Water Cycle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of

 The water cycle involves the following processes:
; Advection: The movement of water through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land. Atmospheric rivers that move large volumes of water vapor over long distances are an example of advection.
;
The water cycle involves the following processes:
; Advection: The movement of water through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land. Atmospheric rivers that move large volumes of water vapor over long distances are an example of advection.
;
 Since the middle of the 20th century, human-caused climate change has resulted in observable changes in the global water cycle.Arias, P.A., N. Bellouin, E. Coppola, R.G. Jones, G. Krinner, J. Marotzke, V. Naik, M.D. Palmer, G.-K. Plattner, J. Rogelj, M. Rojas, J. Sillmann, T. Storelvmo, P.W. Thorne, B. Trewin, K. Achuta Rao, B. Adhikary, R.P. Allan, K. Armour, G. Bala, R. Barimalala, S. Berger, J.G. Canadell, C. Cassou, A. Cherchi, W. Collins, W.D. Collins, S.L. Connors, S. Corti, F. Cruz, F.J. Dentener, C. Dereczynski, A. Di Luca, A. Diongue Niang, F.J. Doblas-Reyes, A. Dosio, H. Douville, F. Engelbrecht, V. Eyring, E. Fischer, P. Forster, B. Fox-Kemper, J.S. Fuglestvedt, J.C. Fyfe, et al., 2021
Since the middle of the 20th century, human-caused climate change has resulted in observable changes in the global water cycle.Arias, P.A., N. Bellouin, E. Coppola, R.G. Jones, G. Krinner, J. Marotzke, V. Naik, M.D. Palmer, G.-K. Plattner, J. Rogelj, M. Rojas, J. Sillmann, T. Storelvmo, P.W. Thorne, B. Trewin, K. Achuta Rao, B. Adhikary, R.P. Allan, K. Armour, G. Bala, R. Barimalala, S. Berger, J.G. Canadell, C. Cassou, A. Cherchi, W. Collins, W.D. Collins, S.L. Connors, S. Corti, F. Cruz, F.J. Dentener, C. Dereczynski, A. Di Luca, A. Diongue Niang, F.J. Doblas-Reyes, A. Dosio, H. Douville, F. Engelbrecht, V. Eyring, E. Fischer, P. Forster, B. Fox-Kemper, J.S. Fuglestvedt, J.C. Fyfe, et al., 2021
Technical Summary
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 33−144. doi:10.1017/9781009157896.002. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report in 2021 predicted that these changes will continue to grow significantly at the global and regional level. These findings are a continuation of scientific consensus expressed in the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report from 2007 and other special reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change which had already stated that the water cycle will continue to "intensify" throughout the 21st century.
 Human activities, other than those that lead to global warming from greenhouse gas emissions, can also alter the water cycle. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report stated that there is "abundant evidence that changes in land use and land cover alter the water cycle globally, regionally and locally, by changing precipitation, evaporation, flooding, groundwater, and the availability of freshwater for a variety of uses".Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021
Human activities, other than those that lead to global warming from greenhouse gas emissions, can also alter the water cycle. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report stated that there is "abundant evidence that changes in land use and land cover alter the water cycle globally, regionally and locally, by changing precipitation, evaporation, flooding, groundwater, and the availability of freshwater for a variety of uses".Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021
Water Cycle Changes
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. Examples for such land use changes are converting fields to urban areas or clearing forests. Such changes can affect the ability of soils to soak up surface water. Deforestation can also "directly reduce soil moisture, evaporation and rainfall locally but can also cause regional temperature changes that affect rainfall patterns". Aquifer drawdown or
Ecclesiastes 1:6-7
. Scholars are not in agreement as to the date of Ecclesiastes, though most scholars point to a date during the time of King Solomon, son of David and Bathsheba, "three thousand years ago, there is some agreement that the time period is 962–922 BCE. Furthermore, it was also observed that when the clouds were full, they emptied rain on the earth
Ecclesiastes 11:3
. In addition, during 793–740 BCE a Hebrew prophet, Amos, stated that water comes from the sea and is poured out on the earth
Amos 5:8
. In the Biblical Book of Job, dated between 7th and 2nd centuries BCE, there is a description of precipitation in the hydrologic cycle, "For he maketh small the drops of water: they pour down rain according to the vapour thereof; which the clouds do drop and distil upon man abundantly"
Job 36:27-28
.
