Sound-on-film on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sound-on-film is a class of
Sound-on-film is a class of 
Multichannel Film Sound
(MKPE) {{Audio formats Audiovisual introductions in 1919 Film and video technology Film sound production History of film Motion picture film formats Sound
 Sound-on-film is a class of
Sound-on-film is a class of sound film
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronization, synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decad ...
processes where the sound accompanying a picture is recorded on photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an analog sound track or digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
** Digital camera, which captures and stores digital ...
sound track, and may record the signal either optically or magnetically. Earlier technologies were sound-on-disc, meaning the film's soundtrack would be on a separate phonograph record
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts near ...
.
History
Sound on film can be dated back to the early 1880s, when Charles E. Fritts filed a patent claiming the idea. In 1923 a patent was filed by E. E. Ries, for a variable density soundtrack recording, which was submitted to the SMPE (now SMPTE), which used the mercury vapor lamp as a modulating device to create a variable-density soundtrack. Later, Case Laboratories andLee De Forest
Lee de Forest (August 26, 1873 – June 30, 1961) was an American inventor and a fundamentally important early pioneer in electronics. He invented the first electronic device for controlling current flow; the three-element " Audion" triode v ...
attempted to commercialize this process, when they developed an Aeolite glow lamp, which was deployed at Movietone Newsreel at the Roxy Theatre in 1927. In 1928, Fox Film
The Fox Film Corporation (also known as Fox Studios) was an American Independent film production studio formed by William Fox (1879–1952) in 1915, by combining his earlier Greater New York Film Rental Company and Box Office Attractions Film C ...
purchased Case Laboratories and produced its first talking film ''In Old Arizona
''In Old Arizona'' is a 1928 American pre-Code Western film directed by Raoul Walsh and Irving Cummings, nominated for five Academy Awards, including Best Picture. The film, which was based on the character of the Cisco Kid in the 1907 story " ...
'' using the Aeolite system. The variable-density sound system was popular until the mid-1940s.
Opposite with variable-density, in the early 1920s, variable-area sound recording was first experimented on by the General Electric Company
The General Electric Company (GEC) was a major British industrial conglomerate involved in consumer and defence electronics, communications, and engineering. The company was founded in 1886, was Britain's largest private employer with over 250 ...
, and later was applied by RCA which refined GE's technology. After the mid-1940s, variable-area system superseded the variable-density system, and became the major analog sound-on-film system until modern day.
Analog sound-on-film recording
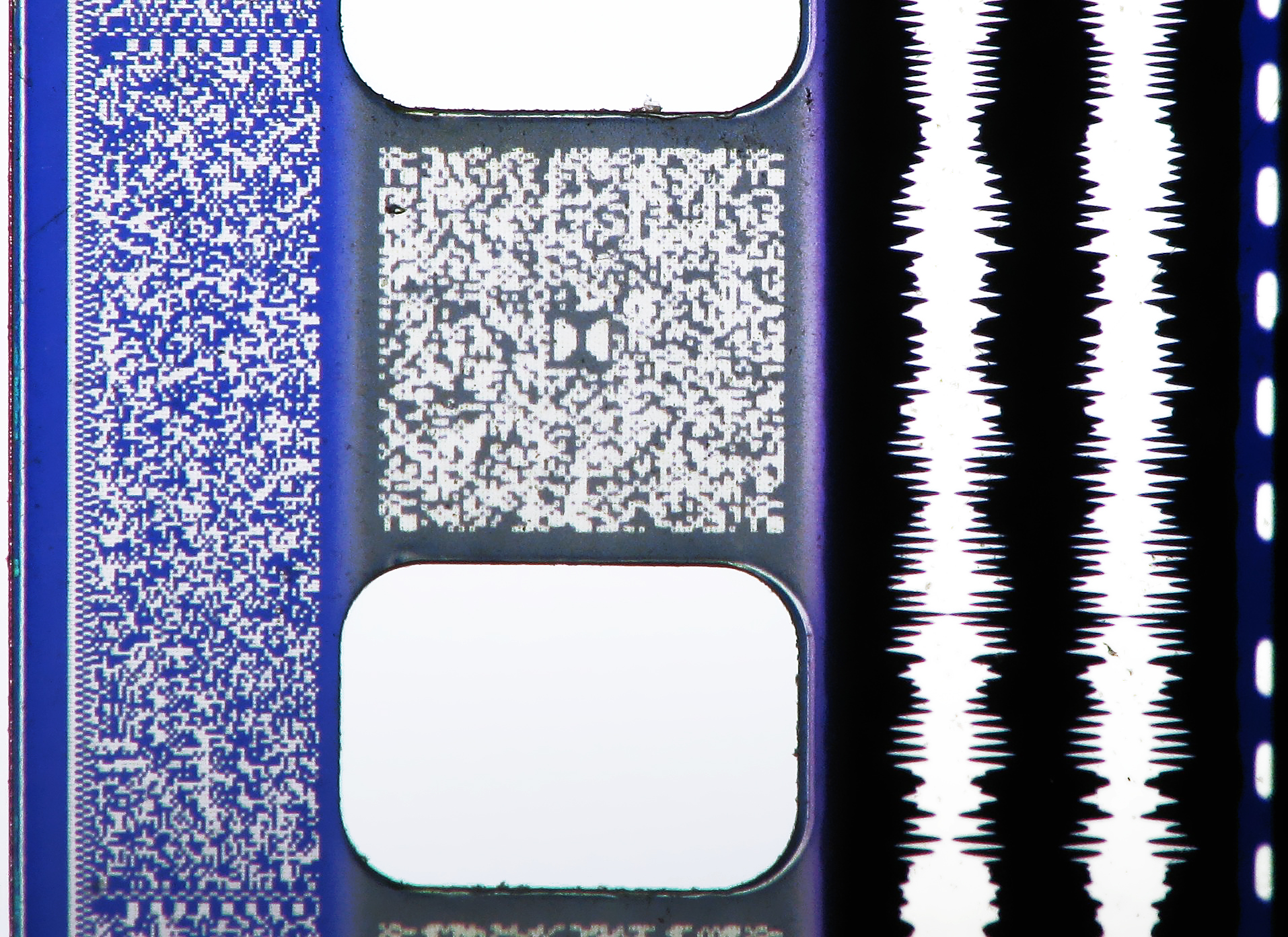
The most prevalent current method of recording analogue sound on a film print is by stereo variable-area (SVA) recording, a technique first used in the mid-1970s as Dolby Stereo. A two-channel audio signal is recorded as a pair of lines running parallel with the film's direction of travel through the projector's screen. The lines change area (grow broader or narrower) depending on the magnitude of the signal. The projector shines light from a small lamp, called an exciter, through a perpendicular slit onto the film. The image on the small slice of exposed track modulates the intensity of the light, which is collected by a photosensitive element: a photocell, aphotodiode
A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons.
The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The packag ...
