|
Étienne Lenoir
Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir, also known as Jean J. Lenoir (12 January 1822 – 4 August 1900), was a Belgian-French engineer who developed the internal combustion engine in 1858. Prior designs for such engines were patented as early as 1807 ( De Rivaz engine), but none were commercially successful. Lenoir's engine was commercialized in sufficient quantities to be considered a success, a first for the internal combustion engine. He was born in Mussy-la-Ville (then in Luxembourg, part of the Belgian Province of Luxembourg since 1839). In 1838, he immigrated to France, taking up residence in Paris, where he developed an interest in electroplating. His interest in the subject led him to make several electrical inventions, including an improved electric telegraph. Lenoir engine By 1859, Lenoir's experimentation with electricity led him to develop the first internal combustion engine which burned a mixture of coal gas and air ignited by a "jumping sparks" ignition system by Ruhm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small landlocked country in Western Europe. It borders Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembourg, is one of the four institutional seats of the European Union (together with Brussels, Frankfurt, and Strasbourg) and the seat of several EU institutions, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its French and German neighbors; while Luxembourgish is legally the only national language of the Luxembourgish people, French and German are also used in administrative and judicial matters and all three are considered administrative languages of the cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition System
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol (gasoline) road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles. Compression ignition Diesel engines ignite the fuel-air mixture by the heat of compression and do not need a spark. They usually have glowplugs that preheat the combustion chamber to allow starting in cold weather. Other engines may use a flame, or a heated tube, for ignition. While this was common for very early engines it is now rare. The first electric spark ignition was probably Alessandro Volta's toy electric pistol from the 1780s. Siegfried Marcus patented his "Electrical igniting device for gas engines" on 7 October 1884. History Magneto systems The simplest form of spark ignition is that using a magneto. The engine s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official (the Pope or the Ecumenical Patriarch)—but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". It lends its name to a system of government, tsarist autocracy or tsarism. "Tsar" and its variants were the official titles of the following states: * Bulgarian Empire (First Bulgarian Empire in 681–1018, Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185–1396), and also used in Tsardom of Bulgaria, in 1908–1946 * Serbian Empire, in 1346–1371 * Tsardom of Russia, in 1547–1721 (replaced in 1721 by ''imperator'' in Russian Empire, but still remaining in use, also officially in relation to several regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
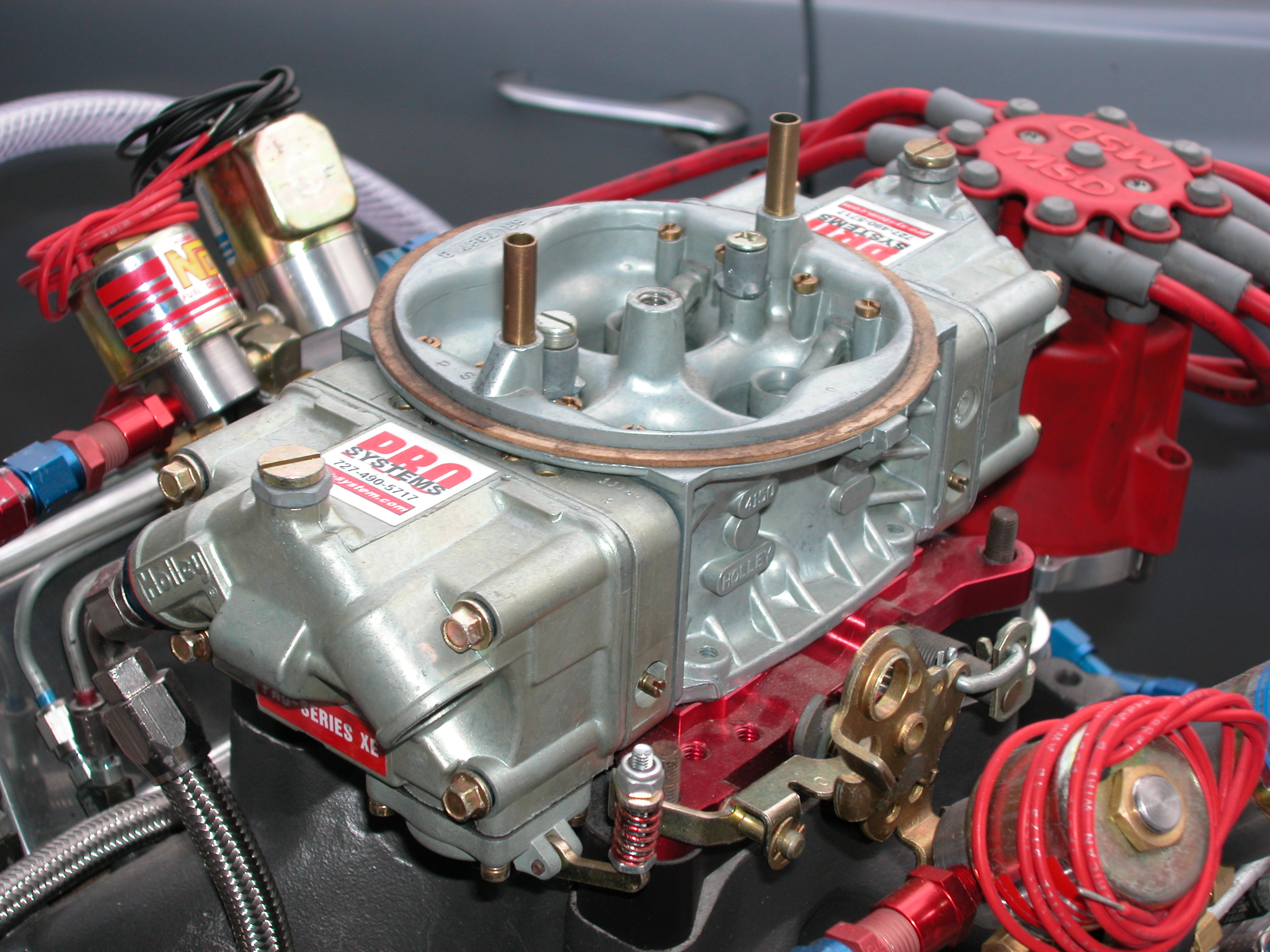
Carburettor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil. A fossil fuel, petroleum is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, mostly zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath sedimentary rock and subjected to both prolonged heat and pressure. Petroleum is primarily recovered by oil drilling. Drilling is carried out after studies of structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, and reservoir characterisation. Recent developments in technologies have also led to exploitation of other unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil shale. Once extracted, oil is refined and separated, most easily by distillation, into innumerable products for direct use or use in manufacturing. Products include fuels such as gasol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenoir Hippomobile
Lenoir may refer to: Locations: * Lenoir, North Carolina, United States * Lenoir County, North Carolina, United States * Lenoir City, Tennessee In Universities: * Lenoir-Rhyne University * Lenoir Dining Hall, a dining hall at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill In other topics: * USS Lenoir (AKA-74), a World War II attack cargo ship * Lenoir cycle, the basis of the first commercially produced internal combustion engine As a name: * Lenoir (surname) Lenoir or LeNoire is a surname that may refer to: * Alban Lenoir (born 1980), French actor, screenwriter and stuntman *Alexandre Lenoir (1761–1839), French archaeologist * Billy Lenoir (1942–2007), American tennis player *Charles-Amable Lenoir ... See also * Richard-Lenoir (Paris Metro) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservatoire National Des Arts Et Métiers
