Salamanders on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Salamanders are a group of
 The skin lacks scales and is moist and smooth to the touch, except in
The skin lacks scales and is moist and smooth to the touch, except in
 Some aquatic species, such as sirens and
Some aquatic species, such as sirens and
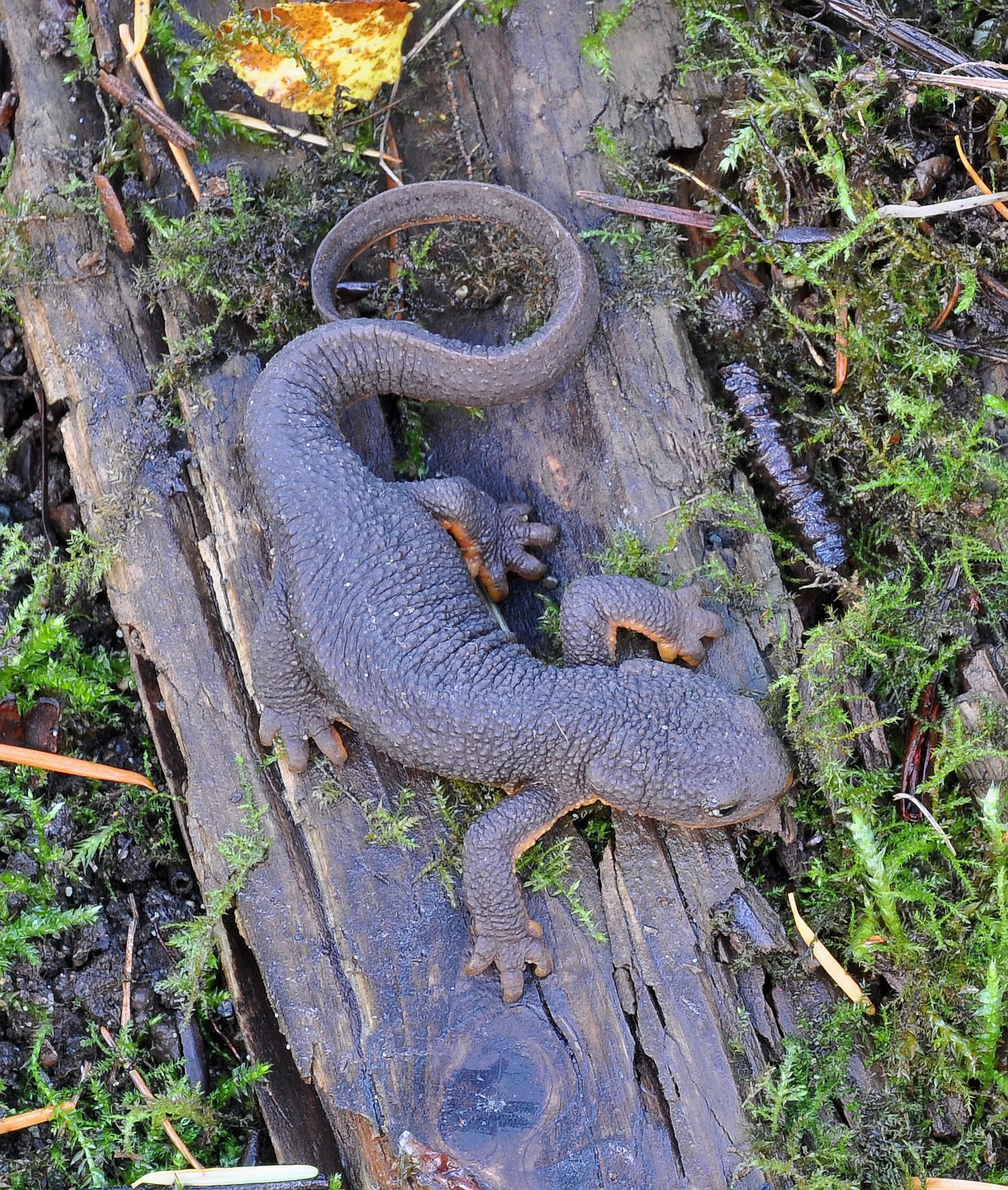 The skin of salamanders, in common with other amphibians, is thin, permeable to water, serves as a respiratory membrane, and is well-supplied with glands. It has highly cornified outer layers, renewed periodically through a skin shedding process controlled by hormones from the
The skin of salamanders, in common with other amphibians, is thin, permeable to water, serves as a respiratory membrane, and is well-supplied with glands. It has highly cornified outer layers, renewed periodically through a skin shedding process controlled by hormones from the


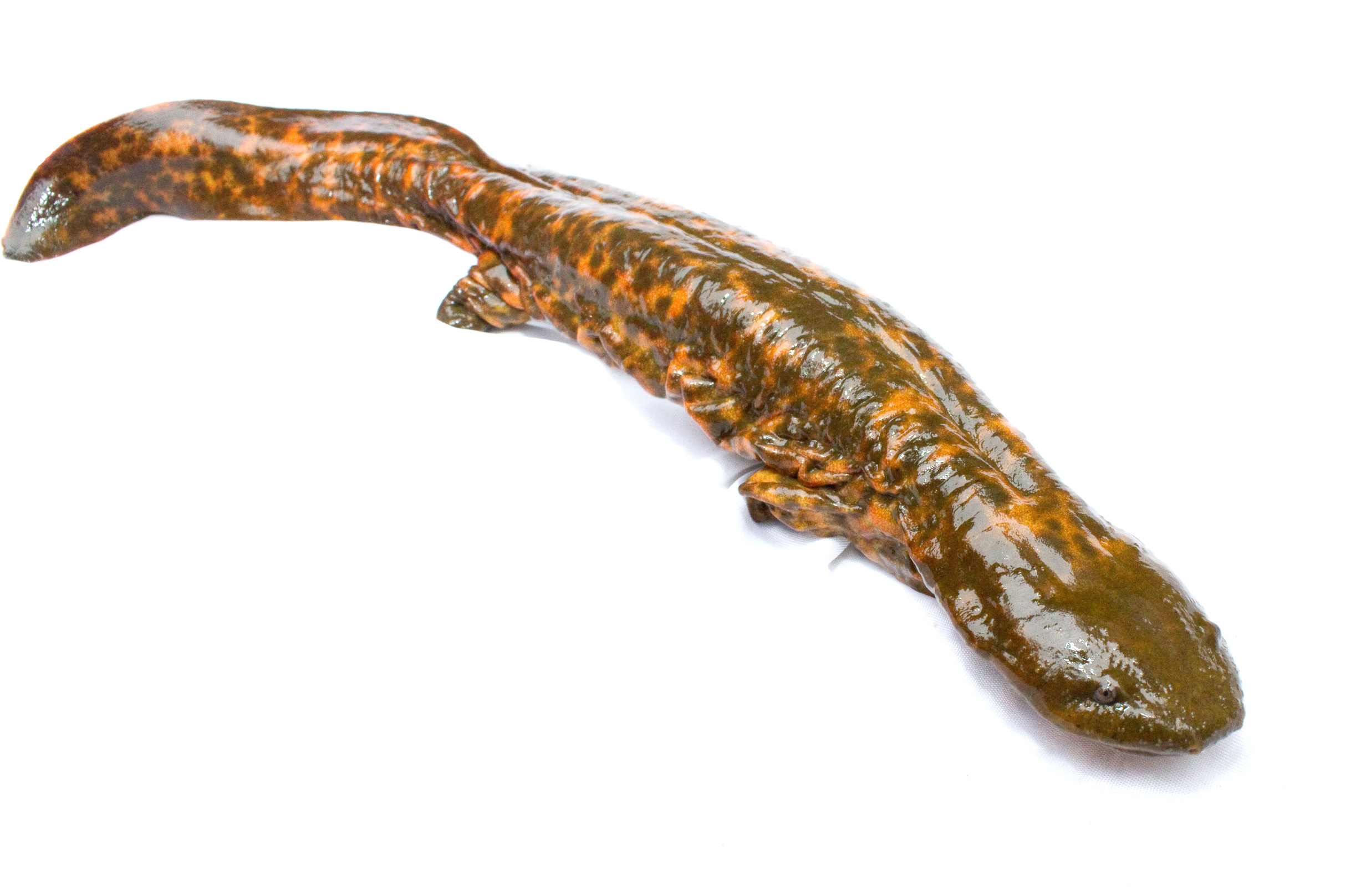
 In the ''Necturus'', external gills begin to form as a means of combating hypoxia in the egg as egg yolk is converted into metabolically active tissue. However, molecular changes in the mudpuppy during post-embryonic development primarily due to the
In the ''Necturus'', external gills begin to form as a means of combating hypoxia in the egg as egg yolk is converted into metabolically active tissue. However, molecular changes in the mudpuppy during post-embryonic development primarily due to the
 Most species of salamander have small teeth in both their upper and lower jaws. Unlike
Most species of salamander have small teeth in both their upper and lower jaws. Unlike
 Skin secretions of the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') fed to rats have been shown to produce aversion to the flavor, and the rats avoided the presentational medium when it was offered to them again. The fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra'') has a ridge of large granular glands down its spine which are able to squirt a fine jet of toxic fluid at its attacker. By angling its body appropriately, it can accurately direct the spray for a distance of up to .
