Sea Surface Temperature on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the ocean temperature close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the
Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. Land surface temperatures have increased faster than Ocean temperature, ocean temperatures as the ocean absorbs about 92% of excess heat generated by
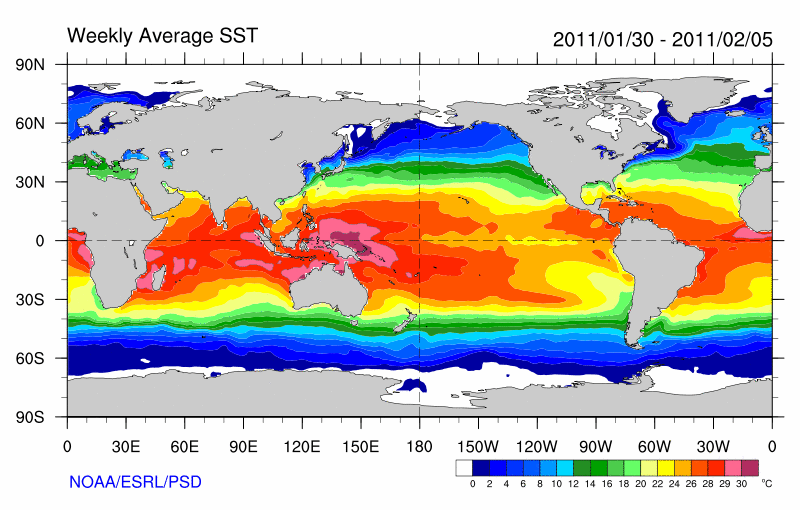
 There are a variety of techniques for measuring this parameter that can potentially yield different results because different things are actually being measured. Away from the immediate sea surface, general temperature measurements are accompanied by a reference to the specific depth of measurement. This is because of significant differences encountered between measurements made at different depths, especially during the daytime when low wind speed and high sunshine conditions may lead to the formation of a warm layer at the ocean's surface and strong vertical temperature gradients (a diurnal thermocline). Sea surface temperature measurements are confined to the top portion of the ocean, known as the near-surface layer.
There are a variety of techniques for measuring this parameter that can potentially yield different results because different things are actually being measured. Away from the immediate sea surface, general temperature measurements are accompanied by a reference to the specific depth of measurement. This is because of significant differences encountered between measurements made at different depths, especially during the daytime when low wind speed and high sunshine conditions may lead to the formation of a warm layer at the ocean's surface and strong vertical temperature gradients (a diurnal thermocline). Sea surface temperature measurements are confined to the top portion of the ocean, known as the near-surface layer.
 Weather satellites have been available to determine sea surface temperature information since 1967, with the first global composites created during 1970. Since 1982,
Weather satellites have been available to determine sea surface temperature information since 1967, with the first global composites created during 1970. Since 1982,
/span> (National Aeronautic and Space Administration) Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)
/span> SST satellites have been providing global SST data since 2000, available with a one-day lag. NOAA's GOES (Geostationary Orbiting Earth Satellites)
/span> satellites are geo-stationary above the Western Hemisphere which enables to them to deliver SST data on an hourly basis with only a few hours of lag time. There are several difficulties with satellite-based absolute SST measurements. First, in infrared remote sensing methodology the radiation emanates from the top "skin" of the ocean, approximately the top 0.01 mm or less, which may not represent the bulk temperature of the upper meter of ocean due primarily to effects of solar surface heating during the daytime, reflected radiation, as well as sensible heat loss and surface evaporation. All these factors make it somewhat difficult to compare satellite data to measurements from buoys or shipboard methods, complicating ground truth efforts. Secondly, the satellite cannot look through clouds, creating a cool bias in satellite-derived SSTs within cloudy areas. However, passive microwave techniques can accurately measure SST and penetrate cloud cover. Within atmospheric sounder channels on weather satellites, which peak just above the ocean's surface, knowledge of the sea surface temperature is important to their calibration.