The Water Cycle
United States Geological Survey
United States Geological Survey
The Water Cycle: Following The Water
(NASA Visualization Explorer with videos) {{DEFAULTSORT:Water Cycle Biogeochemical cycle Forms of water Hydrology Soil physics Water Articles containing video clips Limnology Oceanography
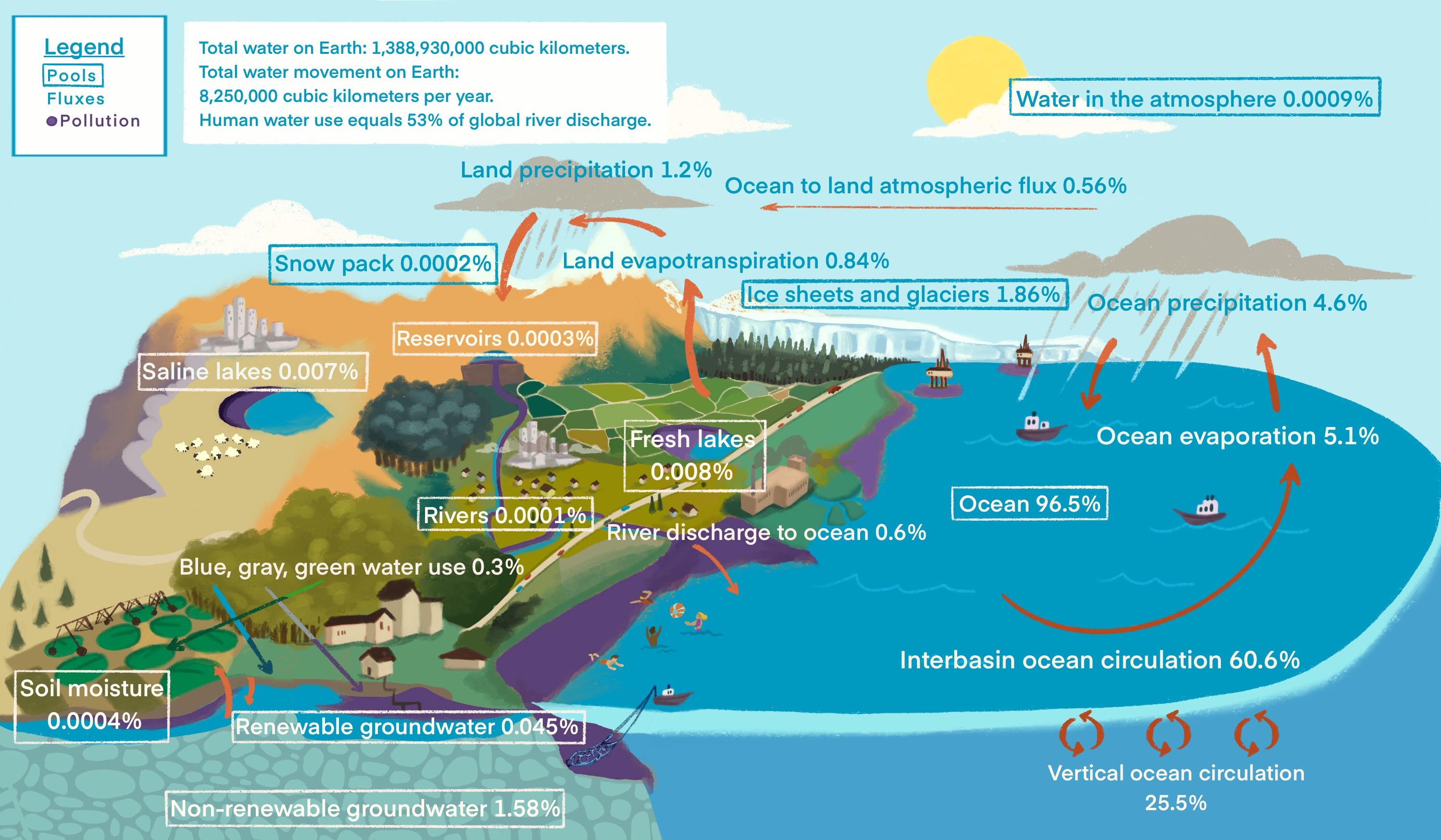
 The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
on, above and below the surface of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
, fresh water, saline water (salt water) and atmospheric water is variable depending on a wide range of climatic variables. The water moves from one reservoir to another, such as from river to ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
, or from the ocean to the atmosphere, by the physical processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, surface runoff, and subsurface flow. In doing so, the water goes through different forms: liquid, solid (ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaqu ...
