Star system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as
online versions at
and at
of physical multiple stars, 551 out of the 728 systems described are triple. However, because of suspected
 Most multiple-star systems are organized in what is called a ''hierarchical system'': the stars in the system can be divided into two smaller groups, each of which traverses a larger orbit around the system's center of mass. Each of these smaller groups must also be hierarchical, which means that they must be divided into smaller subgroups which themselves are hierarchical, and so on. Each level of the hierarchy can be treated as a ''
Most multiple-star systems are organized in what is called a ''hierarchical system'': the stars in the system can be divided into two smaller groups, each of which traverses a larger orbit around the system's center of mass. Each of these smaller groups must also be hierarchical, which means that they must be divided into smaller subgroups which themselves are hierarchical, and so on. Each level of the hierarchy can be treated as a ''
 In a ''physical'' triple star system, each star
In a ''physical'' triple star system, each star
 Hierarchical multiple star systems with more than three stars can produce a number of more complicated arrangements. These arrangements can be organized by what Evans (1968) called ''mobile diagrams'', which look similar to ornamental mobiles hung from the ceiling. Examples of hierarchical systems are given in the figure to the right (''Mobile diagrams''). Each level of the diagram illustrates the decomposition of the system into two or more systems with smaller size. Evans calls a diagram ''multiplex'' if there is a node with more than two ''children'', i.e. if the decomposition of some subsystem involves two or more orbits with comparable size. Because, as we have already seen for triple stars, this may be unstable, multiple stars are expected to be ''simplex'', meaning that at each level there are exactly two ''children''. Evans calls the number of levels in the diagram its ''hierarchy''.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 1, as in (b), describes a binary system.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 2 may describe a triple system, as in (c), or a quadruple system, as in (d).
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 3 may describe a system with anywhere from four to eight components. The mobile diagram in (e) shows an example of a quadruple system with hierarchy 3, consisting of a single distant component orbiting a close binary system, with one of the components of the close binary being an even closer binary.
* A real example of a system with hierarchy 3 is Castor, also known as Alpha Geminorum or α Gem. It consists of what appears to be a
Hierarchical multiple star systems with more than three stars can produce a number of more complicated arrangements. These arrangements can be organized by what Evans (1968) called ''mobile diagrams'', which look similar to ornamental mobiles hung from the ceiling. Examples of hierarchical systems are given in the figure to the right (''Mobile diagrams''). Each level of the diagram illustrates the decomposition of the system into two or more systems with smaller size. Evans calls a diagram ''multiplex'' if there is a node with more than two ''children'', i.e. if the decomposition of some subsystem involves two or more orbits with comparable size. Because, as we have already seen for triple stars, this may be unstable, multiple stars are expected to be ''simplex'', meaning that at each level there are exactly two ''children''. Evans calls the number of levels in the diagram its ''hierarchy''.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 1, as in (b), describes a binary system.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 2 may describe a triple system, as in (c), or a quadruple system, as in (d).
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 3 may describe a system with anywhere from four to eight components. The mobile diagram in (e) shows an example of a quadruple system with hierarchy 3, consisting of a single distant component orbiting a close binary system, with one of the components of the close binary being an even closer binary.
* A real example of a system with hierarchy 3 is Castor, also known as Alpha Geminorum or α Gem. It consists of what appears to be a
, Brian D. Mason, Gary L. Wycoff, and William I. Hartkopf, Astrometry Department,
 A. A. Tokovinin's Multiple Star Catalogue uses a system in which each subsystem in a mobile diagram is encoded by a sequence of digits. In the mobile diagram (d) above, for example, the widest system would be given the number 1, while the subsystem containing its primary component would be numbered 11 and the subsystem containing its secondary component would be numbered 12. Subsystems which would appear below this in the mobile diagram will be given numbers with three, four, or more digits. When describing a non-hierarchical system by this method, the same subsystem number will be used more than once; for example, a system with three visual components, A, B, and C, no two of which can be grouped into a subsystem, would have two subsystems numbered 1 denoting the two binaries AB and AC. In this case, if B and C were subsequently resolved into binaries, they would be given the subsystem numbers 12 and 13.
