Stegodon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the
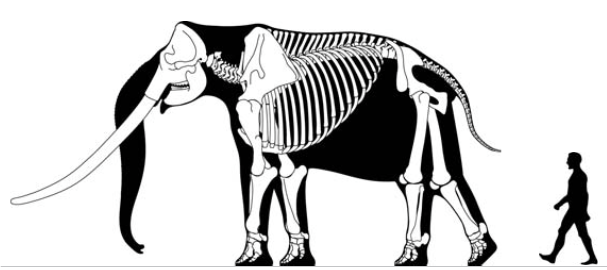 Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the
Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the
 Similar to modern-day elephants, stegodonts were likely good swimmers, as their
Similar to modern-day elephants, stegodonts were likely good swimmers, as their
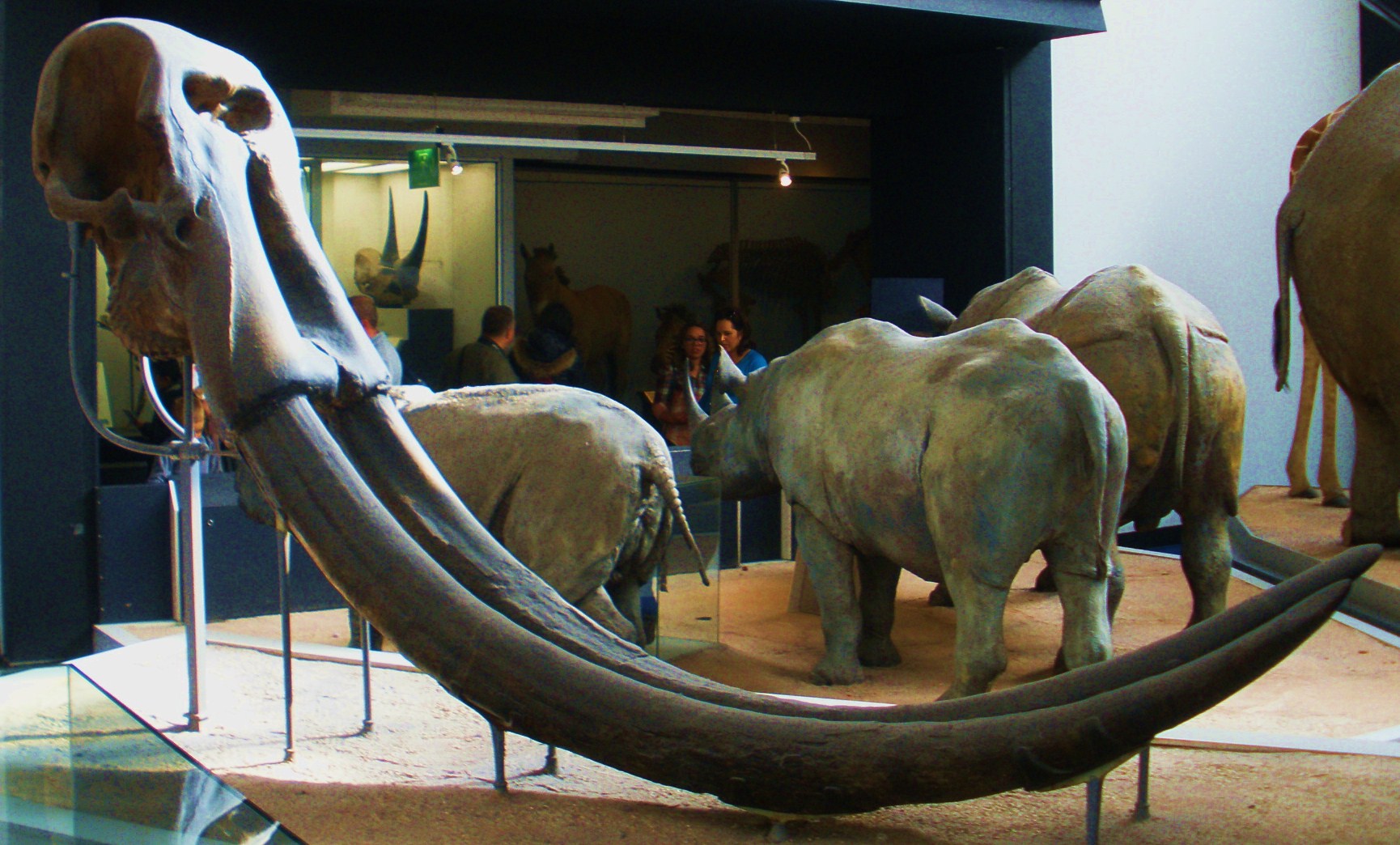


 In the past, stegodonts were believed to be the
In the past, stegodonts were believed to be the
"Comparisons of Stegodon and Elephantid Abundances in the Late Pleistocene of Southern China"
, The World of Elephants – Second International Congress, (Rome, 2001), 345–349. However, Turvey ''et al.'' (2013) reported that one of the faunal assemblages including supposed fossils of Holocene ''Stegodon'' (from Gulin, Sichuan Province) is actually late Pleistocene in age; other supposed fossils of Holocene stegodonts were lost and their age cannot be verified. The authors concluded that the latest confirmed occurrences of ''Stegodon'' from China are from the late Pleistocene, and that its Holocene survival cannot be substantiated.
