surface of the Earth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Earth is the third
 The oldest material found in the
The oldest material found in the
 As the molten outer layer of Earth cooled it formed the first solid crust, which is thought to have been mafic in composition. The first
As the molten outer layer of Earth cooled it formed the first solid crust, which is thought to have been mafic in composition. The first
 During the
During the
 Earth's expected long-term future is tied to that of the Sun. Over the next , solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next by 40%. Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, possibly reducing concentration to levels lethally low for current plants ( for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately . A lack of vegetation would result in the loss of oxygen in the atmosphere, making current animal life impossible. Due to the increased luminosity, Earth's mean temperature may reach in 1.5 billion years, and all ocean water will evaporate and be lost to space, which may trigger a runaway greenhouse effect, within an estimated 1.6 to 3 billion years. Even if the Sun were stable and eternal, a significant fraction of the water in the modern oceans would descend into the mantle, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges as the core of the Earth slowly cools.
The Sun will evolve to become a red giant in about . Models predict that the Sun will expand to roughly , about 250 times its present radius. Earth's fate is less clear. As a red giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its mass, so, without tidal effects, Earth will move to an orbit from the Sun when the star reaches its maximum radius, otherwise, with tidal effects, it may enter the Sun's atmosphere and be vaporized, with the heavier elements sinking to the core of the dying sun.
Earth's expected long-term future is tied to that of the Sun. Over the next , solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next by 40%. Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, possibly reducing concentration to levels lethally low for current plants ( for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately . A lack of vegetation would result in the loss of oxygen in the atmosphere, making current animal life impossible. Due to the increased luminosity, Earth's mean temperature may reach in 1.5 billion years, and all ocean water will evaporate and be lost to space, which may trigger a runaway greenhouse effect, within an estimated 1.6 to 3 billion years. Even if the Sun were stable and eternal, a significant fraction of the water in the modern oceans would descend into the mantle, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges as the core of the Earth slowly cools.
The Sun will evolve to become a red giant in about . Models predict that the Sun will expand to roughly , about 250 times its present radius. Earth's fate is less clear. As a red giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its mass, so, without tidal effects, Earth will move to an orbit from the Sun when the star reaches its maximum radius, otherwise, with tidal effects, it may enter the Sun's atmosphere and be vaporized, with the heavier elements sinking to the core of the dying sun.
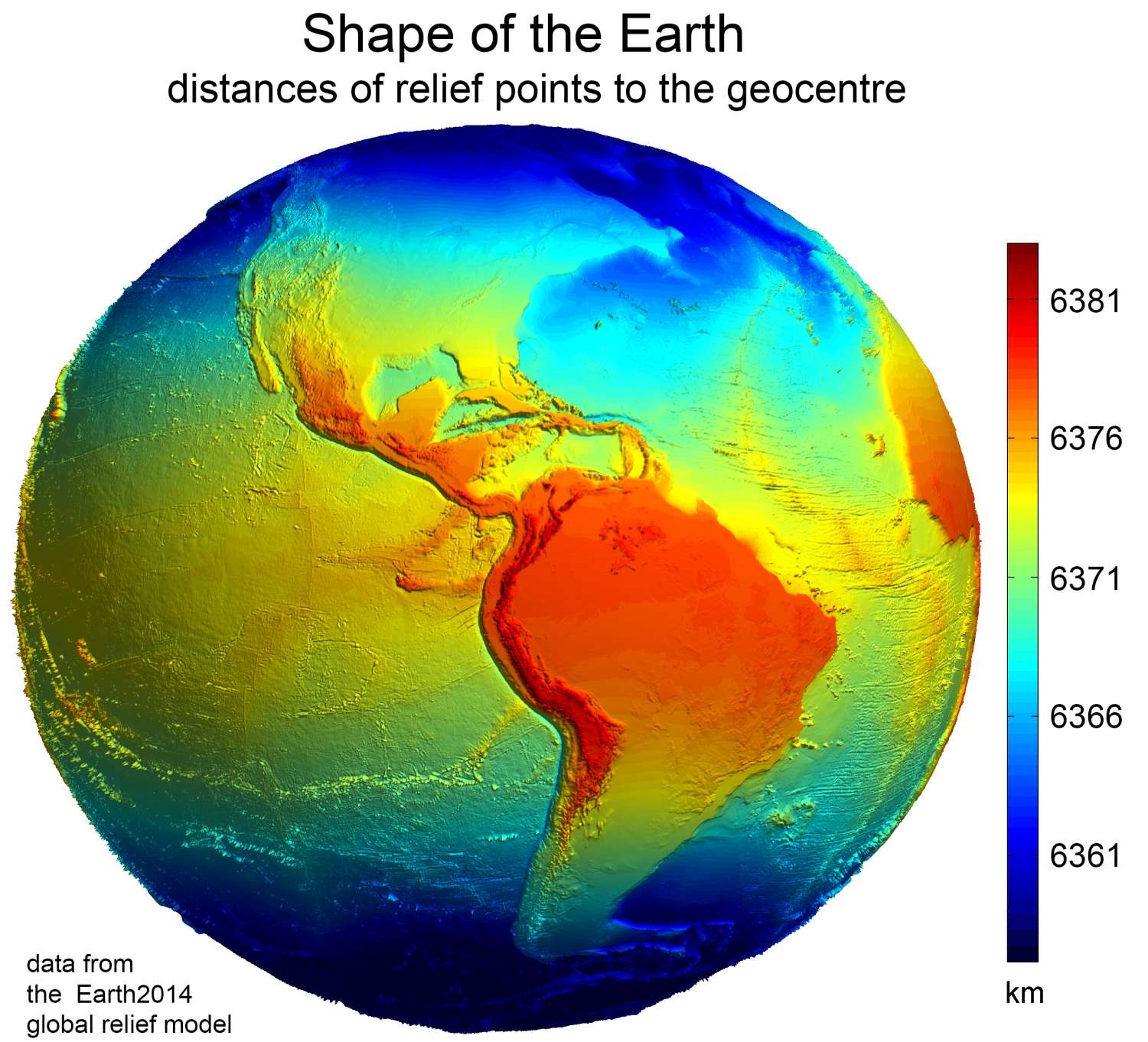 Earth has a rounded shape, through hydrostatic equilibrium, with an average diameter of , making it the fifth largest planetary sized and largest terrestrial object of the
Earth has a rounded shape, through hydrostatic equilibrium, with an average diameter of , making it the fifth largest planetary sized and largest terrestrial object of the
 Earth's surface is the boundary between the atmosphere and the solid Earth and oceans. Defined in this way, it has an area of about . Earth can be divided into two hemispheres: by
Earth's surface is the boundary between the atmosphere and the solid Earth and oceans. Defined in this way, it has an area of about . Earth can be divided into two hemispheres: by
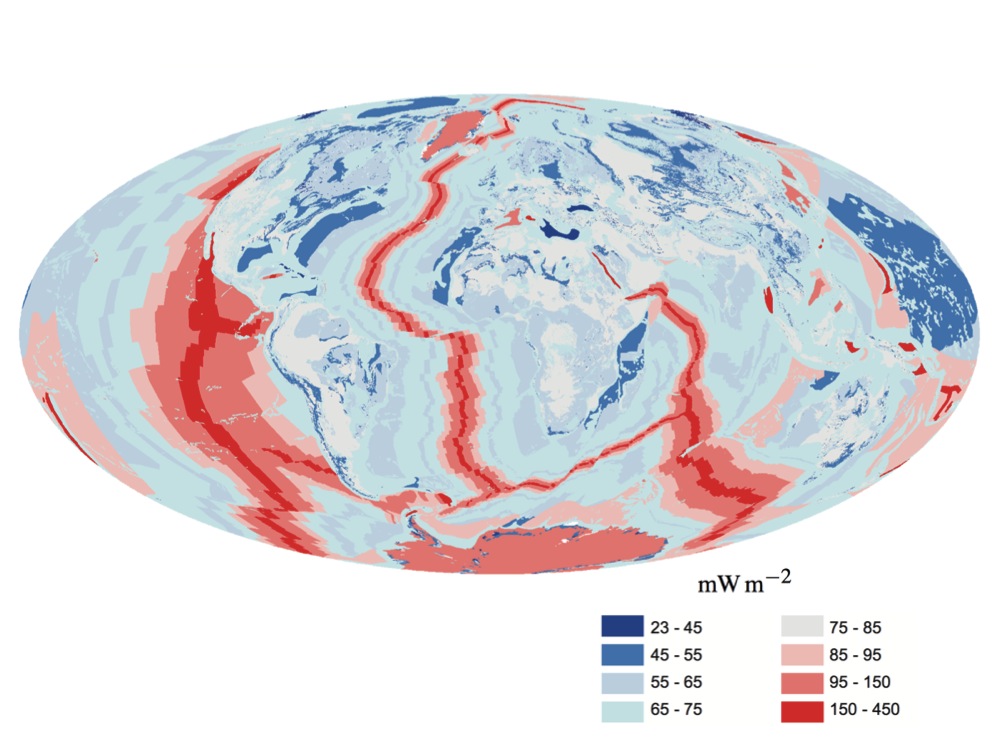 The major contributors to Earth's internal heat are primordial heat (heat left over from Earth's formation) and radiogenic heat (heat produced by radioactive decay). The major heat-producing
The major contributors to Earth's internal heat are primordial heat (heat left over from Earth's formation) and radiogenic heat (heat produced by radioactive decay). The major heat-producing
 The main part of Earth's magnetic field is generated in the core, the site of a dynamo process that converts the kinetic energy of thermally and compositionally driven convection into electrical and magnetic field energy. The field extends outwards from the core, through the mantle, and up to Earth's surface, where it is, approximately, a
The main part of Earth's magnetic field is generated in the core, the site of a dynamo process that converts the kinetic energy of thermally and compositionally driven convection into electrical and magnetic field energy. The field extends outwards from the core, through the mantle, and up to Earth's surface, where it is, approximately, a
 Earth's rotation period relative to the Sun—its mean solar day—is of mean solar time (). Because Earth's solar day is now slightly longer than it was during the 19th century due to tidal deceleration, each day varies between longer than the mean solar day.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars, called its ''stellar day'' by the
Earth's rotation period relative to the Sun—its mean solar day—is of mean solar time (). Because Earth's solar day is now slightly longer than it was during the 19th century due to tidal deceleration, each day varies between longer than the mean solar day.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars, called its ''stellar day'' by the
 Earth orbits the Sun, making Earth the third-closest planet to the Sun and part of the inner Solar System. Earth's average orbital distance is about , which is the basis for the
Earth orbits the Sun, making Earth the third-closest planet to the Sun and part of the inner Solar System. Earth's average orbital distance is about , which is the basis for the
 The Moon is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, although Charon is larger relative to the
The Moon is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, although Charon is larger relative to the
 Earth's co-orbital asteroids population consists of quasi-satellites, objects with a horseshoe orbit and trojans. There are at least seven quasi-satellites, including 469219 Kamoʻoalewa, ranging in diameter from 10 m to 5000 m. A trojan asteroid companion, , is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in
Earth's co-orbital asteroids population consists of quasi-satellites, objects with a horseshoe orbit and trojans. There are at least seven quasi-satellites, including 469219 Kamoʻoalewa, ranging in diameter from 10 m to 5000 m. A trojan asteroid companion, , is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in
 Earth's hydrosphere is the sum of Earth's water and its distribution. Most of Earth's hydrosphere consists of Earth's global ocean. Earth's hydrosphere also consists of water in the atmosphere and on land, including clouds, inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground waters. The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons or about 1/4400 of Earth's total mass. The oceans cover an area of with a mean depth of , resulting in an estimated volume of .
