World Egg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many
The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many
 The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many
The world egg, cosmic egg or mundane egg is a mythological motif found in the cosmogonies of many culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
s that is present in Proto-Indo-European culture
Proto-Indo-European society is the reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the ancient speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language, ancestor of all modern Indo-European languages.
Scientific approaches
Many of the modern ideas in this ...
and other cultures and civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
s. Typically, the world egg is a beginning of some sort, and the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
or some primordial being comes into existence by "hatching" from the egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
, sometimes lain on the primordial waters of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
.
Eggs symbolize the unification of two complementary principles (represented by the egg white and the yolk) from which life or existence, in its most fundamental philosophical sense, emerges.
Vedic mythology
The earliest idea of the "cosmic egg" comes from some of theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
scriptures. The Sanskrit term for it is Brahmanda (ब्रह्माण्ड) which is derived from two words – 'Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 21 ...
' (ब्रह्मा) the 'creator god' in Hinduism and 'anda' (अण्ड) meaning 'egg'. Certain Purana
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
s such as the Brahmanda Purana speak of this in detail.
The Rig Veda (RV 10.121) uses a similar name for the source of the universe: Hiranyagarbha
Hiraṇyagarbha (Sanskrit: हिरण्यगर्भः ; literally the 'golden womb', poetically translated as 'universal womb') is the source of the creation of universe or the manifested cosmos in Vedic philosophy. It finds mention in on ...
(हिरण्यगर्भ) which literally means "golden fetus" or "golden womb" and is associated with the universal source Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' ( sa, ब्रह्मन्) connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality in the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part X ...
where the whole of all existence is believed to be supported. The Upanishads
The Upanishads (; sa, उपनिषद् ) are late Vedic Sanskrit texts that supplied the basis of later Hindu philosophy.Wendy Doniger (1990), ''Textual Sources for the Study of Hinduism'', 1st Edition, University of Chicago Press, , ...
elaborate that the Hiranyagarbha
Hiraṇyagarbha (Sanskrit: हिरण्यगर्भः ; literally the 'golden womb', poetically translated as 'universal womb') is the source of the creation of universe or the manifested cosmos in Vedic philosophy. It finds mention in on ...
floated around in emptiness for a while, and then broke into two halves which formed Dyaus (the Heavens) and Prithvi
Prithvi or Prithvi Mata (Sanskrit: पृथ्वी, ', also पृथिवी, ', "the Vast One") is the Sanskrit name for the earth, as well as the name of a devi (goddess) in Hinduism and some branches of Buddhism. In the Vedas, her cons ...
(Earth). The Rig Veda has a similar coded description of the division of the universe in its early stages.
Zoroastrian mythology
According to Zoroastrian cosmology, the period of (material) creation, also to last 3,000 years, began after the treaty, whenOhrmazd
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna''. ...
recited the Ahunwar (Av. Ahuna Vairiia) prayer, revealing to Ahriman
Angra Mainyu (; Avestan: 𐬀𐬢𐬭𐬀⸱𐬨𐬀𐬌𐬥𐬌𐬌𐬎 ''Aŋra Mainiiu'') is the Avestan-language name of Zoroastrianism's hypostasis of the "destructive/evil spirit" and the main adversary in Zoroastrianism either of the ...
his ultimate defeat and causing him to fall back into the darkness in a stupor, which lasted for the entire period of the creation. During this time Ohrmazd fashioned his creations in material (''gētīg'') form, by celebrating a “spiritual ''yasna
Yasna (;"Yasna"
'' Amahraspands (Av. Aməša Spənta). First he created the sky (protected by Šahrewar, Av. Xšaθra Vairiia), which enclosed the world like the shell of an egg. The second creation was water (protected by Hordād, Av. Haurvatāt), which filled the lower half of the “egg.” The third creation, earth (protected by Spandārmad, Av. Spənta Ārmaiti), shaped like a flat disk, floated on the primeval waters. On it stood the fourth, fifth, and sixth creations, respectively the single plant or tree (protected by Amurdād; Av. Amərətāt), the uniquely created bull (protected by Wahman, Av. Vohu Manah), and the first man, Gayōmard (Av. Gaiiō.marətan, protected by Ohrmazd himself). The seventh creation, fire (protected by Ardwahišt; Av. Aṧa Vahišta), was said to have permeated all other creations. During the 3,000 years of the period of material creation these creations were motionless, and the sun stood still in the middle of the sky.