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
words , , 'to cover', + , , 'tooth' because of the distinctive ridges on the animal's molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
) is an extinct genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of proboscidea
The Proboscidea (; , ) are a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family ( Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. Fr ...
n, related to elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
s. It was originally assigned to the family Elephantidae
Elephantidae is a family of large, herbivorous proboscidean mammals collectively called elephants and mammoths. These are terrestrial large mammals with a snout modified into a trunk and teeth modified into tusks. Most genera and species in the ...
along with modern elephants but is now placed in the extinct family Stegodontidae
Stegodontidae is an extinct family of proboscideans from Africa and Asia (with a single occurrence in Europe) from the Miocene (15.97 mya) to the Late Pleistocene, with some studies suggesting that some survived into the Holocene in China ...
. Like elephants, ''Stegodon'' had teeth with plate-like lophs that are different from those of more primitive proboscideans like gomphotheres
Gomphotheres are any members of the diverse, extinct taxonomic family Gomphotheriidae. Gomphotheres were elephant-like proboscideans, but do not belong to the family Elephantidae. They were widespread across Afro-Eurasia and North America during ...
and mastodons. The oldest fossils of the genus are found in Late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
strata in Asia, likely originating from the more archaic ''Stegolophodon
''Stegolophodon'' is an extinct genus of stegodontid proboscideans, with two tusks and a trunk. It lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, and may have evolved into ''Stegodon
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the Ancient Greek words ...
,'' shortly afterwards migrating into Africa. While the genus became extinct in Africa during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
.
Morphology
Size
 Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the
Some species of ''Stegodon'' were amongst the largest proboscideans. ''S. zdanskyi'' is known from an old male (50-plus years old) from the Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
that is tall and would have weighed approximately in life. It had a humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a r ...
long, a femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates ...
long, and a pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
wide. Size varies across species, large stegodonts are comparable in size with modern elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
s. Aside from ''S. zdanskyi,'' species like ''S. ganesha, S. miensis, S. orientalis, S. elephantoides'' and ''S. kaisensis'' are also relatively large bodied. Large stegodonts usually occur in the mainland. There also exist medium sized stegodonts present in large islands like those of Japan and Java. These stegodonts may include: ''S. aurorae, S. trigonocephalus, S. insignis'' and ''S. florensis florensis''. Stegodonts that live in smaller islands usually result in further dwarfism.
Dwarfism
''S. florensis insularis'' is an extinct subspecies of ''Stegodon'' endemic to the island ofFlores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and t ...
, Indonesia, and an example of insular dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is disti ...
. The direct ancestor of ''S. florensis insularis'' is the larger-bodied ''S. florensis florensis'', from Early Pleistocene and early Middle Pleistocene sites on Flores.Van Den Bergh, G. D., Aweb, R. D., Morwood, M. J., Sutiknab, T., Jatmikob and Saptomo, E. W. 2008. The youngest stegodon remains in Southeast Asia from the Late Pleistocene archaeological site Liang Bua, Flores, Indonesia. Quaternary International 182(1): 16–48. Remains of ''S. florensis insularis'' are known from the cave of Liang Bua
Liang Bua is a limestone cave on the island of Flores, Indonesia, slightly north of the town of Ruteng in Manggarai Regency, East Nusa Tenggara. The cave demonstrated archaeological and paleontological potential in the 1950s and 1960s as describe ...
.fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s are frequently encountered on Asian islands (such as Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
, Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and t ...
, Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, ...
