Visual Angle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's
Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's
The representation of perceived angular size in human primary visual cortex.
''Nature Neuroscience, 9,'' 429–434 (1 March 2006). * McCready, D
The Moon Illusion Explained
for the display of letters or symbols for a specified Snellen line on your computer monitor at exactly the right size (note: you must follow the instructions for calibration). {{DEFAULTSORT:Visual Angle Vision Angle
 Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's
Visual angle is the angle a viewed object subtends at the eye, usually stated in degrees of arc.
It also is called the object's angular size
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it ...
.
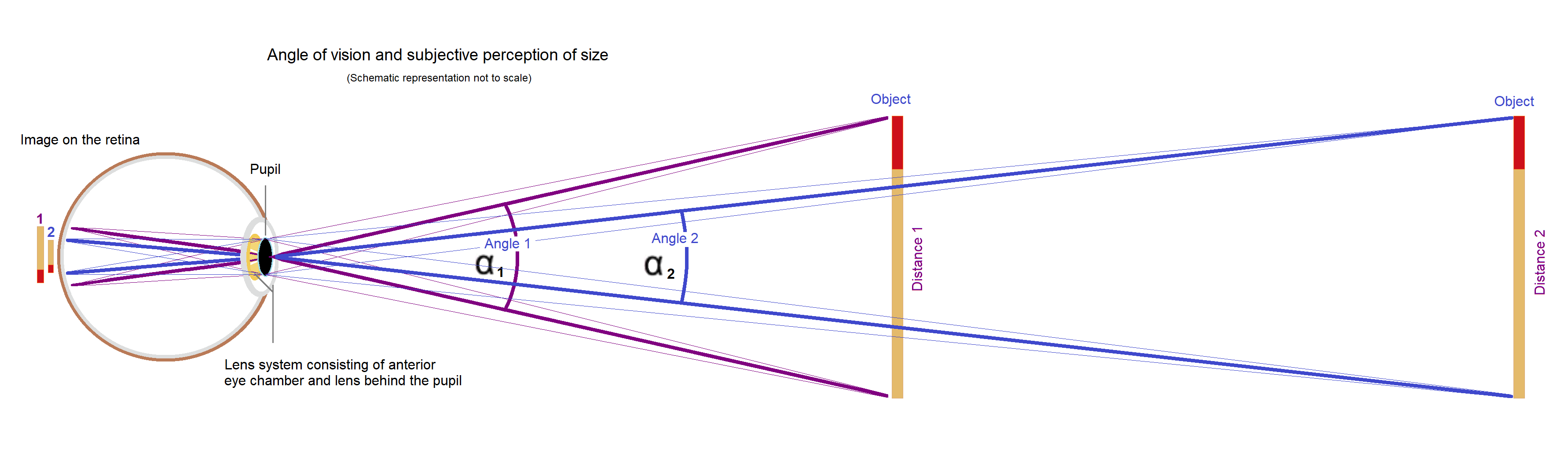
The diagram on the right shows an observer's eye looking at a frontal extent (the vertical arrow) that has a linear size , located in the distance from point .
For present purposes, point can represent the eye's nodal point
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the '' focal points'', the principal points, and the nodal points. For ''ideal'' ...
s at about the center of the lens, and also represent the center of the eye's entrance pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the front (the object side) of the lens system. The corresponding image of the aperture as seen through the back of the lens system ...
that is only a few millimeters in front of the lens.
The three lines from object endpoint heading toward the eye indicate the bundle of light rays that pass through the cornea, pupil and lens to form an optical image of endpoint on the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which the ...
at point .
The central line of the bundle represents the chief ray
In optics a ray is an idealized geometrical model of light, obtained by choosing a curve that is perpendicular to the ''wavefronts'' of the actual light, and that points in the direction of energy flow. Rays are used to model the propagation o ...
.
The same holds for object point and its retinal image at .
The visual angle is the angle between the chief rays of and .
Measuring and computing
The visual angle can be measured directly using atheodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building and ...
placed at point .
Or, it can be calculated (in radians) using the formula, .
However, for visual angles smaller than about 10 degrees, this simpler formula provides very close approximations:
:
The retinal image and visual angle
As the above sketch shows, areal image
{{citations needed, date=June 2019
In optics, an ''image'' is defined as the collection of focus points of light rays coming from an object. A real image is the collection of focus points actually made by converging/diverging rays, while a ...
of the object is formed on the retina between points and . (See visual system
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (th ...
