supraglottic airway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Airway management includes a set of maneuvers and medical procedures performed to prevent and relieve



 Prevention techniques focus on preventing airway obstruction by the tongue and reducing the likelihood of aspiration of stomach contents or blood. The head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are useful for the former while the recovery position is useful for the latter. If head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are performed with any objects in the airways it may dislodge them further down the airways and thereby cause more blockage and harder removal.
The head-tilt/chin-lift is the primary maneuver used in any patient in whom
Prevention techniques focus on preventing airway obstruction by the tongue and reducing the likelihood of aspiration of stomach contents or blood. The head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are useful for the former while the recovery position is useful for the latter. If head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are performed with any objects in the airways it may dislodge them further down the airways and thereby cause more blockage and harder removal.
The head-tilt/chin-lift is the primary maneuver used in any patient in whom  The jaw-thrust maneuver is an effective airway technique, particularly in the patient in whom cervical spine injury is a concern. It is easiest when the patient is positioned
The jaw-thrust maneuver is an effective airway technique, particularly in the patient in whom cervical spine injury is a concern. It is easiest when the patient is positioned
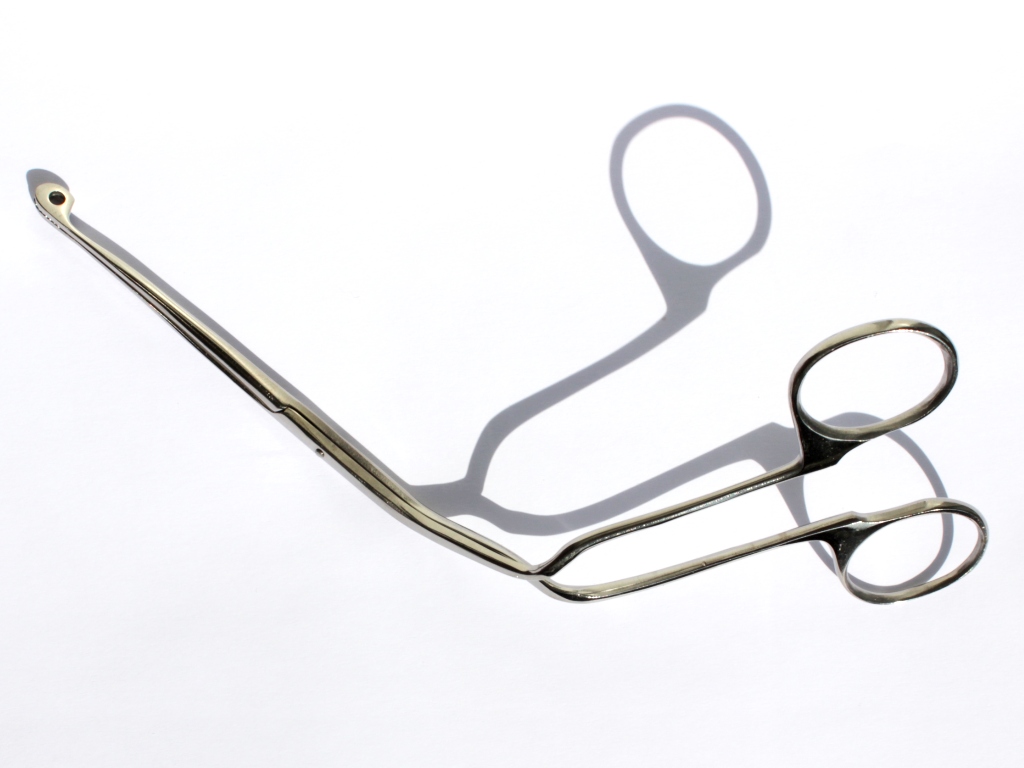 The ingestion and aspiration of foreign objects pose a common and dangerous problem in young children. It remains one of the leading cause of death in children under the age of 5. Common food items (baby carrots, peanuts, etc.) and household objects (coins, metals, etc.) may lodge in various levels of the airway tract and cause significant obstruction of the airway. Complete obstruction of the airway represents a
The ingestion and aspiration of foreign objects pose a common and dangerous problem in young children. It remains one of the leading cause of death in children under the age of 5. Common food items (baby carrots, peanuts, etc.) and household objects (coins, metals, etc.) may lodge in various levels of the airway tract and cause significant obstruction of the airway. Complete obstruction of the airway represents a
 ''Oropharyngeal airways'' are curved, rigid plastic devices, inserted into the patient's mouth. Oropharyngeal airways are produced in various lengths and diameters to accommodate for gender and anatomical variations. It is especially useful in patients with excessive tongue and other soft tissues. OPAs prevent airway obstruction by ensuring that the patient's
''Oropharyngeal airways'' are curved, rigid plastic devices, inserted into the patient's mouth. Oropharyngeal airways are produced in various lengths and diameters to accommodate for gender and anatomical variations. It is especially useful in patients with excessive tongue and other soft tissues. OPAs prevent airway obstruction by ensuring that the patient's
 In contrast to supraglottic devices, infraglottic devices create a conduit between the mouth, passing through the glottis, and into the trachea. There are many infraglottic methods available and the chosen technique is reliant on the accessibility of medical equipment, competence of the clinician and the patient's injury or disease.
