Selenography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Selenography is the study of the surface and physical features of the
Selenography is the study of the surface and physical features of the
 The idea that the Moon is not perfectly smooth originates to at least , when
The idea that the Moon is not perfectly smooth originates to at least , when

 The oldest known illustration of the Moon was found in a
The oldest known illustration of the Moon was found in a 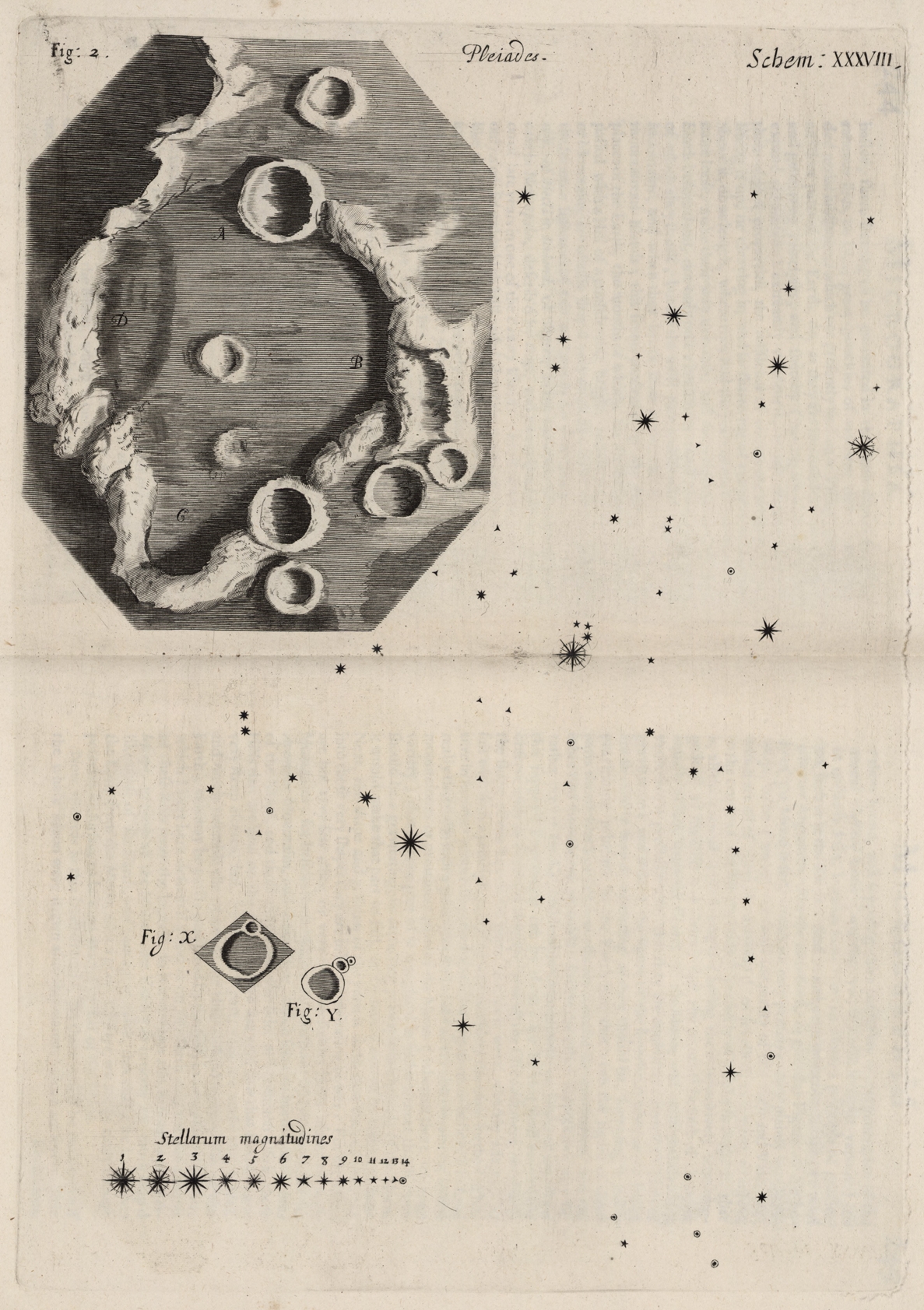 In 1647,
In 1647,  Many of the craters were denominated topically pursuant to the octant in which they were located. Craters in Octants I, II, and III were primarily denominated based on names from
Many of the craters were denominated topically pursuant to the octant in which they were located. Craters in Octants I, II, and III were primarily denominated based on names from
 The following is a list of historically-notable lunar
maps and atlases, arranged in chronological order by
publication date.