A. A. Tokovinin's Multiple Star Catalogue uses a system in which each subsystem in a mobile diagram is encoded by a sequence of digits. In the mobile diagram (d) above, for example, the widest system would be given the number 1, while the subsystem containing its primary component would be numbered 11 and the subsystem containing its secondary component would be numbered 12. Subsystems which would appear below this in the mobile diagram will be given numbers with three, four, or more digits. When describing a non-hierarchical system by this method, the same subsystem number will be used more than once; for example, a system with three visual components, A, B, and C, no two of which can be grouped into a subsystem, would have two subsystems numbered 1 denoting the two binaries AB and AC. In this case, if B and C were subsequently resolved into binaries, they would be given the subsystem numbers 12 and 13.
 *
*
 *
*
Leos Ondra, accessed on line 26 May 2007. * HD 98800 * The
/ref> * KOI-2626 is the first quadruple star system with an Earth-sized planet. *
AR Cassiopeiae
, entry in th
Multiple Star Catalog
Alpha Centauri, APOD, 2002 April 25
General news on triple star systems, TSN, 2008 April 22
is located at the U.S. Naval Observatory
{{DEFAULTSORT:Star System
comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s).
A star system of two stars is known as a '' binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. If there are no tidal
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music
* Tidal (servic ...
effects, no perturbation from other forces, and no transfer of mass from one star to the other, such a system is stable, and both stars will trace out an elliptical orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, i ...
around the barycenter
In astronomy, the barycenter (or barycentre; ) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that orbit one another and is the point about which the bodies orbit. A barycenter is a dynamical point, not a physical object. It is an important con ...
of the system indefinitely. ''(See Two-body problem
In classical mechanics, the two-body problem is to predict the motion of two massive objects which are abstractly viewed as point particles. The problem assumes that the two objects interact only with one another; the only force affecting each ...
)''. Examples of binary systems are Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CM ...
, Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Minoris, which is Latinized ...
and Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a galactic X-ray source in the constellation Cygnus and was the first such source widely accepted to be a black hole. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the ...
, the last of which probably consists of a star and a black hole.
Multiple star systems
A multiple star system consists of three or more stars that appear fromEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
to be close to one another in the sky. This may result from the stars actually being physically close and gravitationally bound to each other, in which case it is a ''physical'' multiple star, or this closeness may be merely apparent, in which case it is an ''optical'' multiple star Physical multiple stars are also commonly called ''multiple stars'' or ''multiple star systems''.
Most multiple star systems are ''triple stars''. Systems with four or more components are less likely to occur. Multiple-star systems are called ''triple'', ''ternary'', or ''trinary'' if they contain 3 stars; ''quadruple'' or ''quaternary'' if they contain 4 stars; ''quintuple'' or ''quintenary'' with 5 stars; ''sextuple'' or ''sextenary'' with 6 stars; ''septuple'' or ''septenary'' with 7 stars. These systems are smaller than open star cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and ...
s, which have more complex dynamics and typically have from 100 to 1,000 stars. Most multiple star systems known are triple; for higher multiplicities, the number of known systems with a given multiplicity decreases exponentially with multiplicity. For example, in the 1999 revision of Tokovinin's catalogonline versions at
and at
of physical multiple stars, 551 out of the 728 systems described are triple. However, because of suspected
selection effect
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained is representative of the population int ...
s, the ability to interpret these statistics is very limited.
Multiple-star systems can be divided into two main dynamical classes:
: (1) hierarchical systems, which are stable, and consist of nested orbits that don't interact much, and so each level of the hierarchy can be treated as a ''Two-body problem
In classical mechanics, the two-body problem is to predict the motion of two massive objects which are abstractly viewed as point particles. The problem assumes that the two objects interact only with one another; the only force affecting each ...
''
or
: (2) the trapezia
''Trapezia'' is a genus of guard crabs in the family Trapeziidae. Like other members of this family, they live in association with corals, feeding on coral tissue and mucus, and defending the corals from predators, like starfish. It contains th ...
which have unstable strongly interacting orbits and are modelled as an ''n-body problem
In physics, the -body problem is the problem of predicting the individual motions of a group of celestial objects interacting with each other gravitationally.Leimanis and Minorsky: Our interest is with Leimanis, who first discusses some histor ...
'', exhibiting chaotic behavior. They can have 2, 3, or 4 stars.
