Uncrewed spacecraft on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be
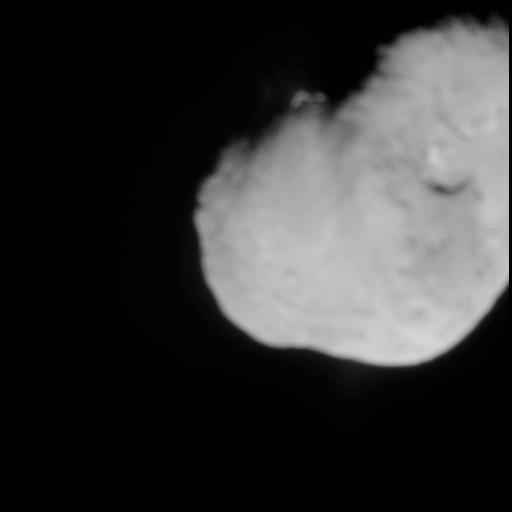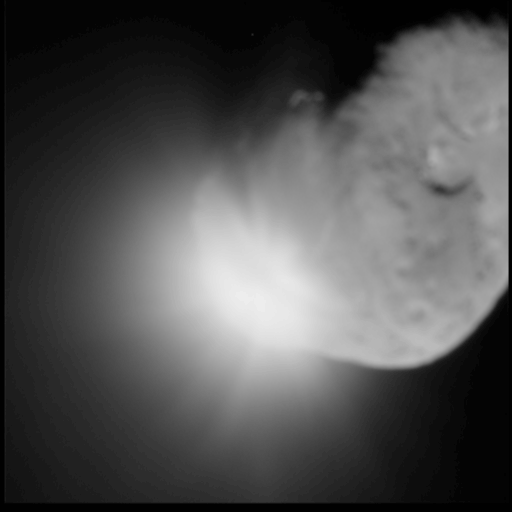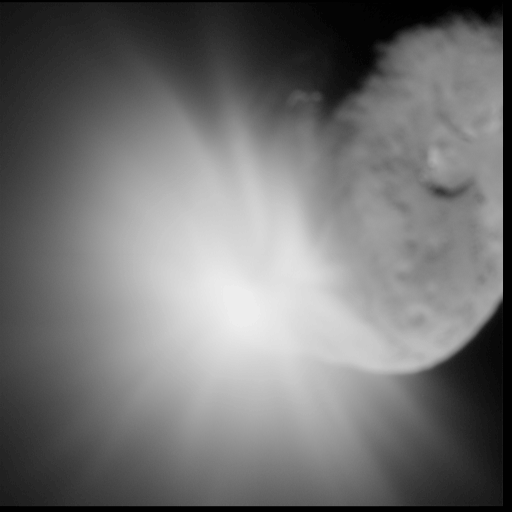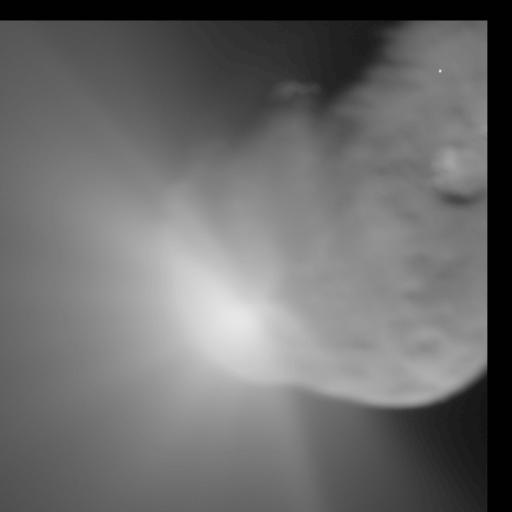 * International Cometary Explorer — passed through gas tail of comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner (1985)
* Giotto — European — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Vega 1 & 2 —
* International Cometary Explorer — passed through gas tail of comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner (1985)
* Giotto — European — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Vega 1 & 2 —
 Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be
Unmanned spacecraft or uncrewed spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board, used for robotic spaceflight. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input; they may be remote controlled
Teleoperation (or remote operation) indicates operation of a system or machine at a distance. It is similar in meaning to the phrase "remote control" but is usually encountered in research, academia and technology. It is most commonly associa ...
, remote guided or even autonomous, meaning they have a pre-programmed list of operations, which they will execute unless otherwise instructed.