or CCD.
In the early years of the 21st century distributors changed to using cyan dye optical soundtracks on color stocks instead of applicated tracks, which use environmentally unfriendly chemicals to retain a silver (black-and-white) soundtrack. Because traditional incandescent exciter lamps produce copious amounts of infra-red light, and cyan tracks do not absorb infra-red light, this change required theaters to replace the incandescent exciter lamp with a complementary colored red LED or laser. These LED or laser exciters are backwards-compatible with older tracks.
Earlier processes, used on 70 mm film
70 mm film (or 65 mm film) is a wide high-resolution film gauge for motion picture photography, with a negative area nearly 3.5 times as large as the standard 35 mm motion picture film format. As used in cameras, the film is wid ...
prints and special presentations of 35 mm film prints, recorded sound magnetically on ferric oxide
Iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Fe2O3. It is one of the three main oxides of iron, the other two being iron(II) oxide (FeO), which is rare; and iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4), which also occurs naturall ...
tracks bonded to the film print, outside the sprocket holes. 16 mm and Super 8 formats sometimes used a similar magnetic track on the camera film, bonded to one side of the film on which the sprocket holes had not been punched ("single perforated") for the purpose. Film of this form is no longer manufactured, but single-perforated film without the magnetic track (allowing an optical sound track) or, in the case of 16 mm, utilising the soundtrack area for a wider picture (Super 16 format) is readily available.
Digital sound-on-film formats
Three different digital soundtrack systems for 35 mm cinema release prints were introduced during the 1990s. They are:Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3, is the name for what has now become a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Formerly named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, the audio compression is loss ...
, which is stored between the perforations on the sound side; SDDS
is a cinema sound system developed by Sony, in which compressed digital sound information is recorded on both outer edges of the 35 mm film release print. The system supports up to eight independent channels of sound: five front chann ...
, stored in two redundant strips along the outside edges (beyond the perforations); and DTS, in which sound data is stored on separate compact disc
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. In August 1982, the first compact disc was manufactured. It was then released in O ...
s synchronized by a timecode track on the film just to the right of the analog soundtrack and left of the frame ( sound-on-disc). Because these soundtrack systems appear on different parts of the print, one movie can contain all of them, allowing broad distribution without regard for the sound system installed at individual theatres.
Sound-on-film formats
Almost all sound formats used with motion-picture film have been sound-on-film formats, including:Optical analog formats
* Fox/Western Electric
The Western Electric Company was an American electrical engineering and manufacturing company officially founded in 1869. A wholly owned subsidiary of American Telephone & Telegraph for most of its lifespan, it served as the primary equipment ma ...
(Westrex) Movietone, are variable-density formats of sound film
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronization, synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decad ...
. (No longer used, but still playable on modern 35 mm projectors.)
* Tri-Ergon
The Tri-Ergon sound-on-film system was developed from around 1919 by three German inventors, Josef Engl (1893–1942), Joseph Massolle (1889–1957), and Hans Vogt (1890–1979).
