Terahertz Radiation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency
(THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency
(THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of
 Terahertz radiation falls in between
Terahertz radiation falls in between
electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
s within the ITU-designated band of frequencies from 0.3 to 3 terahertz (THz),
although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and is considered by some sources as 30 THz. One terahertz is 1012 Hz or 1000 GHz. Wavelengths of radiation in the terahertz band correspondingly range from 1 mm to 0.1 mm = 100 µm. Because terahertz radiation begins at a wavelength of around 1 millimeter and proceeds into shorter wavelengths, it is sometimes known as the ''submillimeter band'', and its radiation as ''submillimeter waves'', especially in astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. This band of electromagnetic radiation lies within the transition region between microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
and far infrared
Far infrared (FIR) is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Far infrared is often defined as any radiation with a wavelength of 15 micrometers (μm) to 1 mm (corresponding to a range of about 20 THz to ...
, and can be regarded as either.
Terahertz radiation is strongly absorbed by the gases
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
of the atmosphere, and in air is attenuated to zero within a few meters,
so it is not practical for terrestrial radio communication. It can penetrate thin layers of materials but is blocked by thicker objects. THz beams transmitted through materials can be used for material characterization, layer inspection, relief measurement, and as a lower-energy alternative to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s for producing high resolution images of the interior of solid objects.
Terahertz radiation occupies a middle ground where the ranges of microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
s and infrared light
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
waves overlap, known as the “terahertz gap
Terahertz radiation – also known as submillimeter radiation, terahertz waves, tremendously high frequency
(THF), T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux or THz – consists of electromagnetic waves within the ITU-designated band of frequ ...
”; it is called a “gap” because the technology for its generation and manipulation is still in its infancy. The generation and modulation of electromagnetic waves in this frequency range ceases to be possible by the conventional electronic devices used to generate radio waves and microwaves, requiring the development of new devices and techniques.
Description
 Terahertz radiation falls in between
Terahertz radiation falls in between infrared radiation
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
and microwave radiation
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency rang ...
in the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging fro ...
, and it shares some properties with each of these. Terahertz radiation travels in a line of sight
The line of sight, also known as visual axis or sightline (also sight line), is an imaginary line between a viewer/observer/ spectator's eye(s) and a subject of interest, or their relative direction. The subject may be any definable object taken ...
and is non-ionizing. Like microwaves, terahertz radiation can penetrate a wide variety of non-conducting materials; clothing, paper, cardboard
Cardboard is a generic term for heavy paper-based products. The construction can range from a thick paper known as paperboard to corrugated fiberboard which is made of multiple plies of material. Natural cardboards can range from grey to light ...
, wood, masonry
Masonry is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term ''masonry'' can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are bricks, building ...
, plastic and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
