and Fukui Prefecture to the south. Kanazawa is the capital and largest city of Ishikawa Prefecture, with other major cities including Hakusan, Komatsu, and Kaga. Ishikawa is located on the Sea of Japan coast and features the most of the Noto Peninsula which forms Toyama Bay, one of the largest bays in Japan. Ishikawa Prefecture is part of the historic Hokuriku region and formerly an important populated center that contained some of the wealthiest '' han'' (domains) of the Japanese feudal era. Ishikawa Prefecture is home to Kanazawa Castle, Kenroku-en one of the Three Great Gardens of Japan, Nyotaimori ("body sushi"), and Kutani ware. History Ishikawa was formed in 1872 from the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Foundation
A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site. There are many reasons that a geotechnical engineer would recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, such as for a skyscraper. Some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints like property lines. There are different terms used to describe different types of deep foundations including the pile (which is analogous to a pole), the pier (which is analogous to a column), drilled shafts, and caissons. Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep foundations are typically put in place using excavation and drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Plain
An alluvial plain is a largely flat landform created by the deposition of sediment over a long period of time by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A floodplain is part of the process, being the smaller area over which the rivers flood at a particular period of time, whereas the alluvial plain is the larger area representing the region over which the floodplains have shifted over geological time. As the highlands erode due to weathering and water flow, the sediment from the hills is transported to the lower plain. Various creeks will carry the water further to a river, lake, bay, or ocean. As the sediments are deposited during flood conditions in the floodplain of a creek, the elevation of the floodplain will be raised. As this reduces the channel floodwater capacity, the creek will, over time, seek new, lower paths, forming a meander (a curving sinuous path). The leftover higher locations, typically natural levees at the margins o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daiwa Department Store After Fukui Earthquake
Daiwa may refer to: Places: *Daiwa, Hiroshima, a former town in Kamo District, Hiroshima, Japan *Daiwa, Shimane, a former village in Ōchi District, Shimane, Japan Companies and related: * Daiwa Securities Group, a Japanese security brokerage *Daiwa House, a Japanese homebuilder *The Daiwa Anglo-Japanese Foundation, a United Kingdom-based charity * Daiwa Adrian Prize, awarded by the Daiwa Anglo-Japanese Foundation *Globeride , formerly until 2009, is a Japanese manufacturing company that produces fishing equipment in addition to tennis, golf and biking gears. Globeride's fishing products, sold under the Daiwa brand, account for the majority of its sales, includ ... (formerly Daiwa Seiko Corporation), a Japanese producer of fishing and outdoor equipment * Daiwa Major, a Thoroughbred racehorse {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saga, Saga
is the capital city of Saga Prefecture, located on the island of Kyushu, Japan. Saga was the capital of Saga Domain in the Edo period, and the largest city of former Hizen Province. As of August 1, 2020, the city had an estimated population of 232,736 and a population density of 539 persons per km2. The total area is 431.84 km2. Saga is located in the southeast part of Saga Prefecture. After the 2005 merger the city became very long north to south, bordering the Ariake Sea to the south and Fukuoka Prefecture to the southeast and north. The northern half of the city contains the Sefuri Mountains. Saga can also be regarded as within the Greater Fukuoka metropolitan area, and by extension, Fukuoka-Kitakyushu Metropolitan Area. History Municipal timeline *April 1, 1889 - The modern municipal system was established and the city of Saga is founded. At the same time, the current city region is occupied by 21 villages from three districts. ** Kanzaki District: Hasuike and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mito, Ibaraki
is the capital city of Ibaraki Prefecture, in the northern Kantō region of Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 269,330 in 123,282 households and a population density of 1239 persons per km2. The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 27.1%. The total area of the city is . Geography Mito is located in central Ibaraki Prefecture. Mito Station is about 10 km inland from the Pacific Ocean which Naka River, flowing from the north to the east of the city, pours into. Immediately south is Lake Senba, a recreational area. A main street extends from Mito Station to the west, and residential areas to the south and the west in particular. Surrounding municipalities Ibaraki Prefecture * Hitachinaka * Kasama * Naka * Ibaraki * Ōarai * Shirosato Climate Mito has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with light snowfall. The average annual temperature in Mito is 13.6 °C. The average annual rainfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanazu, Fukui
is a city located in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 27,107 in 10,140 households and the population density of 232 persons per km². The total area of the city was . It is one of the few Hiragana cities in Japan. Awara is a city famous for its onsen resorts and natural hotwater springs. Geography Awara is located in far northern Fukui Prefecture, bordered by Ishikawa Prefecture to the north and the Sea of Japan to the northeast, The city of Sakai surrounds the city to the east, south and west. Neighbouring municipalities *Fukui Prefecture ** Sakai *Ishikawa Prefecture ** Kaga Climate Awara has a Humid climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm, wet summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Awara is 14.2 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2481 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.8 °C, and lowest in January, at ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)