Many habitable spacecraft also have varying levels of robotic features. For example, the space stations Salyut 7 and Mir, and the International Space Station module Zarya Zarya may refer to:
*Zorya, personification of dawn in Slavic mythology
* Zarya (antenna), a type of medium-wave broadcasting antenna used in former Soviet Union
*Zarya (ISS module) is a module of the International Space Station.
* ''Zarya'' (magazi ...
, were capable of remote guided station-keeping and docking maneuvers with both resupply craft and new modules. The most common uncrewed spacecraft categories are robotic spacecraft, unmanned resupply spacecraft, space probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; o ...
Examples
Selected lunar probes
* Luna program — USSR Lunar exploration (1959–1976) * Ranger program — US Lunar hard-landing probes (1961–1965) * Zond program — USSR Lunar exploration (1964–1970) * Surveyor program — US Lunar soft-landing probe (1966–1968) * Lunar Orbiter program — US Lunar orbital (1966–1967) * Lunokhod program — USSR Lunar Rover probes (1970–1973) * MUSES-A ('' Hiten'' and '' Hagoromo'') — Japanese Lunar orbital and hard-landing probes (1990–1993) * '' Clementine'' — US Lunar orbital (1998) * '' Lunar Prospector'' — US Lunar orbital (1998–1999) * ''Smart 1
The Smart #1 (stylised as "smart #1") is a battery electric subcompact crossover SUV developed and produced by Smart Automobile, a joint venture between Mercedes-Benz Group and Geely Holding. It is the first vehicle produced by the joint ve ...
'' — European Lunar orbital (2003)
* '' SELENE'' — Japanese lunar orbiter (2007)
* '' Chang'e 1'' — Chinese lunar orbiter (2007)
* ''Chandrayaan 1
Chandrayaan-1 (, ) was the first Indian lunar probe under the Chandrayaan program. It was launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008, and operated until August 2009. The mission included a lunar orbiter and an impact ...
'' — Indian lunar orbiter (2008)
* '' Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter'' — US Lunar orbiter (2009)
* '' LCROSS'' — US Lunar hard-landing probe (2009)
* '' Chang'e 2'' — Chinese Lunar orbiter (2010)
* '' Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory'' — US Lunar orbiters (2011)
Mars probes
* Zond program — failed USSR flyby probe * Mars probe program — USSR orbiters and landers * Viking program — twoNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
orbiters and landers (1974)
* Phobos program — failed USSR orbiters and Phobos landers
* '' Mars Pathfinder'' — NASA lander and rover (1997)
* Mars Surveyor '98 program ('' Mars Climate Orbiter'' and '' Mars Polar Lander'') — failed NASA probes
* Mars Global Surveyor — NASA orbiter
* Mars Odyssey — NASA orbiter, reached Mars on October 24, 2001
* Mars Observer — failed NASA Mars orbiter
* Mars Express ('' Mars Express Orbiter'' and ''Beagle 2
The ''Beagle 2'' is an inoperative British Mars lander that was transported by the European Space Agency's 2003 ''Mars Express'' mission. It was intended to conduct an astrobiology mission that would have looked for evidence of past life on Mar ...
'') — European orbiter and failed lander 2003
* Mars Exploration Rovers — NASA rovers (2004)
* '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' — NASA orbiter, entered Martian orbit March 10, 2006
* '' Phoenix'' — NASA lander, landed May 25, 2008
* '' Mars Science Laboratory'' — NASA rover, launched November 26, 2011
* '' Mars Orbiter Mission '' — Indian orbiter launched by ISRO on 5 November, 2013
* '' Mars 2020'' — NASA rover and helicopter, launched July 30, 2020
Venus probes
* Venera program — USSR Venus orbiter and lander (1961–1984) * Pioneer Venus project — US Venus orbiter and entry probes(1978) * Vega program — USSR mission to Venus andComet Halley
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the on ...
(1984)
* Magellan probe
The ''Magellan'' spacecraft was a robotic space probe launched by NASA of the United States, on May 4, 1989, to map the surface of Venus by using synthetic-aperture radar and to measure the planetary gravitational field.
The ''Magellan' ...
— US Venus orbiter (1989)
* Venus Express — ESA probe sent for the observation of the Venus's weather (2005)
Gas giant probes
* Pioneer program — USJupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
and Saturn flybys
* Voyager program — US Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune flyby and study of interstellar medium
* Galileo probe
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It ...