Creation
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Egg Creation myths Eggs in culture pl:Jajko w kulturze#Symbolika
'' Amahraspands (Av. Aməša Spənta). First he created the sky (protected by Šahrewar, Av. Xšaθra Vairiia), which enclosed the world like the shell of an egg. The second creation was water (protected by Hordād, Av. Haurvatāt), which filled the lower half of the “egg.” The third creation, earth (protected by Spandārmad, Av. Spənta Ārmaiti), shaped like a flat disk, floated on the primeval waters. On it stood the fourth, fifth, and sixth creations, respectively the single plant or tree (protected by Amurdād; Av. Amərətāt), the uniquely created bull (protected by Wahman, Av. Vohu Manah), and the first man, Gayōmard (Av. Gaiiō.marətan, protected by Ohrmazd himself). The seventh creation, fire (protected by Ardwahišt; Av. Aṧa Vahišta), was said to have permeated all other creations. During the 3,000 years of the period of material creation these creations were motionless, and the sun stood still in the middle of the sky.
Yazidism
TheYazidi
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
qewls mention the universe as having originated from a white pearl that existed in pre-eternity. At the beginning of the time prior to the creation, God emerged from the cosmic pearl, which rested on the horns of a bull that stood on the back of a fish. After God and the pearl separated, the universe burst out of the pearl and became visible as waves rippled across from pearl to form the primeval Cosmic Ocean
A cosmic ocean or celestial river is a mythological motif found in the mythology of many cultures and civilizations, representing the world or cosmos as enveloped by primordial waters.
In ancient creation texts, the primordial waters are often ...
. As the pearl burst open, the beginning of the material universe was set in motion. ''Mihbet'' (meaning 'love') came into being and was laid as the original foundation, colours began to form, and red, yellow and white began to shine from the burst pearl.
Mandaeism
Mandaean creation accounts often mention the universe as having originated from a primal "fruit" (''pira'') or sometimes "egg" (''hilbuna''). According to Book 3 of the '' Right Ginza'', one of theMandaean scriptures
This article contains a list of Mandaean texts (Mandaean religious texts written in Classical Mandaic). Well-known texts include the ''Ginza Rabba'' (also known as the ''Sidra Rabbā'') and the '' Qolastā''. Texts for Mandaean priests includ ...
, the universe originated from a "fruit (''pira'') within a fruit." In the ''Right Ginza'', egg whites are described as hidden heavenly "mansions," or shkinta
In Mandaeism, a shkinta ( myz, ࡔࡊࡉࡍࡕࡀ, translit=škinta, lit=shekinah) or shkina (''škina'') is a celestial dwelling inhabited by uthras in the World of Light that is analogous to the shekhinah in Jewish mysticism. In Tibil (the ...
(i.e., shekhinah
Shekhinah, also spelled Shechinah ( Hebrew: שְׁכִינָה ''Šəḵīnā'', Tiberian: ''Šăḵīnā'') is the English transliteration of a Hebrew word meaning "dwelling" or "settling" and denotes the presence of God, as it were, in a pla ...
).
Greek/Orphic mythology
TheOrphic Egg
Orphism (more rarely Orphicism; grc, Ὀρφικά, Orphiká) is the name given to a set of religious beliefs and practices originating in the ancient Greek and Hellenistic world, associated with literature ascribed to the mythical poet Orpheus ...
in the ancient Greek Orphic tradition is the cosmic egg from which hatched the primordial hermaphroditic
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have s ...
deity Phanes
Phanes ( grc, Φάνης, Phánēs, genitive ) or Protogonus () was the mystic primeval deity of procreation and the generation of new life, who was introduced into Greek mythology by the Orphic tradition; other names for this Classical Gree ...
/Protogonus (variously equated also with Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
, Pan, Metis
Metis or Métis may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and America whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peoples and early European settlers, prima ...
, Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
, Erikepaios In the Orphic religion, Erikepaios ( grc, Ἠρικαπαῖος/Ἠρικεπαῖος, Ērikapaîos/Ērikepaîos, power; la, Ericepaeus) was a title for the god Phanes, mentioned in Orphic poetry and the associated Dionysian Mysteries, a non-Gr ...
and Bromius
Bromius ( grc, Βρόμιος) in ancient Greece was used as an epithet of Dionysus/Bacchus. It signifies "noisy", "roaring", or "boisterous", from , to roar. According to Richard Buxton, Bromius (Bromios) is another name for a fundamental divin ...