s. The penetration depth is typically less than that of microwave radiation. Like infrared, terahertz radiation has limited penetration through fog and cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
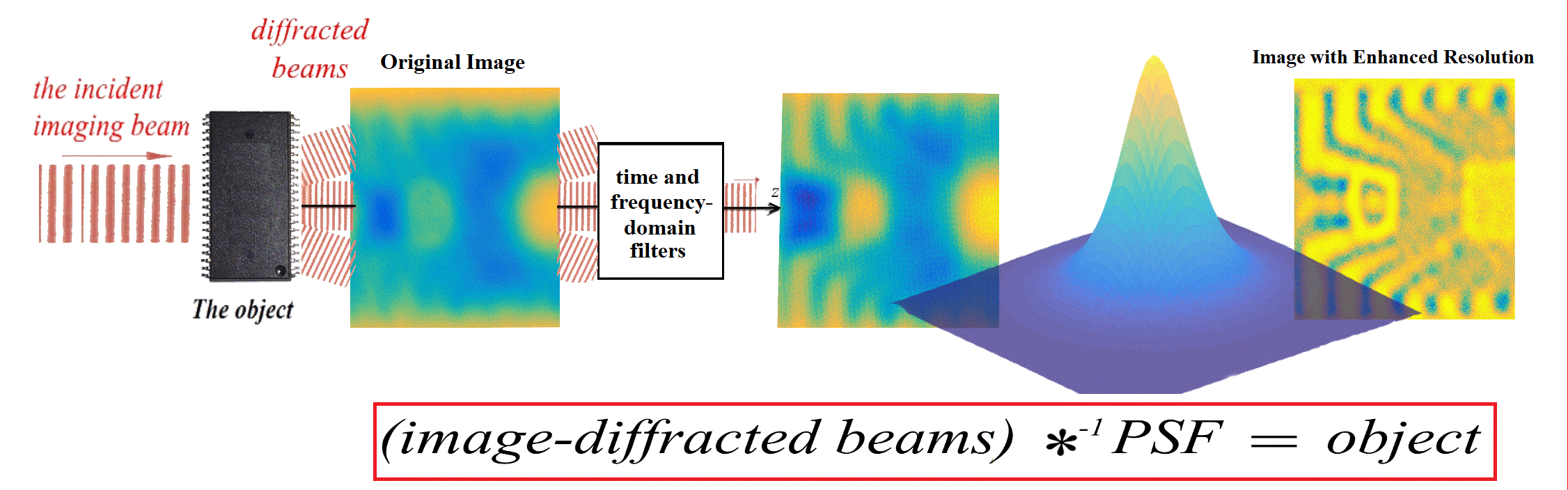
s and cannot penetrate liquid water or metal. Terahertz radiation can penetrate some distance through body tissue like x-rays, but unlike them is non-ionizing, so it is of interest as a replacement for medical X-rays. Due to its longer wavelength, images made using terahertz waves have lower resolution than X-rays and need to be enhanced (see figure at right).
The earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
is a strong absorber of terahertz radiation, so the range of terahertz radiation in air is limited to tens of meters, making it unsuitable for long-distance communications. However, at distances of ~10 meters the band may still allow many useful applications in imaging and construction of high bandwidth wireless network
A wireless network is a computer network that uses wireless data connections between network nodes.
Wireless networking is a method by which homes, telecommunications networks and business installations avoid the costly process of introducing ...
ing systems, especially indoor systems. In addition, producing and detecting coherent terahertz radiation remains technically challenging, though inexpensive commercial sources now exist in the 0.3–1.0 THz range (the lower part of the spectrum), including gyrotron
High-power 140 GHz gyrotron for plasma heating in the Wendelstein 7-X fusion experiment, Germany.
A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of e ...
s, backward wave oscillator
A backward wave oscillator (BWO), also called carcinotron or backward wave tube, is a vacuum tube that is used to generate microwaves up to the terahertz range. Belonging to the traveling-wave tube family, it is an oscillator with a wide electr ...
s, and resonant-tunneling diodes.
Sources
Natural
Terahertz radiation is emitted as part of the black-body radiation from anything with a temperature greater than about 2kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
s. While this thermal emission is very weak, observations at these frequencies are important for characterizing cold 10–20 K cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
in interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is generally an accumulation of gas, plasma, and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in ...
s in the Milky Way galaxy, and in distant starburst galaxies
A starburst galaxy is one undergoing an exceptionally high rate of star formation, as compared to the long-term average rate of star formation in the galaxy or the star formation rate observed in most other galaxies. For example, the star formatio ...
.
Telescopes operating in this band include the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope, the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory
The Caltech Submillimeter Observatory (CSO) was a 10.4-meter (34 ft) diameter submillimeter wavelength telescope situated alongside the 15-meter (49 ft) James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) at Mauna Kea Observatories. It was engaged in ...
and the Submillimeter Array at the Mauna Kea Observatory
The Mauna Kea Observatories (MKO) are a group of independent astronomical research facilities and large telescope observatories that are located at the summit of Mauna Kea on the Big Island of Hawaiʻi, United States. The facilities are locate ...
in Hawaii, the BLAST
Blast or The Blast may refer to:
*Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner
*Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front
Film
* ''Blast'' (1997 film), ...
balloon borne telescope, the Herschel Space Observatory, the Heinrich Hertz Submillimeter Telescope at the Mount Graham International Observatory in Arizona, and at the recently built Atacama Large Millimeter Array
The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) is an astronomical interferometer of 66 radio telescopes in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, which observe electromagnetic radiation at millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths. The ...