* Michel van Langren, engraved map, 1645.
*
The following is a list of historically-notable lunar
maps and atlases, arranged in chronological order by
publication date.
* Michel van Langren, engraved map, 1645.
*
NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature
(1982), Leif E. Andersson and Ewen A. Whitaker
Observing the Moon: The Modern Astronomer's GuideLunar control networks (USGS)
Kevin S. Jung
Consolidated Lunar Atlas
Virtual exhibition about the topography of the Moon
on the digital library of
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
(also known as geography of the Moon, or selenodesy). Like geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
and areography, selenography is a subdiscipline within the field of planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their ...
. Historically, the principal concern of selenographists was the mapping and naming of the lunar terrane identifying maria, crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
* Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
* Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surf ...
s, mountain ranges, and other various features. This task was largely finished when high resolution images of the near and far sides of the Moon were obtained by orbiting spacecraft during the early space era. Nevertheless, some regions of the Moon remain poorly imaged (especially near the poles) and the exact locations of many features (like crater depths) are uncertain by several kilometers. Today, selenography is considered to be a subdiscipline of selenology, which itself is most often referred to as simply "lunar science." The word selenography is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
lunar deity Σελήνη ''Selene
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Selene (; grc-gre, Σελήνη , meaning "Moon"''A Greek–English Lexicon's.v. σελήνη) is the goddess and the personification of the Moon. Also known as Mene, she is traditionally the daughter of ...
'' and γράφω graphō, "I write".
History
 The idea that the Moon is not perfectly smooth originates to at least , when
The idea that the Moon is not perfectly smooth originates to at least , when Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
asserted that the Moon's "lofty mountains and hollow valleys" were the cause of its markings. However, not until the end of the 15th century AD did serious study of selenography begin. Around AD 1603, William Gilbert made the first lunar drawing based on naked-eye observation. Others soon followed, and when the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
was invented, initial drawings of poor accuracy were made, but soon thereafter improved in tandem with optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
. In the early 18th century, the libration
In lunar astronomy, libration is the wagging or wavering of the Moon perceived by Earth-bound observers and caused by changes in their perspective. It permits an observer to see slightly different hemispheres of the surface at different tim ...
s of the Moon were measured, which revealed that more than half of the lunar surface was visible to observers on Earth. In 1750, Johann Meyer produced the first reliable set of lunar coordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is sig ...
that permitted astronomers to locate lunar features.
Lunar mapping became systematic in 1779 when Johann Schröter began meticulous observation and measurement of lunar topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
. In 1834 Johann Heinrich von Mädler published the first large cartograph (map) of the Moon, comprising 4 sheets in size, and he subsequently published ''The Universal Selenography''. All lunar measurement was based on direct observation until March 1840, when J.W. Draper JW may refer to:
*Jack Wills, a clothing company
* Jehovah's Witnesses, a Christian religious group
*''John Wick'', an action film starring Keanu Reeves
*Joko Widodo, 7th President of Indonesia, 16th Governor of Jakarta and 15th Mayor of Surakarta
...
, using a 5 inch reflector, produced a daguerreotype
Daguerreotype (; french: daguerréotype) was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.
Invented by Louis Daguerre a ...
of the Moon and thus introduced photography to astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. At first, the images were of very poor quality, but as with the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
200 years earlier, their quality rapidly improved. By 1890 lunar photography had become a recognized subdiscipline of astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
.
Lunar photography
The 20th century witnessed more advances in selenography. In 1959, theSoviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
spacecraft Luna 3
Luna 3, or E-2A No.1 ( rus, Луна 3}) was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1959 as part of the Luna programme. It was the first mission to photograph the far side of the Moon and the third Soviet space probe to be sent to the neighborhood of th ...
transmitted the first photographs of the far side of the Moon
The far side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces away from Earth, opposite to the near side, because of synchronous rotation in the Moon's orbit. Compared to the near side, the far side's terrain is rugged, with a multitu ...