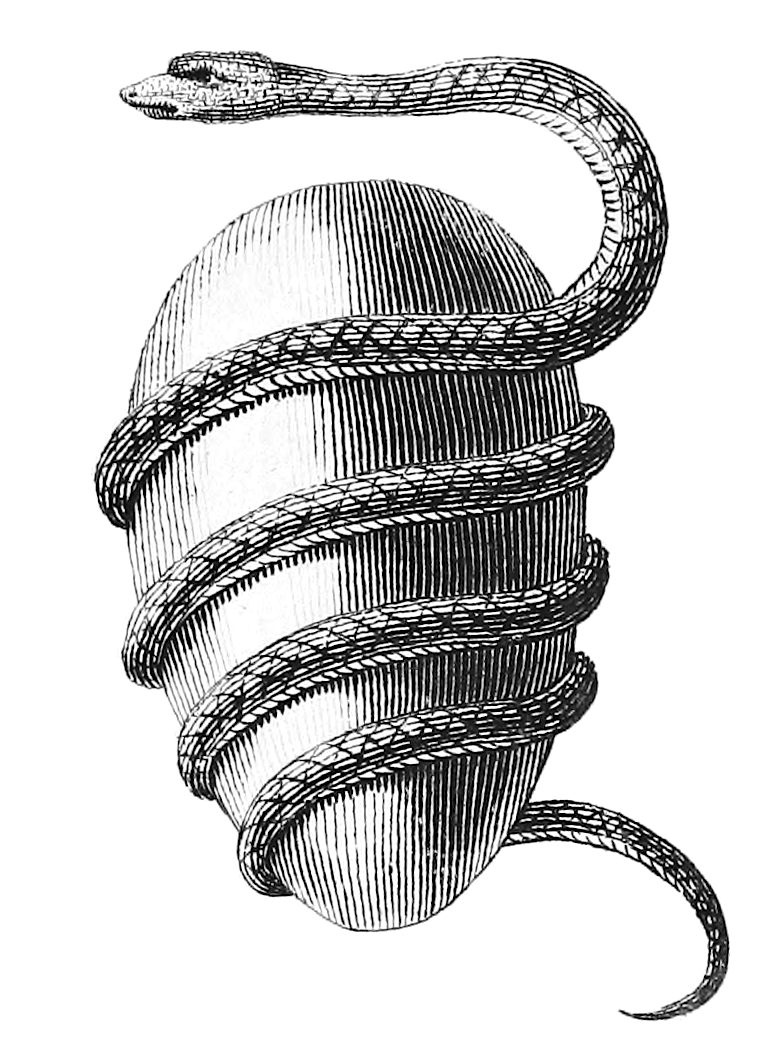
) who in turn created the other gods. The egg is often depicted with a serpent wound around it.
Many threads of earlier myths are apparent in the new tradition. Phanes
Phanes ( grc, Φάνης, Phánēs, genitive ) or Protogonus () was the mystic primeval deity of procreation and the generation of new life, who was introduced into Greek mythology by the Orphic tradition; other names for this Classical Gree ...
was believed to have been hatched from the World egg of Chronos
Chronos (; grc-gre, Χρόνος, , "time"), also spelled Khronos or Chronus, is a personification of time in pre-Socratic philosophy and later literature.
Chronos is frequently confused with, or perhaps consciously identified with, the Tita ...
(Time) and Ananke
In ancient Greek religion, Ananke (; grc, Ἀνάγκη), from the common noun , "force, constraint, necessity") is the personification of inevitability, compulsion and necessity. She is customarily depicted as holding a spindle. One of the ...
(Necessity) or Nyx (Night). His older wife Nyx called him Protogenus. As she created nighttime, he created daytime. He also created the method of creation by mingling. He was made the ruler of the deities and passed the sceptre
A sceptre is a staff or wand held in the hand by a ruling monarch as an item of royal or imperial insignia. Figuratively, it means royal or imperial authority or sovereignty.
Antiquity
Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia
The '' Was'' and other ...
to Nyx. This new Orphic tradition states that Nyx later gave the sceptre to her son Uranos before it passed to Cronus and then to Zeus, who retained it.
Egyptian mythology
The ancient Egyptians accepted multiple creation myths as valid, including those of the Hermopolitan, Heliopolitan, and Memphite theologies. Under the Hermopolitan theology, there is the Ogdoad, which represents the conditions before thegods
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
were created (Van Dijk, 1995).