The
Skin secretions of the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') fed to rats have been shown to produce aversion to the flavor, and the rats avoided the presentational medium when it was offered to them again. The fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra'') has a ridge of large granular glands down its spine which are able to squirt a fine jet of toxic fluid at its attacker. By angling its body appropriately, it can accurately direct the spray for a distance of up to .
The
 Many salamanders do not use vocalisations, and in most species the sexes look alike, so they use olfactory and tactile cues to identify potential mates, and
Many salamanders do not use vocalisations, and in most species the sexes look alike, so they use olfactory and tactile cues to identify potential mates, and  Not all species of salamanders follow this path.
Not all species of salamanders follow this path.
 A general decline in living amphibian species has been linked with the fungal disease
A general decline in living amphibian species has been linked with the fungal disease
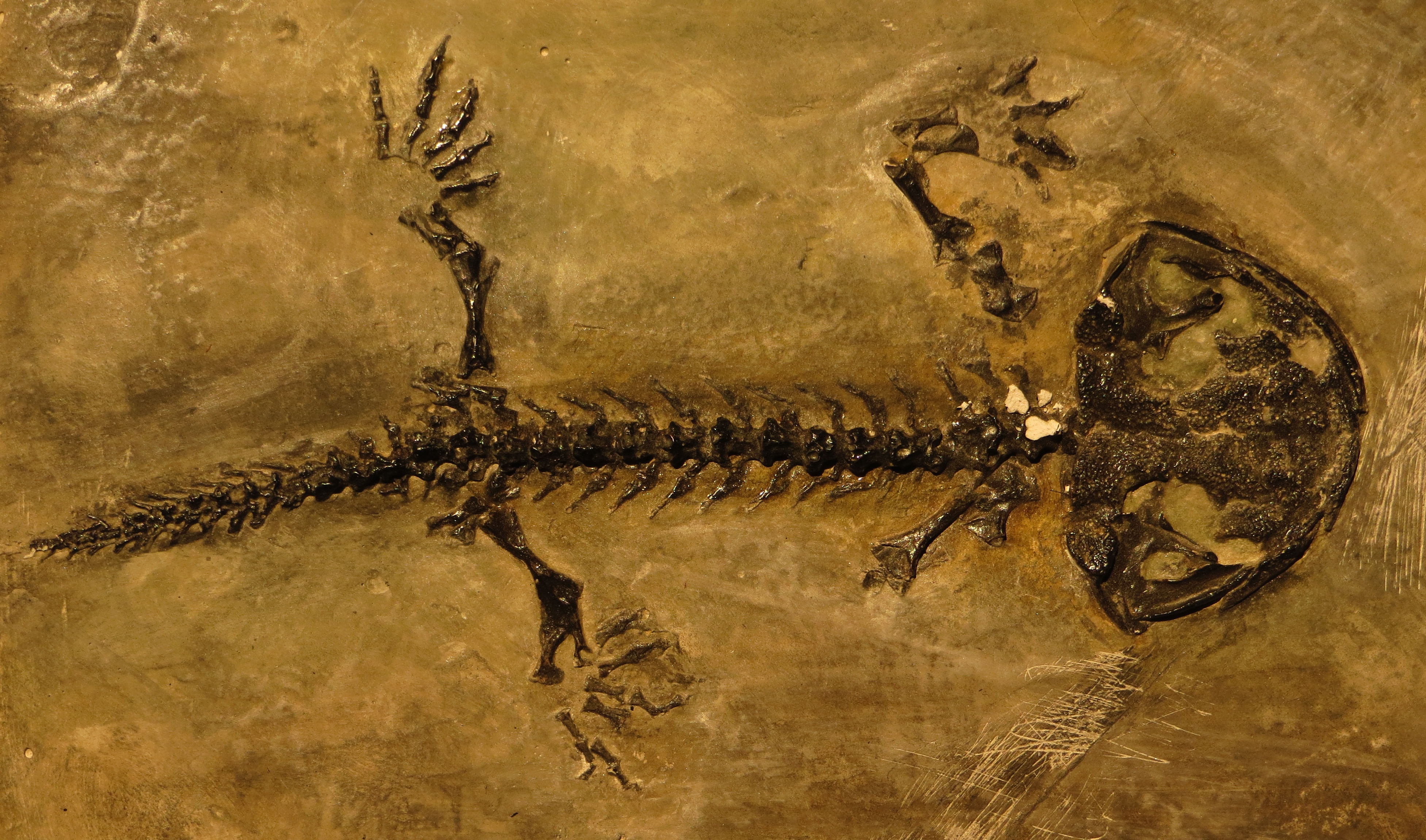 The earliest known salamander-line lissamphibian is '' Triassurus'' from the Middle-Late Triassic of Kyrgyzstan. Other fossil salamanders are known from the Middle-Late Jurassic of Eurasia, including '' Kokartus honorarius'' from the
The earliest known salamander-line lissamphibian is '' Triassurus'' from the Middle-Late Triassic of Kyrgyzstan. Other fossil salamanders are known from the Middle-Late Jurassic of Eurasia, including '' Kokartus honorarius'' from the
 Legends have developed around the salamander over the centuries, many related to fire. This connection likely originates from the tendency of many salamanders to dwell inside rotting logs. When the log was placed into a fire, the salamander would attempt to escape, lending credence to the belief that salamanders were created from flames.
The association of the salamander with fire appeared first in ancient Rome, with
Legends have developed around the salamander over the centuries, many related to fire. This connection likely originates from the tendency of many salamanders to dwell inside rotting logs. When the log was placed into a fire, the salamander would attempt to escape, lending credence to the belief that salamanders were created from flames.