). For small angles, the size of this retinal image is
:
where is the distance from the nodal points to the retina, about 17 mm.
Examples
If one looks at a one-centimeter object at a distance of one meter and a two-centimeter object at a distance of two meters, both subtend the same visual angle of about 0.01 rad or 0.57°. Thus they have the same retinal image size . That is just a bit larger than the retinal image size for the moon, which is about , because, with moon's mean diameter , and earth to moon mean distance averaging (), . Also, for some easy observations, if one holds one's index finger at arm's length, the width of the index fingernail subtends approximately one degree, and the width of the thumb at the first joint subtends approximately two degrees. Therefore, if one is interested in the performance of the eye or the first processing steps in thevisual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
, it does not make sense to refer to the absolute size of a viewed object (its linear size ). What matters is the visual angle which determines the size of the retinal image.
Terminological confusions
In astronomy the term ''apparent size'' refers to the physical angle orangular diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it ...
.
But in psychophysics
Psychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, ...
and experimental psychology
Experimental psychology refers to work done by those who apply experimental methods to psychological study and the underlying processes. Experimental psychologists employ human participants and animal subjects to study a great many topics, in ...
the adjective "apparent" refers to a person's subjective experience.
So, "apparent size" has referred to how large an object looks, also often called its "perceived size".
Additional confusion has occurred because there are two qualitatively different "size" experiences for a viewed object. One is the perceived visual angle (or apparent visual angle) which is the subjective correlate of , also called the object's perceived or apparent angular size.
The perceived visual angle is best defined as the difference between the perceived directions of the object's endpoints from oneself.
The other "size" experience is the object's perceived linear size (or apparent linear size) which is the subjective correlate of , the object's physical width or height or diameter.
Widespread use of the ambiguous terms "apparent size" and "perceived size" without specifying the units of measure has caused confusion.
Representation of visual angle in visual cortex
The brain'sprimary visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and ...
(area V1 or Brodmann area 17) contains a spatially isomorphic
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word i ...
representation of the retina (see retinotopy
Retinotopy (from Greek τόπος, place) is the mapping of visual input from the retina to neurons, particularly those neurons within the visual stream. For clarity, 'retinotopy' can be replaced with 'retinal mapping', and 'retinotopic' with 'r ...
). Loosely speaking, it is a distorted "map" of the retina. Accordingly, the size of a given retinal image determines the extent of the neural activity pattern eventually generated in area V1 by the associated retinal activity pattern. Murray, Boyaci, & Kersten (2006) recently used Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
(fMRI) to show that an increase in a viewed target's visual angle, which increases , also increases the extent of the corresponding neural activity pattern in area V1.
The observers in experiment carried out by Murray and colleagues viewed a flat picture with two discs that subtended the same visual angle and formed retinal images of the same size , but the perceived angular size of one was about 17% larger than for the other, due to differences in the background patterns for the disks. It was shown that the areas of the activity in V1 related to the disks were of unequal size, despite the fact that the retinal images were the same size. This size difference in area V1 correlated with the 17% illusory difference between the perceived visual angles. This finding has implications for spatial illusions such as the visual angle illusion.
See also
*Visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
* Visual angle illusion
Notes
References
* Baird, J. C. (1970). ''Psychophysical analysis of visual space.'' Oxford, London: Pergamon Press. * Joynson, R. B. (1949). The problem of size and distance. ''Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 1'', 119–135. * McCready, D. (1965). Size-distance perception and accommodation-convergence micropsia: A critique. ''Vision Research. 5,'' 189–206. * McCready, D. (1985). On size, distance and visual angle perception. ''Perception & Psychophysics, 37'', 323–334. * Murray, S.O., Boyaci, H, & Kersten, D. (2006The representation of perceived angular size in human primary visual cortex.
''Nature Neuroscience, 9,'' 429–434 (1 March 2006). * McCready, D
The Moon Illusion Explained
External links
for the display of letters or symbols for a specified Snellen line on your computer monitor at exactly the right size (note: you must follow the instructions for calibration). {{DEFAULTSORT:Visual Angle Vision Angle