Slope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is used for slope, but its earliest use in English appears in O'Brien (1844) who wrote the equation of a straight line as and it can also be found in Todhunter (1888) who wrote it as "''y'' = ''mx'' + ''c''".
Slope is calculated by finding the
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is used for slope, but its earliest use in English appears in O'Brien (1844) who wrote the equation of a straight line as and it can also be found in Todhunter (1888) who wrote it as "''y'' = ''mx'' + ''c''".
Slope is calculated by finding the
 The slope of a line in the plane containing the ''x'' and ''y'' axes is generally represented by the letter ''m'', and is defined as the change in the ''y'' coordinate divided by the corresponding change in the ''x'' coordinate, between two distinct points on the line. This is described by the following equation:
:
(The Greek letter '' delta'', Δ, is commonly used in mathematics to mean "difference" or "change".)
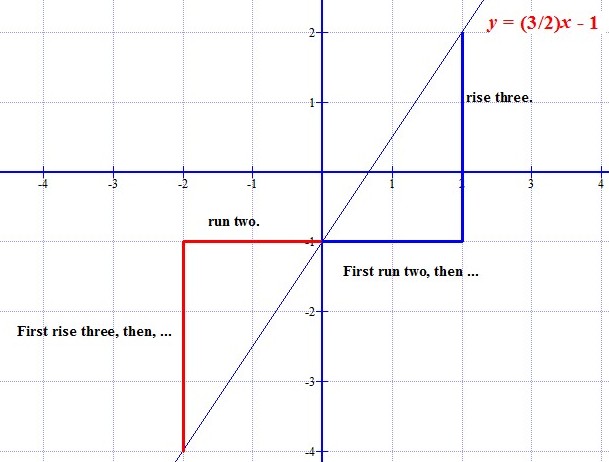
Given two points and , the change in from one to the other is (''run''), while the change in is (''rise''). Substituting both quantities into the above equation generates the formula:
:
The formula fails for a vertical line, parallel to the axis (see
The slope of a line in the plane containing the ''x'' and ''y'' axes is generally represented by the letter ''m'', and is defined as the change in the ''y'' coordinate divided by the corresponding change in the ''x'' coordinate, between two distinct points on the line. This is described by the following equation:
:
(The Greek letter '' delta'', Δ, is commonly used in mathematics to mean "difference" or "change".)
Given two points and , the change in from one to the other is (''run''), while the change in is (''rise''). Substituting both quantities into the above equation generates the formula:
:
The formula fails for a vertical line, parallel to the axis (see

File:Nederlands verkeersbord J6.svg, Slope warning sign in the
 The concept of a slope is central to differential calculus. For non-linear functions, the rate of change varies along the curve. The
The concept of a slope is central to differential calculus. For non-linear functions, the rate of change varies along the curve. The
ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of the "vertical change" to the "horizontal change" between (any) two distinct points on a line. Sometimes the ratio is expressed as a quotient ("rise over run"), giving the same number for every two distinct points on the same line. A line that is decreasing has a negative "rise". The line may be practical – as set by a road surveyor, or in a diagram that models a road or a roof either as a description or as a plan.
The ''steepness'', incline, or grade of a line is measured by the absolute value of the slope. A slope with a greater absolute value indicates a steeper line. The ''direction'' of a line is either increasing, decreasing, horizontal or vertical.
*A line is increasing if it goes up from left to right. The slope is positive, i.e. .
*A line is decreasing if it goes down from left to right. The slope is negative, i.e. .
*If a line is horizontal the slope is zero. This is a constant function.
*If a line is vertical the slope is ''undefined'' (see below).
The rise of a road between two points is the difference between the altitude of the road at those two points, say ''y''1 and ''y''2, or in other words, the rise is (''y''2 − ''y''1) = Δ''y''. For relatively short distances, where the Earth's curvature may be neglected, the run is the difference in distance from a fixed point measured along a level, horizontal line, or in other words, the run is (''x''2 − ''x''1) = Δ''x''. Here the slope of the road between the two points is simply described as the ratio of the altitude change to the horizontal distance between any two points on the line.
In mathematical language, the slope ''m'' of the line is
:
The concept of slope applies directly to grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
s or gradients in geography and civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
. Through trigonometry, the slope ''m'' of a line is related to its angle of inclination ''θ'' by the tangent function
:
Thus, a 45° rising line has a slope of +1 and a 45° falling line has a slope of −1.
