Sun and planet gear on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The sun and planet gear is a method of converting
The sun and planet gear is a method of converting
 The sun and planet
The sun and planet
Henry Ford Museum Watt Rotative Engine
{{Steam engine configurations Gears Steam engines Piston engines Engine technology Linkages (mechanical) Scottish inventions British inventions Industrial Revolution
 The sun and planet gear is a method of converting
The sun and planet gear is a method of converting reciprocating motion
Reciprocating motion, also called reciprocation, is a repetitive up-and-down or back-and-forth linear motion. It is found in a wide range of mechanisms, including reciprocating engines and pumps. The two opposite motions that comprise a single r ...
to rotary motion
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed- axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's ...
and was used in the first rotative beam engines.
It was invented by the Scottish engineer William Murdoch
William Murdoch (sometimes spelled Murdock) (21 August 1754 – 15 November 1839) was a Scottish engineer and inventor.
Murdoch was employed by the firm of Boulton & Watt and worked for them in Cornwall, as a steam engine erector for ten yea ...
, an employee of Boulton and Watt
Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the Eng ...
, but was patented by James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was ...
in October 1781.
It was invented to bypass the patent on the crank, already held by James Pickard. It played an important part in the development of devices for rotation in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
.
Operation
 The sun and planet
The sun and planet gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic ...
converted the vertical motion of a beam, driven by a steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be ...
, into circular motion using a 'planet', a cogwheel
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic p ...
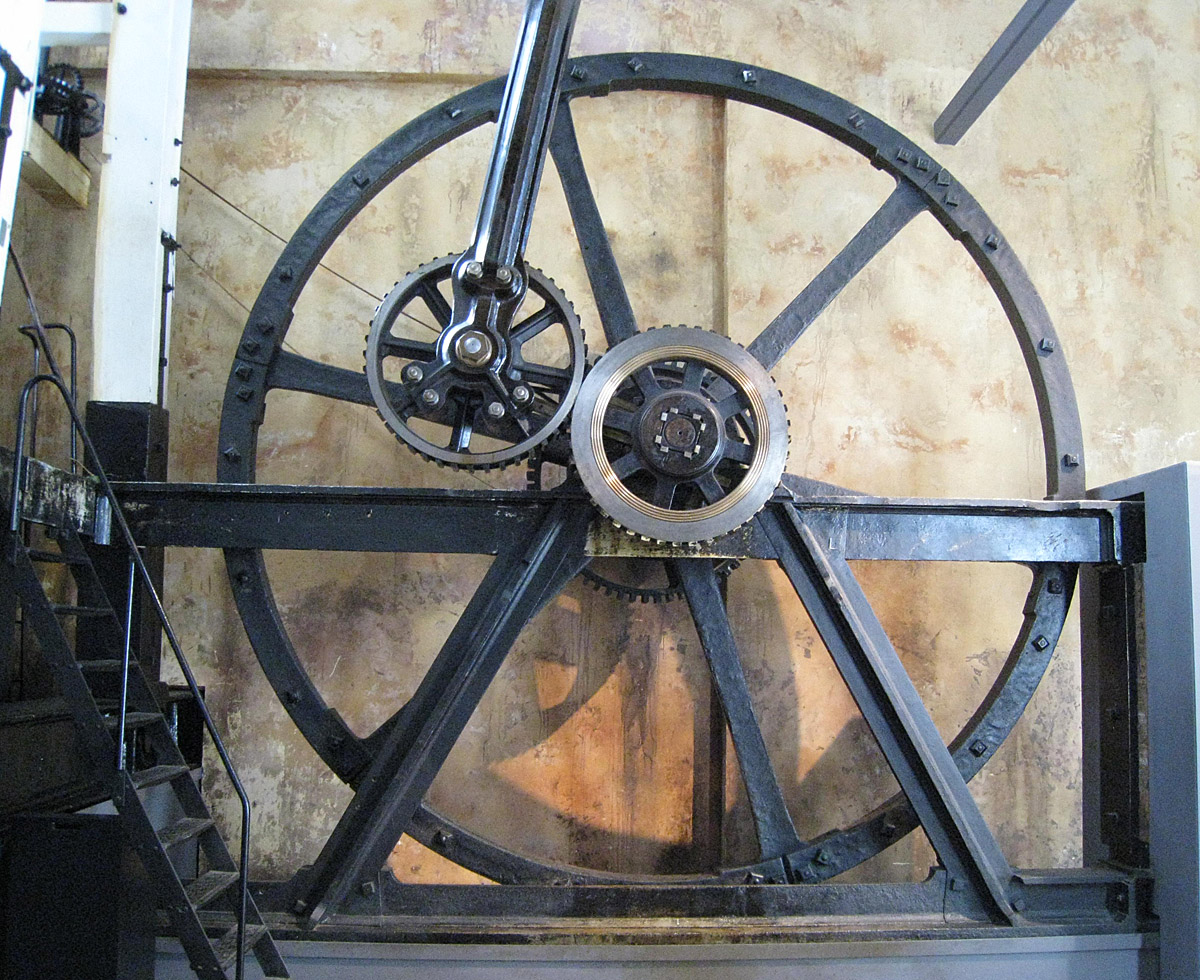
fixed at the end of the connecting rod (connected to the beam) of the engine. With the motion of the beam, this revolved around, and turned, the 'sun', a second rotating cog fixed to the drive shaft, thus generating rotary motion. An interesting feature of this arrangement, when compared to that of a simple crank, is that when both sun and planet have the same number of teeth, the drive shaft completes two revolutions for each double stroke of the beam instead of one. The planet gear is fixed to the connecting rod and thus does not rotate around its own axis.
Note that the axles of the two gears are usually tied to each other by a freely rotating link (not shown in the animation) that keeps the two gears engaged but does not contribute to the drive torque. This link appears, at first sight, to be similar to a crank but the drive is not transmitted through it. Thus, it did not contravene the crank patent.
See also
*Epicyclic gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gea ...
References
External links
Henry Ford Museum Watt Rotative Engine
{{Steam engine configurations Gears Steam engines Piston engines Engine technology Linkages (mechanical) Scottish inventions British inventions Industrial Revolution