, giving the first view of it in history. The United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
launched the Ranger spacecraft between 1961 and 1965 to photograph the lunar surface until the instant they impacted it, the Lunar Orbiters between 1966 and 1967 to photograph the Moon from orbit, and the Surveyors between 1966 and 1968 to photograph and softly land on the lunar surface. The Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Lunokhod
Lunokhod ( rus, Луноход, p=lʊnɐˈxot, "Moonwalker") was a series of Soviet robotic lunar rovers designed to land on the Moon between 1969 and 1977. Lunokhod 1 was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on an extraterrestrial ...
s 1 (1970) and 2 (1973) traversed almost 50 km of the lunar surface, making detailed photographs of the lunar surface. The Clementine spacecraft obtained the first nearly global cartograph (map) of the lunar topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
, and also multispectral images. Successive missions transmitted photographs of increasing resolution.
Lunar topography
The Moon has been measured by the methods of laser altimetry and stereo image analysis, including data obtained during several missions. The most visible topographical feature is the giant far side South Pole-Aitken basin, which possesses the lowestelevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
s of the Moon. The highest elevations are found just to the northeast of this basin, and it has been suggested that this area might represent thick ejecta
Ejecta (from the Latin: "things thrown out", singular ejectum) are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic materials (tephra) that came out of a volcanic explosion and magma ...
deposits that were emplaced during an oblique South Pole-Aitken basin impact event. Other large impact basins, such as the maria Imbrium, Serenitatis, Crisium, Smythii, and Orientale, also possess regionally low elevations and elevated rims.
Another distinguishing feature of the Moon's shape is that the elevations are on average about 1.9 km higher on the far side than the near side. If it is assumed that the crust is in isostatic equilibrium
Isostasy (Greek ''ísos'' "equal", ''stásis'' "standstill") or isostatic equilibrium is the state of gravitational equilibrium between Earth's crust (or lithosphere) and mantle such that the crust "floats" at an elevation that depends on its ...
, and that the density of the crust is everywhere the same, then the higher elevations would be associated with a thicker crust. Using gravity, topography and seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
data, the crust is thought to be on average about thick, with the far-side crust being on average thicker than the near side by about 15 km.
Lunar cartography and toponymy

 The oldest known illustration of the Moon was found in a
The oldest known illustration of the Moon was found in a passage grave
A passage grave or passage tomb consists of one or more burial chambers covered in earth or with stone, and having a narrow access passage made of large stones. These structures usually date from the Neolithic Age, and are found largely in Wester ...
in Knowth
Knowth (; ga, Cnóbha) is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of the World Heritage Site of Brú na Bóinne located 8.4 km west of Drogheda in Ireland's valley of the River Boyne. It is the largest passage grave of the Br ...
, County Meath
County Meath (; gle, Contae na Mí or simply ) is a county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. It is bordered by Dublin to the southeast, Louth to the northeast, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
. The tomb was carbon dated to 3330–2790 BC. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on ...
made and annotated some sketches of the Moon in c. 1500. William Gilbert made a drawing of the Moon in which he denominated a dozen surface features in the late 16th century; it was published posthumously In ''De Mondo Nostro Sublunari Philosophia Nova''. After the invention of the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
, Thomas Harriot
Thomas Harriot (; – 2 July 1621), also spelled Harriott, Hariot or Heriot, was an English astronomer, mathematician, ethnographer and translator to whom the theory of refraction is attributed. Thomas Harriot was also recognized for his con ...
(1609), Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He ...
(1609), and Christoph Scheiner
Christoph Scheiner SJ (25 July 1573 (or 1575) – 18 June 1650) was a Jesuit priest, physicist and astronomer in Ingolstadt.
Biography Augsburg/Dillingen: 1591–1605
Scheiner was born in Markt Wald near Mindelheim in Swabia, earlier markgrav ...
(1614) made drawings also.
Michiel Florent van Langren was an early-modern pioneer in the history of lunar cartography and selenography. Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999), 'Chapter 3: Van Langren (Langrenus) and the Birth of Selenography,'; in Ewen A. Whitaker, ''Mapping and Naming the Moon: A History of Lunar Cartography and Nomenclature''. (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1999), pp. 37–47 The first serious denominations of the surface features of the Moon, based on telescopic observation, were made by Van Langren in 1645. His work is considered the first true cartograph (map) of the Moon because it demarcated the various lunar maria, crater
Crater may refer to:
Landforms
* Impact crater, a depression caused by two celestial bodies impacting each other, such as a meteorite hitting a planet
* Explosion crater, a hole formed in the ground produced by an explosion near or below the surf ...
s, and mountains and ranges. Many of his denominations were distinctly Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, denominating craters in honor of Catholic royalty and capes and promontories in honor of Catholic saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Or ...