As a generalization of this practical description, the mathematics of differential calculus defines the slope of a curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight.
Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that ...
at a point as the slope of the tangent line at that point. When the curve is given by a series of points in a diagram or in a list of the coordinates of points, the slope may be calculated not at a point but between any two given points. When the curve is given as a continuous function, perhaps as an algebraic expression In mathematics, an algebraic expression is an expression built up from integer constants, variables, and the algebraic operations ( addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and exponentiation by an exponent that is a rational number). ...
, then the differential calculus provides rules giving a formula for the slope of the curve at any point in the middle of the curve.
This generalization of the concept of slope allows very complex constructions to be planned and built that go well beyond static structures that are either horizontals or verticals, but can change in time, move in curves, and change depending on the rate of change of other factors. Thereby, the simple idea of slope becomes one of the main basis of the modern world in terms of both technology and the built environment.
Definition

 The slope of a line in the plane containing the ''x'' and ''y'' axes is generally represented by the letter ''m'', and is defined as the change in the ''y'' coordinate divided by the corresponding change in the ''x'' coordinate, between two distinct points on the line. This is described by the following equation:
:
(The Greek letter '' delta'', Δ, is commonly used in mathematics to mean "difference" or "change".)
Given two points and , the change in from one to the other is (''run''), while the change in is (''rise''). Substituting both quantities into the above equation generates the formula:
:
The formula fails for a vertical line, parallel to the axis (see
The slope of a line in the plane containing the ''x'' and ''y'' axes is generally represented by the letter ''m'', and is defined as the change in the ''y'' coordinate divided by the corresponding change in the ''x'' coordinate, between two distinct points on the line. This is described by the following equation:
:
(The Greek letter '' delta'', Δ, is commonly used in mathematics to mean "difference" or "change".)
Given two points and , the change in from one to the other is (''run''), while the change in is (''rise''). Substituting both quantities into the above equation generates the formula:
:
The formula fails for a vertical line, parallel to the axis (see Division by zero
In mathematics, division by zero is division where the divisor (denominator) is zero. Such a division can be formally expressed as \tfrac, where is the dividend (numerator). In ordinary arithmetic, the expression has no meaning, as there is ...
), where the slope can be taken as infinite
Infinite may refer to:
Mathematics
* Infinite set, a set that is not a finite set
*Infinity, an abstract concept describing something without any limit
Music
*Infinite (group), a South Korean boy band
*''Infinite'' (EP), debut EP of American m ...
, so the slope of a vertical line is considered undefined.
Examples
Suppose a line runs through two points: ''P'' = (1, 2) and ''Q'' = (13, 8). By dividing the difference in -coordinates by the difference in -coordinates, one can obtain the slope of the line: :. :Since the slope is positive, the direction of the line is increasing. Since , ''m'', < 1, the incline is not very steep (incline < 45°). As another example, consider a line which runs through the points (4, 15) and (3, 21). Then, the slope of the line is : :Since the slope is negative, the direction of the line is decreasing. Since , ''m'', > 1, this decline is fairly steep (decline > 45°).Algebra and geometry
Examples
For example, consider a line running through points (2,8) and (3,20). This line has a slope, , of : One can then write the line's equation, in point-slope form: : or: : The angle θ between −90° and 90° that this line makes with the -axis is : Consider the two lines: and . Both lines have slope . They are not the same line. So they are parallel lines. Consider the two lines and . The slope of the first line is . The slope of the second line is . The product of these two slopes is −1. So these two lines are perpendicular.Statistics
In statistics, the gradient of the least-squares regression best-fitting line for a given sample of data may be written as: :, This quantity ''m'' is called as the ''regression slope
In statistics, linear regression is a linear approach for modelling the relationship between a scalar response and one or more explanatory variables (also known as dependent and independent variables). The case of one explanatory variable is cal ...
'' for the line . The quantity is Pearson's correlation coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, pronounced ) ― also known as Pearson's ''r'', the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), the bivariate correlation, or colloquially simply as the correlation coefficient ...
