Stitch (textile arts) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
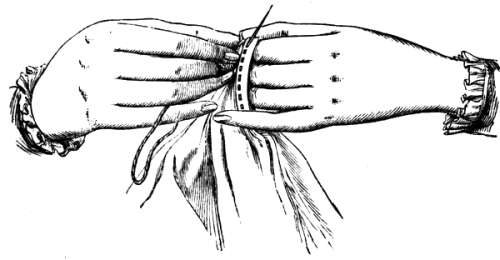 In the textile arts, a stitch is a single turn or loop of thread, or yarn. Stitches are the fundamental elements of
In the textile arts, a stitch is a single turn or loop of thread, or yarn. Stitches are the fundamental elements of
 In the textile arts, a stitch is a single turn or loop of thread, or yarn. Stitches are the fundamental elements of
In the textile arts, a stitch is a single turn or loop of thread, or yarn. Stitches are the fundamental elements of sewing
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a sewing needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving ...
, knitting
Knitting is a method by which yarn is manipulated to create a textile, or fabric. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Knitting creates stitches: loops of yarn in a row, either flat or i ...
, embroidery
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen ...
, crochet
Crochet (; ) is a process of creating textiles by using a crochet hook to interlock loops of yarn, thread, or strands of other materials. The name is derived from the French term ''crochet'', meaning 'hook'. Hooks can be made from a variety of ...
, and needle lace-making, whether by hand or machine.Picken (1957), p. 322 A variety of stitches, each with one or more names, are used for specific purposes.
Sewing, embroidery, and lace
Examples include: * Backstitch * Overcast stitch *Cross stitch
Cross-stitch is a form of sewing and a popular form of counted-thread embroidery in which X-shaped stitches in a tiled, raster-like pattern are used to form a picture. The stitcher counts the threads on a piece of evenweave fabric (such as li ...
* Buttonhole or blanket stitch
* Chain stitch
* Knot stitch
These stitches and their variations are named according to the position of the needle and direction of sewing (''running stitch'', ''backstitch''), the form or shape of the stitch (''chain stitch'', '' feather stitch'') or the purpose of the stitch ( tailor's tack, ''hem stitch'').''Reader's Digest'' (1976), pp. 122–143
Sewing machine
A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with Thread (yarn), thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. ...
stitches are classified by their structure:
*Chain stitch, made with one thread
* Lockstitch, made with two threads
*Overlock
An overlock is a kind of stitch that sews over the edge of one or two pieces of cloth for edging, hemming, or seaming. Usually an overlock sewing machine will cut the edges of the cloth as they are fed through (such machines being called ser ...
, made with one to five threads
* Coverstitch, made with two or four threads (a twine)
Fancy machine stitches mimic traditional hand stitches using variations on the basic stitches.
Knitting
In knitting, a stitch is a single loop of yarn, secured to the loops beside it to form a row or ''course'' of stitches and to the loops above and below it to form a ''wale''. In securing the previous stitch in a wale, the next stitch can pass through the previous loop either from below or above. If the former, the stitch is denoted as a knit stitch or a plain stitch; if the latter, as a purl stitch. The two stitches are related in that a knit stitch seen from one side of the fabric appears as a purl stitch on the other side.Crochet
Incrochet
Crochet (; ) is a process of creating textiles by using a crochet hook to interlock loops of yarn, thread, or strands of other materials. The name is derived from the French term ''crochet'', meaning 'hook'. Hooks can be made from a variety of ...
, stitches are made by pulling a loop of thread through the work with a crochet hook. Crochet stitches are named based on their structure. In the English-speaking crochet world, basic stitches have different names that vary by country. The differences are usually referred to as UK/US or British/American.
Notes
References
* * {{sewing Textile arts Sewing