In contrast to supraglottic devices, infraglottic devices create a conduit between the mouth, passing through the glottis, and into the trachea. There are many infraglottic methods available and the chosen technique is reliant on the accessibility of medical equipment, competence of the clinician and the patient's injury or disease.
 Surgical methods for airway management rely on making a surgical incision below the glottis in order to achieve direct access to the
Surgical methods for airway management rely on making a surgical incision below the glottis in order to achieve direct access to the
 Airway represents the "A" in the ABC mnemonic for trauma resuscitation.
Management of the airway in trauma can be particularly complicated, and is dependent on the mechanism, location, and severity of injury to the airway and its surrounding tissues. Injuries to the cervical spine, traumatic disruption of the airway itself, edema in the setting of caustic or thermal trauma, and the combative patient are examples of scenarios a provider may need to take into account in assessing the urgency of securing an airway and the means of doing so.
The pre-hospital setting provides unique challenges to management of the airway including tight spaces, neck immobilization, poor lighting, and often the added complexity of attempting procedures during transport. When possible, basic airway management should be prioritized including head-tilt-chin-lift maneuvers, and bag-valve masking. If ineffective, a supraglottic airway can be utilized to aid in oxygenation and maintenance of a patent airway. An oropharyngeal airway is acceptable, however nasopharyngeal airways should be avoided in trauma, particularly if a
Airway represents the "A" in the ABC mnemonic for trauma resuscitation.
Management of the airway in trauma can be particularly complicated, and is dependent on the mechanism, location, and severity of injury to the airway and its surrounding tissues. Injuries to the cervical spine, traumatic disruption of the airway itself, edema in the setting of caustic or thermal trauma, and the combative patient are examples of scenarios a provider may need to take into account in assessing the urgency of securing an airway and the means of doing so.