— US Jupiter orbiter and atmosphere probe (ended 2003)
* '' Cassini-Huygens'' — US-European Saturn orbiter and Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
lander Huygens (1997–2017)
* Juno — US Jupiter orbiter (2011–present)
Comet and asteroid probes
 * International Cometary Explorer — passed through gas tail of comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner (1985)
* Giotto — European — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Vega 1 & 2 —
* International Cometary Explorer — passed through gas tail of comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner (1985)
* Giotto — European — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Vega 1 & 2 — USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
— flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Sakigake — Japanese — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* Suisei — Japanese — flyby of comet 1P/Halley (1986)
* '' NEAR Shoemaker'' — US — asteroid 433 Eros orbiter, which later landed on the asteroid's surface, launched 1996
* '' Deep Space 1'' — US — comet 19P/Borrelly and asteroid flyby, 1998–2000
* Stardust
Stardust may refer to:
* A type of cosmic dust, composed of particles in space
Entertainment Songs
* “Stardust” (1927 song), by Hoagy Carmichael
* “Stardust” (David Essex song), 1974
* “Stardust” (Lena Meyer-Landrut song), 2012
* ...
— US — comet 81P/Wild flyby and sample return, launched 1999, flew-by 2004, returned January 15, 2006
* '' CONTOUR'' — US — comet flyby mission (comets 2P, 73P and 6P); lost due to solid rocket motor failure shortly after launch in 2002
* '' Hayabusa'' — Japanese — asteroid rendezvous, lander and sample return, launched 2003, returned June 13, 2010
* ''Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The R ...
'' — European — comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko orbiter and lander ( Philae); launched 2004
* Deep Impact — successful US comet 9P/Tempel impactor, launched 2005
* Deep Impact/EPOXI — US — comet 103P/Hartley flyby (extended Deep Impact mission) — 2010
* Stardust/NExT — US — comet 9P/Tempel flyby (extended Stardust mission) — 2011
* ''Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the appearance of indirect sunlight being scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc has reached 18° below the observer's ...
'' — US launched on September 27, 2007 — orbited Vesta in 2011, and currently orbiting Ceres since 2015
Solar observation probes
* Ulysses — solar particles and fields (ended 2009) *Genesis
Genesis may refer to:
Bible
* Book of Genesis, the first book of the biblical scriptures of both Judaism and Christianity, describing the creation of the Earth and of mankind
* Genesis creation narrative, the first several chapters of the Book of ...
— first solar wind sample return mission, 2001–2004 (crash)
* ''Interstellar Boundary Explorer
Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX or Explorer 91 or SMEX-10) is a NASA satellite in Earth orbit that uses energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) to image the interaction region between the Solar System and interstellar space. The mission is par ...
'' (IBEX) — launched October 19, 2008.
* Advanced Composition Explorer — solar particles and fields observation at Earth-Sun point
* STEREO — pair of probes in solar orbits providing 3D observations of Sun
* SOHO
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster, part of the West End of London. Originally a fashionable district for the aristocracy, it has been one of the main entertainment districts in the capital since the 19th century.
The area was deve ...
— Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, observer for Sun's corona and core located at point
Other Solar System probes
* Zond program — USSR flyby missions to the Moon, Venus, and Mars * Mariner program — US Mercury, Venus and Mars flybys * MESSENGER — US Mercury orbiter, launched 2004 * '' New Horizons'' — US launched on January 19, 2006 — first probe to visitPluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
, successful flyby on 14 July 2015
Interstellar or cosmic observation probes
* Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe — 2001–2010; cosmic microwave backgroundTechnology demonstrators
* OREX (Orbital Re-Entry EXperiment) — Japanese atmospheric reentry and heat shield demonstrator (successfully flown in February 1994) * Atmospheric Reentry Demonstrator (ARD) — European atmospheric reentry and heat shield demonstrator (successfully flown in October 1998) * HYFLEX (Hypersonic Flight Experiment) — Japanese uncrewed spaceplane atmospheric reentry demonstrator (successfully flown in February 1996) * Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle (IXV) — European uncrewed spaceplane atmospheric reentry demonstrator (successfully flown in February 2015)Uncrewed resupply spacecraft
See also
* List of uncrewed spacecraft by program * List of passive satellites {{Robotics Uncrewed spacecraft, Space robots