. Due to Earth's atmospheric absorption spectrum, the opacity of the atmosphere to submillimeter radiation restricts these observatories to very high altitude sites, or to space.
Artificial
, viable sources of terahertz radiation are thegyrotron
High-power 140 GHz gyrotron for plasma heating in the Wendelstein 7-X fusion experiment, Germany.
A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of e ...
, the backward wave oscillator
A backward wave oscillator (BWO), also called carcinotron or backward wave tube, is a vacuum tube that is used to generate microwaves up to the terahertz range. Belonging to the traveling-wave tube family, it is an oscillator with a wide electr ...
("BWO"), the organic gas far infrared laser, Schottky diode multipliers, varactor ( varicap) multipliers, quantum cascade laser Quantum-cascade lasers (QCLs) are semiconductor lasers that emit in the mid- to far-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and were first demonstrated by Jérôme Faist, Federico Capasso, Deborah Sivco, Carlo Sirtori, Albert Hutchinson, ...
,
the free electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a (fourth generation) light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions and behaves in many ways like a laser, but instead of using stimulated emission from atomic or molecula ...
, synchrotron light sources, photomixing sources, single-cycle or pulsed sources used in terahertz time domain spectroscopy such as photoconductive, surface field, photo-Dember and optical rectification
Electro-optic rectification (EOR), also referred to as optical rectification, is a non-linear optical process that consists of the generation of a quasi-DC polarization in a non-linear medium at the passage of an intense optical beam. For typica ...
emitters, and electronic oscillators based on resonant tunneling diodes have been shown to operate up to 700 GHz.
There have also been solid-state sources of millimeter and submillimeter waves for many years. AB Millimeter in Paris, for instance, produces a system that covers the entire range from 8 GHz to 1000 GHz with solid state sources and detectors. Nowadays, most time-domain work is done via ultrafast lasers.
In mid-2007, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory, along with collaborators in Turkey and Japan, announced the creation of a compact device that could lead to portable, battery-operated terahertz radiation sources. The device uses high-temperature superconducting crystals, grown at the University of Tsukuba
is a public research university located in Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. It is a top 10 Designated National University, and was ranked Type A by the Japanese government as part of the Top Global University Project.
The university has 28 colle ...
in Japan. These crystals comprise stacks of Josephson junction
In physics, the Josephson effect is a phenomenon that occurs when two superconductors are placed in proximity, with some barrier or restriction between them. It is an example of a macroscopic quantum phenomenon, where the effects of quantum mec ...
s, which exhibit a property known as the Josephson effect
In physics, the Josephson effect is a phenomenon that occurs when two superconductors are placed in proximity, with some barrier or restriction between them. It is an example of a macroscopic quantum phenomenon, where the effects of quantum mec ...
: when external voltage is applied, alternating current flows across the junctions at a frequency proportional to the voltage. This alternating current induces an electromagnetic field. A small voltage (around two millivolts per junction) can induce frequencies in the terahertz range.
In 2008, engineers at Harvard University achieved room temperature emission of several hundred nanowatts of coherent terahertz radiation using a semiconductor source. THz radiation was generated by nonlinear mixing of two modes in a mid-infrared quantum cascade laser. Previous sources had required cryogenic cooling, which greatly limited their use in everyday applications.
In 2009, it was discovered that the act of unpeeling adhesive tape generates non-polarized terahertz radiation, with a narrow peak at 2 THz and a broader peak at 18 THz. The mechanism of its creation is tribocharging of the adhesive tape and subsequent discharge; this was hypothesized to involve bremsstrahlung
''Bremsstrahlung'' (), from "to brake" and "radiation"; i.e., "braking radiation" or "deceleration radiation", is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typicall ...
with absorption or energy density focusing during dielectric breakdown
Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrical insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes an electrical conductor and electric current flows through it. All insulating mate ...
of a gas.
In 2013, researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology's Broadband Wireless Networking Laboratory and the Polytechnic University of Catalonia developed a method to create a graphene antenna: an antenna that would be shaped into graphene strips from 10 to 100 nanometers wide and one micrometer long. Such an antenna could be used to emit radio waves in the terahertz frequency range.