 Sea surface temperature affects the behavior of the
Sea surface temperature affects the behavior of the

 Ocean temperature of at least 26.5
Ocean temperature of at least 26.5
Global map of current sea surface temperaturesGlobal map of current sea surface temperature anomalies
SQUAM
SST Quality Monitor (A near real-time Global QC Tool for monitoring time-series stability & cross-platform consistency of satellite SST)
iQuam
in situ SST Quality Monitor (A near real-time quality control & monitoring system for in situ SST measured by ships and buoys)
MICROS
Monitoring of IR Clear-sky Radiances over Oceans for SST {{DEFAULTSORT:Sea Surface Temperature Aquatic ecology Meteorological phenomena Marine meteorology Oceanography Thermodynamic cycles Articles containing video clips
sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a short distance of the shore. Localized areas of heavy snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughou ...
can form in bands downwind of warm water bodies within an otherwise cold air mass. Warm sea surface temperatures are known to be a cause of tropical cyclogenesis over the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's oceans. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake, due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. SST changes diurnally, like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less SST variation on breezy days than on calm days. In addition, ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth conto ...
s such as the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), can affect SST's on multi-decadal time scales, a major impact results from the global thermohaline
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The adjective ''thermohaline'' derives from '' thermo-'' referring to tem ...
circulation, which affects average SST significantly throughout most of the world's oceans.
Coastal SSTs can cause offshore winds to generate upwelling, which can significantly cool or warm nearby landmasses, but shallower waters over a continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
are often warmer. Onshore winds can cause a considerable warm-up even in areas where upwelling is fairly constant, such as the northwest coast of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. Its values are important within numerical weather prediction as the SST influences the atmosphere above, such as in the formation of sea breeze
A sea breeze or onshore breeze is any wind that blows from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass; it develops due to differences in air pressure created by the differing heat capacities of water and dry land. As such, sea breezes a ...
s and sea fog
''Sea Fog'' (; ''Haemoo'') is a 2014 South Korean film directed by Shim Sung-bo. The film is adapted from the 2007 stage play ''Haemoo'', which in turn was based on the true story of 25 Korean-Chinese illegal immigrants who suffocated to death ...
. It is also used to calibrate measurements from weather satellites.
It is very likely that global mean sea surface temperature increased by 0.88°C between 1850-1900 and 2011-2020 due to global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, with most of that warming (0.60°C) occurring between 1980 and 2020.Fox-Kemper, B., H.T. Hewitt, C. Xiao, G. Aðalgeirsdóttir, S.S. Drijfhout, T.L. Edwards, N.R. Golledge, M. Hemer, R.E. Kopp, G. Krinner, A. Mix, D. Notz, S. Nowicki, I.S. Nurhati, L. Ruiz, J.-B. Sallée, A.B.A. Slangen, and Y. Yu, 2021Chapter 9: Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change
I
Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
[Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.011. Land surface temperatures have increased faster than Ocean temperature, ocean temperatures as the ocean absorbs about 92% of excess heat generated by
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
Definitions
Sea surface temperature (SST), or ocean surface temperature, is the watertemperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
close to the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
's surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
surface.
The temperature further below that is called ''ocean temperature'' or ''deeper ocean temperature''. Ocean temperatures (more than 20 metres below the surface) also vary by region and time, and they contribute to variations in ocean heat content and ocean stratification. The increase of both ocean surface temperature and deeper ocean temperature is an important effect of climate change on oceans.
Variations and changes
Local variations
The SST has a diurnal range, just like the Earth's atmosphere above, though to a lesser degree due to its greater specific heat. On calm days, the temperature can vary by . The temperature of the ocean at depth lags the Earth's atmosphere temperature by 15 days per , which means for locations like the Aral Sea, temperatures near its bottom reach a maximum in December and a minimum in May and June. Near the coastline, some offshore and longshore winds move the warm waters near the surface offshore, and replace them with cooler water from below in the process known as Ekman transport. This pattern generally increases nutrients for marine life in the region, and can have a profound effect in some regions where the bottom waters are particularly nutrient-rich. Offshore ofriver delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rare ...
s, freshwater flows over the top of the denser seawater, which allows it to heat faster due to limited vertical mixing. Remotely sensed SST can be used to detect the surface temperature signature due to tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
s. In general, an SST cooling is observed after the passing of a hurricane, primarily as the result of mixed layer deepening and surface heat losses. In the wake of several day long Saharan dust outbreaks across the adjacent northern Atlantic Ocean, sea surface temperatures are reduced 0.2 C to 0.4 C (0.3 to 0.7 F). Other sources of short-term SST fluctuation include extratropical cyclones, rapid influxes of glacial fresh water and concentrated phytoplankton blooms due to seasonal cycles or agricultural run-off.
