Satraps on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A satrap () was a governor of the
A satrap () was a governor of the
 Although the first large-scale use of satrapies, or provinces, originates from the inception of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, beginning at around 530BCE, provincial organization actually originated during the Median era from at least 648BCE.
Up to the time of the conquest of
Although the first large-scale use of satrapies, or provinces, originates from the inception of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, beginning at around 530BCE, provincial organization actually originated during the Median era from at least 648BCE.
Up to the time of the conquest of  The satrap was in charge of the land that he owned as an administrator, and found himself surrounded by an all-but-royal court; he collected the taxes, controlled the local officials and the subject tribes and cities, and was the supreme judge of the province before whose "chair" (''Nehemiah''3:7) every civil and criminal case could be brought. He was responsible for the safety of the roads (cf.Xenophon), and had to put down brigands and rebels.
He was assisted by a council of Persians, to which also provincials were admitted and which was controlled by a royal secretary and emissaries of the king, especially the "eye of the king", who made an annual inspection and exercised permanent control.
The satrap was in charge of the land that he owned as an administrator, and found himself surrounded by an all-but-royal court; he collected the taxes, controlled the local officials and the subject tribes and cities, and was the supreme judge of the province before whose "chair" (''Nehemiah''3:7) every civil and criminal case could be brought. He was responsible for the safety of the roads (cf.Xenophon), and had to put down brigands and rebels.
He was assisted by a council of Persians, to which also provincials were admitted and which was controlled by a royal secretary and emissaries of the king, especially the "eye of the king", who made an annual inspection and exercised permanent control.
 There were further checks on the power of each satrap: besides his secretarial scribe, his chief financial official (Old Persian ''ganzabara'') and the general in charge of the regular army of his province and of the fortresses were independent of him and periodically reported directly to the ''shah'', in person. The satrap was allowed to have troops in his own service.
The great satrapies (provinces) were often divided into smaller districts, the governors of which were also called satraps and (by Greco-Roman authors) also called ''hyparchs'' (actually ''Hyparkhos'' in Greek, 'vice-regents'). The distribution of the great satrapies was changed repeatedly, and often two of them were given to the same man.
There were further checks on the power of each satrap: besides his secretarial scribe, his chief financial official (Old Persian ''ganzabara'') and the general in charge of the regular army of his province and of the fortresses were independent of him and periodically reported directly to the ''shah'', in person. The satrap was allowed to have troops in his own service.