If all of Earth's crustal surface were at the same elevation as a smooth sphere, the depth of the resulting world ocean would be . About 97.5% of the water is saline; the remaining 2.5% is
Earth's hydrosphere is the sum of Earth's water and its distribution. Most of Earth's hydrosphere consists of Earth's global ocean. Earth's hydrosphere also consists of water in the atmosphere and on land, including clouds, inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground waters. The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons or about 1/4400 of Earth's total mass. The oceans cover an area of with a mean depth of , resulting in an estimated volume of .
If all of Earth's crustal surface were at the same elevation as a smooth sphere, the depth of the resulting world ocean would be . About 97.5% of the water is saline; the remaining 2.5% is
 The
The
 The upper atmosphere, the atmosphere above the troposphere, is usually divided into the
The upper atmosphere, the atmosphere above the troposphere, is usually divided into the
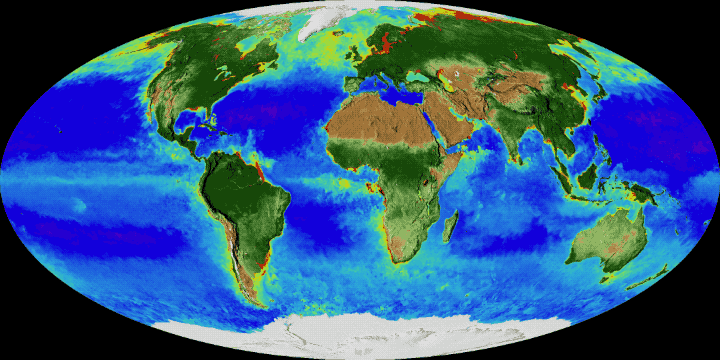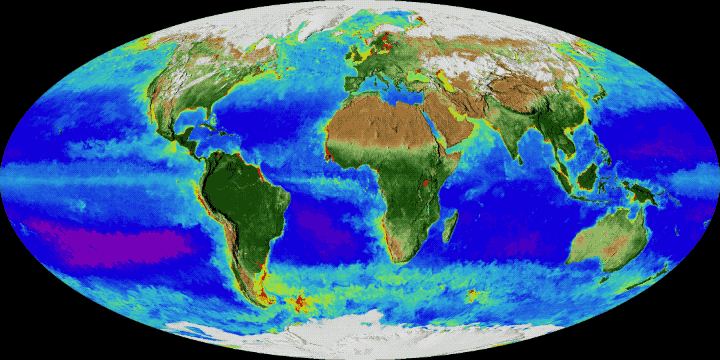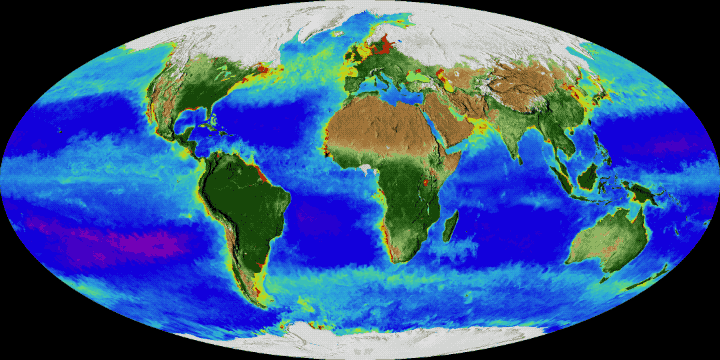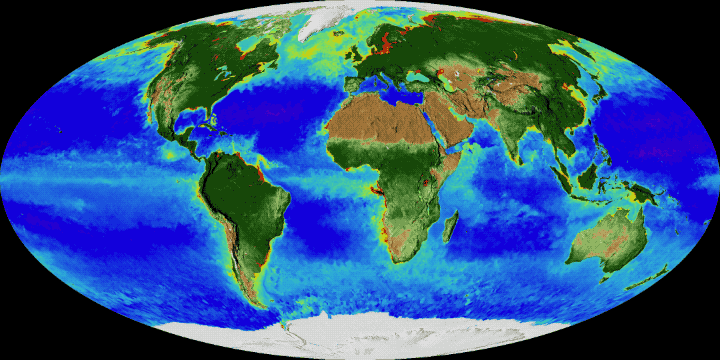 Earth is the only known place that has ever been habitable for life. Earth's life developed in Earth's early bodies of water some hundred million years after Earth formed. Earth's life has been shaping and inhabiting many particular
Earth is the only known place that has ever been habitable for life. Earth's life developed in Earth's early bodies of water some hundred million years after Earth formed. Earth's life has been shaping and inhabiting many particular 
 Originating from earlier
Originating from earlier
 Human activities have impacted Earth's environments. Through activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, humans have been increasing the amount of
Human activities have impacted Earth's environments. Through activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, humans have been increasing the amount of
 Human cultures have developed many views of the planet. The standard astronomical symbols of Earth are a quartered circle, , representing the four corners of the world, and a
Human cultures have developed many views of the planet. The standard astronomical symbols of Earth are a quartered circle, , representing the four corners of the world, and a
Earth – Profile
– Solar System Exploration –
Earth Observatory
– NASA * Earth – Videos – International Space Station: *
Video (01:02)
on YouTube – Earth (time-lapse) *
Video (00:27)
on YouTube – Earth and
Google Earth 3D
interactive map
Interactive 3D visualization of the Sun, Earth and Moon system
GPlates Portal
(University of Sydney) {{Subject bar, wikt=Earth, q=Earth, m=Earth, n=Earth, v=Earth, s=Earth, b=Earth, commons=Earth, portal1=Biology, portal2=Earth sciences, portal3=Ecology, portal4=Geography, portal5=Volcanoes, portal6=Solar system, portal7=Outer space, portal8=Weather, portal9=World Astronomical objects known since antiquity Global natural environment Nature Planets of the Solar System Solar System Terrestrial planets
planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
from the Sun and the only astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
known to harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
sustaining liquid surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering 70.8% of Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
al landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land that is in one piece and not noticeably broken up by oceans. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the fiel ...
es within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large sheets of ice at Earth's polar desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s retain more water than Earth's groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
, lakes, rivers, and atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
es, and earthquakes. Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
capable of deflecting most of the destructive solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
s and cosmic radiation.