The tropical ocean has been warming faster than other regions since 1950, with the greatest rates of warming in the tropical Indian Ocean, western Pacific Ocean, and western boundary currents of the subtropical gyres. However, the eastern Pacific Ocean, subtropical North Atlantic Ocean, and Southern Ocean have warmed more slowly than the global average or have experienced cooling since the 1950s.
Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation
The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) is an important driver of North Atlantic SST and Northern Hemisphere climate, but the mechanisms controlling AMO variability remain poorly understood. Atmospheric internal variability, changes in ocean circulation, or anthropogenic drivers may control the multidecadal temperature variability associated with AMO. These changes in North Atlantic SST may influence winds in the subtropical North Pacific and produce warmer SSTs in the western Pacific Ocean.
Regional variations
El Niño is defined by prolonged differences in Pacific Ocean surface temperatures when compared with the average value. The accepted definition is a warming or cooling of at least 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) averaged over the east-central tropical Pacific Ocean. Typically, this anomaly happens at irregular intervals of 2–7 years and lasts nine months to two years. The average period length is 5 years. When this warming or cooling occurs for only seven to nine months, it is classified as El Niño/La Niña "conditions"; when it occurs for more than that period, it is classified as El Niño/La Niña "episodes". The sign of an El Niño in the sea surface temperature pattern is when warm water spreads from the west Pacific and theIndian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
to the east Pacific. It takes the rain with it, causing extensive drought in the western Pacific and rainfall in the normally dry eastern Pacific. El Niño's warm rush of nutrient-poor tropical water, heated by its eastward passage in the Equatorial Current, replaces the cold, nutrient-rich surface water of the Humboldt Current. When El Niño conditions last for many months, extensive ocean warming and the reduction in Easterly Trade winds limits upwelling of cold nutrient-rich deep water and its economic impact to local fishing for an international market can be serious.
Among scientists, there is medium confidence that the tropical Pacific will transition to a mean pattern resembling that of El Niño on centennial time scale, but there is still high uncertainty in tropical Pacific SST projections because it is difficult to capture El Niño variability in climate models.
Recent increase due to climate change
Overall, scientists project that all regions of the oceans will warm by 2050, but models disagree for SST changes expected in the subpolar North Atlantic, the equatorial Pacific, and the Southern Ocean. The future global mean SST increase for the period 1995-2014 to 2081-2100 is 0.86°C under the most modest greenhouse gas emissions scenarios, and up to 2.89°C under the most severe emissions scenarios.Measurement
 There are a variety of techniques for measuring this parameter that can potentially yield different results because different things are actually being measured. Away from the immediate sea surface, general temperature measurements are accompanied by a reference to the specific depth of measurement. This is because of significant differences encountered between measurements made at different depths, especially during the daytime when low wind speed and high sunshine conditions may lead to the formation of a warm layer at the ocean's surface and strong vertical temperature gradients (a diurnal thermocline). Sea surface temperature measurements are confined to the top portion of the ocean, known as the near-surface layer.
There are a variety of techniques for measuring this parameter that can potentially yield different results because different things are actually being measured. Away from the immediate sea surface, general temperature measurements are accompanied by a reference to the specific depth of measurement. This is because of significant differences encountered between measurements made at different depths, especially during the daytime when low wind speed and high sunshine conditions may lead to the formation of a warm layer at the ocean's surface and strong vertical temperature gradients (a diurnal thermocline). Sea surface temperature measurements are confined to the top portion of the ocean, known as the near-surface layer.
Thermometers
SST was one of the first oceanographic variables to be measured.Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading int ...
suspended a mercury thermometer
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Mercur ...
from a ship while travelling between the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
in his survey of the Gulf Stream in the late eighteenth century. SST was later measured by dipping a thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermometer ...
into a bucket of water that was manually drawn from the sea surface. The first automated technique for determining SST was accomplished by measuring the temperature of water in the intake port of large ships, which was underway by 1963. These observations have a warm bias of around due to the heat of the engine room.