) and vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (British English and Canadian English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Her ...
. The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle as it is the source of 86% of global evaporation.
The water cycle involves the exchange of energy, which leads to temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various Conversion of units of temperature, temp ...
changes. When water evaporates, it takes up energy from its surroundings and cools the environment. When it condenses, it releases energy and warms the environment. These heat exchanges influence climate.
The evaporative phase of the cycle purifies water which then replenishes the land with freshwater. The flow of liquid water and ice transports minerals across the globe. It is also involved in reshaping the geological features of the Earth, through processes including erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
and sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to the ...
. The water cycle is also essential for the maintenance of most life and ecosystems on the planet.
Description

Overall process
The water cycle is powered from the energy emitted by the sun. This energy heats water in the ocean and seas. Water evaporates as water vapor into theair
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
. Some ice and snow sublimates directly into water vapor. Evapotranspiration is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. The water molecule has smaller molecular mass than the major components of the atmosphere, nitrogen () and oxygen () and hence is less dense. Due to the significant difference in density, buoyancy drives humid air higher. As altitude increases, air pressure decreases and the temperature drops (see Gas laws
The gas laws were developed at the end of the 18th century, when scientists began to realize that relationships between pressure, volume and temperature of a sample of gas could be obtained which would hold to approximation for all gases.
Boyl ...
). The lower temperature causes water vapor to condense into tiny liquid water droplets which are heavier than the air, and which fall unless supported by an updraft. A huge concentration of these droplets over a large area in the atmosphere become visible as cloud, while condensation near ground level is referred to as fog.
Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, bu ...
moves water vapor around the globe; cloud particles collide, grow, and fall out of the upper atmospheric layers as precipitation. Some precipitation falls as snow, hail, or sleet, and can accumulate in ice caps and glaciers, which can store frozen water for thousands of years. Most water falls as rain back into the ocean or onto land, where the water flows over the ground as surface runoff. A portion of this runoff enters rivers, with streamflow moving water towards the oceans. Runoff and water emerging from the ground ( groundwater) may be stored as freshwater in lakes. Not all runoff flows into rivers; much of it soaks into the ground as infiltration. Some water infiltrates deep into the ground and replenishes aquifers, which can store freshwater for long periods of time. Some infiltration stays close to the land surface and can seep back into surface-water bodies (and the ocean) as groundwater discharge or be taken up by plants and transfered back to the atmosphere as water vapor by transpiration. Some groundwater finds openings in the land surface and emerges as freshwater springs. In river valleys and floodplains, there is often continuous water exchange between surface water and ground water in the hyporheic zone
The hyporheic zone is the region of sediment and porous space beneath and alongside a stream bed, where there is mixing of shallow groundwater and surface water. The flow dynamics and behavior in this zone (termed hyporheic flow or underflow) is re ...
. Over time, the water returns to the ocean, to continue the water cycle.
The ocean plays a key role in the water cycle. The ocean holds "97% of the total water on the planet; 78% of global precipitation occurs over the ocean, and it is the source of 86% of global evaporation".
Physical processes
 The water cycle involves the following processes:
; Advection: The movement of water through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land. Atmospheric rivers that move large volumes of water vapor over long distances are an example of advection.
;
The water cycle involves the following processes:
; Advection: The movement of water through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land. Atmospheric rivers that move large volumes of water vapor over long distances are an example of advection.
;Canopy interception
Canopy interception is the rainfall that is intercepted by the canopy of a tree and successively evaporates from the leaves. Precipitation that is not intercepted will fall as throughfall or stemflow on the forest floor.
Many methods exist to m ...
: The precipitation that is intercepted by plant foliage eventually evaporates back to the atmosphere rather than falling to the ground.
; Condensation: The transformation of water vapor to liquid water droplets in the air, creating clouds and fog.
; Deposition: This refers to changing of water vapor directly to ice.