s. The lunar ''maria'' were denominated in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
for terrestrial seas and oceans. Minor craters were denominated in honor of astronomers, mathematicians, and other famous scholars. In 1647,
In 1647, Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:
*
*
*
*
*of the Royal Society
* (in German also known as ''Hevel''; pl, Jan Heweliusz; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor ...
produced the rival work '' Selenographia'', which was the first lunar atlas. Hevelius ignored the nomenclature of Van Langren and instead denominated the lunar topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
according to terrestrial features, such that the names of lunar features corresponded to the toponyms of their geographical terrestrial counterparts, especially as the latter were denominated by the ancient Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
civilizations. This work of Hevelius influenced his contemporary European astronomers, and the ''Selenographia'' was the standard reference on selenography for over a century.
Giambattista Riccioli, SJ, a Catholic priest
The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned (" ordained") with the Holy orders of the Catholic Church. Technically, bishops are a priestly order as well; however, in layman's terms ''priest'' refers onl ...
and scholar who lived in northern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
authored the present scheme of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
lunar nomenclature. His '' Almagestum novum'' was published in 1651 as summary of then current astronomical thinking and recent developments. In particular he outlined the arguments in favor of and against various cosmological models, both heliocentric and geocentric. ''Almagestum Novum'' contained scientific reference matter based on contemporary knowledge, and contemporary educators across Europe widely used it. Although this handbook of astronomy has long since been superseded, its system of lunar nomenclature is used even today.
The lunar illustrations in the ''Almagestum novum'' were drawn by a fellow Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
educator named Francesco Grimaldi, SJ. The nomenclature was based on a subdivision of the visible lunar surface into octants that were numbered in Roman style from I to VIII. Octant I referenced the northwest section and subsequent octants proceeded clockwise in alignment with compass directions. Thus Octant VI was to the south and included Clavius and Tycho Craters.
The Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
nomenclature had 2 components: the first denominated the broad features of ''terrae'' (lands) and ''maria'' (seas) and the second denominated the craters. Riccioli authored lunar toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s derived from the names of various conditions, including climactic ones, whose causes were historically attributed to the Moon. Thus there were the seas of crises ("Mare Crisium"), serenity ("Mare Serenitatis"), and fertility ("Mare Fecunditatis"). There were also the seas of rain ("Mare Imbrium"), clouds ("Mare Nubium"), and cold ("Mare Frigoris"). The topographical features between the ''maria'' were comparably denominated, but were opposite the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s of the ''maria''. Thus there were the lands of sterility ("Terra Sterilitatis"), heat ("Terra Caloris"), and life ("Terra Vitae"). However, these names for the highland regions were supplanted on later cartographs (maps). See List of features on the Moon#Terra for a complete list.
 Many of the craters were denominated topically pursuant to the octant in which they were located. Craters in Octants I, II, and III were primarily denominated based on names from
Many of the craters were denominated topically pursuant to the octant in which they were located. Craters in Octants I, II, and III were primarily denominated based on names from ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
, such as Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
, and Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientis ...
. Toward the middle in Octants IV, V, and VI craters were denominated based on names from the ancient Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, such as Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
, Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
, and Taruntius. Toward the southern half of the lunar cartograph (map) craters were denominated in honor of scholars, writers, and philosophers
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
of medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and Arabic regions. The outer extremes of Octants V, VI, and VII, and all of Octant VIII were denominated in honor of contemporaries of Giambattista Riccioli. Features of Octant VIII were also denominated in honor of Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...
, Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...
, and Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
. These persons were "banished" to it far from the "ancients," as a gesture to the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
. Many craters around the Mare Nectaris
Mare Nectaris (Latin ''nectaris'', the "Sea of Nectar") is a small lunar mare or sea (a volcanic lava plain noticeably darker than the rest of the Moon's surface) located south of Mare Tranquillitatis southwest of Mare Fecunditatis, on the near ...
were denominated in honor of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Or ...
s pursuant to the nomenclature of Van Langren. All of them were, however, connected in some mode with astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. Later cartographs (maps) removed the "St." from their toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s.
The lunar nomenclature of Giambattista Riccioli was widely used after the publication of his ''Almagestum Novum'', and many of its toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s are presently used. The system was scientifically inclusive and was considered eloquent and poetic in style, and therefore it appealed widely to his contemporaries. It was also readily extensible with new toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s for additional features. Thus it replaced the nomenclature of Van Langren and Hevelius.