Terahertz gap
In engineering, the terahertz gap is afrequency band
A frequency band is an interval in the frequency domain, delimited by a lower frequency and an upper frequency. The term may refer to a radio band or an interval of some other spectrum.
The frequency range of a system is the range over which i ...
in the THz region for which practical technologies for generating and detecting the radiation do not exist. It is defined as 0.1 to 10 THz (wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
s of 3 mm to 30 µm) although the upper boundary is somewhat arbitrary and is considered by some sources as 30 THz (a wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
of 10 µm). Currently, at frequencies within this range, useful power generation and receiver technologies are inefficient and unfeasible.
Mass production of devices in this range and operation at room temperature (at which energy ''kT'' is equal to the energy of a photon with a frequency of 6.2 THz) are mostly impractical. This leaves a gap between mature microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ra ...
technologies in the highest frequencies of the radio spectrum
The radio spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies from 0 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, called radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particula ...
and the well-developed optical engineering Optical engineering is the field of science and engineering encompassing the physical phenomena and technologies associated with the generation, transmission, manipulation, detection, and utilization of light. Optical engineers use optics to solve ...
of infrared detector
An infrared detector is a detector that reacts to infrared (IR) radiation. The two main types of detectors are thermal and photonic (photodetectors).
The thermal effects of the incident IR radiation can be followed through many temperature depen ...
s in their lowest frequencies. This radiation is mostly used in small-scale, specialized applications such as submillimetre astronomy
Submillimetre astronomy or submillimeter astronomy (see spelling differences) is the branch of observational astronomy that is conducted at submillimetre wavelengths (i.e., terahertz radiation) of the electromagnetic spectrum. Astronomers pla ...
. Research
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
that attempts to resolve this issue has been conducted since the late 20th century.
Closure of the terahertz gap
Most vacuum electronic devices that are used for microwave generation can be modified to operate at terahertz frequencies, including the magnetron, gyrotron, synchrotron, and free electron laser. Similarly, microwave detectors such as the tunnel diode have been re-engineered to detect at terahertz and infrared frequencies as well. However, many of these devices are in prototype form, are not compact, or exist at university or government research labs, without the benefit of cost savings due to mass production.Research
Medical imaging
UnlikeX-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s, terahertz radiation is not ionizing radiation and its low photon energies in general do not damage living tissues and DNA. Some frequencies of terahertz radiation can penetrate several millimeters of tissue with low water content (e.g., fatty tissue) and reflect back. Terahertz radiation can also detect differences in water content and density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
of a tissue. Such methods could allow effective detection of epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercell ...
cancer with an imaging system that is safe, non-invasive, and painless. In response to the demand for COVID-19 screening terahertz spectroscopy and imaging has been proposed as a rapid screening tool.
The first images generated using terahertz radiation date from the 1960s; however, in 1995 images generated using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy generated a great deal of interest.
Some frequencies of terahertz radiation can be used for 3D imaging
In computer vision and computer graphics, 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance of real objects.
This process can be accomplished either by active or passive methods. If the model is allowed to change its shape ...
of teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, t ...
and may be more accurate than conventional X-ray imaging in dentistry.
Security
Terahertz radiation can penetrate fabrics and plastics, so it can be used in surveillance, such assecurity" \n\n\nsecurity.txt is a proposed standard for websites' security information that is meant to allow security researchers to easily report security vulnerabilities. The standard prescribes a text file called \"security.txt\" in the well known locat ...
screening, to uncover concealed weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, ...
s on a person, remotely. This is of particular interest because many materials of interest have unique spectral "fingerprints" in the terahertz range. This offers the possibility to combine spectral identification with imaging. In 2002, the European Space Agency (ESA) Star Tiger team, based at the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (Oxfordshire, UK), produced the first passive terahertz image of a hand. By 2004, ThruVision Ltd, a spin-out from the Council for the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils
The Council for the Central Laboratory of the Research Councils (CCLRC) was a UK government body that carried out civil research in science and engineering.
On 1 April 2007 CCLRC merged with PPARC to form the Science and Technology Facilities Co ...
(CCLRC) Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, had demonstrated the world's first compact THz camera for security screening applications. The prototype system successfully imaged guns and explosives concealed under clothing. Passive detection of terahertz signatures avoid the bodily privacy concerns of other detection by being targeted to a very specific range of materials and objects.
