vector meson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
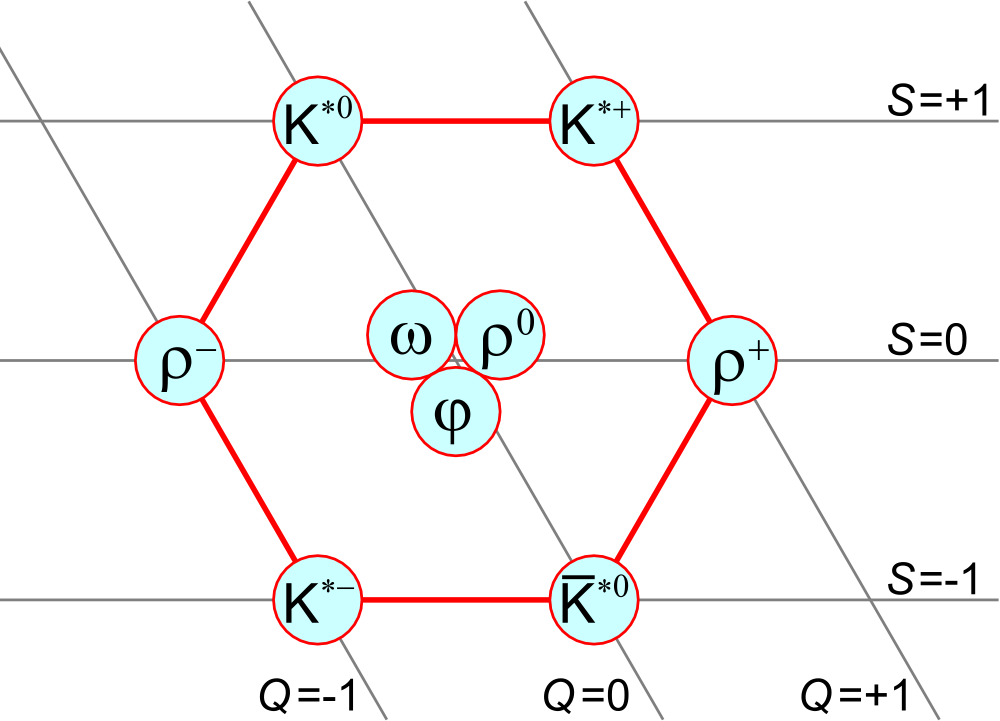 In
In
 In
In high energy physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standa ...
, a vector meson is a meson
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, ...
with total spin 1 and odd parity
Parity may refer to:
* Parity (computing)
** Parity bit in computing, sets the parity of data for the purpose of error detection
** Parity flag in computing, indicates if the number of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the ...
(usually noted as ). Vector mesons have been seen in experiments since the 1960s, and are well known for their spectroscopic
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
pattern of masses.
The vector mesons contrast with the pseudovector meson
In high energy physics, a pseudovector meson or axial vector meson is a meson with total spin 1 and even parity (+) (usually noted as
:Compare to a vector meson, which has a total spin 1 and odd parity
Charge parity (C) in addition ...
s, which also have a total spin 1 but instead have even parity. The vector and pseudovector mesons are also dissimilar in that the spectroscopy of vector mesons tends to show nearly pure states of constituent quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly ...
flavors
Flavor or flavour is either the sensory perception of taste or smell, or a flavoring in food that produces such perception.
Flavor or flavour may also refer to:
Science
*Flavors (programming language), an early object-oriented extension to Li ...
, whereas pseudovector mesons and scalar mesons tend to be expressed as composites of mixed states.
Uniquely pure flavor states
Since the development of thequark model
In particle physics, the quark model is a classification scheme for hadrons in terms of their valence quarks—the quarks and antiquarks which give rise to the quantum numbers of the hadrons. The quark model underlies "flavor SU(3)", or the Ei ...
by Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann (; September 15, 1929 – May 24, 2019) was an American physicist who received the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles. He was the Robert Andrews Millikan Professor of Theoretical ...
(and also independently by George Zweig
George Zweig (; born May 30, 1937) is a Russian-American physicist. He was trained as a particle physicist under Richard Feynman. He introduced, independently of Murray Gell-Mann, the quark model (although he named it "aces"). He later turned his ...
), the vector mesons have demonstrated the spectroscopy of pure states. The fact that the rho meson
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the sa ...