The pre-hospital setting provides unique challenges to management of the airway including tight spaces, neck immobilization, poor lighting, and often the added complexity of attempting procedures during transport. When possible, basic airway management should be prioritized including head-tilt-chin-lift maneuvers, and bag-valve masking. If ineffective, a supraglottic airway can be utilized to aid in oxygenation and maintenance of a patent airway. An oropharyngeal airway is acceptable, however nasopharyngeal airways should be avoided in trauma, particularly if a 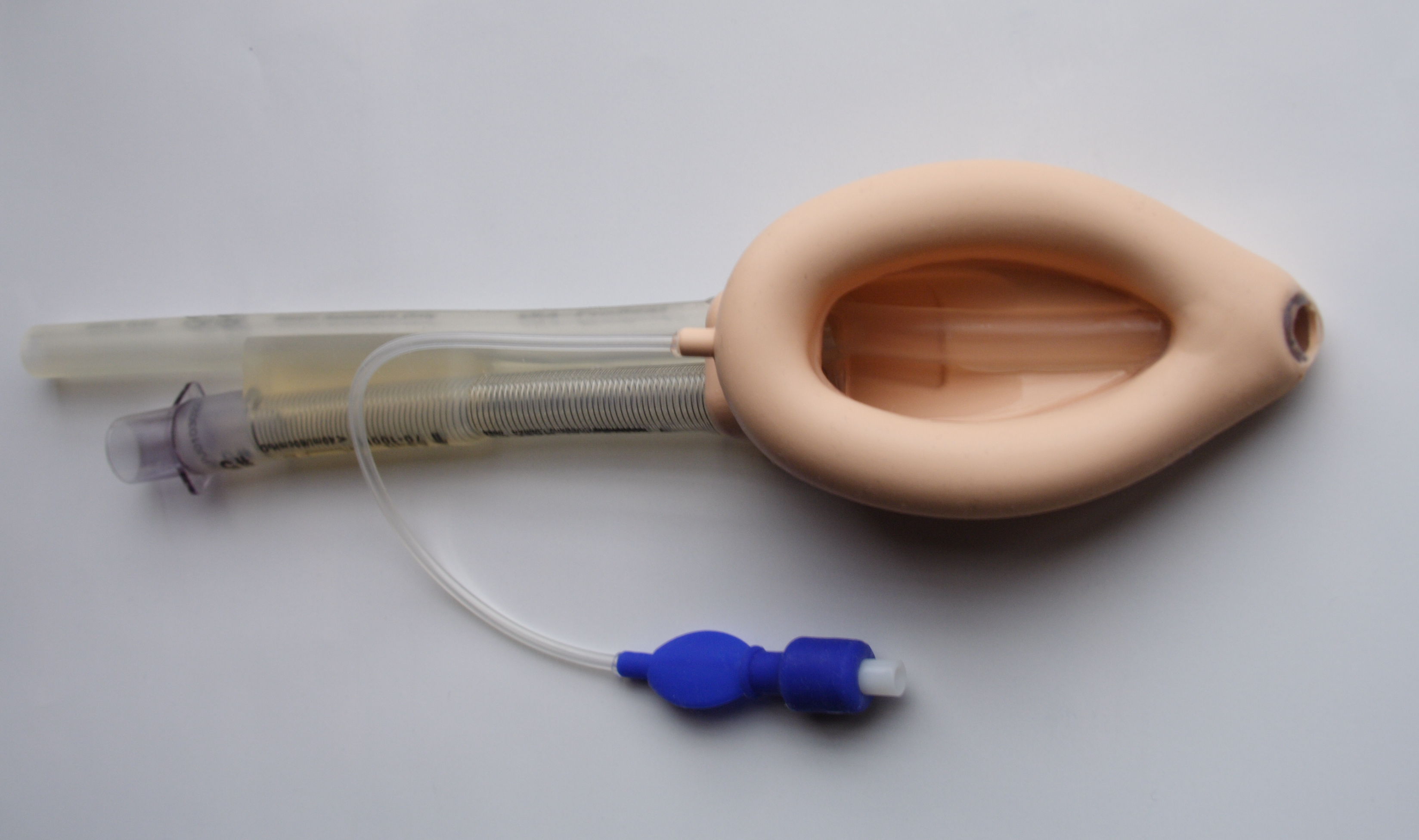 Management of the airway in the emergency department is optimal given the presence of trained personnel from multiple specialties, as well as access to "difficult airway equipment" ( videolaryngoscopy, eschmann tracheal tube introducer, fiberoptic bronchoscopy, surgical methods, etc.). Of primary concern is the condition and patency of the maxillofacial structures, larynx,
Management of the airway in the emergency department is optimal given the presence of trained personnel from multiple specialties, as well as access to "difficult airway equipment" ( videolaryngoscopy, eschmann tracheal tube introducer, fiberoptic bronchoscopy, surgical methods, etc.). Of primary concern is the condition and patency of the maxillofacial structures, larynx,
airway obstruction
Airway obstruction is a blockage of respiration in the airway that hinders the free flow of air. It can be broadly classified into being either in the upper airway (UPA) or lower airway (LOA).
Airway obstruction is a life-threatening condition ...
. This ensures an open pathway for gas exchange between a patient's lungs and the atmosphere. This is accomplished by either clearing a previously obstructed airway; or by preventing airway obstruction in cases such as anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the foll ...
, the obtunded patient, or medical sedation. Airway obstruction can be caused by the tongue, foreign objects, the tissues of the airway itself, and bodily fluids such as blood and gastric contents ( aspiration).