; Evaporation: The transformation of water from liquid to gas phases as it moves from the ground or bodies of water into the overlying atmosphere. The source of energy for evaporation is primarily solar radiation. Evaporation often implicitly includes transpiration from plants, though together they are specifically referred to as evapotranspiration. Total annual evapotranspiration amounts to approximately of water, of which evaporates from the oceans. 86% of global evaporation occurs over the ocean.
; Infiltration: The flow of water from the ground surface into the ground. Once infiltrated, the water becomes soil moisture or groundwater. A recent global study using water stable isotopes, however, shows that not all soil moisture is equally available for groundwater recharge or for plant transpiration.
;Percolation
Percolation (from Latin ''percolare'', "to filter" or "trickle through"), in physics, chemistry and materials science, refers to the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials.
It is described by Darcy's law.
Broader applicatio ...
: Water flows vertically through the soil and rocks under the influence of gravity.
; Precipitation: Condensed water vapor that falls to the Earth's surface. Most precipitation occurs as rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water ...
, but also includes snow, hail, fog drip
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily in ...
, graupel, and sleet. Approximately of water falls as precipitation each year, of it over the oceans. The rain on land contains of water per year and a snowing only . 78% of global precipitation occurs over the ocean.
; Runoff: The variety of ways by which water moves across the land. This includes both surface runoff and channel runoff. As it flows, the water may seep into the ground, evaporate into the air, become stored in lakes or reservoirs, or be extracted for agricultural or other human uses.
;Snow melt
In hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many part ...
: The runoff produced by melting snow.
; Sublimation: The state change directly from solid water (snow or ice) to water vapor by passing the liquid state.
;Subsurface flow
Subsurface flow, in hydrology, is the flow of water beneath earth's surface as part of the water cycle.
In the water cycle, when precipitation falls on the earth's land, some of the water flows on the surface forming streams and rivers. The rema ...
: The flow of water underground, in the vadose zone and aquifers
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characterist ...
. Subsurface water may return to the surface (e.g. as a spring or by being pumped) or eventually seep into the oceans. Water returns to the land surface at lower elevation than where it infiltrated, under the force of gravity or gravity induced pressures. Groundwater tends to move slowly and is replenished slowly, so it can remain in aquifers for thousands of years.
; Transpiration: The release of water vapor from plants and soil into the air.
Residence times
The '' residence time'' of a reservoir within the hydrologic cycle is the average time a water molecule will spend in that reservoir (''see adjacent table''). It is a measure of the average age of the water in that reservoir. Groundwater can spend over 10,000 years beneath Earth's surface before leaving. Particularly old groundwater is calledfossil water
Fossil water or paleowater is an ancient body of water that has been contained in some undisturbed space, typically groundwater in an aquifer, for millennia. Other types of fossil water can include subglacial lakes, such as Antarctica's Lake Vos ...
. Water stored in the soil remains there very briefly, because it is spread thinly across the Earth, and is readily lost by evaporation, transpiration, stream flow, or groundwater recharge. After evaporating, the residence time in the atmosphere is about 9 days before condensing and falling to the Earth as precipitation.
The major ice sheets – Antarctica and Greenland – store ice for very long periods. Ice from Antarctica has been reliably dated to 800,000 years before present, though the average residence time is shorter.
In hydrology, residence times can be estimated in two ways. The more common method relies on the principle of conservation of mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass can ...
( water balance) and assumes the amount of water in a given reservoir is roughly constant. With this method, residence times are estimated by dividing the volume of the reservoir by the rate by which water either enters or exits the reservoir. Conceptually, this is equivalent to timing how long it would take the reservoir to become filled from empty if no water were to leave (or how long it would take the reservoir to empty from full if no water were to enter).
An alternative method to estimate residence times, which is gaining in popularity for dating groundwater, is the use of isotopic techniques. This is done in the subfield of isotope hydrology Isotope hydrology is a field of geochemistry and hydrology that uses naturally occurring stable and radioactive isotopic techniques to evaluate the age and origins of surface and groundwater and the processes within the atmospheric hydrologic cycle ...
.