In January 2013, the NYPD
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement agency within the City of New York, the largest and one of the oldest in ...
announced plans to experiment with the new technology to detect concealed weapon
Concealed carry, or carrying a concealed weapon (CCW), is the practice of carrying a weapon (usually a sidearm such as a handgun), either in proximity to or on one's person or in public places in a manner that hides or conceals the weapon's pr ...
s, prompting Miami blogger and privacy activist Jonathan Corbett to file a lawsuit against the department in Manhattan federal court that same month, challenging such use: "For thousands of years, humans have used clothing to protect their modesty and have quite reasonably held the expectation of privacy for anything inside of their clothing, since no human is able to see through them." He sought a court order to prohibit using the technology without reasonable suspicion or probable cause. By early 2017, the department said it had no intention of ever using the sensors given to them by the federal government.
Scientific use and imaging
In addition to its current use insubmillimetre astronomy
Submillimetre astronomy or submillimeter astronomy (see spelling differences) is the branch of observational astronomy that is conducted at submillimetre wavelengths (i.e., terahertz radiation) of the electromagnetic spectrum. Astronomers pla ...
, terahertz radiation spectroscopy could provide new sources of information for chemistry and biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
.
Recently developed methods of THz time-domain spectroscopy (THz TDS) and THz tomography have been shown to be able to image samples that are opaque in the visible and near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
regions of the spectrum. The utility of THz-TDS is limited when the sample is very thin, or has a low absorbance
Absorbance is defined as "the logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls)". Alternatively, for samples which scatter light, absorbance may be defined as "the negative lo ...
, since it is very difficult to distinguish changes in the THz pulse caused by the sample from those caused by long-term fluctuations in the driving laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fi ...
source or experiment. However, THz-TDS produces radiation that is both coherent and spectrally broad, so such images can contain far more information than a conventional image formed with a single-frequency source.
Submillimeter waves are used in physics to study materials in high magnetic fields, since at high fields (over about 11 tesla), the electron spin Larmor frequencies are in the submillimeter band. Many high-magnetic field laboratories perform these high-frequency EPR experiments, such as the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
The National High Magnetic Field Laboratory (MagLab) is a facility at Florida State University, the University of Florida, and Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, that performs magnetic field research in physics, biology, bioengineering ...
(NHMFL) in Florida.
Terahertz radiation could let art historians see murals hidden beneath coats of plaster or paint in centuries-old buildings, without harming the artwork.
In additional, THz imaging has been done with lens antennas to capture radio image of the object.
THz driven dielectric wakefield acceleration
New types of particle accelerators that could achieve multi Giga-electron volts per metre (GeV/m) accelerating gradients are of utmost importance to reduce the size and cost of future generations of high energy colliders as well as provide a widespread availability of compact accelerator technology to smaller laboratories around the world. Gradients in the order of 100 MeV/m have been achieved by conventional techniques and are limited by RF-induced plasma breakdown. Beam driven dielectric wakefield accelerators (DWAs) typically operate in the Terahertz frequency range, which pushes the plasma breakdown threshold for surface electric fields into the multi-GV/m range. DWA technique allows to accommodate a significant amount of charge per bunch, and gives an access to conventional fabrication techniques for the accelerating structures. To date 0.3 GeV/m accelerating and 1.3 GeV/m decelerating gradients have been achieved using a dielectric lined waveguide with sub-millimetre transverse aperture. An accelerating gradient larger than 1 GeV/m, can potentially be produced by the Cherenkov Smith-Purcell radiative mechanism in a dielectric capillary with a variable inner radius. When an electron bunch propagates through the capillary, its self-field interacts with the dielectric material and produces wakefields that propagate inside the material at the Cherenkov angle. The wakefields are slowed down below the speed of light, as the relative dielectric permittivity of the material is larger than 1. The radiation is then reflected from the capillary's metallic boundary and diffracted back into the vacuum region, producing high accelerating fields on the capillary axis with a distinct frequency signature. In presence of a periodic boundary the Smith-Purcell radiation imposes frequency dispersion. A preliminary study with corrugated capillaries has shown some modification to the spectral content and amplitude of the generated wakefields, but the possibility of using Smith-Purcell effect in DWA is still under consideration.Communication
In May 2012, a team of researchers from theTokyo Institute of Technology
is a national research university located in Greater Tokyo Area, Japan. Tokyo Tech is the largest institution for higher education in Japan dedicated to science and technology, one of first five Designated National University and selected as ...
published in ''Electronics Letters
'' Electronics Letters ''is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published biweekly by the Institution of Engineering and Technology. It specializes in the rapid publication of short communications on all areas of electronic engineering, including op ...