Later astronomers and lunar cartographers augmented the nomenclature with additional toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s. The most notable among these contributors was Johann H. Schröter, who published a very detailed cartograph (map) of the Moon in 1791 titled the ''Selenotopografisches Fragmenten''. Schröter's adoption of Riccioli's nomenclature perpetuated it as the universally standard lunar nomenclature. A vote of the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU) in 1935 established the lunar nomenclature of Riccioli
Giovanni Battista Riccioli, SJ (17 April 1598 – 25 June 1671) was an Italian astronomer and a Catholic priest in the Jesuit order. He is known, among other things, for his experiments with pendulums and with falling bodies, for his discussion ...
, which included 600 lunar toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s, as universally official and doctrinal.
The IAU later expanded and updated the lunar nomenclature in the 1960s, but new toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s were limited to toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s honoring deceased scientists. After Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
spacecraft photographed the far side
''The Far Side'' is a single-panel comic created by Gary Larson and syndicated by Chronicle Features and then Universal Press Syndicate, which ran from December 31, 1979, to January 1, 1995 (when Larson retired as a cartoonist). Its surrealist ...
of the Moon, many of the newly discovered features were denominated in honor of Soviet scientists and engineers. The IAU assigned all subsequent new lunar toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s. Some craters were denominated in honor of space explorers.
Satellite craters
Johann H. Mädler authored the nomenclature for satellite craters. The subsidiary craters surrounding a major crater were identified by a letter. These subsidiary craters were usually smaller than the crater with which they were associated, with some exceptions. The craters could be assigned letters "A" through "Z," with "I" omitted. Because the great majority of thetoponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s of craters were masculine, the major craters were generically denominated "patronymic
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor.
Patronymics are still in use, including mandatory use, in many countries worldwide, alt ...
" craters.
The assignment of the letters to satellite craters was originally somewhat haphazard. Letters were typically assigned to craters in by order of significance rather than location. Precedence depended on the angle of illumination from the Sun at the time of the telescopic observation, which could change during the lunar day. In many cases the assignments were seemingly random. In a number of cases the satellite crater was located closer to a major crater with which it was not associated. To identify the patronymic crater, Mädler placed the identifying letter to the side of the midpoint of the feature that was closest to the associated major crater. This also had the advantage of permitting omission of the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
s of the major craters from the cartographs (maps) when their subsidiary features were labelled.
Over time, lunar observers assigned many of the satellite craters an eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
. The International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU) assumed authority to denominate lunar features in 1919. The commission for denominating these features formally adopted the convention of using capital Roman letters to identify craters and valleys.
When suitable cartographs (maps) of the far side of the Moon became available by 1966, Ewen A. Whitaker denominated satellite features based on the angle of their location relative to the major crater with which they were associated. A satellite crater located due north of the major crater was identified as "Z". The full 360° circle around the major crater was then subdivided evenly into 24 parts, like a 24-hour clock. Each "hour" angle, running clockwise, was assigned a letter, beginning with "A" at 1 o'clock. The letters "I" and "O" were omitted, resulting in only 24 letters. Thus a crater due south of its major crater was identified as "M".
Reference elevation
The Moon obviously lacks anymean sea level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the '' ...
to be used as vertical datum.
The USGS
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
's Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions ...
(LOLA), an instrument on NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions t ...
(LRO), employs a digital elevation model
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete g ...
(DEM) that uses the nominal lunar radius of .
The selenoid (the geoid
The geoid () is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity of Earth, including gravitational attraction and Earth's rotation, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended ...
for the Moon) has been measured gravimetrically by the GRAIL
The Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) was an American lunar science mission in NASA's Discovery Program which used high-quality gravitational field mapping of the Moon to determine its interior structure. The two small spacecraf ...
twin satellites.
Historical lunar maps
 The following is a list of historically-notable lunar
maps and atlases, arranged in chronological order by
publication date.
* Michel van Langren, engraved map, 1645.
*
The following is a list of historically-notable lunar
maps and atlases, arranged in chronological order by
publication date.
* Michel van Langren, engraved map, 1645.
* Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:
*
*
*
*
*of the Royal Society
* (in German also known as ''Hevel''; pl, Jan Heweliusz; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor ...
, '' Selenographia'', 1647.
* Giovanni Riccioli and Francesco Grimaldi, '' Almagestum novum'', 1651.
* Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian (naturalised French) mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the ...
, engraved map, 1679 (reprinted in 1787).