Water in storage
The water cycle describes the processes that drive the movement of water throughout the hydrosphere. However, much more water is "in storage" for long periods of time than is actually moving through the cycle. The storehouses for the vast majority of all water on Earth are the oceans. It is estimated that of the 1,386,000,000 km3 of the world's water supply, about 1,338,000,000 km3 is stored in oceans, or about 97%. It is also estimated that the oceans supply about 90% of the evaporated water that goes into the water cycle. The Earth's ice caps, glaciers, and permanent snowpack stores another 24,064,000 km3 accounting for only 1.7% of the planet's total water volume. However, this quantity of water is 68.7% of all freshwater on the planet.Changes caused by humans
Water cycle intensification due to climate change
Technical Summary
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 33−144. doi:10.1017/9781009157896.002. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report in 2021 predicted that these changes will continue to grow significantly at the global and regional level. These findings are a continuation of scientific consensus expressed in the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report from 2007 and other special reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change which had already stated that the water cycle will continue to "intensify" throughout the 21st century.
Glacial retreat
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 affects the availability of fresh water for irrigation and domestic use, mountain recreation, animals and plants that depend on glacier-melt, and, in the longer term, the level of the oceans. Deglaciation occur ...
is also an example of a changing water cycle, where the supply of water to glaciers from precipitation cannot keep up with the loss of water from melting and sublimation. Glacial retreat since 1850 due to global warming has been extensive.
Changes due to other human activities
 Human activities, other than those that lead to global warming from greenhouse gas emissions, can also alter the water cycle. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report stated that there is "abundant evidence that changes in land use and land cover alter the water cycle globally, regionally and locally, by changing precipitation, evaporation, flooding, groundwater, and the availability of freshwater for a variety of uses".Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021
Human activities, other than those that lead to global warming from greenhouse gas emissions, can also alter the water cycle. The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report stated that there is "abundant evidence that changes in land use and land cover alter the water cycle globally, regionally and locally, by changing precipitation, evaporation, flooding, groundwater, and the availability of freshwater for a variety of uses".Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. Examples for such land use changes are converting fields to urban areas or clearing forests. Such changes can affect the ability of soils to soak up surface water. Deforestation can also "directly reduce soil moisture, evaporation and rainfall locally but can also cause regional temperature changes that affect rainfall patterns". Aquifer drawdown or
overdrafting
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. Groundwater depletion is comparable to a bank account in which mor ...
and the pumping of fossil water increases the total amount of water in the hydrosphere because water that was "previously in the ground is now in direct contact with the atmosphere, being available for evaporation".
Related processes
Biogeochemical cycling
While the water cycle is itself a biogeochemical cycle, flow of water over and beneath the Earth is a key component of the cycling of other biogeochemicals. Runoff is responsible for almost all of the transport oferoded
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is disti ...
sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sa ...
and phosphorus from land to waterbodies. The salinity of the oceans is derived from erosion and transport of dissolved salts from the land. Cultural eutrophication of lakes is primarily due to phosphorus, applied in excess to agricultural fields in fertilizers, and then transported overland and down rivers. Both runoff and groundwater flow play significant roles in transporting nitrogen from the land to waterbodies. The dead zone at the outlet of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
is a consequence of nitrates from fertilizer being carried off agricultural fields and funnelled down the river system
In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by har ...
to the Gulf of Mexico. Runoff also plays a part in the carbon cycle, again through the transport of eroded rock and soil.
Slow loss over geologic time
The hydrodynamic wind within the upper portion of a planet's atmosphere allows light chemical elements such asHydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
to move up to the exobase
The thermopause is the atmospheric boundary of Earth's energy system, located at the top of the thermosphere. The temperature of the thermopause could range from nearly absolute zero to .
Below this, the atmosphere is defined to be active on the i ...
, the lower limit of the exosphere, where the gases can then reach escape velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for a free, non- propelled object to escape from the gravitational influence of a primary body, thus reaching an infinite distance from it. It is typically ...
, entering outer space without impacting other particles of gas. This type of gas loss from a planet into space is known as planetary wind
Atmospheric escape is the loss of planetary atmospheric gases to outer space. A number of different mechanisms can be responsible for atmospheric escape; these processes can be divided into thermal escape, non-thermal (or suprathermal) escape, and ...
. Planets with hot lower atmospheres could result in humid upper atmospheres that accelerate the loss of hydrogen.