The great satrapies (provinces) were often divided into smaller districts, the governors of which were also called satraps and (by Greco-Roman authors) also called ''hyparchs'' (actually ''Hyparkhos'' in Greek, 'vice-regents'). The distribution of the great satrapies was changed repeatedly, and often two of them were given to the same man.
 As the provinces were the result of consecutive conquests (the homeland had a special status, exempt from provincial tribute), both primary and sub-satrapies were often defined by former states and/or ethno-religious identity. One of the keys to the Achaemenid success was their open attitude to the culture and religion of the conquered people, so the Persian culture was the one most affected as the Great King endeavoured to meld elements from all his subjects into a new imperial style, especially at his capital,
As the provinces were the result of consecutive conquests (the homeland had a special status, exempt from provincial tribute), both primary and sub-satrapies were often defined by former states and/or ethno-religious identity. One of the keys to the Achaemenid success was their open attitude to the culture and religion of the conquered people, so the Persian culture was the one most affected as the Great King endeavoured to meld elements from all his subjects into a new imperial style, especially at his capital,  Whenever central authority in the empire weakened, the satrap often enjoyed practical independence, especially as it became customary to appoint him also as general-in-chief of the army district, contrary to the original rule. "When his office became hereditary, the threat to the central authority could not be ignored" (Olmstead). Rebellions of satraps became frequent from the middle of the 5thcentury BCE. Darius I struggled with widespread rebellions in the satrapies, and under
Whenever central authority in the empire weakened, the satrap often enjoyed practical independence, especially as it became customary to appoint him also as general-in-chief of the army district, contrary to the original rule. "When his office became hereditary, the threat to the central authority could not be ignored" (Olmstead). Rebellions of satraps became frequent from the middle of the 5thcentury BCE. Darius I struggled with widespread rebellions in the satrapies, and under
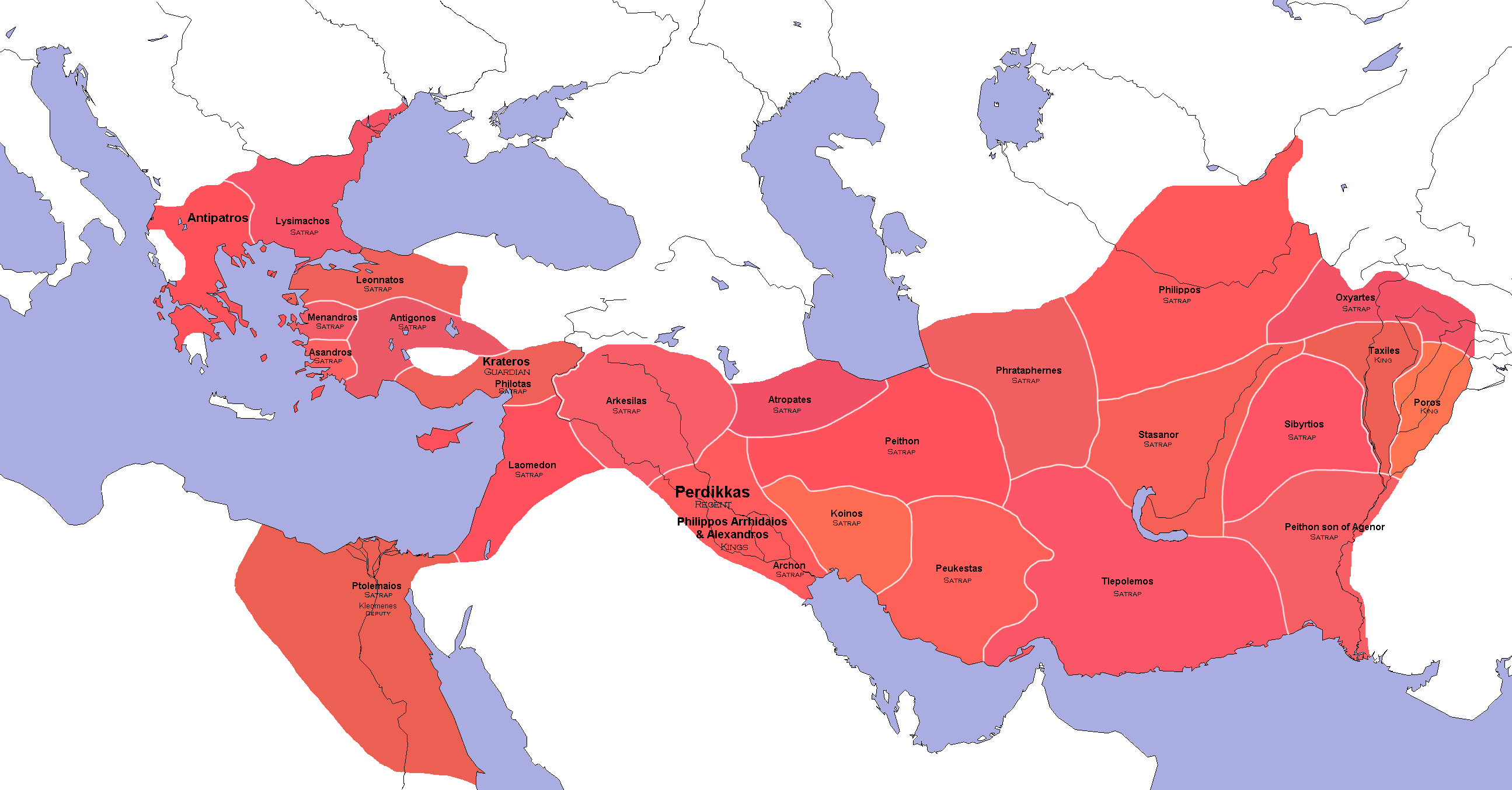 The satrapic administration and title were retained—even for Greco-Macedonian incumbents—by
The satrapic administration and title were retained—even for Greco-Macedonian incumbents—by
 The Western Satraps or Kshatrapas (35–405 CE) of the
The Western Satraps or Kshatrapas (35–405 CE) of the
Livius.org: Satraps and satrapies
{{Authority control Positions of subnational authority Achaemenid Empire Types of administrative division Gubernatorial titles Iranian inventions
 A satrap () was a governor of the
A satrap () was a governor of the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
s of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
empires.
The satrap served as viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption.
A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap.
Etymology
The word is derived via Latin fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are grouped ...