'' that it had set a new record for wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
data transmission by using T-rays and proposed they be used as bandwidth for data transmission in the future. The team's proof of concept
Proof of concept (POC or PoC), also known as proof of principle, is a realization of a certain method or idea in order to demonstrate its feasibility, or a demonstration in principle with the aim of verifying that some concept or theory has prac ...
device used a resonant tunneling diode (RTD) negative resistance oscillator to produce waves in the terahertz band. With this RTD, the researchers sent a signal at 542 GHz, resulting in a data transfer rate of 3 Gigabits per second. It doubled the record for data transmission rate set the previous November. The study suggested that Wi-Fi using the system would be limited to approximately , but could allow data transmission at up to 100 Gbit/s.
In 2011, Japanese electronic parts maker Rohm and a research team at Osaka University produced a chip capable of transmitting 1.5 Gbit/s using terahertz radiation.
Potential uses exist in high-altitude telecommunications, above altitudes where water vapor causes signal absorption: aircraft to satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioi ...
, or satellite to satellite.
Amateur radio
A number of administrations permit amateur radio experimentation within the 275–3000 GHz range or at even higher frequencies on a national basis, under license conditions that are usually based on RR5.565 of the ITU Radio Regulations. Amateur radio operators utilizing submillimeter frequencies often attempt to set two-way communication distance records. In theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, WA1ZMS and W4WWQ set a record of on 403 GHz using CW (Morse code) on 21 December 2004. In Australia, at 30 THz a distance of was achieved by stations VK3CV and VK3LN on 8 November 2020.
Manufacturing
Many possible uses of terahertz sensing and imaging are proposed inmanufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to ...
, quality control, and process monitoring. These in general exploit the traits of plastics and cardboard
Cardboard is a generic term for heavy paper-based products. The construction can range from a thick paper known as paperboard to corrugated fiberboard which is made of multiple plies of material. Natural cardboards can range from grey to light ...
being transparent to terahertz radiation, making it possible to inspect packaged goods. The first imaging system based on optoelectronic terahertz time-domain spectroscopy were developed in 1995 by researchers from AT&T Bell Laboratories and was used for producing a transmission image of a packaged electronic chip. This system used pulsed laser beams with duration in range of picoseconds. Since then commonly used commercial/ research terahertz imaging systems have used pulsed lasers to generate terahertz images. The image can be developed based on either the attenuation or phase delay of the transmitted terahertz pulse.
Since the beam is scattered more at the edges and also different materials have different absorption coefficients, the images based on attenuation indicates edges and different materials inside of an objects. This approach is similar to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
transmission imaging, where images are developed based on attenuation of the transmitted beam.
In the second approach, terahertz images are developed based on the time delay of the received pulse. In this approach, thicker parts of the objects are well recognized as the thicker parts cause more time delay of the pulse. Energy of the laser spots are distributed by a Gaussian function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function of the base form
f(x) = \exp (-x^2)
and with parametric extension
f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right)
for arbitrary real constants , and non-zero . It is ...
. The geometry and behavior of Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation with high monochromaticity whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. Thi ...
in the Fraunhofer region imply that the electromagnetic beams diverge more as the frequencies of the beams decrease and thus the resolution decreases. This implies that terahertz imaging systems have higher resolution than scanning acoustic microscope (SAM) but lower resolution than X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
imaging systems. Although terahertz can be used for inspection of packaged objects, it suffers from low resolution for fine inspections. X-ray image and terahertz images of an electronic chip are brought in the figure on the right.
Obviously the resolution of X-ray is higher than terahertz image, but X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
is ionizing and can be impose harmful effects on certain objects such as semiconductors and live tissues.