Earth has a dynamic atmosphere, which sustains Earth's surface conditions and protects it from most meteoroid
A meteoroid ( ) is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are distinguished as objects significantly smaller than ''asteroids'', ranging in size from grains to objects up to wide. Objects smaller than meteoroids are classifie ...
s and UV-light at entry. It has a composition of primarily nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
. Water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
is widely present in the atmosphere, forming clouds that cover most of the planet. The water vapor acts as a greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
and, together with other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, particularly carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO2), creates the conditions for both liquid surface water and water vapor to persist via the capturing of energy from the Sun's light. This process maintains the current average surface temperature of , at which water is liquid under normal atmospheric pressure. Differences in the amount of captured energy between geographic regions (as with the equatorial region receiving more sunlight than the polar regions) drive atmospheric and ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s, producing a global climate system
Earth's climate system is a complex system with five interacting components: the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (air), the hydrosphere (water), the cryosphere (ice and permafrost), the lithosphere (earth's upper rocky layer) and the biosphere ( ...
with different climate regions, and a range of weather phenomena such as precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
, allowing components such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
to cycle.
Earth is rounded into an ellipsoid with a circumference of about . It is the densest planet in the Solar System. Of the four rocky planets, it is the largest and most massive. Earth is about eight light-minutes (1 AU) away from the Sun and orbits it, taking a year (about 365.25 days) to complete one revolution. Earth rotates around its own axis in slightly less than a day (in about 23 hours and 56 minutes). Earth's axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the perpendicular to its orbital plane around the Sun, producing seasons. Earth is orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an ...
ed by one permanent natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a deriv ...
, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, which orbits Earth at —1.28 light seconds—and is roughly a quarter as wide as Earth. The Moon's gravity helps stabilize Earth's axis, causes tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s and gradually slows Earth's rotation. Likewise Earth's gravitational pull has already made the Moon's rotation tidally locked, keeping the same near side facing Earth.
Earth, like most other bodies in the Solar System, formed about 4.5 billion years ago from gas and dust in the early Solar System. During the first billion years of Earth's history, the ocean formed and then life developed within it. Life spread globally and has been altering Earth's atmosphere and surface, leading to the Great Oxidation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE) or Great Oxygenation Event, also called the Oxygen Catastrophe, Oxygen Revolution, Oxygen Crisis or Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Earth's Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere an ...
two billion years ago. Humans emerged 300,000 years ago in Africa and have spread across every continent on Earth. Humans depend on Earth's biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
and natural resources for their survival, but have increasingly impacted the planet's environment. Humanity's current impact on Earth's climate and biosphere is unsustainable, threatening the livelihood of humans and many other forms of life, and causing widespread extinctions.
Etymology
TheModern English
Modern English, sometimes called New English (NE) or present-day English (PDE) as opposed to Middle and Old English, is the form of the English language that has been spoken since the Great Vowel Shift in England
England is a Count ...
word ''Earth'' developed, via Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
, from an Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
noun most often spelled '. It has cognates in every Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania, and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
, from which has been reconstructed. In its earliest attestation, the word ' was used to translate the many senses of Latin ' and Greek : the ground, its soil, dry land, the human world, the surface of the world (including the sea), and the globe itself. As with Roman (or ) and Greek , Earth may have been a personified goddess in Germanic paganism
Germanic paganism or Germanic religion refers to the traditional, culturally significant religion of the Germanic peoples. With a chronological dating, chronological range of at least one thousand years in an area covering Scandinavia, the Bri ...
: late Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia as the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The ...
included ('Earth'), a giantess often given as the mother of Thor
Thor (from ) is a prominent list of thunder gods, god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding æsir, god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology, sacred g ...
.
Historically, ''Earth'' has been written in lowercase. During the Early Middle English period, its definite sense as "the globe" began being expressed using the phrase ''the earth''. By the period of Early Modern English
Early Modern English (sometimes abbreviated EModEFor example, or EMnE) or Early New English (ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transit ...
, capitalization of nouns began to prevail, and ''the earth'' was also written ''the Earth'', particularly when referenced along with other heavenly bodies. More recently, the name is sometimes simply given as ''Earth'', by analogy with the names of the other planets, though ''earth'' and forms with ''the earth'' remain common. House styles now vary: Oxford spelling recognizes the lowercase form as the more common, with the capitalized form an acceptable variant. Another convention capitalizes ''Earth'' when appearing as a name, such as a description of the "Earth's atmosphere", but employs the lowercase when it is preceded by ''the'', such as "the atmosphere of the earth". It almost always appears in lowercase in colloquial expressions such as "what on earth are you doing?"
The name ''Terra'' is occasionally used in scientific writing; it also sees use in science fiction to distinguish humanity's inhabited planet from others, while in poetry ''Tellus'' has been used to denote personification of the Earth. ''Terra'' is also the name of the planet in some Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, languages that evolved from Latin, like Italian and Portuguese, while in other Romance languages the word gave rise to names with slightly altered spellings, like the Spanish and the French . The Latinate form ( ) of the Greek poetic name ( or ) is rare, though the alternative spelling ''Gaia'' has become common due to the Gaia hypothesis
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living organisms interact with their Inorganic compound, inorganic surroundings on Earth to form a Synergy, synergistic and Homeostasis, s ...
, in which case its pronunciation is rather than the more traditional English .
There are a number of adjectives for the planet Earth. The word ''earthly'' is derived from ''Earth''. From the Latin comes ''terran'' , ''terrestrial'' , and (via French) ''terrene'' , and from the Latin comes ''tellurian'' and ''telluric''.
Natural history
Formation
 The oldest material found in the
The oldest material found in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
is dated to Ga (billion years) ago. By the primordial Earth had formed. The bodies in the Solar System formed and evolved with the Sun. In theory, a solar nebula partitions a volume out of a molecular cloud
A molecular cloud—sometimes called a stellar nursery if star formation is occurring within—is a type of interstellar cloud of which the density and size permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, ...
by gravitational collapse, which begins to spin and flatten into a circumstellar disk, and then the planets grow out of that disk with the Sun. A nebula contains gas, ice grains, and dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcan ...
(including primordial nuclides). According to nebular theory, planetesimals formed by accretion, with the primordial Earth being estimated as likely taking anywhere from 70 to 100 million years to form.
Estimates of the age of the Moon range from 4.5 Ga to significantly younger. A leading hypothesis is that it was formed by accretion from material loosed from Earth after a Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
-sized object with about 10% of Earth's mass, named Theia, collided with Earth. It hit Earth with a glancing blow and some of its mass merged with Earth. Between approximately 4.0 and , numerous asteroid impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment caused significant changes to the greater surface environment of the Moon and, by inference, to that of Earth.
After formation
Earth's atmosphere and oceans were formed by volcanic activity andoutgassing
Outgassing (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality) is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation (whic ...
. Water vapor from these sources condensed into the oceans, augmented by water and ice from asteroids, protoplanet
A protoplanet is a large planetary embryo that originated within a protoplanetary disk and has undergone internal melting to produce a differentiated interior. Protoplanets are thought to form out of kilometer-sized planetesimals that gravitatio ...
s, and comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s. Sufficient water to fill the oceans may have been on Earth since it formed. In this model, atmospheric greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es kept the oceans from freezing when the newly forming Sun had only 70% of its current luminosity. By , Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from structure of Earth, Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from ...
was established, which helped prevent the atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
.
 As the molten outer layer of Earth cooled it formed the first solid crust, which is thought to have been mafic in composition. The first
As the molten outer layer of Earth cooled it formed the first solid crust, which is thought to have been mafic in composition. The first continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
, which was more felsic
In geology, felsic is a grammatical modifier, modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted ...
in composition, formed by the partial melting of this mafic crust. The presence of grains of the mineral zircon of Hadean age in Eoarchean sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s suggests that at least some felsic crust existed as early as , only after Earth's formation. There are two main models of how this initial small volume of continental crust evolved to reach its current abundance: (1) a relatively steady growth up to the present day, which is supported by the radiometric dating of continental crust globally and (2) an initial rapid growth in the volume of continental crust during the Archean
The Archean ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan), in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history of Earth, history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic and t ...
, forming the bulk of the continental crust that now exists, which is supported by isotopic evidence from hafnium in zircons and neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
in sedimentary rocks. The two models and the data that support them can be reconciled by large-scale recycling of the continental crust, particularly during the early stages of Earth's history.
New continental crust forms as a result of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
, a process ultimately driven by the continuous loss of heat from Earth's interior. Over the period of hundreds of millions of years, tectonic forces have caused areas of continental crust to group together to form supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
s that have subsequently broken apart. At approximately , one of the earliest known supercontinents, Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago (Ga) and broke up 750–633 million years ago (Ma). wer ...
, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia at , then finally Pangaea, which also began to break apart at .
The most recent pattern of ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
s began about , and then intensified during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
about . High- and middle-latitude regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating about every 21,000, 41,000 and 100,000 years. The Last Glacial Period, colloquially called the "last ice age", covered large parts of the continents, to the middle latitudes, in ice and ended about 11,700 years ago.
Origin of life and evolution
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
s led to the first self-replicating molecules about four billion years ago. A half billion years later, the last common ancestor of all current life arose. The evolution of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
allowed the Sun's energy to be harvested directly by life forms. The resultant molecular oxygen () accumulated in the atmosphere and due to interaction with ultraviolet solar radiation, formed a protective ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the a ...