''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in .
In the Parthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
(language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
(the language of the Sassanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
), it is recorded in the forms ''šahrab'' and ''šasab'', respectively.
In modern Persian
New Persian ( fa, فارسی نو), also known as Modern Persian () and Dari (), is the current stage of the Persian language spoken since the 8th to 9th centuries until now in Greater Iran and surroundings. It is conventionally divided into thre ...
the descendant of khshathrapavan is ''shahrbān'' (), but the components have undergone semantic shift
Semantic change (also semantic shift, semantic progression, semantic development, or semantic drift) is a form of language change regarding the evolution of word usage—usually to the point that the modern meaning is radically different from ...
so the word now means "town keeper" (''shahr'' [] meaning "town" + ''ban'' [] meaning "keeper").
History
Medo-Persian
 Although the first large-scale use of satrapies, or provinces, originates from the inception of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, beginning at around 530BCE, provincial organization actually originated during the Median era from at least 648BCE.
Up to the time of the conquest of
Although the first large-scale use of satrapies, or provinces, originates from the inception of the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, beginning at around 530BCE, provincial organization actually originated during the Median era from at least 648BCE.
Up to the time of the conquest of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
by Cyrus the Great, emperors ruled the lands they conquered through client king
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
s and governors. The main difference was that in Persian culture the concept of kingship was indivisible from divinity: divine authority validated the divine right of kings. The twenty-six satraps established by Cyrus were never kings, but viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
s ruling in the king's name, although in political reality many took advantage of any opportunity to carve themselves an independent power base. Darius the Great gave the satrapies a definitive organization, increased their number to thirty-six, and fixed their annual tribute ( Behistun inscription).
 The satrap was in charge of the land that he owned as an administrator, and found himself surrounded by an all-but-royal court; he collected the taxes, controlled the local officials and the subject tribes and cities, and was the supreme judge of the province before whose "chair" (''Nehemiah''3:7) every civil and criminal case could be brought. He was responsible for the safety of the roads (cf.Xenophon), and had to put down brigands and rebels.
He was assisted by a council of Persians, to which also provincials were admitted and which was controlled by a royal secretary and emissaries of the king, especially the "eye of the king", who made an annual inspection and exercised permanent control.
The satrap was in charge of the land that he owned as an administrator, and found himself surrounded by an all-but-royal court; he collected the taxes, controlled the local officials and the subject tribes and cities, and was the supreme judge of the province before whose "chair" (''Nehemiah''3:7) every civil and criminal case could be brought. He was responsible for the safety of the roads (cf.Xenophon), and had to put down brigands and rebels.
He was assisted by a council of Persians, to which also provincials were admitted and which was controlled by a royal secretary and emissaries of the king, especially the "eye of the king", who made an annual inspection and exercised permanent control.
 There were further checks on the power of each satrap: besides his secretarial scribe, his chief financial official (Old Persian ''ganzabara'') and the general in charge of the regular army of his province and of the fortresses were independent of him and periodically reported directly to the ''shah'', in person. The satrap was allowed to have troops in his own service.
The great satrapies (provinces) were often divided into smaller districts, the governors of which were also called satraps and (by Greco-Roman authors) also called ''hyparchs'' (actually ''Hyparkhos'' in Greek, 'vice-regents'). The distribution of the great satrapies was changed repeatedly, and often two of them were given to the same man.
There were further checks on the power of each satrap: besides his secretarial scribe, his chief financial official (Old Persian ''ganzabara'') and the general in charge of the regular army of his province and of the fortresses were independent of him and periodically reported directly to the ''shah'', in person. The satrap was allowed to have troops in his own service.
The great satrapies (provinces) were often divided into smaller districts, the governors of which were also called satraps and (by Greco-Roman authors) also called ''hyparchs'' (actually ''Hyparkhos'' in Greek, 'vice-regents'). The distribution of the great satrapies was changed repeatedly, and often two of them were given to the same man.
 As the provinces were the result of consecutive conquests (the homeland had a special status, exempt from provincial tribute), both primary and sub-satrapies were often defined by former states and/or ethno-religious identity. One of the keys to the Achaemenid success was their open attitude to the culture and religion of the conquered people, so the Persian culture was the one most affected as the Great King endeavoured to meld elements from all his subjects into a new imperial style, especially at his capital,
As the provinces were the result of consecutive conquests (the homeland had a special status, exempt from provincial tribute), both primary and sub-satrapies were often defined by former states and/or ethno-religious identity. One of the keys to the Achaemenid success was their open attitude to the culture and religion of the conquered people, so the Persian culture was the one most affected as the Great King endeavoured to meld elements from all his subjects into a new imperial style, especially at his capital, Persepolis
, native_name_lang =
, alternate_name =
, image = Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption = Ruins of the Gate of All Nations, Persepolis.