Airway management is commonly divided into two categories: basic and advanced.
Basic techniques are generally non-invasive and do not require specialized medical equipment or advanced training. These include head and neck maneuvers to optimize ventilation, abdominal thrusts
Abdominal thrusts, also known as the Heimlich maneuver or Heimlich manoeuvre, is a first aid procedure used to treat upper airway obstructions (or choking) by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its creation. ...
, and back blows.
Advanced techniques require specialized medical training and equipment, and are further categorized anatomically into supraglottic devices (such as oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
and nasopharyngeal airway
In medicine, a nasopharyngeal airway, also known as an NPA, nasal trumpet (because of its flared end), or nose hose, is a type of ''airway adjunct'', a tube that is designed to be inserted through the nasal passage down into the posterior pharynx ...
s), infraglottic techniques (such as tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
), and surgical methods (such as cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, o ...
and tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The r ...
).
Airway management is a primary consideration in the fields of cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spon ...
, anaesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), a ...
, emergency medicine, intensive care medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
, neonatology, and first aid
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with either a minor or serious illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery. It includes initial in ...
. The "A" in the ABC treatment mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imag ...
is for airway.
Basic airway management
Basic airway management involves maneuvers that do not require specialized medical equipment (in contrast to advanced airway management). It is mainly used in first aid since it isnon-invasive
A medical procedure is defined as ''non-invasive'' when no break in the skin is created and there is no contact with the mucosa, or skin break, or internal body cavity beyond a natural or artificial body orifice. For example, deep palpation and p ...
, quick, and relatively simple to perform. The simplest way to determine if the airway is obstructed is by assessing whether the patient is able to speak. Basic airway management can be divided into treatment and prevention of an obstruction in the airway.
Treatment
Treatment includes different maneuvers that aim to remove the foreign body that is obstructing the airway. This type of obstruction most often occurs when someone is eating or drinking. Most modern protocols, including those of the American Heart Association, American Red Cross and theEuropean Resuscitation Council
The European Resuscitation Council (ERC) is the European Interdisciplinary Council for Resuscitation Medicine and Emergency Medical Care
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illness
A disease is a ...
, recommend several stages, designed to apply increasingly more pressure. Most protocols recommend first encouraging the victims to cough, and allowing them an opportunity to spontaneously clear the foreign body if they are coughing forcefully. If the person's airway continues to be blocked, more forceful maneuvers such as hard back slaps and abdominal thrusts
Abdominal thrusts, also known as the Heimlich maneuver or Heimlich manoeuvre, is a first aid procedure used to treat upper airway obstructions (or choking) by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its creation. ...
(''Heimlich maneuver'') can be performed. Some guidelines recommend alternating between abdominal thrusts and back slaps while others recommend the same starting with the back slaps first. Having the person lean forward reduces the chances of the foreign body going back down the airway when coming up.
Performing abdominal thrusts on someone else involves standing behind them, and providing inward and upward forceful compressions in the upper abdomen, concretely in the area located between the chest and the belly button. The rescuer usually gives the compressions using a fist that is grasped with the other hand.
Abdominal thrusts can also be performed on oneself with the help of the objects near, for example: by leaning over a chair. Anyway, when the choking victim is oneself, one of the more reliable options is the usage of any specific anti-choking device. In adults, there is limited evidence that the head down position can be used for self-treatment of suffocation and appears to be an option only if other maneuvers do not work. In contrast, in children under 1 it is recommended that the child be placed in a head down position as this appears to help increase the effectiveness of back slaps and abdominal thrusts.
When the victim can not receive pressures on the abdomen (it can happen in case of pregnancy or excessive obesity, for example), chest thrusts are advised instead of abdominal thrusts. The chest thrusts are the same type of compressions but applied on the lower half of the chest bone (not in the very extreme, which is a point named xiphoid process and could be broken).
The American Medical Association and Australian Resuscitation Council advocate sweeping the fingers across the back of the throat to attempt to dislodge airway obstructions, once the choking victim becomes unconscious. However, many modern protocols and literature recommend against the use of the finger sweep. If the person is conscious, they should be able to remove the foreign object themselves, and if they are unconscious, a finger sweep can cause more harm. A finger sweep can push the foreign body further down the airway, making it harder to remove, or cause aspiration by inducing the person to vomit. Additionally, there is the potential for harm to the rescuer if they are unable to clearly see the oral cavity (for example, cutting a finger on jagged teeth).