An aspect within the Ogdoad is the Cosmic Egg, from which all things are born. Life comes from the Cosmic Egg; the sun god Ra was born from the primordial egg in a stage known as the first occasion (Dunand, 2004).
Phoenician mythology
A philosophical creation story traced to "the cosmogony of ''Taautus
Taautus of Byblos, according to the Phoenician writer Sanchuniathon, was the son of Misor and the inventor of writing, who was bequeathed the land of Egypt by Cronus.
Sanchuniathon's writings, through the translation of Philo, were transmitted to ...
'', whom Philo of Byblos explicitly identified with the Egyptian Thoth
Thoth (; from grc-koi, Θώθ ''Thṓth'', borrowed from cop, Ⲑⲱⲟⲩⲧ ''Thōout'', Egyptian: ', the reflex of " eis like the Ibis") is an ancient Egyptian deity. In art, he was often depicted as a man with the head of an ibis or ...
—"the first who thought of the invention of letters, and began the writing of records"— which begins with Erebus
In Greek mythology, Erebus (; grc, Ἔρεβος, Érebos, "deep darkness, shadow".), or Erebos, is the personification of darkness and one of the primordial deities. Hesiod's ''Theogony'' identifies him as one of the first five beings in exis ...
and Wind, between which ''Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
'' 'Desire' came to be. From this was produced ''Môt'' which seems to be the Phoenician/Ge'ez/Hebrew/Arabic/Ancient Egyptian word for 'Death' but which the account says may mean 'mud'. In a mixed confusion, the germs of life appear, and intelligent animals called ''Zophasemin'' (explained probably correctly as 'observers of heaven') formed together as an egg, perhaps. The account is not clear. Then Môt burst forth into light and the heavens were created and the various elements found their stations.
Following the etymological line of Jacob Bryant
Jacob Bryant (1715–1804) was an English scholar and mythographer, who has been described as "the outstanding figure among the mythagogues who flourished in the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries."
Life
Bryant was born at Plymout ...
one might also consider with regard to the meaning of ''Môt'', that according to the Ancient Egyptians ''Ma'at
Maat or Maʽat ( Egyptian:
mꜣꜥt /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and regul ...
'' was the personification of the fundamental order of the universe, without which all of creation would perish. She was also considered the wife of Thoth.
Chinese mythology
In the myth ofPangu
Pangu (, ) is a primordial being and creation figure in Chinese mythology who separated heaven and earth and became geographic features such as mountains and rivers.
Legends
The first writer to record the myth of Pangu was Xu Zheng during t ...
, developed by Taoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao ...
monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedica ...
s hundreds of years after Lao Zi
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state of ...
, the universe began as an egg that symbolizes the primordial state of Taiji
Tai chi (), short for Tai chi ch'üan ( zh, s=太极拳, t=太極拳, first=t, p=Tàijíquán, labels=no), sometimes called " shadowboxing", is an internal Chinese martial art practiced for defense training, health benefits and meditation. T ...
. A primeval hermaphroditic
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have s ...
giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''gigas'', cognate giga-) are beings of human-like appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 fr ...
named Pangu
Pangu (, ) is a primordial being and creation figure in Chinese mythology who separated heaven and earth and became geographic features such as mountains and rivers.
Legends
The first writer to record the myth of Pangu was Xu Zheng during t ...
, born inside the egg, broke it into two halves: the upper half became the sky, while the lower half became the earth. As the god grew taller, the sky and the earth grew thicker and were separated further. Finally Pangu died and his body parts became the sun, moon, different parts of the earth and living things.
Finnish mythology
In the ''Kalevala
The ''Kalevala'' ( fi, Kalevala, ) is a 19th-century work of epic poetry compiled by Elias Lönnrot from Karelian and Finnish oral folklore and mythology, telling an epic story about the Creation of the Earth, describing the controversies and ...
'', the Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
national epic, there is a myth of the world being created from the fragments of an egg laid by a goldeneye
''GoldenEye'' is a 1995 spy film, the seventeenth in the ''James Bond'' series produced by Eon Productions, and the first to star Pierce Brosnan as the fictional MI6 agent James Bond. Directed by Martin Campbell, it was the first in the se ...
on the knee of Ilmatar
In the ''Kalevala'', the Finnish national epic, Ilmatar () was a virgin spirit and goddess of the air.
Origins
The name Ilmatar is derived from the Finnish word ''ilma'', meaning "air," and the female suffix ''-tar'', corresponding to English ...