, Sumba
Sumba ( id, Pulau Sumba) is an island in eastern Indonesia. It is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of , and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as a ...
in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
; Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as ...
and Mindanao
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
; Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
; and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
), all locations not connected by land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea leve ...
s with the Asian continent even during periods of low sea level (during the cold phases of the Pleistocene). A general evolutionary trend in large mammals on islands is island dwarfing. Many among the dwarfed species of Stegodonts came from the lineage of ''S. ganesha, S. zdanskyi'' and ''S. elephantoides''. The smallest dwarf species known is ''S. sumbaensis'' from Sumba, with an estimated body mass of 250 kg. The slightly larger ''S. sondaari'', known from Early Pleistocene layers on the Indonesian island of Flores, had an estimated body weight of between 355 and 650 kg. Another estimate gives a shoulder height of and a weight of . Philippine pygmy stegodonts also have a small stature bigger than or around the size of ''S. sondaari'' and ''S. sompoensis'' of Celebes, with ''S. mindanensis'' having a projected weight of 400'' ''kg. ''S. luzonensis'' and ''S. sompoensis'' have estimated masses of around 1,300 kg and 1,000 kg respectively. A medium- to large-sized stegodont, ''S. florensis'', with a body weight of about 1,700 kg, appeared about 850,000 years ago, and then also evolved into a dwarf form, ''S. f. insularis'', with an estimated body mass of about 570 kg. Another estimate gives a shoulder height of and a weight of . The latter was contemporaneous with, and hunted by, the dwarf hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
''Homo floresiensis
''Homo floresiensis'' also known as "Flores Man"; nicknamed "Hobbit") is an extinct species of small archaic human that inhabited the island of Flores, Indonesia, until the arrival of modern humans about 50,000 years ago.
The remains of an in ...
'', and disappeared about 49,600 years ago, earlier than initially thought. Dwarf stegodonts were believed to be the main prey of the still-extant Komodo dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant ...
before modern humans introduced their modern main prey in its range, banded pig, rusa deer
The Javan rusa or Sunda sambar (''Rusa timorensis'') is a deer native to Indonesia and East Timor. Introduced populations exist in a wide variety of locations in the Southern Hemisphere.
Taxonomy
Seven subspecies of the Javan rusa are recognis ...
, and water buffalo
The water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis''), also called the domestic water buffalo or Asian water buffalo, is a large bovid originating in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Today, it is also found in Europe, Australia, North America, So ...
.
Ecology
Like modern elephants, but unlike more primitive probscideans, ''Stegodon'' is thought to have chewed using a proal movement (a forward stroke from the back to the front) of the lower jaws. Based on dental microwear analysis, populations of ''Stegodon'' from the Pleistocene of China and Southeast Asia were found to bebrowsers
Browse, browser or browsing may refer to:
Programs
* Web browser, a program used to access the World Wide Web
*Code browser, a program for navigating source code
* File browser or file manager, a program used to manage files and related objects
* ...
, with clear niche differentiation
In ecology, niche differentiation (also known as niche segregation, niche separation and niche partitioning) refers to the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. The competitive excl ...
from sympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species s ...
'' Elephas'' populations, which tended towards mixed feeding (both browsing and grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and ot ...
).
Taxonomy

 In the past, stegodonts were believed to be the
In the past, stegodonts were believed to be the ancestor
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
s of the true elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
s and mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks an ...
s, but currently they are believed to have no modern descendants. ''Stegodon'' is likely derived from ''Stegolophodon
''Stegolophodon'' is an extinct genus of stegodontid proboscideans, with two tusks and a trunk. It lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs, and may have evolved into ''Stegodon
''Stegodon'' ("roofed tooth" from the Ancient Greek words ...
'', an extinct genus known from the Miocene of Asia. ''Stegodon'' is generally considered to be more closely related to elephants and mammoths than either gomphotheres
Gomphotheres are any members of the diverse, extinct taxonomic family Gomphotheriidae. Gomphotheres were elephant-like proboscideans, but do not belong to the family Elephantidae. They were widespread across Afro-Eurasia and North America during ...
or mastodons. Some taxonomist
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are give ...
s consider the stegodonts a subfamily of the Elephantidae. The most important difference between ''Stegodon'' and (other) Elephantidae can be observed in the molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
. Stegodont molars consist of a series of low, roof-shaped ridges, whereas in elephants, each ridge has become a high-crowned plate. Furthermore, stegodont skeletons are more robust and compact than those of elephants.