() in the upper atmosphere. The incorporation of smaller cells within larger ones resulted in the development of complex cells called eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s. True multicellular organisms formed as cells within colonies became increasingly specialized. Aided by the absorption of harmful ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
by the ozone layer, life colonized Earth's surface. Among the earliest fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
evidence for life is microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
in Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
, biogenic
A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of p ...
graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
found in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks in Western Greenland, and remains of biotic material found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. The earliest direct evidence of life on Earth is contained in 3.45 billion-year-old Australian rocks showing fossils of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s. During the
During the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
, , much of Earth might have been covered in ice. This hypothesis has been termed "Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth is a historical geology, geohistorical hypothesis that proposes that during one or more of Earth's greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse climates, the planet's planetary surface, surface became nearly entirely freezing, fr ...
", and it is of particular interest because it preceded the Cambrian explosion, when multicellular life forms significantly increased in complexity. Following the Cambrian explosion, , there have been at least five major mass extinctions and many minor ones. Apart from the proposed current Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
event, the most recent was , when an asteroid impact triggered the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs and other large reptiles, but largely spared small animals such as insects, mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, lizards and birds. Mammalian life has diversified over the past , and several million years ago, an African ape species gained the ability to stand upright. This facilitated tool use and encouraged communication that provided the nutrition and stimulation needed for a larger brain, which led to the evolution of humans. The development of agriculture, and then civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
, led to humans having an influence on Earth and the nature and quantity of other life forms that continues to this day.
Future
 Earth's expected long-term future is tied to that of the Sun. Over the next , solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next by 40%. Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, possibly reducing concentration to levels lethally low for current plants ( for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately . A lack of vegetation would result in the loss of oxygen in the atmosphere, making current animal life impossible. Due to the increased luminosity, Earth's mean temperature may reach in 1.5 billion years, and all ocean water will evaporate and be lost to space, which may trigger a runaway greenhouse effect, within an estimated 1.6 to 3 billion years. Even if the Sun were stable and eternal, a significant fraction of the water in the modern oceans would descend into the mantle, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges as the core of the Earth slowly cools.
The Sun will evolve to become a red giant in about . Models predict that the Sun will expand to roughly , about 250 times its present radius. Earth's fate is less clear. As a red giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its mass, so, without tidal effects, Earth will move to an orbit from the Sun when the star reaches its maximum radius, otherwise, with tidal effects, it may enter the Sun's atmosphere and be vaporized, with the heavier elements sinking to the core of the dying sun.
Earth's expected long-term future is tied to that of the Sun. Over the next , solar luminosity will increase by 10%, and over the next by 40%. Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, possibly reducing concentration to levels lethally low for current plants ( for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately . A lack of vegetation would result in the loss of oxygen in the atmosphere, making current animal life impossible. Due to the increased luminosity, Earth's mean temperature may reach in 1.5 billion years, and all ocean water will evaporate and be lost to space, which may trigger a runaway greenhouse effect, within an estimated 1.6 to 3 billion years. Even if the Sun were stable and eternal, a significant fraction of the water in the modern oceans would descend into the mantle, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges as the core of the Earth slowly cools.
The Sun will evolve to become a red giant in about . Models predict that the Sun will expand to roughly , about 250 times its present radius. Earth's fate is less clear. As a red giant, the Sun will lose roughly 30% of its mass, so, without tidal effects, Earth will move to an orbit from the Sun when the star reaches its maximum radius, otherwise, with tidal effects, it may enter the Sun's atmosphere and be vaporized, with the heavier elements sinking to the core of the dying sun.
Physical characteristics
Size and shape
 Earth has a rounded shape, through hydrostatic equilibrium, with an average diameter of , making it the fifth largest planetary sized and largest terrestrial object of the
Earth has a rounded shape, through hydrostatic equilibrium, with an average diameter of , making it the fifth largest planetary sized and largest terrestrial object of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
.
Due to Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in progra ...
it has the shape of an ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathemat ...
, bulging at its equator; its diameter is longer there than at its poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
. Earth's shape also has local topographic variations; the largest local variations, like the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deep sea, deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maxi ...
( below local sea level), shortens Earth's average radius by 0.17% and Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
( above local sea level) lengthens it by 0.14%. Since Earth's surface is farthest out from its center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the d ...
at its equatorial bulge, the summit of the volcano Chimborazo
Chimborazo () is a stratovolcano situated in Ecuador in the Cordillera Occidental (Ecuador), Cordillera Occidental range of the Andes. Its last known Types of volcanic eruptions, eruption is believed to have occurred around AD 550. Although not ...
in Ecuador () is its farthest point out. Parallel to the rigid land topography the ocean exhibits a more dynamic topography.
To measure the local variation of Earth's topography, geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional spac ...
employs an idealized Earth producing a geoid shape. Such a shape is gained if the ocean is idealized, covering Earth completely and without any perturbations such as tides and winds. The result is a smooth but irregular geoid surface, providing a mean sea level as a reference level for topographic measurements.
Surface
 Earth's surface is the boundary between the atmosphere and the solid Earth and oceans. Defined in this way, it has an area of about . Earth can be divided into two hemispheres: by
Earth's surface is the boundary between the atmosphere and the solid Earth and oceans. Defined in this way, it has an area of about . Earth can be divided into two hemispheres: by latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
into the polar Northern and Southern hemispheres; or by longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
into the continental Eastern and Western hemispheres.
Most of Earth's surface is ocean water: 70.8% or . This vast pool of salty water is often called the ''world ocean'', and makes Earth with its dynamic hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to ch ...
a water world or ocean world. Indeed, in Earth's early history the ocean may have covered Earth completely. The world ocean is commonly divided into the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Antarctic or Southern Ocean, and Arctic Ocean, from largest to smallest. The ocean covers Earth's oceanic crust, with the shelf seas covering the shelves of the continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
to a lesser extent. The oceanic crust forms large oceanic basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, most of the ocean basins are large Structural basin, geologic basins that are below sea level.
Most commonly the ocea ...
s with features like abyssal plains, seamounts, submarine volcanoes, oceanic trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent, long, narrow topography, topographic depression (geology), depressions of the seabed, ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers ...
es, submarine canyons, oceanic plateaus, and a globe-spanning mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
system. At Earth's polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid geographical zone, zones or polar zones, of Earth are Earth's polar ice caps, the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North Pole, North and South Poles), lying within the pol ...
, the ocean surface is covered by seasonally variable amounts of sea ice that often connects with polar land, permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
and ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s, forming polar ice cap
A polar ice cap or polar cap is a high-latitude region of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite that is covered in ice.
There are no requirements with respect to size or composition for a body of ice to be termed a polar ice cap, nor a ...
s.
Earth's land covers 29.2%, or of Earth's surface. The land surface includes many islands around the globe, but most of the land surface is taken by the four continental landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land that is in one piece and not noticeably broken up by oceans. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the fiel ...
es, which are (in descending order): Africa-Eurasia, America (landmass), Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, and Australia (landmass). These landmasses are further broken down and grouped into the continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
s. The terrain
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientati ...
of the land surface varies greatly and consists of mountains, desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s, plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
s, plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
s, and other landform
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement ...
s. The elevation of the land surface varies from a low point of at the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valle ...
, to a maximum altitude of at the top of Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
. The mean height of land above sea level is about .
Land can be covered
Cover or covers may refer to:
Packaging
* Another name for a lid
* Cover (philately), generic term for envelope or package
* Album cover, the front of the packaging
* Book cover or magazine cover
** Book design
** Back cover copy, part of ...
by surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
, snow, ice, artificial structures or vegetation. Most of Earth's land hosts vegetation, but considerable amounts of land are ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacier, glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are the Antarctic ice sheet and the Greenland ice sheet. Ice s ...
s (10%, not including the equally large area of land under permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
) or desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
s (33%).
The pedosphere
The pedosphere () is the Earth's crust, outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. The ...
is the outermost layer of Earth's land surface and is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. Soil is crucial for land to be arable. Earth's total arable land is 10.7% of the land surface, with 1.3% being permanent cropland. Earth has an estimated of cropland and of pastureland.
The land surface and the ocean floor form the top of Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
, which together with parts of the upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (geology), crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle (Earth), lower man ...
form Earth's lithosphere. Earth's crust may be divided into oceanic and continental crust. Beneath the ocean-floor sediments, the oceanic crust is predominantly basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
ic, while the continental crust may include lower density materials such as granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
, sediments and metamorphic rocks. Nearly 75% of the continental surfaces are covered by sedimentary rocks, although they form about 5% of the mass of the crust.
Earth's surface topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
comprises both the topography of the ocean surface, and the shape
A shape is a graphics, graphical representation of an object's form or its external boundary, outline, or external Surface (mathematics), surface. It is distinct from other object properties, such as color, Surface texture, texture, or material ...
of Earth's land surface. The submarine terrain of the ocean floor has an average bathymetric depth of 4 km, and is as varied as the terrain above sea level. Earth's surface is continually being shaped by internal plate tectonic
Plate may refer to:
Cooking
* Plate (dishware), broad, mainly flat vessel commonly used to serve food
* Plates, tableware, dishes or dishware used for setting a table, serving food and dining
* Plate, the content of such a plate (for example: r ...
processes including earthquakes and volcanism; by weathering and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
driven by ice, water, wind and temperature; and by biological processes including the growth and decomposition of biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
into soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
.
Tectonic plates
Earth's mechanically rigid outer layer ofEarth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
and upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (geology), crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle (Earth), lower man ...