Historical interpretations
Floating land mass
In ancient times, it was widely thought that the land mass floated on a body of water, and that most of the water in rivers has its origin under the earth. Examples of this belief can be found in the works of Homer (circa 800 BCE).Hebrew Bible
In the ancient Near East, Hebrew scholars observed that even though the rivers ran into the sea, the sea never became full. Some scholars conclude that the water cycle was described completely during this time in this passage: "The wind goeth toward the south, and turneth about unto the north; it whirleth about continually, and the wind returneth again according to its circuits. All the rivers run into the sea, yet the sea is not full; unto the place from whence the rivers come, thither they return again"Ecclesiastes 1:6-7
. Scholars are not in agreement as to the date of Ecclesiastes, though most scholars point to a date during the time of King Solomon, son of David and Bathsheba, "three thousand years ago, there is some agreement that the time period is 962–922 BCE. Furthermore, it was also observed that when the clouds were full, they emptied rain on the earth
Ecclesiastes 11:3
. In addition, during 793–740 BCE a Hebrew prophet, Amos, stated that water comes from the sea and is poured out on the earth
Amos 5:8
. In the Biblical Book of Job, dated between 7th and 2nd centuries BCE, there is a description of precipitation in the hydrologic cycle, "For he maketh small the drops of water: they pour down rain according to the vapour thereof; which the clouds do drop and distil upon man abundantly"
Job 36:27-28
.
Understanding of precipitation and percolation
In the Adityahridayam (a devotional hymn to the Sun God) ofRamayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
, a Hindu epic dated to the 4th century BCE, it is mentioned in the 22nd verse that the Sun heats up water and sends it down as rain. By roughly 500 BCE, Greek scholars were speculating that much of the water in rivers can be attributed to rain. The origin of rain was also known by then. These scholars maintained the belief, however, that water rising up through the earth contributed a great deal to rivers. Examples of this thinking included Anaximander (570 BCE) (who also speculated about the evolution of land animals from fish) and Xenophanes of Colophon
Xenophanes of Colophon (; grc, Ξενοφάνης ὁ Κολοφώνιος ; c. 570 – c. 478 BC) was a Greek philosopher, theologian, poet, and critic of Homer from Ionia who travelled throughout the Greek-speaking world in early Classical An ...
(530 BCE). Chinese scholars such as Chi Ni Tzu (320 BCE) and Lu Shih Ch'un Ch'iu (239 BCE) had similar thoughts.
The idea that the water cycle is a closed cycle can be found in the works of Anaxagoras of Clazomenae (460 BCE) and Diogenes of Apollonia (460 BCE). Both Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
(390 BCE) and Aristotle (350 BCE) speculated about percolation as part of the water cycle. Aristotle correctly hypothesized that the sun played a role in the Earth's hydraulic cycle in his book '' Meteorology,'' writing "By it he sun'sagency the finest and sweetest water is everyday carried up and is dissolved into vapor and rises to the upper regions, where it is condensed again by the cold and so returns to the earth.", and believed that clouds were composed of cooled and condensed water vapor.
Up to the time of the Renaissance, it was wrongly assumed that precipitation alone was insufficient to feed rivers, for a complete water cycle, and that underground water pushing upwards from the oceans were the main contributors to river water. Bartholomew of England held this view (1240 CE), as did Leonardo da Vinci (1500 CE) and Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fe ...
(1644 CE).
Discovery of the correct theory
The first published thinker to assert that rainfall alone was sufficient for the maintenance of rivers wasBernard Palissy
Bernard Palissy (c. 1510c. 1589) was a French Huguenot potter, hydraulics engineer and craftsman, famous for having struggled for sixteen years to imitate Chinese porcelain. He is best known for his so-called "rusticware", typically highly decor ...
(1580 CE), who is often credited as the "discoverer" of the modern theory of the water cycle. Palissy's theories were not tested scientifically until 1674, in a study commonly attributed to Pierre Perrault
Pierre Perrault (29 June 1927 – 24 June 1999) was a Québécois documentary film director. He directed 20 films between 1963 and 1996. He was one of the most important filmmakers in Canada, although largely unknown outside of Québec. In ...
. Even then, these beliefs were not accepted in mainstream science until the early nineteenth century.
See also
* * * * * * * *References
External links
The Water Cycle
United States Geological Survey
United States Geological Survey
The Water Cycle: Following The Water
(NASA Visualization Explorer with videos) {{DEFAULTSORT:Water Cycle Biogeochemical cycle Forms of water Hydrology Soil physics Water Articles containing video clips Limnology Oceanography