Hierarchical systems
 Most multiple-star systems are organized in what is called a ''hierarchical system'': the stars in the system can be divided into two smaller groups, each of which traverses a larger orbit around the system's center of mass. Each of these smaller groups must also be hierarchical, which means that they must be divided into smaller subgroups which themselves are hierarchical, and so on. Each level of the hierarchy can be treated as a ''
Most multiple-star systems are organized in what is called a ''hierarchical system'': the stars in the system can be divided into two smaller groups, each of which traverses a larger orbit around the system's center of mass. Each of these smaller groups must also be hierarchical, which means that they must be divided into smaller subgroups which themselves are hierarchical, and so on. Each level of the hierarchy can be treated as a ''two-body problem
In classical mechanics, the two-body problem is to predict the motion of two massive objects which are abstractly viewed as point particles. The problem assumes that the two objects interact only with one another; the only force affecting each ...
'' by considering close pairs as if they were a single star. In these systems there is little interaction between the orbits and the stars' motion will continue to approximate stable Keplerian orbits around the system's center of mass, unlike the unstable trapezia
''Trapezia'' is a genus of guard crabs in the family Trapeziidae. Like other members of this family, they live in association with corals, feeding on coral tissue and mucus, and defending the corals from predators, like starfish. It contains th ...
systems or the even more complex dynamics of the large number of stars in star clusters and galaxies.
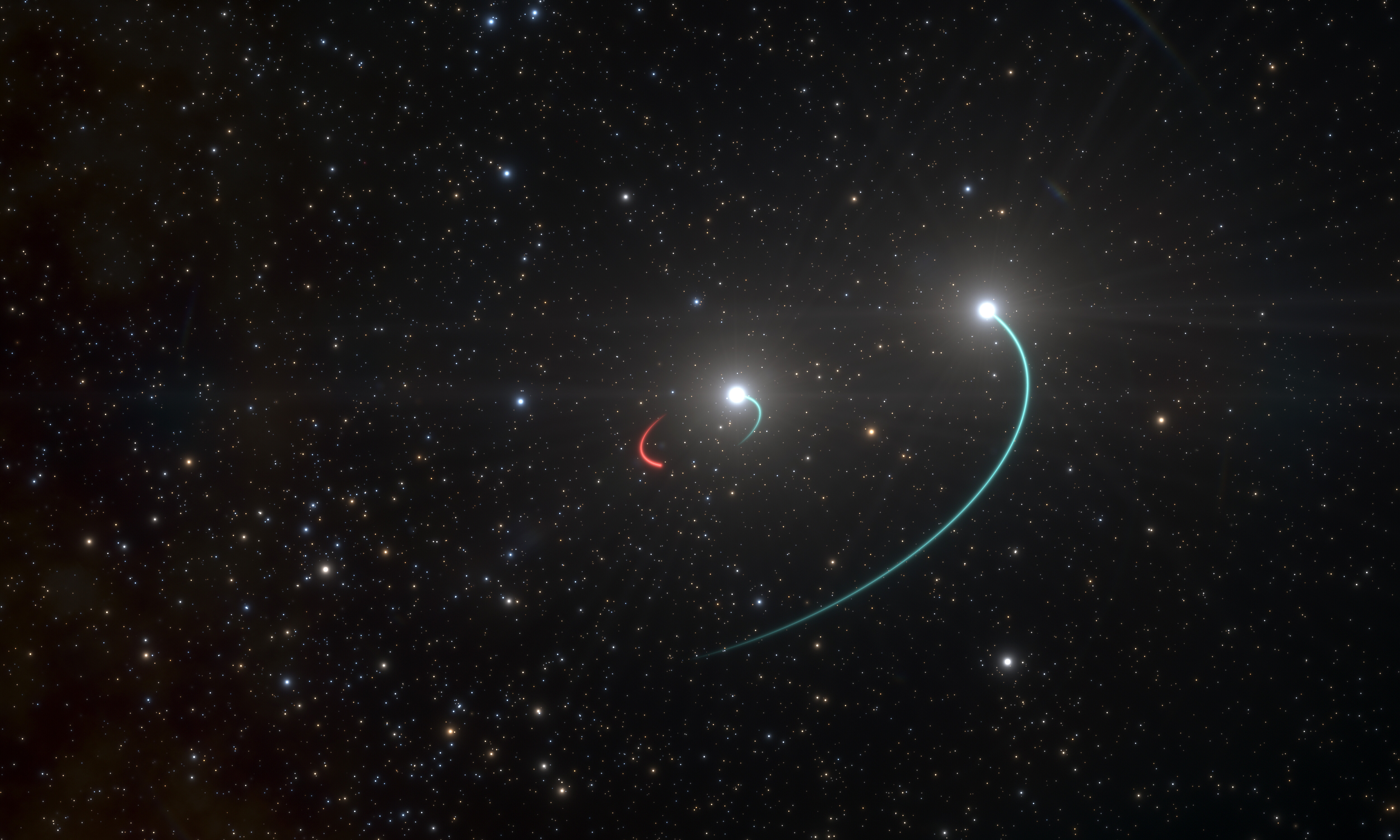
Triple star systems
 In a ''physical'' triple star system, each star
In a ''physical'' triple star system, each star orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
s the center of mass of the system. Usually, two of the stars form a close binary system
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies which are close enough that their gravitational attraction causes them to orbit each other around a barycenter ''(also see animated examples)''. More restrictive definitions require that th ...
, and the third orbits this pair at a distance much larger than that of the binary orbit. This arrangement is called ''hierarchical''. The reason for this arrangement is that if the inner and outer orbits are comparable in size, the system may become dynamically unstable, leading to a star being ejected from the system. HR 6819
HR 6819, also known as HD 167128 or QV Telescopii (abbreviated QV Tel), is a double star system in the southern constellation of Telescopium. It is in the south-western corner of the constellation, near Pavo to the so ...
is an example of a physical hierarchical triple system, which has an outer star orbiting an inner physical binary composed of a star and a stellar black hole
(although the notion that HR 6819 is a triple system has recently been challenged).
Triple stars that are ''not'' all gravitationally bound might comprise a physical binary and an ''optical'' companion (such as Beta Cephei) or, in rare cases, a purely ''optical'' triple star (such as Gamma Serpentis).
Higher multiplicities
 Hierarchical multiple star systems with more than three stars can produce a number of more complicated arrangements. These arrangements can be organized by what Evans (1968) called ''mobile diagrams'', which look similar to ornamental mobiles hung from the ceiling. Examples of hierarchical systems are given in the figure to the right (''Mobile diagrams''). Each level of the diagram illustrates the decomposition of the system into two or more systems with smaller size. Evans calls a diagram ''multiplex'' if there is a node with more than two ''children'', i.e. if the decomposition of some subsystem involves two or more orbits with comparable size. Because, as we have already seen for triple stars, this may be unstable, multiple stars are expected to be ''simplex'', meaning that at each level there are exactly two ''children''. Evans calls the number of levels in the diagram its ''hierarchy''.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 1, as in (b), describes a binary system.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 2 may describe a triple system, as in (c), or a quadruple system, as in (d).
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 3 may describe a system with anywhere from four to eight components. The mobile diagram in (e) shows an example of a quadruple system with hierarchy 3, consisting of a single distant component orbiting a close binary system, with one of the components of the close binary being an even closer binary.
* A real example of a system with hierarchy 3 is Castor, also known as Alpha Geminorum or α Gem. It consists of what appears to be a
Hierarchical multiple star systems with more than three stars can produce a number of more complicated arrangements. These arrangements can be organized by what Evans (1968) called ''mobile diagrams'', which look similar to ornamental mobiles hung from the ceiling. Examples of hierarchical systems are given in the figure to the right (''Mobile diagrams''). Each level of the diagram illustrates the decomposition of the system into two or more systems with smaller size. Evans calls a diagram ''multiplex'' if there is a node with more than two ''children'', i.e. if the decomposition of some subsystem involves two or more orbits with comparable size. Because, as we have already seen for triple stars, this may be unstable, multiple stars are expected to be ''simplex'', meaning that at each level there are exactly two ''children''. Evans calls the number of levels in the diagram its ''hierarchy''.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 1, as in (b), describes a binary system.
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 2 may describe a triple system, as in (c), or a quadruple system, as in (d).
* A simplex diagram of hierarchy 3 may describe a system with anywhere from four to eight components. The mobile diagram in (e) shows an example of a quadruple system with hierarchy 3, consisting of a single distant component orbiting a close binary system, with one of the components of the close binary being an even closer binary.
* A real example of a system with hierarchy 3 is Castor, also known as Alpha Geminorum or α Gem. It consists of what appears to be a visual binary A visual binary is a gravitationally bound binary star system that can be resolved into two stars. These stars are estimated, via Kepler's third law, to have periods ranging from a few years to thousands of years. A visual binary consists of two st ...
star which, upon closer inspection, can be seen to consist of two spectroscopic binary stars. By itself, this would be a quadruple hierarchy 2 system as in (d), but it is orbited by a fainter more distant component, which is also a close red dwarf binary. This forms a sextuple system of hierarchy 3.
* The maximum hierarchy occurring in A. A. Tokovinin's Multiple Star Catalogue, as of 1999, is 4. For example, the stars Gliese 644A and Gliese 644B form what appears to be a close visual binary star; because Gliese 644B is a spectroscopic binary, this is actually a triple system. The triple system has the more distant visual companion Gliese 643 and the still more distant visual companion Gliese 644C, which, because of their common motion with Gliese 644AB, are thought to be gravitationally bound to the triple system. This forms a quintuple system whose mobile diagram would be the diagram of level 4 appearing in (f).;
Higher hierarchies are also possible. Most of these higher hierarchies either are stable or suffer from internal perturbations. Others consider complex multiple stars will in time theoretically disintegrate into less complex multiple stars, like more common observed triples or quadruples are possible.
Trapezia
Trapezia are usually very young, unstable systems. These are thought to form in stellar nurseries, and quickly fragment into stable multiple stars, which in the process may eject components as galactic high-velocity stars. They are named after the multiple star system known as theTrapezium Cluster
The Trapezium or Orion Trapezium Cluster, also known by its Bayer designation of Theta1 Orionis, is a tight open cluster of stars in the heart of the Orion Nebula, in the constellation of Orion. It was discovered by Galileo Galilei. On 4 F ...
in the heart of the Orion Nebula. Such systems are not rare, and commonly appear close to or within bright nebulae. These stars have no standard hierarchical arrangements, but compete for stable orbits. This relationship is called ''interplay''. Such stars eventually settle down to a close binary with a distant companion, with the other star(s) previously in the system ejected into interstellar space at high velocities. This dynamic may explain the runaway star
In astronomy, stellar kinematics is the Observational astronomy, observational study or measurement of the kinematics or motions of stars through space.
Stellar kinematics encompasses the measurement of stellar Velocity, velocities in the Milky W ...
s that might have been ejected during a collision of two binary star groups or a multiple system. This event is credited with ejecting AE Aurigae
AE Aurigae (abbreviated as AE Aur) is a runaway star in the constellation Auriga; it lights the Flaming Star Nebula.
Description
AE Aurigae is a blue O-type main sequence dwarf with a mean apparent magnitude of +6.0. It is classif ...
, Mu Columbae
Mu Columbae (μ Col, μ Columbae) is a star in the constellation of Columba. It is one of the few O-class stars that are visible to the unaided eye. The star is known to lie approximately 1,300 light years from the Solar System (with an e ...
and 53 Arietis at above 200 km·s−1 and has been traced to the Trapezium cluster
The Trapezium or Orion Trapezium Cluster, also known by its Bayer designation of Theta1 Orionis, is a tight open cluster of stars in the heart of the Orion Nebula, in the constellation of Orion. It was discovered by Galileo Galilei. On 4 F ...
in the Orion Nebula some two million years ago.
Designations and nomenclature
Multiple star designations
The components of multiple stars can be specified by appending the suffixes ''A'', ''B'', ''C'', etc., to the system's designation. Suffixes such as ''AB'' may be used to denote the pair consisting of ''A'' and ''B''. The sequence of letters ''B'', ''C'', etc. may be assigned in order of separation from the component ''A''.Format, The Washington Double Star Catalog, Brian D. Mason, Gary L. Wycoff, and William I. Hartkopf, Astrometry Department,
United States Naval Observatory
United States Naval Observatory (USNO) is a scientific and military facility that produces geopositioning, navigation and timekeeping data for the United States Navy and the United States Department of Defense. Established in 1830 as the Depo ...
. Accessed on line 20 August 2008. Components discovered close to an already known component may be assigned suffixes such as ''Aa'', ''Ba'', and so forth.