(ρ) and omega meson
The omega meson () is a flavourless meson formed from a superposition of an up quark–antiquark and a down quark–antiquark pair. It is part of the vector meson nonet and mediates the nuclear force along with pions and rho mesons.
Propert ...
(ω) have nearly equal mass centered on 770–, while the phi meson
In particle physics, the phi meson or meson is a vector meson formed of a strange quark and a strange antiquark. It was the meson's unusual propensity to decay into and that led to the discovery of the OZI rule. It has a mass of and a mea ...
(φ) has a higher mass around , indicates that the light-quark vector mesons appear in nearly pure states, with the φ meson having a nearly 100 percent amplitude of hidden strangeness
In particle physics, strangeness ("''S''") is a property of particles, expressed as a quantum number, for describing decay of particles in strong and electromagnetic interactions which occur in a short period of time. The strangeness of a parti ...
.
These nearly pure states characteristic of the vector mesons are not at all evident in the pseudoscalar meson
In high-energy physics, a pseudoscalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and odd parity (usually notated as
Pseudoscalar mesons are commonly seen in proton-proton scattering and proton-antiproton annihilation, and include the pion (), ...
or scalar meson multiplets
In physics and particularly in particle physics, a multiplet is the state space for 'internal' degrees of freedom of a particle, that is, degrees of freedom associated to a particle itself, as opposed to 'external' degrees of freedom such as the ...
, and may be only slightly realized among the tensor meson and pseudovector meson multiplets. This fact makes the vector mesons an excellent probe of the quark flavor content of other types of mesons, measured through the respective decay rate
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
s of non-vector mesons into the different types of vector mesons. Such experiments are very revealing for theorists who seek to determine the flavor content of mixed state mesons.
Backbone of meson spectroscopy
At higher masses, the vector mesons includecharm
Charm may refer to:
Social science
* Charisma, a person or thing's pronounced ability to attract others
* Superficial charm, flattery, telling people what they want to hear
Science and technology
* Charm quark, a type of elementary particle
* Ch ...
and bottom quark
The bottom quark or b quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation heavy quark with a charge of − ''e''.
All quarks are described in a similar way by electroweak and quantum chromodynamics, but the bottom quark has exce ...
s in their structure. In this realm, the radiative processes tend to stand out, with heavy tensor and scalar mesons decaying dominantly into vector mesons by photon emission. Pseudovector mesons transition by a similar process into pseudoscalar mesons. Because much of the spectrum of heavy mesons is tied by radiative processes to the vector mesons, one may think of vector mesons as forming a sort of backbone to the spectroscopy of mesons in general.
Some vector mesons can, compared to other mesons, be measured to a very high precision. This stems from the fact that they have the same quantum numbers as the photon, , where ''J'' = angular momentum quantum number
The azimuthal quantum number is a quantum number for an atomic orbital that determines its orbital angular momentum and describes the shape of the orbital. The azimuthal quantum number is the second of a set of quantum numbers that describe th ...
, ''P'' = parity
Parity may refer to:
* Parity (computing)
** Parity bit in computing, sets the parity of data for the purpose of error detection
** Parity flag in computing, indicates if the number of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the ...
, ''C'' = C parity
In physics, the C parity or charge parity is a multiplicative quantum number of some particles that describes their behavior under the symmetry operation of charge conjugation.
Charge conjugation changes the sign of all quantum charges (that is, ...
. Therefore they appear in electron-positron collisions in the process , which provides experimentally a clear signal compared to other measurements, which have to use hadronic processes. Vector mesons play a huge role in the study of the strong hadronic force.
List of vector mesons
* ρ meson * ω meson * φ meson * K*(892) meson * D* meson * meson * mesonHypothetical
* θ mesonSee also
*List of mesons
:''This list is of all known and predicted scalar, pseudoscalar and vector mesons. See list of particles for a more detailed list of particles found in particle physics.''
This article contains a list of mesons, unstable subatomic particles ...
* Vector meson dominance
* Vector boson
In particle physics, a vector boson is a boson whose spin equals one. The vector bosons that are regarded as elementary particles in the Standard Model are the gauge bosons, the force carriers of fundamental interactions: the photon of electromagne ...
References
Mesons Subatomic particles with spin 1 {{particle-stub