volcano tectonic earthquake on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A volcano tectonic earthquake is caused by the movement of
 One possible scenario resulting in a possible volcano tectonic earthquake is tectonic subduction zones. The compression of plates at these subduction zones forces the magma beneath them to move. Magma can not move through the newly compressed crust in as easily a manner. This means it tends to pool in
One possible scenario resulting in a possible volcano tectonic earthquake is tectonic subduction zones. The compression of plates at these subduction zones forces the magma beneath them to move. Magma can not move through the newly compressed crust in as easily a manner. This means it tends to pool in
 Volcano tectonic
Volcano tectonic
magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ...
beneath the surface of the Earth. The movement results in pressure changes where the rock around the magma has experienced stress. At some point, this stress can cause the rock to break or move. This seismic activity
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
is used by scientists to monitor volcanoes. The earthquakes may also be related to dike intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
or occur as earthquake swarm
In seismology, an earthquake swarm is a sequence of seismic events occurring in a local area within a relatively short period. The time span used to define a swarm varies, but may be days, months, or years. Such an energy release is different f ...
s.
Cause of volcano tectonic earthquakes
 One possible scenario resulting in a possible volcano tectonic earthquake is tectonic subduction zones. The compression of plates at these subduction zones forces the magma beneath them to move. Magma can not move through the newly compressed crust in as easily a manner. This means it tends to pool in
One possible scenario resulting in a possible volcano tectonic earthquake is tectonic subduction zones. The compression of plates at these subduction zones forces the magma beneath them to move. Magma can not move through the newly compressed crust in as easily a manner. This means it tends to pool in magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it up ...
s beneath the surface and between the converging tectonic plates. Many of the famous and most well known volcanoes fall on this line, including the Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring ...
. As the plates move, magma underground may be forced in and out of these chambers. This movement is capable of causing the unstable earth around it to cave in or shift. The movement of this magma as described causes measurable seismic activity. This is separate from earthquakes directly related to faults.
Scientists monitoring volcanoes have noticed that magma movement may lead to earthquake swarms depending on the movement of magma and the interaction with rock beneath the ground. Additionally, the volatility of volcanoes and the accompanying earthquakes has been shown to be linked to dike induced stress and the interaction this causes between the magma, rock, and wall of the chamber.
Importance
 Volcano tectonic
Volcano tectonic seismicity
Seismicity is a measure encompassing earthquake occurrences, mechanisms, and magnitude at a given geographical location. As such, it summarizes a region's seismic activity. The term was coined by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter in ...
is an important tool in being able to predict the eruptions of volcanoes. Seismic activity occurs as a precursor to most large eruptions. We can use tectonic events to predict eruptions in long-dormant volcanoes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
. Some notable examples of eruptions preceded by volcano tectonic earthquakes include ones at Nevado del Ruiz (1985), Pinatubo (1991), Unzen (1990), and Cotopaxi (2002). Quakes with volcano-tectonic characteristics accompany magmatic intrusions in near real time.
Use in monitoring volcanoes
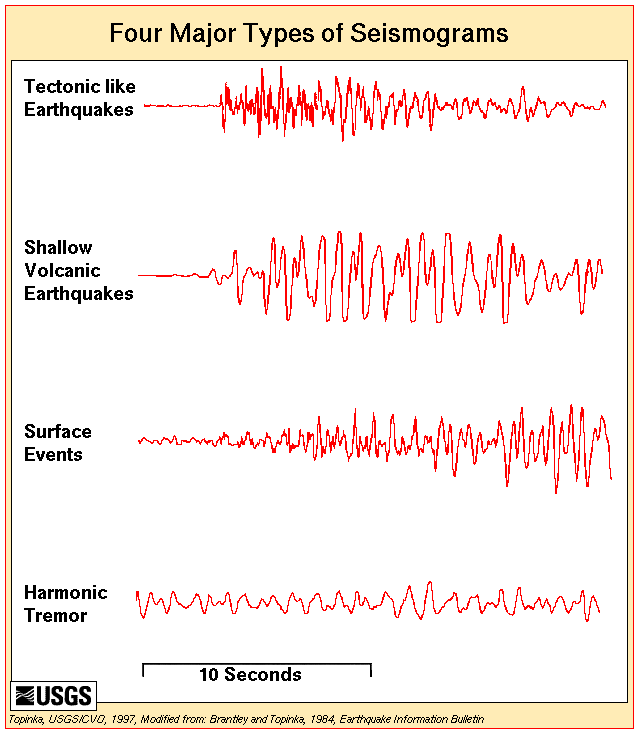
Nearly every recorded volcanic eruption has been preceded by some form of earthquake activity beneath or near the volcano. Due to the relation between magma movement, earthquakes, and possible eruptions, approximately 200 of the world's volcanoes are seismically monitored. The recording of several years of background seismic data has allowed for classification of volcanic earthquakes. These earthquakes tend to occur in swarms as opposed to mainshock–aftershock sequences, have smaller maximum sizes than tectonic structure earthquakes, have similar waveform patterns, increase in number before eruptions, and occur near or beneath the site of the eruption. Other types of seismic activity monitored in relation tovolcanoes
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
and their eruptions are long period seismic wave
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic ener ...
s, which are caused by sudden sporadic movement of magma that had previously not been moving due to a blockage, and harmonic tremor, which indicates steady magma movement deep in the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Volcano Tectonic Earthquake Volcanism Seismology