vertebral artery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The vertebral arteries are major
 The vertebral artery may be divided into four parts:
* The first (preforaminal) part runs upward and backward between the anterior scalene and the longus colli muscles. In front of it are the internal jugular and
The vertebral artery may be divided into four parts:
* The first (preforaminal) part runs upward and backward between the anterior scalene and the longus colli muscles. In front of it are the internal jugular and  The fourth (intradural or intracranial) part pierces the dura mater and inclines medially to the front of the
The fourth (intradural or intracranial) part pierces the dura mater and inclines medially to the front of the
arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and posterior part of brain.
Structure
The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6thcervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
(C6), or occasionally (in 7.5% of cases) at the level of C7. They then proceed superiorly, in the transverse foramen of each cervical vertebra. Once they have passed through the transverse foramen of C1 (also known as the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
), the vertebral arteries travel across the posterior arch of C1 and through the suboccipital triangle before entering the foramen magnum.
Nunziante Ippolito, a Neapolitan physician, identified the "angle of Nunziante Ippolito" to find the vertebral artery, between the anterior scalene muscle and the longus colli muscle.
Inside the skull, the two vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery at the base of the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
. The basilar artery is the main blood supply to the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
and connects to the Circle of Willis
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies blood to the brain and surrounding structures in reptiles, birds and mammals, including huma ...
to potentially supply the rest of the brain if there is compromise to one of the carotids. At each cervical level, the vertebral artery sends branches to the surrounding musculature via the anterior spinal arteries.
 The vertebral artery may be divided into four parts:
* The first (preforaminal) part runs upward and backward between the anterior scalene and the longus colli muscles. In front of it are the internal jugular and
The vertebral artery may be divided into four parts:
* The first (preforaminal) part runs upward and backward between the anterior scalene and the longus colli muscles. In front of it are the internal jugular and vertebral vein
The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the atlas.
They unite with small ...
s, and is crossed by the inferior thyroid artery; the left vertebral is also crossed by the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymph ...
. Behind it are the transverse process of the seventh cervical vertebra, the sympathetic trunk and its inferior cervical ganglion
* The second (foraminal) part runs upward through the transverse foramina of the C6 to C2 vertebrae, and is surrounded by branches from the inferior cervical sympathetic ganglion and by a plexus of veins which unite to form the vertebral vein at the lower part of the neck. It is situated in front of the trunks of the cervical nerves, and pursues an almost vertical course as far as the transverse process of the axis.
* The third (extradural or atlantic) part issues from the C2 foramen transversarium on the medial side of the Rectus capitis lateralis. It is further subdivided into the vertical part V3v passing vertically upwards, crossing the C2 root and entering the foramen transversarium of C1, and the horizontal part V3h, curving medially and posteriorly behind the superior articular process of the atlas, the anterior ramus of the first cervical nerve being on its medial side; it then lies in the groove on the upper surface of the posterior arch of the atlas, and enters the vertebral canal by passing beneath the posterior atlantoöccipital membrane. This part of the artery is covered by the Semispinalis capitis and is contained in the suboccipital triangle—a triangular space bounded by the Rectus capitis posterior major, the Obliquus superior, and the Obliquus inferior. The first cervical or suboccipital nerve lies between the artery and the posterior arch of the atlas.
*  The fourth (intradural or intracranial) part pierces the dura mater and inclines medially to the front of the
The fourth (intradural or intracranial) part pierces the dura mater and inclines medially to the front of the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
; it is placed between the hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated b ...
and the anterior root of the first cervical nerve and beneath the first digitation of the ligamentum denticulatum. At the lower border of the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
, it unites with the vessel of the opposite side to form the basilar artery.
Triangle
Triangle of the vertebral artery is a region within the root of the neck and has following boundaries: * Medial border of anterior scalene muscle (lateral) * Lateral border of longus colli muscle (medial) * Carotid tubercle (apex) * First part of subclavian artery (base) The vertebral artery runs from base to apex (prior to entering the transverse foramen of 6th cervical vertebra). The carotid tubercle separates the vertebral artery which passes directly behind it from the common carotid artery which lies directly in front of it. The ideal site for palpating the carotid pulse is to gently press thecommon carotid artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, inte ...
against the carotid tubercle.
Variation
There is commonly variations in the course and size of the vertebral arteries, usually on both sides artery diameters are asymmetrical. For example, differences in size between left and right vertebral arteries may range from a slight asymmetry to markedhypoplasia
Hypoplasia (; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ.arcuate foramen covers the groove for the vertebral artery on vertebra C1. Rarely, the vertebral arteries enter the subarachnoid space at C1-C2 (3%) or C2-C3 (only three cases have been reported) vertebral levels instead of the atlanto-occipital level.
The portion of vertebral arteries located within the skull (intracranial) have diameters of 3.17 mm. The intracranial length for the left vertebral artery (32.4 mm) is longer than the right (31.5 mm). The angle where vertebral arteries meet the basilar artery (vertebrobasilar junction), is 46 degrees.