Prevention
 Prevention techniques focus on preventing airway obstruction by the tongue and reducing the likelihood of aspiration of stomach contents or blood. The head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are useful for the former while the recovery position is useful for the latter. If head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are performed with any objects in the airways it may dislodge them further down the airways and thereby cause more blockage and harder removal.
The head-tilt/chin-lift is the primary maneuver used in any patient in whom
Prevention techniques focus on preventing airway obstruction by the tongue and reducing the likelihood of aspiration of stomach contents or blood. The head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are useful for the former while the recovery position is useful for the latter. If head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust maneuvers are performed with any objects in the airways it may dislodge them further down the airways and thereby cause more blockage and harder removal.
The head-tilt/chin-lift is the primary maneuver used in any patient in whom cervical spine injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cor ...
is not a concern. This maneuver involves flexion of the neck and extension of the head at Atlanto-occipital joint (also called the sniffing position), which opens up the airway by lifting the tongue away from the back of the throat. Placing a folded towel behind the head accomplishes the same result.
supine
In grammar, a supine is a form of verbal noun used in some languages. The term is most often used for Latin, where it is one of the four principal parts of a verb. The word refers to a position of lying on one's back (as opposed to ' prone', l ...
. The practitioner places their index and middle fingers behind the angle of the mandible to physically push the posterior aspects of the mandible upwards while their thumbs push down on the chin to open the mouth. When the mandible is displaced forward, it pulls the tongue forward and prevents it from occluding the entrance to the trachea.
The recovery position is an important prevention technique for an unconscious person that is breathing casually. This position entails having the person lie in a stable position on their side with the head in a dependent position so fluids do not drain down the airway, reducing the risk of aspiration.
Most airway maneuvers are associated with some movement of the cervical spine
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sau ...
. When there is a possibility of cervical injury, collars are used to help hold the head in-line. Most of these airway maneuvers are associated with some movement of the cervical spine. Even though cervical collars can cause problems maintaining an airway and maintaining a blood pressure, it is not recommended to remove the collar without adequate personnel to manually hold the head in place.
Advanced airway management
In contrast to basic airway management maneuvers such as head-tilt or jaw-thrust, advanced airway management relies on the use of medical equipment. Advanced airway management can be performed "blindly" or with visualization of the glottis by using alaryngoscope
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ...
. Advanced airway management is frequently performed in the critically injured, those with extensive pulmonary disease, or anesthetized patients to facilitate oxygenation and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
. Additionally, implementation of a cuffing system is used to prevent the possibility of asphyxia
Asphyxia or asphyxiation is a condition of deficient supply of oxygen to the body which arises from abnormal breathing. Asphyxia causes generalized hypoxia, which affects primarily the tissues and organs. There are many circumstances that ca ...
tion or airway obstruction.
Many methods are used in Advanced airway management. Examples in increasing order of invasiveness include the use of supraglottic devices such as oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
or nasopharyngeal airway
In medicine, a nasopharyngeal airway, also known as an NPA, nasal trumpet (because of its flared end), or nose hose, is a type of ''airway adjunct'', a tube that is designed to be inserted through the nasal passage down into the posterior pharynx ...
s, infraglottic techniques such as tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
and finally surgical methods.
Removal of foreign objects
 The ingestion and aspiration of foreign objects pose a common and dangerous problem in young children. It remains one of the leading cause of death in children under the age of 5. Common food items (baby carrots, peanuts, etc.) and household objects (coins, metals, etc.) may lodge in various levels of the airway tract and cause significant obstruction of the airway. Complete obstruction of the airway represents a
The ingestion and aspiration of foreign objects pose a common and dangerous problem in young children. It remains one of the leading cause of death in children under the age of 5. Common food items (baby carrots, peanuts, etc.) and household objects (coins, metals, etc.) may lodge in various levels of the airway tract and cause significant obstruction of the airway. Complete obstruction of the airway represents a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
. During such crisis, caretakers may attempt back blows, abdominal thrust, or the Heimlich maneuver
Abdominal thrusts, also known as the Heimlich maneuver or Heimlich manoeuvre, is a first aid procedure used to treat upper airway obstructions (or choking) by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its creation. ...
to dislodge the inhaled object and reestablish airflow into the lungs.