, goddess of the air:
: ''One egg's lower half transformed''
: ''And became the earth below,''
: ''And its upper half transmuted''
: ''And became the sky above;''
: ''From the yolk the sun was made,''
: ''Light of day to shine upon us;''
: ''From the white the moon was formed,''
: ''Light of night to gleam above us;''
: ''All the colored brighter bits''
: ''Rose to be the stars of heaven''
: ''And the darker crumbs changed into''
: ''Clouds and cloudlets in the sky.''
In many original folk poems, the duck - or sometimes an eagle - laid its eggs on the knee of Väinämöinen
Väinämöinen () is a demigod, hero and the central character in Finnish folklore and the main character in the national epic ''Kalevala'' by Elias Lönnrot. Väinämöinen was described as an old and wise man, and he possessed a potent, m ...
.
Polynesian mythology
InCook Islands mythology
Cook Islands mythology comprises historical myths, legends, and folklore passed down by the ancient Cook Islanders over many generations. Many of the Cook Islands legends were recited through ancient songs and chants. The Cook Islands myths and ...
, deep within Avaiki
Avaiki is one of the many names by which the peoples of Polynesia refer to their ancestral and spiritual homelands.
Samoa, Hawaii, Cook Islands
By no means certain, but certainly possible, is an origin in the large islands of Samoa, namely Sav ...
(the Underworld), a place described as resembling a vast hollow coconut shell, there dwelt in the deepest depths, the primordial mother goddess, Varima-te-takere
In Cook Islands mythology, Varima-te-takere ("goddess of the beginning") also called Vari ( ), was the primordial mother of the gods and mortals.
According to Gill, Vari, a female spirit or demon of flesh and blood, was admitted to the lowest ...
. Her domain was described as being so narrow, that her knees touched her chin. It was from this place that she created the first man, Avatea
In Cook Islands mythology, Avatea (also known as Vatea; meaning 'noon' or 'light') was a lunar deity and the father of gods and men in Mangaian myth of origin. His eyes were thought to be the Sun and the Moon; he was also known as the god of lig ...
, a god of light, a hybrid being half man and half fish. He was sent to the Upperworld to shine light in the land of men, and his eyes were believed to be the sun and the moon.
In Samoan and Tahitian mythology, all existence began inside an egg-like shell called Rumia. The first being to exist within Rumia was Tangaloa. Tangaloa instigated the creation of many aspects of reality, the atea/lagi heavens, the papa earth, and additional living creatures (the atua / gods) tightly compressed within the shell. The new creatures eventually worked to release the shell and pushed the heavens and earth apart, resulting in the universe as we know it.
Dogon mythology
InDogon
Dogon may refer to:
*Dogon people, an ethnic group living in the central plateau region of Mali, in West Africa
*Dogon languages, a small, close-knit language family spoken by the Dogon people of Mali
*'' Dogon A.D.'', an album by saxophonist Juliu ...
mythology (West Africa):
"''In the beginning, Amma dogon, alone, was in the shape of an egg: the four collar bones were fused, dividing the egg into air, earth, fire, and water, establishing also the four cardinal directions. Within this cosmic egg was the material and the structure of the universe, and the 266 signs that embraced the essence of all things. The first creation of the world by Amma was, however, a failure. The second creation began when Amma planted a seed within herself, a seed that resulted in the shape of man. But in the process of its gestation, there was a flaw, meaning that the universe would now have within it the possibilities for incompleteness. Now the egg became two placentas, each containing a set of twins, male and female. After sixty years, one of the males, Ogo, broke out of the placenta and attempted to create his own universe, in opposition to that being created by Amma. But he was unable to say the words that would bring such a universe into being. He then descended, as Amma transformed into the earth the fragment of placenta that went with Ogo into the void. Ogo interfered with the creative potential of the earth by having incestuous relations with it. His counterpart, Nommo, a participant in the revolt, was then killed by Amma, the parts of his body cast in all directions, bringing a sense of order to the world. When, five days later, Amma brought the pieces of Nommo's body together, restoring him to life, Nommo became ruler of the universe. He created four spirits, the ancestors of the Dogon people; Amma sent Nommo and the spirits to earth in an ark, and so the earth was restored. Along the way, Nommo uttered the words of Amma, and the sacred words that create were made available to humans. In the meantime, Ogo was transformed by Amma into Yuguru, the Pale Fox, who would always be alone, always be incomplete, eternally in revolt, ever wandering the earth seeking his female soul. ''"
Representations
* In thetemple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
of Daiboth (probably Daibod) at Meaco (now Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along wi ...