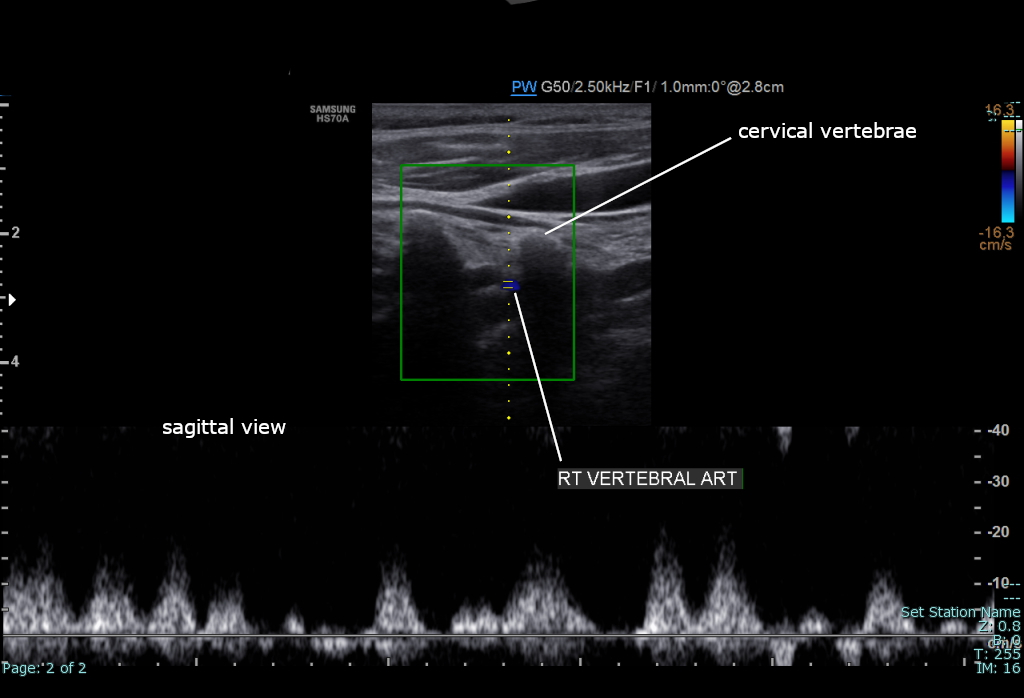 The condition and health of the vertebral carotid arteries is usually evaluated using Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography or phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI).
Typically, blood flow velocities in the carotid artery are measured in terms of peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV).
Normally, vertebral artery blood flow velocity can be 63.6 ± 17.5 cm/s during PSV and 16.1 ± 5.1 cm/s during EDV according to a study done by Kuhl et al. Due to vertebral artery dominance, measurements can vary on both sides, for example, another study by Seidel et al. found that the right side had an average of 45.9 cm/s and the left side 51.5 cm/s during PSV, and 13.8 cm/s on the right side and 16.1 cm/s on the left side during EDV.
The condition and health of the vertebral carotid arteries is usually evaluated using Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography or phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI).
Typically, blood flow velocities in the carotid artery are measured in terms of peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV).
Normally, vertebral artery blood flow velocity can be 63.6 ± 17.5 cm/s during PSV and 16.1 ± 5.1 cm/s during EDV according to a study done by Kuhl et al. Due to vertebral artery dominance, measurements can vary on both sides, for example, another study by Seidel et al. found that the right side had an average of 45.9 cm/s and the left side 51.5 cm/s during PSV, and 13.8 cm/s on the right side and 16.1 cm/s on the left side during EDV.
File:Sobo 1909 3 548.png, The arteries of the base of the brain (inferior view).
File:Circle of Willis en.svg, Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain.
File:Suboccipital triangle dissection.jpg, Relationship of the vertebral artery to the suboccipital muscles.
Vertebral Artery , neuroangio.org
* * * () * * {{Authority control Arteries of the head and neck
Vertebral artery dominance
Vertebral artery dominance (VAD) is typically a normal congenital vascular variation of the vertebral arteries. It refers to the asymmetry of the VA diameters on both sides, with the larger diameter being the dominant side and the smaller diameter being the nondominant side. In one study, the left vertebral artery diameter dominance was present in 54% of cases, while the right diameter was dominant in 30%. In 16% of cases, the left and right arterial diameters were equal.Function
As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upperspinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and posterior part of brain.
Clinical significance
As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upperspinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is conti ...
, cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or eve ...
, and posterior part of brain. A stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
of the arteries may result in a posterior circulation stroke.
Chiropractic
Chiropractic () is a form of alternative medicine concerned with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mechanical disorders of the musculoskeletal system, especially of the spine. It is based on several pseudoscientific ideas.
Many c ...
manipulation of the neck has the potential to cause a vertebral arterial dissection.
Diagnostics
 The condition and health of the vertebral carotid arteries is usually evaluated using Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography or phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI).
Typically, blood flow velocities in the carotid artery are measured in terms of peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV).
Normally, vertebral artery blood flow velocity can be 63.6 ± 17.5 cm/s during PSV and 16.1 ± 5.1 cm/s during EDV according to a study done by Kuhl et al. Due to vertebral artery dominance, measurements can vary on both sides, for example, another study by Seidel et al. found that the right side had an average of 45.9 cm/s and the left side 51.5 cm/s during PSV, and 13.8 cm/s on the right side and 16.1 cm/s on the left side during EDV.
The condition and health of the vertebral carotid arteries is usually evaluated using Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography or phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI).
Typically, blood flow velocities in the carotid artery are measured in terms of peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV).
Normally, vertebral artery blood flow velocity can be 63.6 ± 17.5 cm/s during PSV and 16.1 ± 5.1 cm/s during EDV according to a study done by Kuhl et al. Due to vertebral artery dominance, measurements can vary on both sides, for example, another study by Seidel et al. found that the right side had an average of 45.9 cm/s and the left side 51.5 cm/s during PSV, and 13.8 cm/s on the right side and 16.1 cm/s on the left side during EDV.
Additional images
References
External links
*Vertebral Artery , neuroangio.org
* * * () * * {{Authority control Arteries of the head and neck