In the hospital setting, healthcare practitioners will make the diagnosis of foreign body aspiration from the medical history and physical exam findings. In some cases, providers will order chest radiographs, which may show signs of air-trapping in the affected lung. In advanced airway management, the inhaled foreign objects, however, are either removed by using a simple plastic suction device (such as a Yankauer suction tip) or under direct inspection of the airway with a laryngoscope
Laryngoscopy () is endoscopy of the larynx, a part of the throat. It is a medical procedure that is used to obtain a view, for example, of the vocal folds and the glottis. Laryngoscopy may be performed to facilitate tracheal intubation during ge ...
or bronchoscope. If removal is not possible, other surgical methods should be considered.
Supraglottic techniques
Supraglottic techniques use devices that are designed to have the distal tip resting above the level of the glottis when in its final seated position. Supraglottic devices ensure patency of the upper respiratory tract without entry into the trachea by bridging the oral and pharyngeal spaces. There are many methods of subcategorizing this family of devices including route of insertion, absence or presence of a cuff, and anatomic location of the device's distal end. The most commonly used devices are laryngeal masks and supraglottic tubes, such asoropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
(OPA) and nasopharyngeal airway
In medicine, a nasopharyngeal airway, also known as an NPA, nasal trumpet (because of its flared end), or nose hose, is a type of ''airway adjunct'', a tube that is designed to be inserted through the nasal passage down into the posterior pharynx ...
s (NPA). In general, features of an ideal supraglottic airway include the ability to bypass the upper airway, produce low airway resistance, allow both positive pressure as well as spontaneous ventilation, protect the respiratory tract from gastric and nasal secretions, be easily inserted by even a nonspecialist, produce high first-time insertion rate, remain in place once in seated position, minimize risk of aspiration, and produce minimal side effects.
A ''nasopharyngeal airway'' is a soft rubber or plastic tube that is passed through the nose and into the posterior pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
. Nasopharyngeal airways are produced in various lengths and diameters to accommodate for gender and anatomical variations. Functionally, the device is gently inserted through a patient's nose after careful lubrication with a viscous lidocaine gel. Successful placement will facilitate spontaneous ventilation, masked ventilation, or machine assisted ventilation with a modified nasopharyngeal airway designed with special attachments at the proximal end. Patients generally tolerate NPAs very well. NPAs are preferred over OPAs when the patient's jaw is clenched or if the patient is semiconscious and cannot tolerate an OPA. NPAs, however, are generally not recommended if there is suspicion of a fracture to the base of the skull. In these circumstances, insertion of the NPA can cause neurological damage by entering the cranium during placement. There is no consensus, however, regarding the risk of neurological damage secondary to a basilar skull fracture compared to hypoxia due to insufficient airway management. Other complications of Nasopharyngeal airways use includes laryngospasm, epistaxis, vomiting, and tissue necrosis with prolonged use. ''Oropharyngeal airways'' are curved, rigid plastic devices, inserted into the patient's mouth. Oropharyngeal airways are produced in various lengths and diameters to accommodate for gender and anatomical variations. It is especially useful in patients with excessive tongue and other soft tissues. OPAs prevent airway obstruction by ensuring that the patient's
''Oropharyngeal airways'' are curved, rigid plastic devices, inserted into the patient's mouth. Oropharyngeal airways are produced in various lengths and diameters to accommodate for gender and anatomical variations. It is especially useful in patients with excessive tongue and other soft tissues. OPAs prevent airway obstruction by ensuring that the patient's tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
does not obstruct the epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food in ...
by creating a conduit. Because an oropharyngeal airway can mechanically stimulate the gag reflex The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, the back of the tongue, the area around the tonsils, the uvula, and the back of the throat. It, along with ot ...
, it should only be used in a deeply sedated or unresponsive patient to avoid vomiting and aspiration. Careful attention must be made while inserting an OPA. The user must avoid pushing the tongue further down the patient's throat. This is usually done by inserting the OPA with its curve facing cephalad and rotating it 180 degrees as you enter the posterior pharynx.