The system used a photoelectric recording method and a non-standa ...
, another variable-density format prevalent in Germany and Europe until the 1940s. The US patent rights of this Berlin based company were bought by William Fox in 1926, leading to a patent war with the US film industry lasting until 1935. Tri-Ergon amalgamated with a number of other German competitors from 1928 to form the Dutch-controlled Tobis Film
Tobis Film was a German film production and film distribution company. Founded in the late 1920s as a merger of several companies involved in the switch from silent to sound films, the organisation emerged as a leading German sound studio. Tob ...
syndicate in 1930, licensing the system to UFA GmbH
UFA GmbH, shortened to UFA (), is a film and television production company that unites all production activities of the media conglomerate Bertelsmann in Germany. Its name derives from Universum-Film Aktiengesellschaft (normally abbreviated as ...
Kreimeier, K. (translation: Hill and Wang). 1999. THE UFA STORY. London: University of California Press. as UFA-Klang.
* RCA Photophone, a variable-area format since the late 1920s—now universally used for optical analog soundtracks. Since the late 1970s usually with a Dolby
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. (often shortened to Dolby Labs and known simply as Dolby) is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to ...
encoding matrix.
Encoding matrices
* Dolby Stereo (SVA) *Dolby SR
The Dolby SR (Spectral Recording) noise reduction format was developed by Dolby Laboratories and has been in common use in professional audio since 1986 and in cinema audio since the late 1980s. It is a revised version of Dolby's earlier format ...
* Ultra Stereo
Ultra Stereo is a cinema sound system that was developed in 1984 by chief engineer Jack Cashin.
It was a 4/2/4 photographic sound encoding and decoding procedure compatible with (and using the same technical basic structure, with identical sound ...
Optical digital formats
*Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3, is the name for what has now become a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Formerly named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, the audio compression is loss ...
* Sony Dynamic Digital Sound
is a cinema sound system developed by Sony, in which compressed digital sound information is recorded on both outer edges of the 35 mm film release print. The system supports up to eight independent channels of sound: five front chann ...
Obsolete formats
*Cinema Digital Sound
Cinema Digital Sound (CDS) was a multi-channel surround sound format used for theatrical films in the early 1990s. The system was developed by Eastman Kodak and Optical Radiation Corporation. CDS was quickly superseded by Digital Theatre Systems ...
, an optical format which was the first commercial digital sound format, used between 1990 and 1992
* Fantasound. This was a system developed by RCA and Disney Studios with a multi-channel soundtrack recorded on a separate strip of film from the picture. It was used for the initial release of Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney (; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film p ...
's ''Fantasia
Fantasia International Film Festival (also known as Fantasia-fest, FanTasia, and Fant-Asia) is a film festival that has been based mainly in Montreal since its founding in 1996. Regularly held in July of each year, it is valued by both hardcor ...
'' (1940)
* Phonofilm
Phonofilm is an optical sound-on-film system developed by inventors Lee de Forest and Theodore Case in the early 1920s.
Introduction
In 1919 and 1920, Lee De Forest, inventor of the audion tube, filed his first patents on a sound-on-film proce ...
, patented by Lee De Forest
Lee de Forest (August 26, 1873 – June 30, 1961) was an American inventor and a fundamentally important early pioneer in electronics. He invented the first electronic device for controlling current flow; the three-element " Audion" triode v ...
in 1919, defunct by 1929
See also
* Charles A. Hoxie * List of film formats *List of film sound systems
The following is a list of film sound systems.
Explanation
*The year shown may represent a patent or other developmental milestone rather than the first use in public.
*Technologically identical systems may have been promoted under different tra ...
* Movietone sound system
The Movietone sound system is an optical sound-on-film method of recording sound for motion pictures that guarantees synchronization between sound and picture. It achieves this by recording the sound as a variable-density optical track on the s ...
* Optigan
The Optigan (a portmanteau of Optical Organ) is an electronic keyboard instrument designed for the consumer market. The name stems from the instrument's reliance on pre-recorded optical soundtracks to reproduce sound. Later versions (built under ...
* Phonofilm
Phonofilm is an optical sound-on-film system developed by inventors Lee de Forest and Theodore Case in the early 1920s.
Introduction
In 1919 and 1920, Lee De Forest, inventor of the audion tube, filed his first patents on a sound-on-film proce ...
* RCA Photophone
* Variophone
* Eugène Lauste
Eugène Augustin Lauste (17 January 1857 in Montmartre, France – 27 June 1935 in Montclair, New Jersey) was a French inventor instrumental in the technological development of the history of cinema.
By age 23 he held 53 French patents. He emigr ...
* Joseph Tykociński-Tykociner
References
External links
Multichannel Film Sound
(MKPE) {{Audio formats Audiovisual introductions in 1919 Film and video technology Film sound production History of film Motion picture film formats Sound