A music school is an educational institution specialized in the study, training, and research of music. Such an institution can also be known as a school of music, music academy, music faculty, college of music, music department (of a larger institution), conservatory, conservatorium or conservatoire ( , ). Instruction consists of training in the performance of musical instruments, singing, musical composition, conducting, musicianship, as well as academic and research fields such as musicology, music history and music theory. Music instruction can be provided within the compulsory general education system, or within specialized children's music schools such as the Purcell School. Elementary-school children can access music instruction also in after-school institutions such as music academies or music schools. In Venezuela El Sistema of youth orchestras provides free after-school instrumental instruction through music schools called ''núcleos''. The term "music school" can al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, England
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which in turn is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large format newspaper was released August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 device for buoying vessels by Abraham Lincoln, and the universal joint which now can be found in nearly every automobile manufactured. Current issues includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Franc
The franc (, ; sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amount of money. It was reintroduced (in decimal form) in 1795. After two centuries of inflation, it was redenominated in 1960, with each (NF) being worth 100 old francs. The NF designation was continued for a few years before the currency returned to being simply the franc. Many French residents, though, continued to quote prices of especially expensive items in terms of the old franc (equivalent to the new centime), up to and even after the introduction of the euro (for coins and banknotes) in 2002. The French franc was a commonly held international reserve currency of reference in the 19th and 20th centuries. Between 1998 and 2002, the conversion of francs to euros was carried out at a rate of 6.55957 francs to 1 euro. History The French Franc tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joinville-le-Pont
Joinville-le-Pont () is a commune in the southeastern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the center of Paris. History The commune was created in 1791 under the name La Branche-du-Pont-de-Saint-Maur (literally "The Branch of Saint-Maur's Bridge") by detaching its territory from the commune of Saint-Maur-des-Fossés. The commune was renamed Joinville-le-Pont (literally "Joinville the Bridge") on 29 August 1831. Under Louis-Philippe of France, the Redoute de Gravelle was built in the commune. In 1929, the commune of Joinville-le-Pont lost more than a third of its territory when the city of Paris annexed the Bois de Vincennes, a part of which belonged to Joinville-le-Pont. Geography Climate Joinville-le-Pont has a oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfb''). The average annual temperature in Joinville-le-Pont is . The average annual rainfall is with December as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in July, at around , and lowest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippomobile (car)
The Hippomobile is an automobile invented by Étienne Lenoir in 1863 which carried its own internal combustion engine. It was based on his 1860 invention, the Lenoir gas engine. History In 1863 the Hippomobile, powered by one cylinder internal combustion engine, made a test drive from Paris to Joinville-le-Pont, covering about eleven miles in less than three hours. This was a fair achievement at the time. See also * History of the internal combustion engine Various scientists and engineers contributed to the development of internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794 Robert Street patented an i ... * Motorized wagons * Timeline of transportation technology References External links ''Engine Maturity, Efficiency, and Potential Improvements'' US Dept of Energy, Washington, page 7 1860s cars 1863 introductions Hydrogen cars {{Veteran-auto-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |