Spherical sector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

 In
In geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
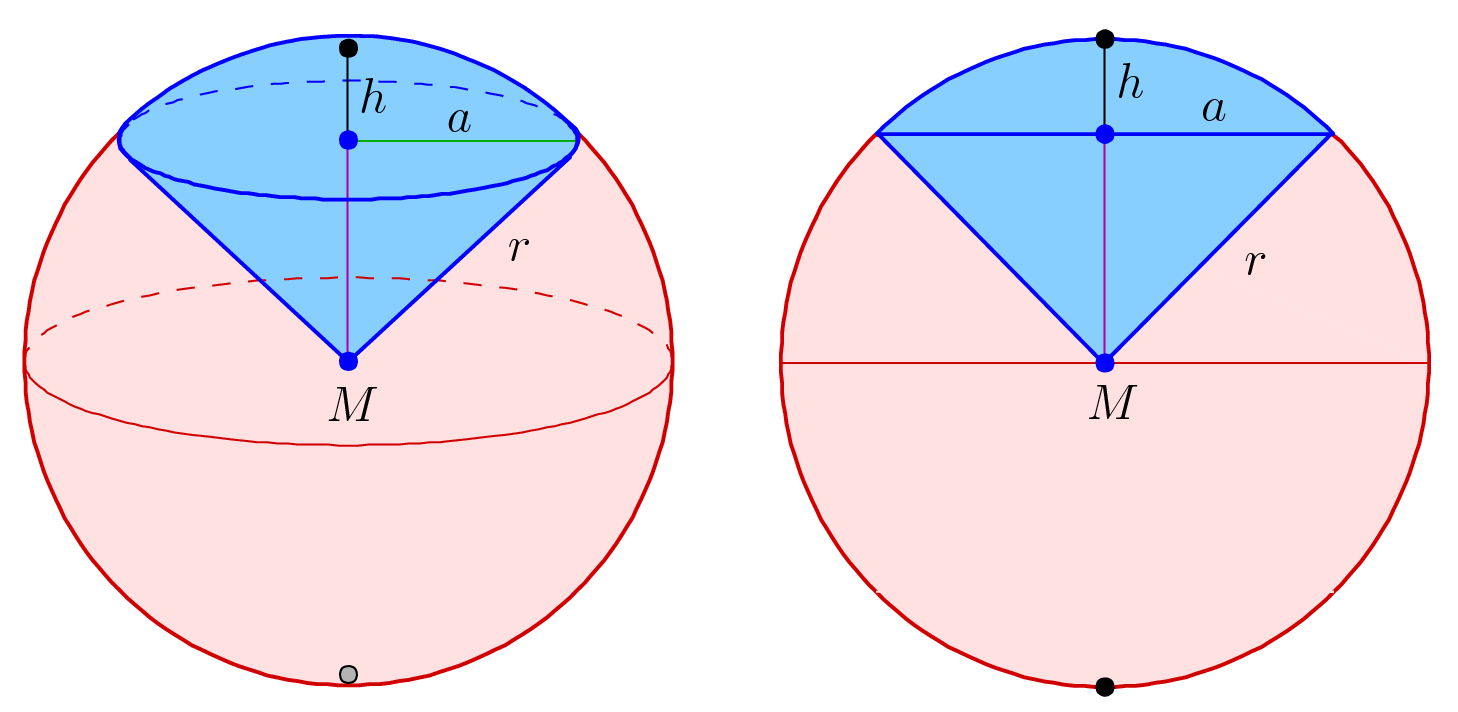
, a spherical sector, also known as a spherical cone, is a portion of a sphere
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the c ...
or of a ball
A ball is a round object (usually spherical, but can sometimes be ovoid) with several uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used f ...
defined by a conical boundary with apex at the center of the sphere. It can be described as the union of a spherical cap
In geometry, a spherical cap or spherical dome is a portion of a sphere or of a ball cut off by a plane. It is also a spherical segment of one base, i.e., bounded by a single plane. If the plane passes through the center of the sphere (formin ...
and the cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
formed by the center of the sphere and the base of the cap. It is the three-dimensional analogue of the sector
Sector may refer to:
Places
* Sector, West Virginia, U.S.
Geometry
* Circular sector, the portion of a disc enclosed by two radii and a circular arc
* Hyperbolic sector, a region enclosed by two radii and a hyperbolic arc
* Spherical sector, a po ...
of a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is cons ...
.
Volume
If the radius of the sphere is denoted by ''r'' and the height of the cap by ''h'', thevolume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). ...
of the spherical sector is
:
This may also be written as
:
where ''φ'' is half the cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines con ...
angle, i.e., ''φ'' is the angle between the rim of the cap and the direction to the middle of the cap as seen from the sphere center.
The volume ''V'' of the sector is related to the area ''A'' of the cap by:
:
Area
The curvedsurface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of ...
of the spherical sector (on the surface of the sphere, excluding the cone surface) is
:
It is also
:
where Ω is the solid angle
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: ) is a measure of the amount of the field of view from some particular point that a given object covers. That is, it is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point.
The poi ...
of the spherical sector in steradian
The steradian (symbol: sr) or square radian is the unit of solid angle in the International System of Units (SI). It is used in three-dimensional geometry, and is analogous to the radian, which quantifies planar angles. Whereas an angle in radian ...
s, the SI unit of solid angle. One steradian is defined as the solid angle subtended by a cap area of ''A'' = ''r''2.
Derivation
The volume can be calculated by integrating thedifferential volume element In mathematics, a volume element provides a means for integrating a function with respect to volume in various coordinate systems such as spherical coordinates and cylindrical coordinates. Thus a volume element is an expression of the form
:dV = ...
:
over the volume of the spherical sector,
:
where the integrals have been separated, because the integrand can be separated into a product of functions each with one dummy variable.
The area can be similarly calculated by integrating the differential spherical area element
:
over the spherical sector, giving
:
where ''φ'' is inclination (or elevation) and ''θ'' is azimuth (right). Notice ''r'' is a constant. Again, the integrals can be separated.
See also
*Circular sector
A circular sector, also known as circle sector or disk sector (symbol: ⌔), is the portion of a disk (a closed region bounded by a circle) enclosed by two radii and an arc, where the smaller area is known as the ''minor sector'' and the large ...
— the analogous 2D figure.
* Spherical cap
In geometry, a spherical cap or spherical dome is a portion of a sphere or of a ball cut off by a plane. It is also a spherical segment of one base, i.e., bounded by a single plane. If the plane passes through the center of the sphere (formin ...
* Spherical segment
In geometry, a spherical segment is the solid defined by cutting a sphere or a ball with a pair of parallel planes.
It can be thought of as a spherical cap with the top truncated, and so it corresponds to a spherical frustum.
The surface o ...
* Spherical wedge
In geometry, a spherical wedge or ungula is a portion of a ball bounded by two plane semidisks and a spherical lune (termed the wedge's ''base''). The angle between the radii lying within the bounding semidisks is the dihedral . If is a semid ...
References
Spherical geometry {{geometry-stub