, the lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
, is divided into tectonic plates. These plates are rigid segments that move relative to each other at one of three boundaries types: at convergent boundaries, two plates come together; at divergent boundaries, two plates are pulled apart; and at transform boundaries, two plates slide past one another laterally. Along these plate boundaries, earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building
Mountain formation occurs due to a variety of geological processes associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust (List of tectonic plates, tectonic plates). Fold (geology), Folding, Fault (geology), faulting, Volcano, volcanic acti ...
, and oceanic trench
Oceanic trenches are prominent, long, narrow topography, topographic depression (geology), depressions of the seabed, ocean floor. They are typically wide and below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor, but can be thousands of kilometers ...
formation can occur. The tectonic plates ride on top of the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere i ...
, the solid but less-viscous part of the upper mantle that can flow and move along with the plates.
As the tectonic plates migrate, oceanic crust is subducted under the leading edges of the plates at convergent boundaries. At the same time, the upwelling of mantle material at divergent boundaries creates mid-ocean ridges. The combination of these processes recycles the oceanic crust back into the mantle. Due to this recycling, most of the ocean floor is less than old. The oldest oceanic crust is located in the Western Pacific and is estimated to be old. By comparison, the oldest dated continental crust is , although zircons have been found preserved as clasts within Eoarchean sedimentary rocks that give ages up to , indicating that at least some continental crust existed at that time.
The seven major plates are the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
, North American, Eurasian, African, Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
, Indo-Australian, and South American
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. Other notable plates include the Arabian Plate, the Caribbean Plate, the Nazca Plate
The Nazca plate or Nasca plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic list of tectonic plates, tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru– ...
off the west coast of South America and the Scotia Plate in the southern Atlantic Ocean. The Australian Plate fused with the Indian Plate between . The fastest-moving plates are the oceanic plates, with the Cocos Plate advancing at a rate of and the Pacific Plate moving . At the other extreme, the slowest-moving plate is the South American Plate, progressing at a typical rate of .
Internal structure
Earth's interior, like that of the other terrestrial planets, is divided into layers by theirchemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
or physical ( rheological) properties. The outer layer is a chemically distinct silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
solid crust, which is underlain by a highly viscous solid mantle. The crust is separated from the mantle by the Mohorovičić discontinuity. The thickness of the crust varies from about under the oceans to for the continents. The crust and the cold, rigid, top of the upper mantle
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (geology), crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle (Earth), lower man ...
are collectively known as the lithosphere, which is divided into independently moving tectonic plates.
Beneath the lithosphere is the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere i ...
, a relatively low-viscosity layer on which the lithosphere rides. Important changes in crystal structure within the mantle occur at below the surface, spanning a transition zone that separates the upper and lower mantle. Beneath the mantle, an extremely low viscosity liquid outer core lies above a solid inner core. Earth's inner core may be rotating at a slightly higher angular velocity
In physics, angular velocity (symbol or \vec, the lowercase Greek letter omega), also known as the angular frequency vector,(UP1) is a pseudovector representation of how the angular position or orientation of an object changes with time, i ...
than the remainder of the planet, advancing by 0.1–0.5° per year, although both somewhat higher and much lower rates have also been proposed. The radius of the inner core is about one-fifth of that of Earth. The density increases with depth. Among the Solar System's planetary-sized objects, Earth is the object with the highest density.
Chemical composition
Earth's mass is approximately (). It is composed mostly of iron (32.1% by mass),oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
(30.1%), silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
(15.1%), magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
(13.9%), sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
(2.9%), nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
(1.8%), calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
(1.5%), and aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
(1.4%), with the remaining 1.2% consisting of trace amounts of other elements. Due to gravitational separation, the core is primarily composed of the denser elements: iron (88.8%), with smaller amounts of nickel (5.8%), sulfur (4.5%), and less than 1% trace elements. The most common rock constituents of the crust are oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s. Over 99% of the crust is composed of various oxides of eleven elements, principally oxides containing silicon (the silicate mineral
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dio ...
s), aluminium, iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, or sodium.
Internal heat
 The major contributors to Earth's internal heat are primordial heat (heat left over from Earth's formation) and radiogenic heat (heat produced by radioactive decay). The major heat-producing
The major contributors to Earth's internal heat are primordial heat (heat left over from Earth's formation) and radiogenic heat (heat produced by radioactive decay). The major heat-producing isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s within Earth are potassium-40
Potassium-40 (K) is a long lived and the main naturally occurring radioactive isotope of potassium. Its half-life is 1.25 billion years. It makes up about 0.012% (120 parts-per notation, ppm) of natural potassium.
Potassium-40 undergoes four dif ...
, uranium-238, and thorium-232. At the center, the temperature may be up to , and the pressure could reach . Because much of the heat is provided by radioactive decay, scientists postulate that early in Earth's history, before isotopes with short half-lives were depleted, Earth's heat production was much higher. At approximately , twice the present-day heat would have been produced, increasing the rates of mantle convection and plate tectonics, and allowing the production of uncommon igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
s such as komatiites that are rarely formed today.
The mean heat loss from Earth is , for a global heat loss of . A portion of the core's thermal energy is transported toward the crust by mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic ho ...
s, a form of convection consisting of upwellings of higher-temperature rock. These plumes can produce hotspots and flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot (geolo ...
s. More of the heat in Earth is lost through plate tectonics, by mantle upwelling associated with mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
s. The final major mode of heat loss is through conduction through the lithosphere, the majority of which occurs under the oceans.
Gravitational field
The gravity of Earth is theacceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector ...
that is imparted to objects due to the distribution of mass within Earth. Near Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag (physics), drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by gravitational attraction. All bodi ...
is approximately . Local differences in topography, geology, and deeper tectonic structure cause local and broad regional differences in Earth's gravitational field, known as gravity anomalies.
Magnetic field
dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
* An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple ...
. The poles of the dipole are located close to Earth's geographic poles. At the equator of the magnetic field, the magnetic-field strength at the surface is , with a magnetic dipole moment of at epoch 2000, decreasing nearly 6% per century (although it still remains stronger than its long time average). The convection movements in the core are chaotic; the magnetic poles drift and periodically change alignment. This causes secular variation of the main field and field reversals at irregular intervals averaging a few times every million years. The most recent reversal occurred approximately 700,000 years ago.
The extent of Earth's magnetic field in space defines the magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
. Ions and electrons of the solar wind are deflected by the magnetosphere; solar wind pressure compresses the day-side of the magnetosphere, to about 10 Earth radii, and extends the night-side magnetosphere into a long tail. Because the velocity of the solar wind is greater than the speed at which waves propagate through the solar wind, a supersonic bow shock precedes the day-side magnetosphere within the solar wind. Charged particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. For example, some elementary particles, like the electron or quarks are charged. Some composite particles like protons are charged particles. An ion, such as a molecule or atom ...
s are contained within the magnetosphere; the plasmasphere is defined by low-energy particles that essentially follow magnetic field lines as Earth rotates. The ring current is defined by medium-energy particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
s that drift relative to the geomagnetic field, but with paths that are still dominated by the magnetic field, and the Van Allen radiation belts are formed by high-energy particles whose motion is essentially random, but contained in the magnetosphere. During magnetic storms and substorms, charged particles can be deflected from the outer magnetosphere and especially the magnetotail, directed along field lines into Earth's ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
, where atmospheric atoms can be excited and ionized, causing an aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
.
Orbit and rotation
Rotation
 Earth's rotation period relative to the Sun—its mean solar day—is of mean solar time (). Because Earth's solar day is now slightly longer than it was during the 19th century due to tidal deceleration, each day varies between longer than the mean solar day.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars, called its ''stellar day'' by the
Earth's rotation period relative to the Sun—its mean solar day—is of mean solar time (). Because Earth's solar day is now slightly longer than it was during the 19th century due to tidal deceleration, each day varies between longer than the mean solar day.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars, called its ''stellar day'' by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service
The International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS), formerly the International Earth Rotation Service, is the body responsible for maintaining global time and reference frame standards, notably through its Earth Orientation P ...
(IERS), is of mean solar time ( UT1), or Earth's rotation period relative to the precessing or moving mean March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the ver ...
(when the Sun is at 90° on the equator), is of mean solar time (UT1) . Thus the sidereal day is shorter than the stellar day by about 8.4 ms.
Apart from meteors within the atmosphere and low-orbiting satellites, the main apparent motion of celestial bodies in Earth's sky is to the west at a rate of 15°/h = 15'/min. For bodies near the celestial equator, this is equivalent to an apparent diameter of the Sun or the Moon every two minutes; from Earth's surface, the apparent sizes of the Sun and the Moon are approximately the same.
Orbit
astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its m ...
(AU) and is equal to roughly 8.3 light minutes or 380 times Earth's distance to the Moon. Earth orbits the Sun every 365.2564 mean solar days, or one sidereal year. With an apparent movement of the Sun in Earth's sky at a rate of about 1°/day eastward, which is one apparent Sun or Moon diameter every 12 hours. Due to this motion, on average it takes 24 hours—a solar day—for Earth to complete a full rotation about its axis so that the Sun returns to the meridian.
The orbital speed of Earth averages about , which is fast enough to travel a distance equal to Earth's diameter, about , in seven minutes, and the distance from Earth to the Moon, , in about 3.5 hours.
The Moon and Earth orbit a common barycenter every 27.32 days relative to the background stars. When combined with the Earth–Moon system's common orbit around the Sun, the period of the synodic month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive Syzygy (astronomy), syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month.
Variations
In Shona people, S ...
, from new moon to new moon, is 29.53 days. Viewed from the celestial north pole, the motion of Earth, the Moon, and their axial rotations are all counterclockwise. Viewed from a vantage point above the Sun and Earth's north poles, Earth orbits in a counterclockwise direction about the Sun. The orbital and axial planes are not precisely aligned: Earth's axis is tilted some 23.44 degrees from the perpendicular to the Earth–Sun plane (the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making.
Fr ...
), and the Earth-Moon plane is tilted up to ±5.1 degrees against the Earth–Sun plane. Without this tilt, there would be an eclipse every two weeks, alternating between lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, ...
s and solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
s.
The Hill sphere
The Hill sphere is a common model for the calculation of a Sphere of influence (astrodynamics), gravitational sphere of influence. It is the most commonly used model to calculate the spatial extent of gravitational influence of an astronomical ...
, or the sphere of gravitational influence, of Earth is about in radius. This is the maximum distance at which Earth's gravitational influence is stronger than that of the more distant Sun and planets. Objects must orbit Earth within this radius, or they can become unbound by the gravitational perturbation of the Sun. Earth, along with the Solar System, is situated in the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
and orbits about 28,000 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astr ...
s from its center. It is about 20 light-years above the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
in the Orion Arm.
Axial tilt and seasons
The axial tilt of Earth is approximately 23.439281° with the axis of the plane of theEarth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an astronomical unit, average distance of , or 8.317 light-second, light-minutes, in a retrograde and prograde motion, counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes & ...
by definition pointing always towards the Celestial Poles
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's rotation around a fixed axis, axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently dire ...
. Due to Earth's axial tilt, the amount of sunlight reaching any given point on the surface varies over the course of the year. This causes the seasonal change in climate, with summer in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
occurring when the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also known as the Northern Tropic, is the Earth's northernmost circle of latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun ...
is facing the Sun, and in the Southern Hemisphere when the Tropic of Capricorn faces the Sun. In each instance, winter occurs simultaneously in the opposite hemisphere.
During the summer, the day lasts longer, and the Sun climbs higher in the sky. In winter, the climate becomes cooler and the days shorter. Above the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
and below the Antarctic Circle there is no daylight at all for part of the year, causing a polar night
Polar night is a phenomenon that occurs in the polar regions of Earth, northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth when the Sun remains below the horizon for more than 24 hours. This only occurs inside the polar circles. The opposite phen ...
, and this night extends for several months at the poles themselves. These same latitudes also experience a midnight sun
Midnight sun, also known as polar day, is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the Sun remains visible at the local midnight. When midnight sun is see ...
, where the sun remains visible all day.
By astronomical convention, the four seasons can be determined by the solstices—the points in the orbit of maximum axial tilt toward or away from the Sun—and the equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun appears directly above the equator, rather than to its north or south. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise directly east and set directly west. This occurs twice each year, arou ...
es, when Earth's rotational axis is aligned with its orbital axis. In the Northern Hemisphere, winter solstice
The winter solstice, or hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's geographical pole, poles reaches its maximum axial tilt, tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern Hemisphere, Northern and So ...
currently occurs around 21 December; summer solstice
The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere ( Northern and Southern). The summer solstice is the day with the longest peri ...
is near 21 June, spring equinox is around 20 March and autumnal equinox is about 22 or 23 September. In the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is reversed, with the summer and winter solstices exchanged and the spring and autumnal equinox dates swapped.
The angle of Earth's axial tilt is relatively stable over long periods of time. Its axial tilt does undergo nutation; a slight, irregular motion with a main period of 18.6 years. The orientation (rather than the angle) of Earth's axis also changes over time, precessing around in a complete circle over each 25,800-year cycle; this precession is the reason for the difference between a sidereal year and a tropical year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky – as viewed from the Earth or another celestial body of the Solar System – thus completing a full cycle of astronom ...
. Both of these motions are caused by the varying attraction of the Sun and the Moon on Earth's equatorial bulge. The poles also migrate a few meters across Earth's surface. This polar motion
Polar motion of the Earth is the motion of the Earth's rotation, Earth's rotational axis relative to its Earth's crust, crust. This is measured with respect to a reference frame in which the solid Earth is fixed (a so-called ''Earth-centered, Ea ...
has multiple, cyclical components, which collectively are termed quasiperiodic motion. In addition to an annual component to this motion, there is a 14-month cycle called the Chandler wobble. Earth's rotational velocity also varies in a phenomenon known as length-of-day variation.
Earth's annual orbit is elliptical rather than circular, and its closest approach to the Sun is called perihelion. In modern times, Earth's perihelion occurs around 3 January, and its aphelion around 4 July. These dates shift over time due to precession and changes to the orbit, the latter of which follows cyclical patterns known as Milankovitch cycles. The annual change in the Earth–Sun distance causes an increase of about 6.8% in solar energy reaching Earth at perihelion relative to aphelion. Because the Southern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun at about the same time that Earth reaches the closest approach to the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere receives slightly more energy from the Sun than does the northern over the course of a year. This effect is much less significant than the total energy change due to the axial tilt, and most of the excess energy is absorbed by the higher proportion of water in the Southern Hemisphere.
Earth–Moon system
Moon
 The Moon is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, although Charon is larger relative to the
The Moon is a relatively large, terrestrial, planet-like natural satellite, with a diameter about one-quarter of Earth's. It is the largest moon in the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, although Charon is larger relative to the dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Su ...
. The natural satellites of other planets are also referred to as "moons", after Earth's. The most widely accepted theory of the Moon's origin, the giant-impact hypothesis, states that it formed from the collision of a Mars-size protoplanet called Theia with the early Earth. This hypothesis explains the Moon's relative lack of iron and volatile elements and the fact that its composition is nearly identical to that of Earth's crust. Computer simulations suggest that two blob-like remnants of this protoplanet could be inside the Earth.
The gravitational attraction between Earth and the Moon causes lunar tides on Earth. The same effect on the Moon has led to its tidal locking
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical body, astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where ...
: its rotation period is the same as the time it takes to orbit Earth. As a result, it always presents the same face to the planet. As the Moon orbits Earth, different parts of its face are illuminated by the Sun, leading to the lunar phase
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is tidally locked with the Earth, the same hemisphere is always facing the Earth. In common usage, the four maj ...
s. Due to their tidal interaction, the Moon recedes from Earth at the rate of approximately . Over millions of years, these tiny modifications—and the lengthening of Earth's day by about 23 μs/yr—add up to significant changes. During the Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
period, for example, (approximately ) there were 400±7 days in a year, with each day lasting 21.9±0.4 hours.
The Moon may have dramatically affected the development of life by moderating the planet's climate. Paleontological evidence and computer simulations show that Earth's axial tilt is stabilized by tidal interactions with the Moon. Some theorists think that without this stabilization against the torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
s applied by the Sun and planets to Earth's equatorial bulge, the rotational axis might be chaotically unstable, exhibiting large changes over millions of years, as is the case for Mars, though this is disputed.
Viewed from Earth, the Moon is just far enough away to have almost the same apparent-sized disk as the Sun. The angular size (or solid angle) of these two bodies match because, although the Sun's diameter is about 400 times as large as the Moon's, it is also 400 times more distant. This allows total and annular solar eclipses to occur on Earth.
Asteroids and artificial satellites
 Earth's co-orbital asteroids population consists of quasi-satellites, objects with a horseshoe orbit and trojans. There are at least seven quasi-satellites, including 469219 Kamoʻoalewa, ranging in diameter from 10 m to 5000 m. A trojan asteroid companion, , is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in
Earth's co-orbital asteroids population consists of quasi-satellites, objects with a horseshoe orbit and trojans. There are at least seven quasi-satellites, including 469219 Kamoʻoalewa, ranging in diameter from 10 m to 5000 m. A trojan asteroid companion, , is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in Earth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an astronomical unit, average distance of , or 8.317 light-second, light-minutes, in a retrograde and prograde motion, counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes & ...
around the Sun. The tiny near-Earth asteroid makes close approaches to the Earth–Moon system roughly every twenty years. During these approaches, it can orbit Earth for brief periods of time.
, there are 4,550 operational, human-made satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
s orbiting Earth. There are also inoperative satellites, including Vanguard 1, the oldest satellite currently in orbit, and over 16,000 pieces of tracked space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include dere ...
. Earth's largest artificial satellite is the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS).
Hydrosphere
 Earth's hydrosphere is the sum of Earth's water and its distribution. Most of Earth's hydrosphere consists of Earth's global ocean. Earth's hydrosphere also consists of water in the atmosphere and on land, including clouds, inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground waters. The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons or about 1/4400 of Earth's total mass. The oceans cover an area of with a mean depth of , resulting in an estimated volume of .
If all of Earth's crustal surface were at the same elevation as a smooth sphere, the depth of the resulting world ocean would be . About 97.5% of the water is saline; the remaining 2.5% is
Earth's hydrosphere is the sum of Earth's water and its distribution. Most of Earth's hydrosphere consists of Earth's global ocean. Earth's hydrosphere also consists of water in the atmosphere and on land, including clouds, inland seas, lakes, rivers, and underground waters. The mass of the oceans is approximately 1.35 metric tons or about 1/4400 of Earth's total mass. The oceans cover an area of with a mean depth of , resulting in an estimated volume of .
If all of Earth's crustal surface were at the same elevation as a smooth sphere, the depth of the resulting world ocean would be . About 97.5% of the water is saline; the remaining 2.5% is fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
. Most fresh water, about 68.7%, is present as ice in ice caps and glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s. The remaining 30% is ground water, 1% surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
(covering only 2.8% of Earth's land) and other small forms of fresh water deposits such as permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
, water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
in the atmosphere, biological binding, etc.
In Earth's coldest regions, snow survives over the summer and changes into ice. This accumulated snow and ice eventually forms into glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s, bodies of ice that flow under the influence of their own gravity. Alpine glaciers form in mountainous areas, whereas vast ice sheets form over land in polar regions. The flow of glaciers erodes the surface, changing it dramatically, with the formation of U-shaped valleys and other landforms. Sea ice in the Arctic covers an area about as big as the United States, although it is quickly retreating as a consequence of climate change.
The average salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
of Earth's oceans is about 35 grams of salt per kilogram of seawater (3.5% salt). Most of this salt was released from volcanic activity or extracted from cool igneous rocks. The oceans are also a reservoir of dissolved atmospheric gases, which are essential for the survival of many aquatic life forms. Sea water has an important influence on the world's climate, with the oceans acting as a large heat reservoir
A thermal reservoir, also thermal energy reservoir or thermal bath, is a thermodynamic system with a heat capacity so large that the temperature of the reservoir changes relatively little when a significant amount of heat is added or extracted. ...
. Shifts in the oceanic temperature distribution can cause significant weather shifts, such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation.
The abundance of water, particularly liquid water, on Earth's surface is a unique feature that distinguishes it from other planets in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. Solar System planets with considerable atmospheres do partly host atmospheric water vapor, but they lack surface conditions for stable surface water. Despite some moons showing signs of large reservoirs of extraterrestrial liquid water, with possibly even more volume than Earth's ocean, all of them are large bodies of water under a kilometers thick frozen surface layer.
Atmosphere
 The
The atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013. ...
at Earth's sea level averages , with a scale height of about . A dry atmosphere is composed of 78.084% nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, 20.946% oxygen, 0.934% argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
, and trace amounts of carbon dioxide and other gaseous molecules. Water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
content varies between 0.01% and 4% but averages about 1%. Clouds cover around two-thirds of Earth's surface, more so over oceans than land. The height of the troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the ...
varies with latitude, ranging between at the poles to at the equator, with some variation resulting from weather and seasonal factors.
Earth's biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
has significantly altered its atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
. Oxygenic photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metaboli ...
evolved , forming the primarily nitrogen–oxygen atmosphere of today. This change enabled the proliferation of aerobic organisms and, indirectly, the formation of the ozone layer due to the subsequent conversion of atmospheric into . The ozone layer blocks ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
solar radiation
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically p ...
, permitting life on land. Other atmospheric functions important to life include transporting water vapor, providing useful gases, causing small meteors to burn up before they strike the surface, and moderating temperature. This last phenomenon is the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
: trace molecules within the atmosphere serve to capture thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including:
* Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential en ...
emitted from the surface, thereby raising the average temperature. Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
, nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
, and ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
are the primary greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Without this heat-retention effect, the average surface temperature would be , in contrast to the current , and life on Earth probably would not exist in its current form.
Weather and climate
Earth's atmosphere has no definite boundary, gradually becoming thinner and fading into outer space. Three-quarters of the atmosphere's mass is contained within the first of the surface; this lowest layer is called the troposphere. Energy from the Sun heats this layer, and the surface below, causing expansion of the air. This lower-density air then rises and is replaced by cooler, higher-density air. The result isatmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies fro ...
that drives the weather and climate through redistribution of thermal energy.
The primary atmospheric circulation bands consist of the trade winds in the equatorial region below 30° latitude and the westerlies in the mid-latitudes between 30° and 60°. Ocean heat content and currents are also important factors in determining climate, particularly the thermohaline circulation that distributes thermal energy from the equatorial oceans to the polar regions.
Earth receives 1361 W/m2 of solar irradiance. The amount of solar energy that reaches Earth's surface decreases with increasing latitude. At higher latitudes, the sunlight reaches the surface at lower angles, and it must pass through thicker columns of the atmosphere. As a result, the mean annual air temperature at sea level decreases by about per degree of latitude from the equator. Earth's surface can be subdivided into specific latitudinal belts of approximately homogeneous climate. Ranging from the equator to the polar regions, these are the tropical (or equatorial), subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
, temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
and polar climates.
Further factors that affect a location's climates are its proximity to oceans, the oceanic and atmospheric circulation, and topology. Places close to oceans typically have colder summers and warmer winters, due to the fact that oceans can store large amounts of heat. The wind transports the cold or the heat of the ocean to the land. Atmospheric circulation also plays an important role: San Francisco and Washington DC are both coastal cities at about the same latitude. San Francisco's climate is significantly more moderate as the prevailing wind direction is from sea to land. Finally, temperatures decrease with height causing mountainous areas to be colder than low-lying areas.
Water vapor generated through surface evaporation is transported by circulatory patterns in the atmosphere. When atmospheric conditions permit an uplift of warm, humid air, this water condenses and falls to the surface as precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
. Most of the water is then transported to lower elevations by river systems and usually returned to the oceans or deposited into lakes. This water cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
is a vital mechanism for supporting life on land and is a primary factor in the erosion of surface features over geological periods. Precipitation patterns vary widely, ranging from several meters of water per year to less than a millimeter. Atmospheric circulation, topographic features, and temperature differences determine the average precipitation that falls in each region.
The commonly used Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
system has five broad groups ( humid tropics, arid, humid middle latitudes, continental and cold polar), which are further divided into more specific subtypes. The Köppen system rates regions based on observed temperature and precipitation. Surface air temperature can rise to around in hot deserts, such as Death Valley
Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the Highest temperature recorded on Earth, hottest place on Earth during summer.
Death Valley's Badwat ...
, and can fall as low as in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
.
Upper atmosphere
 The upper atmosphere, the atmosphere above the troposphere, is usually divided into the
The upper atmosphere, the atmosphere above the troposphere, is usually divided into the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
, mesosphere, and thermosphere. Each layer has a different lapse rate, defining the rate of change in temperature with height. Beyond these, the exosphere
The exosphere is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the density is so low that the molecules are essentially collision-less. In the case of ...
thins out into the magnetosphere, where the geomagnetic fields interact with the solar wind. Within the stratosphere is the ozone layer, a component that partially shields the surface from ultraviolet light and thus is important for life on Earth. The Kármán line, defined as above Earth's surface, is a working definition for the boundary between the atmosphere and outer space.
Thermal energy causes some of the molecules at the outer edge of the atmosphere to increase their velocity to the point where they can escape from Earth's gravity. This causes a slow but steady loss of the atmosphere into space. Because unfixed hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
has a low molecular mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quan ...
, it can achieve escape velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape from contact with or orbit of a primary body, assuming:
* Ballistic trajectory – no other forces are acting on the object, such as ...
more readily, and it leaks into outer space at a greater rate than other gases. The leakage of hydrogen into space contributes to the shifting of Earth's atmosphere and surface from an initially reducing state to its current oxidizing one. Photosynthesis provided a source of free oxygen, but the loss of reducing agents such as hydrogen is thought to have been a necessary precondition for the widespread accumulation of oxygen in the atmosphere. Hence the ability of hydrogen to escape from the atmosphere may have influenced the nature of life that developed on Earth. In the current, oxygen-rich atmosphere most hydrogen is converted into water before it has an opportunity to escape. Instead, most of the hydrogen loss comes from the destruction of methane in the upper atmosphere.
Life on Earth
 Earth is the only known place that has ever been habitable for life. Earth's life developed in Earth's early bodies of water some hundred million years after Earth formed. Earth's life has been shaping and inhabiting many particular
Earth is the only known place that has ever been habitable for life. Earth's life developed in Earth's early bodies of water some hundred million years after Earth formed. Earth's life has been shaping and inhabiting many particular ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s on Earth and has eventually expanded globally forming an overarching biosphere.
Therefore, life has impacted Earth, significantly altering Earth's atmosphere and surface over long periods of time, causing changes like the Great Oxidation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE) or Great Oxygenation Event, also called the Oxygen Catastrophe, Oxygen Revolution, Oxygen Crisis or Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Earth's Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere an ...
. Earth's life has also over time greatly diversified, allowing the biosphere to have different biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s, which are inhabited by comparatively similar plants and animals. The different biomes developed at distinct elevations or water depths, planetary temperature latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s and on land also with different humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
. Earth's species diversity and biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
reaches a peak in shallow waters and with forests, particularly in equatorial, warm and humid conditions. While freezing polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid geographical zone, zones or polar zones, of Earth are Earth's polar ice caps, the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North Pole, North and South Poles), lying within the pol ...
and high altitudes, or extremely arid areas are relatively barren of plant and animal life.
Earth provides liquid water—an environment where complex organic molecules can assemble and interact, and sufficient energy to sustain a metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. Plants and other organisms take up nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s from water, soils and the atmosphere. These nutrients are constantly recycled between different species.
Extreme weather
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual, severe weather, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weat ...
, such as tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s (including hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
s and typhoon
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for a ...
s), occurs over most of Earth's surface and has a large impact on life in those areas. From 1980 to 2000, these events caused an average of 11,800 human deaths per year. Many places are subject to earthquakes, landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides ...
s, tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
s, volcanic eruptions, tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the ...
es, blizzard
A blizzard is a severe Winter storm, snowstorm characterized by strong sustained winds and low visibility, lasting for a prolonged period of time—typically at least three or four hours. A ground blizzard is a weather condition where snow th ...
s, floods, droughts, wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, or a bushfire is an unplanned and uncontrolled fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a ...
s, and other calamities and disasters. Human impact is felt in many areas due to pollution of the air and water, acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists b ...
, loss of vegetation ( overgrazing, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
), loss of wildlife, species extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
, soil degradation, soil depletion and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
. Human activities release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere which cause global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
. This is driving changes such as the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, a global rise in average sea levels, increased risk of drought and wildfires, and migration of species to colder areas.
Human geography
 Originating from earlier
Originating from earlier primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s in Eastern Africa 300,000years ago humans have since been migrating and with the advent of agriculture in the 10th millennium BC increasingly settling
Settling is the process by which particulates move towards the bottom of a liquid and form a sediment. Particles that experience a force, either due to gravity or due to Centrifuge, centrifugal motion will tend to move in a uniform manner in the ...
Earth's land. In the 20th century Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
had been the last continent to see a first and until today limited human presence.
Human population has since the 19th century grown exponentially to seven billion in the early 2010s, and is projected to peak at around ten billion in the second half of the 21st century. Most of the growth is expected to take place in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
.
Distribution and density of human population varies greatly around the world with the majority living in south to eastern Asia and 90% inhabiting only the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
of Earth, partly due to the hemispherical predominance of the world's land mass, with 68% of the world's land mass being in the Northern Hemisphere. Furthermore, since the 19th century humans have increasingly converged into urban areas with the majority living in urban areas by the 21st century.
Beyond Earth's surface humans have lived on a temporary basis, with only a few special-purpose deep underground and underwater presences and a few space station
A space station (or orbital station) is a spacecraft which remains orbital spaceflight, in orbit and human spaceflight, hosts humans for extended periods of time. It therefore is an artificial satellite featuring space habitat (facility), habitat ...
s. The human population virtually completely remains on Earth's surface, fully depending on Earth and the environment it sustains. Since the second half of the 20th century, some hundreds of humans have temporarily stayed beyond Earth, a tiny fraction of whom have reached another celestial body, the Moon.
Earth has been subject to extensive human settlement, and humans have developed diverse societies and cultures. Most of Earth's land has been territorially claimed since the 19th century by sovereign state
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
s (countries) separated by political borders, and 205 such states exist today, with only parts of Antarctica and a few small regions remaining unclaimed. Most of these states together form the United Nations, the leading worldwide intergovernmental organization
Globalization is social change associated with increased connectivity among societies and their elements and the explosive evolution of transportation and telecommunication technologies to facilitate international cultural and economic exchange. ...
, which extends human governance over the ocean and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, and therefore all of Earth.
Natural resources and land use
Earth has resources that have been exploited by humans. Those termed non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, are only replenished over geological timescales. Large deposits of fossil fuels are obtained from Earth's crust, consisting of coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These deposits are used by humans both for energy production and as feedstock for chemical production. Mineral ore bodies have also been formed within the crust through a process of ore genesis, resulting from actions of magmatism, erosion, and plate tectonics. These metals and other elements are extracted by mining, a process which often brings environmental and health damage. Earth's biosphere produces many useful biological products for humans, including food, wood, pharmaceuticals, oxygen, and the recycling of organic waste. The land-based ecosystem depends upontopsoil
Topsoil is the upper layer of soil. It has the highest concentration of organic matter and microorganisms and is where most of the Earth's biological soil activity occurs.
Description
Topsoil is composed of mineral particles and organic mat ...
and fresh water, and the oceanic ecosystem depends on dissolved nutrients washed down from the land. In 2019, of Earth's land surface consisted of forest and woodlands, was shrub and grassland, were used for animal feed production and grazing, and were cultivated as croplands. Of the 1214% of ice-free land that is used for croplands, 2 percentage point
A percentage point or percent point is the unit (measurement), unit for the difference (mathematics), arithmetic difference between two percentages. For example, moving up from 40 percent to 44 percent is an increase of 4 percentage points (altho ...
s were irrigated in 2015. Humans use building materials to construct shelters.
Humans and the environment
greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
es in the atmosphere, altering Earth's energy budget and climate. It is estimated that global temperatures in the year 2020 were warmer than the preindustrial baseline. This increase in temperature, known as global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
, has contributed to the melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, increased risk of drought and wildfires, and migration of species to colder areas.
The concept of planetary boundaries was introduced to quantify humanity's impact on Earth. Of the nine identified boundaries, five have been crossed: Biosphere integrity, climate change, chemical pollution, destruction of wild habitats and the nitrogen cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, atmospheric, terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can ...
are thought to have passed the safe threshold. As of 2018, no country meets the basic needs of its population without transgressing planetary boundaries. It is thought possible to provide all basic physical needs globally within sustainable levels of resource use.
Cultural and historical viewpoint
 Human cultures have developed many views of the planet. The standard astronomical symbols of Earth are a quartered circle, , representing the four corners of the world, and a
Human cultures have developed many views of the planet. The standard astronomical symbols of Earth are a quartered circle, , representing the four corners of the world, and a globus cruciger
The for, la, globus cruciger, cross-bearing orb, also known as ''stavroforos sphaira'' () or "the orb and cross", is an Sphere, orb surmounted by a Christian cross, cross. It has been a Christian Church, Christian symbol of authority since the M ...
, . Earth is sometimes personified as a deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
. In many cultures it is a mother goddess that is also the primary fertility deity. Creation myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Cre ...
s in many religions involve the creation of Earth by a supernatural deity or deities. The Gaia hypothesis
The Gaia hypothesis (), also known as the Gaia theory, Gaia paradigm, or the Gaia principle, proposes that living organisms interact with their Inorganic compound, inorganic surroundings on Earth to form a Synergy, synergistic and Homeostasis, s ...
, developed in the mid-20th century, compared Earth's environments and life as a single self-regulating organism leading to broad stabilization of the conditions of habitability.
Images of Earth taken from space, particularly during the Apollo program, have been credited with altering the way that people viewed the planet that they lived on, called the overview effect, emphasizing its beauty, uniqueness and apparent fragility. In particular, this caused a realization of the scope of effects from human activity on Earth's environment. Enabled by science, particularly Earth observation
Earth observation (EO) is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biosphere, biological systems of the planet Earth. It can be performed via remote sensing, remote-sensing technologies (Earth observation satellites) or throu ...
, humans have started to take action on environmental issues globally, acknowledging the impact of humans and the interconnectedness of Earth's environments.
Scientific investigation has resulted in several culturally transformative shifts in people's view of the planet. Initial belief in a flat Earth was gradually displaced in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
by the idea of a spherical Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Ancient Greek philos ...
, which was attributed to both the philosophers Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
and Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; ; fl. late sixth or early fifth century BC) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic ancient Greece, Greek philosopher from Velia, Elea in Magna Graecia (Southern Italy).
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Veli ...
. Earth was generally believed to be the center of the universe until the 16th century, when scientists first concluded that it was a moving object, one of the planets of the Solar System.
It was only during the 19th century that geologists realized Earth's age was at least many millions of years. Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (26 June 182417 December 1907), was a British mathematician, Mathematical physics, mathematical physicist and engineer. Born in Belfast, he was the Professor of Natural Philosophy (Glasgow), professor of Natur ...
used thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
to estimate the age of Earth to be between 20 million and 400 million years in 1864, sparking a vigorous debate on the subject; it was only when radioactivity and radioactive dating were discovered in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that a reliable mechanism for determining Earth's age was established, proving the planet to be billions of years old.
See also
Notes
References
External links
Earth – Profile
– Solar System Exploration –
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
Earth Observatory
– NASA * Earth – Videos – International Space Station: *
Video (01:02)
on YouTube – Earth (time-lapse) *
Video (00:27)
on YouTube – Earth and
aurora
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
s (time-lapse)
Google Earth 3D
interactive map
Interactive 3D visualization of the Sun, Earth and Moon system
GPlates Portal
(University of Sydney) {{Subject bar, wikt=Earth, q=Earth, m=Earth, n=Earth, v=Earth, s=Earth, b=Earth, commons=Earth, portal1=Biology, portal2=Earth sciences, portal3=Ecology, portal4=Geography, portal5=Volcanoes, portal6=Solar system, portal7=Outer space, portal8=Weather, portal9=World Astronomical objects known since antiquity Global natural environment Nature Planets of the Solar System Solar System Terrestrial planets