Nomenclature in the Multiple Star Catalogue
 A. A. Tokovinin's Multiple Star Catalogue uses a system in which each subsystem in a mobile diagram is encoded by a sequence of digits. In the mobile diagram (d) above, for example, the widest system would be given the number 1, while the subsystem containing its primary component would be numbered 11 and the subsystem containing its secondary component would be numbered 12. Subsystems which would appear below this in the mobile diagram will be given numbers with three, four, or more digits. When describing a non-hierarchical system by this method, the same subsystem number will be used more than once; for example, a system with three visual components, A, B, and C, no two of which can be grouped into a subsystem, would have two subsystems numbered 1 denoting the two binaries AB and AC. In this case, if B and C were subsequently resolved into binaries, they would be given the subsystem numbers 12 and 13.
A. A. Tokovinin's Multiple Star Catalogue uses a system in which each subsystem in a mobile diagram is encoded by a sequence of digits. In the mobile diagram (d) above, for example, the widest system would be given the number 1, while the subsystem containing its primary component would be numbered 11 and the subsystem containing its secondary component would be numbered 12. Subsystems which would appear below this in the mobile diagram will be given numbers with three, four, or more digits. When describing a non-hierarchical system by this method, the same subsystem number will be used more than once; for example, a system with three visual components, A, B, and C, no two of which can be grouped into a subsystem, would have two subsystems numbered 1 denoting the two binaries AB and AC. In this case, if B and C were subsequently resolved into binaries, they would be given the subsystem numbers 12 and 13.
Future multiple star system nomenclature
The current nomenclature for double and multiple stars can cause confusion as binary stars discovered in different ways are given different designations (for example, discoverer designations for visual binary stars andvariable star designations
In astronomy, a variable star designation is a unique identifier given to variable stars. It uses a variation on the Bayer designation format, with an identifying label (as described below) preceding the Latin genitive of the name of the constella ...
for eclipsing binary stars), and, worse, component letters may be assigned differently by different authors, so that, for example, one person's ''A'' can be another's ''C''. Discussion starting in 1999 resulted in four proposed schemes to address this problem:
* KoMa, a hierarchical scheme using upper- and lower-case letters and Arabic and Roman numerals;
* The Urban/Corbin Designation Method, a hierarchical numeric scheme similar to the Dewey Decimal Classification
The Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC), colloquially known as the Dewey Decimal System, is a proprietary library classification system which allows new books to be added to a library in their appropriate location based on subject.
Section 4.1 ...
system;
* The Sequential Designation Method, a non-hierarchical scheme in which components and subsystems are assigned numbers in order of discovery; and
* WMC, the Washington Multiplicity Catalog, a hierarchical scheme in which the suffixes used in the Washington Double Star Catalog
The Washington Double Star Catalog, or WDS, is a catalog of double stars, maintained at the United States Naval Observatory. The catalog contains positions, magnitudes, proper motions and spectral types and has entries for (as of June 2017) 141, ...
are extended with additional suffixed letters and numbers.
For a designation system, identifying the hierarchy within the system has the advantage that it makes identifying subsystems and computing their properties easier. However, it causes problems when new components are discovered at a level above or intermediate to the existing hierarchy. In this case, part of the hierarchy will shift inwards. Components which are found to be nonexistent, or are later reassigned to a different subsystem, also cause problems.
During the 24th General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
in 2000, the WMC scheme was endorsed and it was resolved by Commissions 5, 8, 26, 42, and 45 that it should be expanded into a usable uniform designation scheme. A sample of a catalog using the WMC scheme, covering half an hour of right ascension, was later prepared. The issue was discussed again at the 25th General Assembly in 2003, and it was again resolved by commissions 5, 8, 26, 42, and 45, as well as the Working Group on Interferometry, that the WMC scheme should be expanded and further developed.
The sample WMC is hierarchically organized; the hierarchy used is based on observed orbital periods or separations. Since it contains many visual double stars, which may be optical rather than physical, this hierarchy may be only apparent. It uses upper-case letters (A, B, ...) for the first level of the hierarchy, lower-case letters (a, b, ...) for the second level, and numbers (1, 2, ...) for the third. Subsequent levels would use alternating lower-case letters and numbers, but no examples of this were found in the sample.
Examples
Binary
 *
* Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CM ...
, a binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
consisting of a main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar He ...
type A star and a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
* Procyon
Procyon () is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Minoris, which is Latinized ...