''Extraglottic devices'' are another family of supraglottic devices that are inserted through the mouth to sit on top of the larynx''.'' Extraglottic devices are used in the majority of operative procedures performed under general anaesthesia. Compared to a cuffed tracheal tube, extraglottic devices provide less protection against aspiration but are more easily inserted and causes less laryngeal trauma. Limitations of extraglottic devices arise in morbidly obese patients, lengthy surgical procedures, surgery involving the airways, laparoscopic procedures and others due to its bulkier design and inferior ability to prevent aspiration. In these circumstances, endotracheal intubation is generally preferred. The most commonly used extraglottic device is the laryngeal mask airway
A laryngeal mask airway (LMA), also known as laryngeal mask, is a medical device that keeps a patient's Respiratory tract, airway open during anaesthesia or while they are Unconsciousness, unconscious. It is a type of supraglottic airway device. ...
(LMA). An LMA is a cuffed perilaryngeal sealer that is inserted into the mouth and set over the glottis. Once it is in its seated position, the cuff is inflated. Other variations include devices with oesophageal access ports, so that a separate tube can be inserted from the mouth to the stomach to decompress accumulated gases and drain liquid contents. Other variations of the device can have an endotracheal tube passed through the LMA and into the trachea.
Infraglottic techniques
 In contrast to supraglottic devices, infraglottic devices create a conduit between the mouth, passing through the glottis, and into the trachea. There are many infraglottic methods available and the chosen technique is reliant on the accessibility of medical equipment, competence of the clinician and the patient's injury or disease.
In contrast to supraglottic devices, infraglottic devices create a conduit between the mouth, passing through the glottis, and into the trachea. There are many infraglottic methods available and the chosen technique is reliant on the accessibility of medical equipment, competence of the clinician and the patient's injury or disease. Tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
, often simply referred to as intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blake ...
, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube
Tube or tubes may refer to:
* ''Tube'' (2003 film), a 2003 Korean film
* ''The Tube'' (TV series), a music related TV series by Channel 4 in the United Kingdom
* "Tubes" (Peter Dale), performer on the Soccer AM television show
* Tube (band), a ...
into the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
to maintain an open airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an endotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the Vertebrate trachea, trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate Gas exchange, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many diffe ...
is passed through the mouth and vocal apparatus
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articula ...
into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Alternatives to standard endotracheal tubes include laryngeal tube and combitube
The Combitube—also known as the esophageal tracheal airway or esophageal tracheal double-lumen airway—is a blind insertion airway device (BIAD) used in the pre-hospital and emergency setting.Jorge E. Zamora and Tarit K. Saha,Combitube rescue f ...
.
Surgical methods
lower respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of Respiration (physiology), respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed ...
, bypassing the upper respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to t ...
. Surgical airway management is often performed as a last resort in cases where orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blake ...
are impossible or contraindicated
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain tre ...
. Surgical airway management is also used when a person will need a mechanical ventilator
A ventilator is a piece of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators ...
for a longer period. Surgical methods for airway management include cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, o ...
and tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The r ...
.
A cricothyrotomy is an emergency surgical procedure in which an incision is made through the cricothyroid membrane
The cricothyroid ligament (also known as the cricothyroid membrane or cricovocal membrane) is a ligament in the neck. It connects the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage. It prevents these cartilages from moving too far apart. It is cut dur ...
to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are ...
, or massive facial trauma. Cricothyrotomy is much easier and quicker to perform than tracheotomy, does not require manipulation of the cervical spine and is associated with fewer immediate complications. Some complications of cricothyrotomy include bleeding, infection, and injury to surrounding skin and soft tissue structures.
A tracheotomy is a surgical procedure in which a surgeon makes incision in the neck and a breathing tube is inserted directly into the trachea. A common reason for performing a tracheotomy includes requiring to be put on a mechanical ventilator for a longer period. The advantages of a tracheotomy include less risk of infection and damage to the trachea during the immediate post-surgical period. Although rare, some long term complications of tracheotomies include tracheal stenosis and tracheoinnominate fistulas.