Fixed weather buoys measure the water temperature at a depth of . Measurements of SST have had inconsistencies over the last 130 years due to the way they were taken. In the nineteenth century, measurements were taken in a bucket off of a ship. However, there was a slight variation in temperature because of the differences in buckets. Samples were collected in either a wood or an uninsulated canvas bucket, but the canvas bucket cooled quicker than the wood bucket. The sudden change in temperature between 1940 and 1941 was the result of an undocumented change in procedure. The samples were taken near the engine intake because it was too dangerous to use lights to take measurements over the side of the ship at night.
Many different drifting buoys exist around the world that vary in design, and the location of reliable temperature sensors varies. These measurements are beamed to satellites for automated and immediate data distribution. A large network of coastal buoys in U.S. waters is maintained by the National Data Buoy Center
The National Data Buoy Center (NDBC) is a part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) National Weather Service (NWS). NDBC designs, develops, operates, and maintains a network of data collecting buoys and coastal stati ...
(NDBC). Between 1985 and 1994, an extensive array of moored and drifting buoys was deployed across the equatorial Pacific Ocean designed to help monitor and predict the El Niño phenomenon.
Weather satellites
 Weather satellites have been available to determine sea surface temperature information since 1967, with the first global composites created during 1970. Since 1982,
Weather satellites have been available to determine sea surface temperature information since 1967, with the first global composites created during 1970. Since 1982, satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
s have been increasingly utilized to measure SST and have allowed its spatial and temporal variation to be viewed more fully. Satellite measurements of SST are in reasonable agreement with in situ temperature measurements. The satellite measurement is made by sensing the ocean radiation in two or more wavelengths within the infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
part of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging fro ...
or other parts of the spectrum which can then be empirically related to SST. These wavelengths are chosen because they are:
# within the peak of the blackbody radiation expected from the Earth, and
# able to transmit adequately well through the atmosphere
The satellite-measured SST provides both a synoptic view of the ocean and a high frequency of repeat views, allowing the examination of basin-wide upper ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
dynamics not possible with ships or buoys. NASA's/span> (National Aeronautic and Space Administration) Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)
/span> SST satellites have been providing global SST data since 2000, available with a one-day lag. NOAA's GOES (Geostationary Orbiting Earth Satellites)
/span> satellites are geo-stationary above the Western Hemisphere which enables to them to deliver SST data on an hourly basis with only a few hours of lag time. There are several difficulties with satellite-based absolute SST measurements. First, in infrared remote sensing methodology the radiation emanates from the top "skin" of the ocean, approximately the top 0.01 mm or less, which may not represent the bulk temperature of the upper meter of ocean due primarily to effects of solar surface heating during the daytime, reflected radiation, as well as sensible heat loss and surface evaporation. All these factors make it somewhat difficult to compare satellite data to measurements from buoys or shipboard methods, complicating ground truth efforts. Secondly, the satellite cannot look through clouds, creating a cool bias in satellite-derived SSTs within cloudy areas. However, passive microwave techniques can accurately measure SST and penetrate cloud cover. Within atmospheric sounder channels on weather satellites, which peak just above the ocean's surface, knowledge of the sea surface temperature is important to their calibration.
Importance to the Earth's atmosphere
 Sea surface temperature affects the behavior of the
Sea surface temperature affects the behavior of the Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
above, so their initialization into atmospheric models is important. While sea surface temperature is important for tropical cyclogenesis, it is also important in determining the formation of sea fog and sea breezes. Heat from underlying warmer waters can significantly modify an air mass over distances as short as to . For example, southwest of Northern Hemisphere extratropical cyclones, curved cyclonic flow bringing cold air across relatively warm water bodies can lead to narrow lake-effect snow (or sea effect) bands. Those bands bring strong localized precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
, often in the form of snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughou ...
, since large water bodies such as lakes efficiently store heat that results in significant temperature differences—larger than —between the water surface and the air above. Because of this temperature difference, warmth and moisture are transported upward, condensing into vertically oriented clouds which produce snow showers. The temperature decrease with height and cloud depth are directly affected by both the water temperature and the large-scale environment. The stronger the temperature decrease with height, the taller the clouds get, and the greater the precipitation rate becomes.