) in Japan, the egg is described as floating in an expanse of water, which opened with the assistance of the sacred steer (bull), upon which the world issued forth to this day.
Modern mythology
In 1955 poet and writer Robert Graves published the mythography ''The Greek Myths
''The Greek Myths'' (1955) is a mythography, a compendium of Greek mythology, with comments and analyses, by the poet and writer Robert Graves. Many editions of the book separate it into two volumes. Abridged editions of the work contain only the ...
'', a compendium of Greek mythology normally published in two volumes. Within this work Graves' imaginatively reconstructed "Pelasgian creation myth" features a supreme creatrix, Eurynome
Eurynomê (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρυνόμη, from , ''eurys'', "broad" and , ''nomos'', "pasture" or "law") is a name that refers to the following characters in Greek mythology:
*Eurynome, pre-Olympian queen and wife of Ophion
*Eurynome (Ocean ...
, "The Goddess of All Things", who arose naked from Chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional elements
* Chaos (''Kinnikuman'')
* Chaos (''Sailor Moon'')
* Chaos (''Sesame Park'')
* Chaos (''Warhammer'')
* Chaos, in ''Fabula Nova Crystallis Final Fantasy''
* Cha ...
to part sea from sky so that she could dance upon the waves. Catching the north wind at her back and, rubbing it between her hands, she warms the ''pneuma
''Pneuma'' () is an ancient Greek word for "breath", and in a religious context for " spirit" or "soul". It has various technical meanings for medical writers and philosophers of classical antiquity, particularly in regard to physiology, and is ...
'' and spontaneously generates the serpent Ophion
In some versions of Greek mythology, Ophion (; grc-gre, Ὀφίων "serpent"; ''gen''.: Ὀφίωνος), also called Ophioneus () ruled the world with Eurynome before the two of them were cast down by Cronus and Rhea.
Mythology
Pherecydes of ...
, who mates with her. In the form of a dove upon the waves, she lays the Cosmic Egg and bids Ophion to incubate it by coiling seven times around until it splits in two and hatches "all things that exist... sun, moon, planets, stars, the earth with its mountains and rivers, its trees, herbs, and living creatures".
In modern cosmology
The concept was figuratively re-adopted by modernscience
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
in the 1930s and explored by theoreticians during the following two decades. Current cosmological models maintain that 13.8 billion years ago, the entire mass of the universe was compressed into a gravitational singularity
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular sp ...
, a so-called ‘cosmic egg’ from which it 'hatched', expanding to its current state following the Big Bang.
The idea of a scientific cosmic egg comes from a need to describe the consequences of Vesto Slipher's observation and Edwin Hubble's confirmation of an expanding universe; extrapolated backwards in time, it implies a finite starting-time and a small starting-place, from which the entire cosmos metaphorically hatched. The expansion contradicts the then-established conception of the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. ...
as eternally old, with no start and no growth: Einstein's static universe.
* In 1913, Vesto Slipher published his observations that light from remote galaxies was redshifted, which was Great Debate (astronomy), gradually accepted as meaning that all galaxies (except Andromeda Galaxy, Andromeda) receding from the Earth.
* Alexander Friedmann predicted the same consequence in 1922 from Albert Einstein, Einstein's equations of general relativity, once the previous ad-hoc cosmological constant was removed from it (which had been inserted to conform to the preconceived eternal, static universe).
* Georges Lemaître proposed in 1927 that the cosmos originated from what he called the ''primeval atom''.
* Edwin Hubble observationally confirmed Lemaître's findings two years later, in 1929.
* In the late 1940s, George Gamow's assistant Cosmology, cosmological researcher Ralph Alpher, proposed the name ylem for the primordial substance that existed between the Big Crunch of the previous universe and the Big Bang of our own universe. ''Ylem'' is closely related to the concept of supersymmetry.
See also
*Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 21 ...
* Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' ( sa, ब्रह्मन्) connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality in the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part X ...
* Brahmanda Purana, Brahmanda
* Hiranyagarbha
Hiraṇyagarbha (Sanskrit: हिरण्यगर्भः ; literally the 'golden womb', poetically translated as 'universal womb') is the source of the creation of universe or the manifested cosmos in Vedic philosophy. It finds mention in on ...
* Orphic egg
* Phanes
References
Sources
* * * *External links
Creation
{{DEFAULTSORT:World Egg Creation myths Eggs in culture pl:Jajko w kulturze#Symbolika