, map =
, map_type ...
.
 Whenever central authority in the empire weakened, the satrap often enjoyed practical independence, especially as it became customary to appoint him also as general-in-chief of the army district, contrary to the original rule. "When his office became hereditary, the threat to the central authority could not be ignored" (Olmstead). Rebellions of satraps became frequent from the middle of the 5thcentury BCE. Darius I struggled with widespread rebellions in the satrapies, and under
Whenever central authority in the empire weakened, the satrap often enjoyed practical independence, especially as it became customary to appoint him also as general-in-chief of the army district, contrary to the original rule. "When his office became hereditary, the threat to the central authority could not be ignored" (Olmstead). Rebellions of satraps became frequent from the middle of the 5thcentury BCE. Darius I struggled with widespread rebellions in the satrapies, and under Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
occasionally the greater parts of Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
and Syria were in open rebellion (Revolt of the Satraps
The Great Satraps' Revolt, or the Revolt of the Satraps (366-360 BC), was a rebellion in the Achaemenid Empire of several satraps against the authority of the Great King Artaxerxes II Mnemon. The Satraps who revolted were Datames, Ariobarzanes and ...
).
The last great rebellions were put down by Artaxerxes III
Ochus ( grc-gre, Ὦχος ), known by his dynastic name Artaxerxes III ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 359/58 to 338 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
.
Seleucid
 The satrapic administration and title were retained—even for Greco-Macedonian incumbents—by
The satrapic administration and title were retained—even for Greco-Macedonian incumbents—by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, who conquered the Achaemenid Empire, and by his successors, the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
(and their dynasties) who carved it up, especially in the Seleucid Empire, where the satrap generally was designated as '' strategos'' (in other words, military generals); but their provinces were much smaller than under the Persians. They would ultimately be replaced by conquering empires, especially the Parthians.
Parthian and Sassanian
In theParthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
, the king's power rested on the support of noble families, who ruled large estates and supplied soldiers and tribute to the king. City-states within the empire enjoyed a degree of self-government, and paid tribute to the king. Administration of the Sassanid Empire was considerably more centralized than that of the Parthian Empire; the semi-independent kingdoms and self-governing city states of the Parthian Empire were replaced with a system of "royal cities" which served as the seats of centrally appointed governors called ''shahrabs'' as well as the location of military garrisons. ''Shahrabs'' ruled both the city and the surrounding rural districts. Exceptionally, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
also adopted the title "satrap" for the semi-autonomous princes that governed one of its Armenian provinces, the ''Satrapiae''.
Indian
 The Western Satraps or Kshatrapas (35–405 CE) of the
The Western Satraps or Kshatrapas (35–405 CE) of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
were Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
rulers in the western and central part of the Sindh region of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
, and the Saurashtra and Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syn ...
regions of western India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. They were contemporaneous with the Kushans, who ruled the northern part of the subcontinent from the area of Peshawar
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
and were possibly their overlords, and with the Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the la ...
, who ruled in central India to their south and east and the Kushan state to their immediate west.
See also
*Taxation districts of the Achaemenid Empire
Herodotus divided the Achaemenid Empire into 20 districts for the purpose of tribute payments. The following is a description of the ethnic makeup of the districts and the amount they paid in taxes, translated from Herodotus' '' Histories''.
Acc ...
*Orontid Dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after t ...
* Suzerainty
References
*Further reading
*A. T. Olmstead, ''History of the Persian Empire,'' 1948. *Pauly-Wissowa (comprehensive encyclopaedia on Antiquity; in German). *Robert Dick Wilson. ''The Book of Daniel: A Discussion of the Historical Questions'', 1917. Available on home.earthlink.net. *Rüdiger Schmitt, "Der Titel 'Satrap'", in ''Studies Palmer'' ed. Meid (1976), 373–390. *. *Cormac McCarthy, ''All the Pretty Horses,'' 1992.External links
Livius.org: Satraps and satrapies
{{Authority control Positions of subnational authority Achaemenid Empire Types of administrative division Gubernatorial titles Iranian inventions