Tropical cyclones

 Ocean temperature of at least 26.5
Ocean temperature of at least 26.5°C
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius scale (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the Kelvin scale. The d ...
(79.7 °F) spanning through at minimum a 50-metre
The metre ( British spelling) or meter ( American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its pre ...
depth is one of the precursors needed to maintain a tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
(a type of mesocyclone). These warm waters are needed to maintain the warm core
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
that fuels tropical systems. This value is well above 16.1 °C (60.9 °F), the long term global average surface temperature of the oceans. However, this requirement can be considered only a general baseline because it assumes that the ambient atmospheric environment surrounding an area of disturbed weather presents average conditions. Tropical cyclones have intensified when SSTs were slightly below this standard temperature.
Tropical cyclones are known to form even when normal conditions are not met. For example, cooler air temperatures at a higher altitude (e.g., at the 500 hPa level, or 5.9 km) can lead to tropical cyclogenesis at lower water temperatures, as a certain lapse rate is required to force the atmosphere to be unstable enough for convection. In a moist atmosphere, this lapse rate is 6.5 °C/km, while in an atmosphere with less than 100% relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
, the required lapse rate is 9.8 °C/km.
At the 500 hPa level, the air temperature averages −7 °C (18 °F) within the tropics, but air in the tropics is normally dry at this height, giving the air room to wet-bulb, or cool as it moistens, to a more favorable temperature that can then support convection. A wet-bulb temperature at 500 hPa in a tropical atmosphere of is required to initiate convection if the water temperature is , and this temperature requirement increases or decreases proportionally by 1 °C in the sea surface temperature for each 1 °C change at 500 hpa.
Inside a cold cyclone, 500 hPa temperatures can fall as low as , which can initiate convection even in the driest atmospheres. This also explains why moisture in the mid-levels of the troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. Fro ...
, roughly at the 500 hPa level, is normally a requirement for development. However, when dry air is found at the same height, temperatures at 500 hPa need to be even colder as dry atmospheres require a greater lapse rate for instability than moist atmospheres. At heights near the tropopause, the 30-year average temperature (as measured in the period encompassing 1961 through 1990) was −77 °C (−132 °F). A recent example of a tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
that maintained itself over cooler waters was Epsilon of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season.
See also
* Global surface temperature *The Blob (Pacific Ocean)
The Blob is a large mass of relatively warm water in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of North America that was first detected in late 2013 and continued to spread throughout 2014 and 2015. It is an example of a marine heatwave. Sea surface te ...
* Sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cr ...
* Halocline
In oceanography, a halocline (from Greek ''hals'', ''halos'' 'salt' and ''klinein'' 'to slope') is a cline, a subtype of chemocline caused by a strong, vertical salinity gradient within a body of water. Because salinity (in concert with te ...
refers to a salinity difference often altered by temperature-dependent factors
* Loop Current
A parent to the Florida Current, the Loop Current is a warm ocean current that flows northward between Cuba and the Yucatán Peninsula, moves north into the Gulf of Mexico, loops east and south before exiting to the east through the Florida Str ...
, with plots of sea temperature in the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
* Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO)
* Salinity
* Ghrsst-pp The Group for High Resolution SST (GHRSST) is a follow on activity form the Global Ocean Data Assimilation Experiment (GODAE) high-resolution sea surface temperature pilot project. It provides a global high-resolution (<10 km) data products to ...
the Group for High Resolution SST
* Satellite temperature measurements
* Instrumental temperature record
References
External links
Global map of current sea surface temperatures
SQUAM
SST Quality Monitor (A near real-time Global QC Tool for monitoring time-series stability & cross-platform consistency of satellite SST)
iQuam
in situ SST Quality Monitor (A near real-time quality control & monitoring system for in situ SST measured by ships and buoys)
MICROS
Monitoring of IR Clear-sky Radiances over Oceans for SST {{DEFAULTSORT:Sea Surface Temperature Aquatic ecology Meteorological phenomena Marine meteorology Oceanography Thermodynamic cycles Articles containing video clips