In Bardia National Park in Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, a population of Indian elephants, possibly due to inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders a ...
, exhibits many ''Stegodon''-like morphological features. These primitive features are considered recent mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s rather than atavism
In biology, an atavism is a modification of a biological structure whereby an ancestral genetic trait reappears after having been lost through evolutionary change in previous generations. Atavisms can occur in several ways; one of which is whe ...
s.
Fossils of the small, specialized stegodont ''S. aurorae'' are found in the Osaka Plain
The refers to a 1,600 km² area of flat land, the largest plain in the Kinki region, including a large part of Osaka Prefecture and a southeastern portion of Hyōgo Prefecture. It is bordered on the north by the Hokusetsu Mount Range, on ...
, Japan, and date from around 2 million to 7 million years ago. This species possibly evolved from ''S. shinshuensis''.
Phylogeny
The followingcladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
shows the placement of the genus ''Stegodon'' among other proboscideans, based on hyoid
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. ...
characteristics:
List of species
* ''Stegodon kaisensis'' Late Miocene – Pliocene, Africa * ''Stegodon zdanskyi'' Late Miocene – Pliocene, China * ''Stegodon huananensis'' Early Pleistocene, China * ''Stegodon orientalis'' Middle – Late Pleistocene, China, Southeast Asia, Japan * ''Stegodon namadicus/S. insignis/S. ganesa'' Pliocene – Late Pleistocene, India * ''Stegodon miensis'' Pliocene, Japan * ''Stegodon protoaurorae'' Late Pliocene – Early Pleistocene, Japan * ''Stegodon aurorae
''Stegodon aurorae'', also known as the , is a species of fossil elephantoid known from Early Pleistocene (2.0 Ma – 1.0 Ma) Japan and Taiwan.
Description
The best-preserved ''Stegodon aurorae'' skeleton, that from Taga in Shiga Prefecture, ...
'' Early Pleistocene – early Middle Pleistocene, Japan
* ''Stegodon sondaari'' Early Pleistocene, Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and t ...
* ''Stegodon florensis'' Middle – Late Pleistocene, Flores
Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. Including the Komodo Islands off its west coast (but excluding the Solor Archipelago to the east of Flores), the land area is 15,530.58 km2, and t ...
* ''Stegodon luzonensis'' Pleistocene, Philippines
* ''Stegodon trigonocephalus'' Pleistocene, Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
* ''Stegodon sompoensis'' Pleistocene, Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu ...
* ''Stegodon sumbaensis'' Pleistocene, Sumbawa
Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but th ...
* ''Stegodon timorensis'' Pleistocene, Timor
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, ...
Extinction
''Stegodon'' became extinct in the Indian subcontinent, mainland Southeast Asia and China by the end of theLate Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch withi ...
epoch, while Asian elephants
The Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''), also known as the Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus '' Elephas'' and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the n ...
, which existed in sympatry with ''Stegodon'' in these regions, are still extant. The survival of the Asian elephant as opposed to ''Stegodon'' has been suggested to be due to its more flexible diet in comparison to ''Stegodon''. A review of 130 papers written about 180 different sites with proboscidean remains in southern China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
revealed ''Stegodon'' to have been more common than Asian elephants; the papers gave many recent radiocarbon dates, the youngest being 2,150 BCE (4,100 BP).H. Saegusa"Comparisons of Stegodon and Elephantid Abundances in the Late Pleistocene of Southern China"
, The World of Elephants – Second International Congress, (Rome, 2001), 345–349. However, Turvey ''et al.'' (2013) reported that one of the faunal assemblages including supposed fossils of Holocene ''Stegodon'' (from Gulin, Sichuan Province) is actually late Pleistocene in age; other supposed fossils of Holocene stegodonts were lost and their age cannot be verified. The authors concluded that the latest confirmed occurrences of ''Stegodon'' from China are from the late Pleistocene, and that its Holocene survival cannot be substantiated.
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q772364 Stegodontidae Miocene proboscideans Miocene mammals of Asia Miocene mammals of Africa Pliocene mammals of Africa Pliocene mammals of Asia Pleistocene mammals of Africa Pleistocene mammals of Asia Pliocene proboscideans Pleistocene proboscideans Miocene genus first appearances Prehistoric placental genera Fossil taxa described in 1847 Taxa named by Hugh Falconer Pleistocene genus extinctions