, is the standard deviation of the y-values and is the standard deviation of the x-values. This may also be written as a ratio of covariances:
:
Slope of a road or railway
There are two common ways to describe the steepness of a road or railroad. One is by the angle between 0° and 90° (in degrees), and the other is by the slope in a percentage. See also steep grade railway and rack railway. The formulae for converting a slope given as a percentage into an angle in degrees and vice versa are: : (this is the inverse function of tangent; see trigonometry) and : where ''angle'' is in degrees and the trigonometric functions operate in degrees. For example, a slope of 100 % or 1000 ‰ is an angle of 45°. A third way is to give one unit of rise in say 10, 20, 50 or 100 horizontal units, e.g. 1:10. 1:20, 1:50 or 1:100 (or "1 ''in'' 10", "1 ''in'' 20", etc.) Note that 1:10 is steeper than 1:20. For example, steepness of 20% means 1:5 or an incline with angle 11.3°. Roads and railways have both longitudinal slopes and cross slopes.Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
File:PL road sign A-23.svg, Slope warning sign in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
File: Skloník-klesání.jpg, A 1371-meter distance of a railroad with a 20 ‰ slope. Czech Republic
File: Railway gradient post.jpg, Steam-age railway gradient post indicating a slope in both directions at Meols railway station, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
Calculus
 The concept of a slope is central to differential calculus. For non-linear functions, the rate of change varies along the curve. The
The concept of a slope is central to differential calculus. For non-linear functions, the rate of change varies along the curve. The derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
of the function at a point is the slope of the line tangent to the curve at the point, and is thus equal to the rate of change of the function at that point.
If we let Δ''x'' and Δ''y'' be the distances (along the ''x'' and ''y'' axes, respectively) between two points on a curve, then the slope given by the above definition,
:,
is the slope of a secant line
Secant is a term in mathematics derived from the Latin ''secare'' ("to cut"). It may refer to:
* a secant line, in geometry
* the secant variety, in algebraic geometry
* secant (trigonometry) (Latin: secans), the multiplicative inverse (or recipr ...
to the curve. For a line, the secant between any two points is the line itself, but this is not the case for any other type of curve.
For example, the slope of the secant intersecting ''y'' = ''x''2 at (0,0) and (3,9) is 3. (The slope of the tangent at is also 3 − ''a'' consequence of the mean value theorem.)
By moving the two points closer together so that Δ''y'' and Δ''x'' decrease, the secant line more closely approximates a tangent line to the curve, and as such the slope of the secant approaches that of the tangent. Using differential calculus, we can determine the limit, or the value that Δ''y''/Δ''x'' approaches as Δ''y'' and Δ''x'' get closer to zero; it follows that this limit is the exact slope of the tangent. If ''y'' is dependent on ''x'', then it is sufficient to take the limit where only Δ''x'' approaches zero. Therefore, the slope of the tangent is the limit of Δ''y''/Δ''x'' as Δ''x'' approaches zero, or ''dy''/''dx''. We call this limit the derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
.
:
Its value at a point on the function gives us the slope of the tangent at that point. For example, let ''y'' = ''x''2. A point on this function is (−2,4). The derivative of this function is . So the slope of the line tangent to ''y'' at (−2,4) is . The equation of this tangent line is: or .
Difference of slopes
An extension of the idea of angle follows from the difference of slopes. Consider theshear mapping
In plane geometry, a shear mapping is a linear map that displaces each point in a fixed direction, by an amount proportional to its signed distance from the line that is parallel to that direction and goes through the origin. This type of mappi ...
:
Then is mapped to . The slope of is zero and the slope of is . The shear mapping added a slope of . For two points on with slopes and , the image
:
has slope increased by , but the difference of slopes is the same before and after the shear. This invariance of slope differences makes slope an angular invariant measure, on a par with circular angle (invariant under rotation) and hyperbolic angle, with invariance group of squeeze mapping
In linear algebra, a squeeze mapping, also called a squeeze transformation, is a type of linear map that preserves Euclidean area of regions in the Cartesian plane, but is ''not'' a rotation or shear mapping.
For a fixed positive real number , th ...
s.
See also
* Euclidean distance *Grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
* Inclined plane
* Linear function
In mathematics, the term linear function refers to two distinct but related notions:
* In calculus and related areas, a linear function is a function whose graph is a straight line, that is, a polynomial function of degree zero or one. For dist ...
* Line of greatest slope
Line most often refers to:
* Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity
* Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system
Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to:
Arts ...
* Mediant
* Slope definitions
* Theil–Sen estimator, a line with the median slope among a set of sample points
References
External links
* interactive {{Calculus topics Elementary mathematics Analytic geometry Ratios