* Tobias Mayer
Tobias Mayer (17 February 172320 February 1762) was a German astronomer famous for his studies of the Moon.
He was born at Marbach, in Württemberg, and brought up at Esslingen in poor circumstances. A self-taught mathematician, he earned a l ...
, engraved map, 1749, published in 1775.
* Johann Hieronymus Schröter, ''Selenotopografisches Fragmenten'', 1st volume 1791, 2nd volume 1802.
* John Russell, engraved images, 1805.
* Wilhelm Lohrmann, ''Topographie der sichtbaren Mondoberflaeche'', Leipzig, 1824.
* Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler, ''Mappa Selenographica totam Lunae hemisphaeram visibilem complectens'', Berlin, 1834-36.
* Edmund Neison, ''The Moon'', London, 1876.
* Julius Schmidt, ''Charte der Gebirge des Mondes'', Berlin, 1878.
* Thomas Gwyn Elger, ''The Moon'', London, 1895.
* Johann Krieger, ''Mond-Atlas'', 1898. Two additional volumes were published posthumously in 1912 by the Vienna Academy of Sciences.
* Walter Goodacre
Walter Goodacre (1856 – 1 May 1938) was a British businessman and amateur astronomer.
He was the second Director of the Lunar Section of the British Astronomical Association
The British Astronomical Association (BAA) was formed in 189 ...
, ''Map of the Moon'', London, 1910.
* Mary A. Blagg and Karl Müller, ''Named Lunar Formations'', 2 volumes, London, 1935.
* Philipp Fauth, ''Unser Mond'', Bremen, 1936.
* Hugh P. Wilkins, ''300-inch Moon map'', 1951.
* Gerard Kuiper ''et al.'', ''Photographic Lunar Atlas'', Chicago, 1960.
* Ewen A. Whitaker ''et al.'', ''Rectified Lunar Atlas'', Tucson, 1963.
* Hermann Fauth and Philipp Fauth (posthumously), ''Mondatlas'', 1964.
* Gerard Kuiper ''et al.'', ''System of Lunar Craters'', 1966.
* Yu I. Efremov ''et al.'', ''Atlas Obratnoi Storony Luny'', Moscow, 1967–1975.
* NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
, ''Lunar Topographic Orthophotomaps'', 1978.
* Antonín Rükl
Antonín Rükl (September 22, 1932 – July 12, 2016) was a Czech astronomer, cartographer, and author.
He was born in Čáslav, Czechoslovakia. As a student he developed what was to be a lifelong interest in astronomy. He graduated from the Cze ...
, ''Atlas of the Moon'', 2004.
Galleries
See also
* Areography *Gravitation of the Moon
300px, Radial gravity anomaly at the surface of the Moon in mGal
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is approximately 1.625 m/s2, about 16.6% that on Earth's surface or 0.166 . Over the entire surface, the variatio ...
*Geology of the Moon
The geology of the Moon (sometimes called selenology, although the latter term can refer more generally to " lunar science") is quite different from that of Earth. The Moon lacks a true atmosphere, which eliminates erosion due to weather. It does ...
*Google Moon
Google Earth is a computer program that renders a 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and GIS data onto a 3D globe, allowing users ...
*Lunar mare
The lunar maria (; singular: mare ) are large, dark, basaltic plains on Earth's Moon, formed by ancient asteroid impacts on the far side on the Moon that triggered volcanic activity on the opposite (near) side. They were dubbed , Latin for 'seas' ...
* Lunar grazing occultation
* Planetary nomenclature
*Planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of their ...
*Selenographic coordinates
The selenographic coordinate system is used to refer to locations on the surface of Earth's moon. Any position on the lunar surface can be referenced by specifying two numerical values, which are comparable to the latitude and longitude of Earth. ...
* List of maria on the Moon
* List of craters on the Moon
* List of features on the Moon
*List of mountains on the Moon
Mountains on the Moon have heights defined relative to various vertical datums. In the 1960s, the U.S. Army Mapping Service used elevation relative to 1,737,988 meters from the center of the Moon. In the 1970s, the U.S. Defense Mapping Agency us ...
* List of valleys on the Moon
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature
(1982), Leif E. Andersson and Ewen A. Whitaker
Kevin S. Jung
Consolidated Lunar Atlas
Virtual exhibition about the topography of the Moon
on the digital library of
Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histo ...
{{The Moon
Topography
Geodesy
Lunar science
Space science
Planetary science
Selenographers
Cartography