Airway management in specific situations
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
The optimal method of airway management during CPR is not well established at this time given that the majority of studies on the topic are observational in nature. These studies, however, guide recommendations until prospective, randomized controlled trials are conducted. Current evidence suggests that for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, basic airway interventions (head-tilt–chin-lift maneuvers, bag-valve-masking or mouth-to-mouth ventilations,nasopharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
and/or oropharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
airways) resulted in greater short-term and long-term survival, as well as improved neurological outcomes in comparison to advanced airway interventions (endotracheal intubation, laryngeal mask airway, all types of supraglottic airways (SGA), and trans-tracheal or trans-cricothyroid membrane airways). Given that these are observational studies, caution must be given to the possibility of confounding by indication. That is, patients requiring an advanced airway may have had a poorer prognosis in relation to those requiring basic interventions to begin with.
For the management of in-hospital cardiac arrest however, studies currently support the establishment of an advanced airway. It is well documented that quality chest compressions with minimal interruption result in improved survival. This is suggested to be due, in part, to decreased no-flow-time in which vital organs, including the heart are not adequately perfused. Establishment of an advanced airway (endotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the Vertebrate trachea, trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate Gas exchange, exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many diffe ...
, laryngeal mask airway
A laryngeal mask airway (LMA), also known as laryngeal mask, is a medical device that keeps a patient's Respiratory tract, airway open during anaesthesia or while they are Unconsciousness, unconscious. It is a type of supraglottic airway device. ...
) allows for asynchronous ventilation, reducing the no-flow ratio, as compared to the basic airway ( bag-valve mask) for which compressions must be paused to adequately ventilate the patient.
Bystanders without medical training who see an individual suddenly collapse should call for help and begin chest compressions immediately. The American Heart Association currently supports "Hands-only"™ CPR, which advocates chest compressions without rescue breaths for teens or adults. This is to minimize the reluctance to start CPR due to concern for having to provide mouth-to-mouth resuscitation
Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, a form of artificial ventilation, is the act of assisting or stimulating respiration in which a rescuer presses their mouth against that of the victim and blows air into the person's lungs. Artificial respiration ta ...
.
Trauma
basilar skull fracture
A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include bruising behind the ears, bruising around the eyes, or blood behind the ear drum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and ...
is suspected. Endotracheal intubation carries with it many risks, particularly when paralytics are used, as maintenance of the airway becomes a challenge if intubation fails. It should therefore be attempted by experienced personnel, only when less invasive methods fail or when it is deemed necessary for safe transport of the patient, to reduce risk of failure and the associated increase in morbidity and mortality due to hypoxia.
 Management of the airway in the emergency department is optimal given the presence of trained personnel from multiple specialties, as well as access to "difficult airway equipment" ( videolaryngoscopy, eschmann tracheal tube introducer, fiberoptic bronchoscopy, surgical methods, etc.). Of primary concern is the condition and patency of the maxillofacial structures, larynx,
Management of the airway in the emergency department is optimal given the presence of trained personnel from multiple specialties, as well as access to "difficult airway equipment" ( videolaryngoscopy, eschmann tracheal tube introducer, fiberoptic bronchoscopy, surgical methods, etc.). Of primary concern is the condition and patency of the maxillofacial structures, larynx, trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from the ...
, and bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
as these are all components of the respiratory tract and failure anywhere along this path may impede ventilation. Excessive facial hair, severe burns, and maxillofacial trauma may prevent acquisition of a good mask seal, rendering bag-valve mask ventilation difficult. Edema of the airway can make laryngoscopy difficult, and therefore in those with suspected thermal burns, intubation is recommended in attempts to quickly secure an airway prior to progression of the swelling. Furthermore, blood and vomitus in the airway may prove visualization of the vocal cords difficult rendering direct and video laryngoscopy, as well as fiberoptic bronchoscopy challenging. Establishment of a surgical airway is challenging in the setting of restricted neck extension (such as in a c-collar), laryngotracheal disruption, or distortion of the anatomy by a penetrating force or hematoma. Tracheotomy in the operating room by trained professionals is recommended over cricothyroidotomy in the case of complete laryngotracheal disruption or children under the age of 12.
See also
* Choking, First-Aid treatmentReferences
Further reading
* {{First aid topics