To overcome low resolution of the terahertz systems near-field terahertz imaging systems are under development. In nearfield imaging the detector needs to be located very close to the surface of the plane and thus imaging of the thick packaged objects may not be feasible. In another attempt to increase the resolution, laser beams with frequencies higher than terahertz are used to excite the p-n junctions in semiconductor objects, the excited junctions generate terahertz radiation as a result as long as their contacts are unbroken and in this way damaged devices can be detected. In this approach, since the absorption increases exponentially with the frequency, again inspection of the thick packaged semiconductors may not be doable. Consequently, a tradeoff between the achievable resolution and the thickness of the penetration of the beam in the packaging material should be considered.
THz gap research
Ongoing investigation has resulted in improved emitters (sources) anddetectors
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
, and research in this area has intensified. However, drawbacks remain that include the substantial size of emitters, incompatible frequency ranges, and undesirable operating temperatures, as well as component, device, and detector requirements that are somewhere between solid state electronics
Solid-state electronics means semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment using semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor electr ...
and photonic
Photonics is a branch of optics that involves the application of generation, detection, and manipulation of light in form of photons through emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, and sensing. Though ...
technologies.
Free-electron laser
A free-electron laser (FEL) is a (fourth generation) light source producing extremely brilliant and short pulses of radiation. An FEL functions and behaves in many ways like a laser, but instead of using stimulated emission from atomic or molecula ...
s can generate a wide range of stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation from microwaves, through terahertz radiation to X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
. However, they are bulky, expensive and not suitable for applications that require critical timing (such as wireless communications
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
). Other sources of terahertz radiation which are actively being researched include solid state oscillators (through frequency multiplication), backward wave oscillators (BWOs), quantum cascade laser Quantum-cascade lasers (QCLs) are semiconductor lasers that emit in the mid- to far-infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum and were first demonstrated by Jérôme Faist, Federico Capasso, Deborah Sivco, Carlo Sirtori, Albert Hutchinson, ...
s, and gyrotron
High-power 140 GHz gyrotron for plasma heating in the Wendelstein 7-X fusion experiment, Germany.
A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of e ...
s.
Safety
The terahertz region is between the radio frequency region and the laser optical region. Both the IEEE C95.1–2005 RF safety standard and the ANSI Z136.1–2007 Laser safety standard have limits into the terahertz region, but both safety limits are based on extrapolation. It is expected that effects on biological tissues are thermal in nature and, therefore, predictable by conventional thermal models . Research is underway to collect data to populate this region of the spectrum and validate safety limits. A theoretical study published in 2010 and conducted by Alexandrov et al at the Center for Nonlinear Studies atLos Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
in New Mexico
created mathematical models predicting how terahertz radiation would interact with double-stranded DNA, showing that, even though involved forces seem to be tiny, nonlinear resonance In physics, nonlinear resonance is the occurrence of resonance in a nonlinear system. In nonlinear resonance the system behaviour – resonance frequencies and modes – depends on the amplitude of the oscillations, while for linear systems this is ...
s (although much less likely to form than less-powerful common resonances) could allow terahertz waves to "unzip double-stranded DNA, creating bubbles in the double strand that could significantly interfere with processes such as gene expression and DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
". Experimental verification of this simulation was not done. Swanson's 2010 theoretical treatment of the Alexandrov study concludes that the DNA bubbles do not occur under reasonable physical assumptions or if the effects of temperature are taken into account.
A bibliographical study published in 2003 reported that T-ray intensity drops to less than 1% in the first 500 μm of skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
but stressed that "there is currently very little information about the optical properties of human tissue at terahertz frequencies".
See also
* Far-infrared laser * Full body scanner *Heterojunction bipolar transistor The heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) which uses differing semiconductor materials for the emitter and base regions, creating a heterojunction. The HBT improves on the BJT in that it can handle s ...
*High-electron-mobility transistor
A high-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT), also known as heterostructure FET (HFET) or modulation-doped FET (MODFET), is a field-effect transistor incorporating a junction between two materials with different band gaps (i.e. a heterojunction) ...
(HEMT)
* Picarin
* Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy
References
Further reading
*External links
* * * * {{Authority control Electromagnetic spectrum Terahertz technology