, which is similar to Sirius
* Mira
Mira (), designation Omicron Ceti (ο Ceti, abbreviated Omicron Cet, ο Cet), is a red-giant star estimated to be 200–400 light-years from the Sun in the constellation Cetus.
ο Ceti is a binary stellar system, consisting of a vari ...
, a variable consisting of a red giant and a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
* Delta Cephei, a Cepheid variable
* Epsilon Aurigae
Epsilon Aurigae (ε Aurigae, abbreviated Epsilon Aur, ε Aur) is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Auriga, the charioteer. It is an unusual eclipsing binary system comprising an F0 supergiant (officially named Alma ...
, an eclipsing binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
* Spica
Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analys ...
Trinary
* Alpha Centauri is a triple star composed of a main binary yellow dwarf pair ( Alpha Centauri A andAlpha Centauri B
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from α Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or α Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centaur ...
), and an outlying red dwarf, Proxima Centauri. Together, A and B form a physical binary star, designated as Alpha Centauri AB, α Cen AB, or RHD 1 AB, where the AB denotes this is a binary system
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies which are close enough that their gravitational attraction causes them to orbit each other around a barycenter ''(also see animated examples)''. More restrictive definitions require that th ...
.
The moderately eccentric orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
of the binary can make the components be as close as 11 AU or as far away as 36 AU. Proxima Centauri, also (though less frequently) called Alpha Centauri C, is much farther away (between 4300 and 13,000 AU) from α Cen AB, and orbits the central pair with a period of 547,000 (+66,000/-40,000) years.
* Polaris or Alpha Ursae Minoris (α UMi), the north star, is a triple star system in which the closer companion star is extremely close to the main star—so close that it was only known from its gravitational tug on Polaris A (α UMi A) until it was imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
in 2006.
* Gliese 667
Gliese 667 (142 G. Scorpii) is a triple-star system in the constellation Scorpius lying at a distance of about from Earth. All three of the stars have masses smaller than the Sun. There is a 12th-magnitude star close to the other three, ...
is a triple star system with two K-type main sequence stars and a red dwarf. The red dwarf, C, hosts between two and seven planets, of which one, Cc, alongside the unconfirmed Cf and Ce, are potentially habitable.
* HD 188753 is a triple star system located approximately 149 light-years away from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
in the constellation Cygnus. The system is composed of HD 188753A, a yellow dwarf; HD 188753B, an orange dwarf
A K-type main-sequence star, also referred to as a K-type dwarf or an orange dwarf, is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K and luminosity class V. These stars are intermediate in size between red M-type main-sequence stars ...
; and HD 188753C, a red dwarf. B and C orbit each other every 156 days, and, as a group, orbit A every 25.7 years.
* Fomalhaut
Fomalhaut is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Piscis Austrinus, the "Southern Fish", and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Piscis Austrini, which is Latinized from � ...
(α PsA, α Piscis Austrini) is a triple star system in the constellation Piscis Austrinus
Piscis Austrinus is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere. The name is Latin for "the southern fish", in contrast with the larger constellation Pisces, which represents a pair of fish. Before the 20th century, it was also known a ...
. It was discovered to be a triple system in 2013, when the K type flare star TW Piscis Austrini and the red dwarf LP 876-10 were all confirmed to share proper motion through space. The primary has a massive dust disk similar to that of the early Solar System, but much more massive. It also contains a gas giant, Fomalhaut b. That same year, the tertiary star, LP 876-10 was also confirmed to house a dust disk.
* HD 181068
HD 181068 is a star system in the constellation of Lyra. With an apparent magnitude of 7.09, the system is not visible to the naked eye but may be viewed with a pair of binoculars. Based on parallax measurements made by the Hipparc ...
is a unique triple system, consisting of a red giant and two main-sequence stars. The orbits of the stars are oriented in such a way that all three stars eclipse each other.
Quaternary
 *
* Capella
Capella is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It has the Bayer designation α Aurigae, which is Latinised to Alpha Aurigae and abbreviated Alpha Aur or α Aur. Capella is the sixth-brightest star in ...
, a pair of giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
s orbited by a pair of red dwarfs, around 42 light years away from the Solar System. It has an apparent magnitude of around 0.08, making Capella one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
* 4 Centauri
* Mizar
Mizar is a second- magnitude star in the handle of the Big Dipper asterism in the constellation of Ursa Major. It has the Bayer designation ζ Ursae Majoris ( Latinised as Zeta Ursae Majoris). It forms a well-known naked eye ...
is often said to have been the first binary star discovered when it was observed in 1650 by Giovanni Battista Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli, SJ (17 April 1598 – 25 June 1671) was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order. He is known, among other things, for his experiments with pendulums and with falling bodies, for his discussion ...
, p. 1 but it was probably observed earlier, by Benedetto Castelli
Benedetto Castelli (1578 – 9 April 1643), born Antonio Castelli, was an Italian mathematician. Benedetto was his name in religion on entering the Benedictine Order in 1595.
Life
Born in Brescia, Castelli studied at the University of Padua and ...
and Galileo. Later, spectroscopy of its components Mizar A and B revealed that they are both binary stars themselves.A New View of MizarLeos Ondra, accessed on line 26 May 2007. * HD 98800 * The
Kepler-64
PH1b (standing for "Planet Hunters 1"), or by its NASA designation Kepler-64b, is an extrasolar planet found in a circumbinary orbit in the quadruple star system Kepler-64. The planet was discovered by two amateur astronomers from the Planet H ...
system has the planet PH1 (discovered in 2012 by the Planet Hunters
Planet Hunters is a citizen science project to find exoplanets using human eyes. It does this by having users analyze data from the NASA Kepler space telescope and the NASA Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite. It was launched by a team led by ...
group, a part of the Zooniverse
Zooniverse is a citizen science web portal owned and operated by the Citizen Science Alliance. It is home to some of the Internet's largest, most popular and most successful citizen science projects. The organization grew from the original Gal ...
) orbiting two of the four stars, making it the first known planet to be in a quadruple star system.Planet Hunters/ref> * KOI-2626 is the first quadruple star system with an Earth-sized planet. *
Xi Tauri
Xi Tauri (ξ Tau, ξ Tauri) is a hierarchical quadruple system in the constellation Taurus.
Xi Tauri is a spectroscopic and eclipsing quadruple star. It consists of three blue-white B-type main sequence stars and an F-type main ...
(ξ Tau, ξ Tauri), located about 222 light years away, is a spectroscopic
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
and eclipsing quadruple star consisting of three blue-white B- type main-sequence star
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hert ...
s, along with an F-type star
An F-type main-sequence star (F V) is a main-sequence, hydrogen-fusing star of spectral type F and luminosity class V. These stars have from 1.0 to 1.4 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 6,000 and 7,600 K.Tables VII ...
. Two of the stars
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth ma ...
are in a close orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
and revolve around each other once every 7.15 days. These in turn orbit the third star once every 145 days. The fourth star orbits the other three stars roughly every fifty years.
Quintenary
* Beta Capricorni * Delta Orionis * HD 155448 *KIC 4150611 KIC may represent:
* The IATA airport code for Mesa Del Rey Airport
* The ICAO airline code for Kiwi Travel International Airlines
* The ISO 639-3 language code for Kickapoo, see ISO 639:kic
* Kepler Input Catalog of stars
* ketoisocaproate, the ...
* 1SWASP J093010.78+533859.5
Sextenary
*Beta Tucanae
Beta Tucanae, Latinized from β Tucanae, is a group of six stars which appear to be at least loosely bound into a system in the constellation Tucana. Three of the stars are luminous and distinct enough to have been given their own Bayer ...
* Castor
* HD 139691
* TYC 7037-89-1
* If Alcor is considered part of the Mizar
Mizar is a second- magnitude star in the handle of the Big Dipper asterism in the constellation of Ursa Major. It has the Bayer designation ζ Ursae Majoris ( Latinised as Zeta Ursae Majoris). It forms a well-known naked eye ...
system, the system can be considered a sextuple.
Septenary
* Nu Scorpii * AR Cassiopeiae, entry in th
Multiple Star Catalog
Octonary
*Gamma Cassiopeiae
Gamma Cassiopeiae, Latinized from γ Cassiopeiae, is a bright star at the center of the distinctive "W" asterism in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cassiopeia. Although it is a fairly bright star with an apparent visual mag ...
See also
* Exoplanet *Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
Footnotes
References
External links
* *Alpha Centauri, APOD, 2002 April 25
General news on triple star systems, TSN, 2008 April 22
is located at the U.S. Naval Observatory
Individual specimens
* *{{DEFAULTSORT:Star System