The association of the salamander with fire appeared first in ancient Rome, with  The mythical ruler Prester John supposedly had a robe made from salamander hair; the "Emperor of India" possessed a suit made from a thousand skins; Pope Alexander III had a tunic which he valued highly and William Caxton (1481) wrote: "This Salemandre berithe wulle, of which is made cloth and gyrdles that may not brenne in the fyre." The salamander was said to be so toxic that by twining around a tree, it could poison the fruit and so kill any who ate them and by falling into a well, could kill all who drank from it.
In his autobiography, Benvenuto Cellini relates:
The Japanese giant salamander has been the subject of legend and artwork in Japan, in the ''ukiyo-e'' work by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. The well-known Japanese mythological creature known as the Kappa (folklore), ''kappa'' may be inspired by this salamander.
The mythical ruler Prester John supposedly had a robe made from salamander hair; the "Emperor of India" possessed a suit made from a thousand skins; Pope Alexander III had a tunic which he valued highly and William Caxton (1481) wrote: "This Salemandre berithe wulle, of which is made cloth and gyrdles that may not brenne in the fyre." The salamander was said to be so toxic that by twining around a tree, it could poison the fruit and so kill any who ate them and by falling into a well, could kill all who drank from it.
In his autobiography, Benvenuto Cellini relates:
The Japanese giant salamander has been the subject of legend and artwork in Japan, in the ''ukiyo-e'' work by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. The well-known Japanese mythological creature known as the Kappa (folklore), ''kappa'' may be inspired by this salamander.
Tree of Life: Caudata
Salamander Gallery
Caudata Culture
Critter Crossings: Salamander Tunnels
at U.S. Department of Transportation
ArchéoZooThèque : Urodele skeleton drawing
: available in vector, image and PDF formats {{Authority control Salamanders, Aposematic animals Articles containing video clips Extant Late Jurassic first appearances Taxa named by André Marie Constant Duméril
amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s typically characterized by their lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia altho ...
-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
, especially in the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
; most species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
are found in the Holarctic realm
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical regi ...
, with some species present in the Neotropical realm
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In bioge ...
.
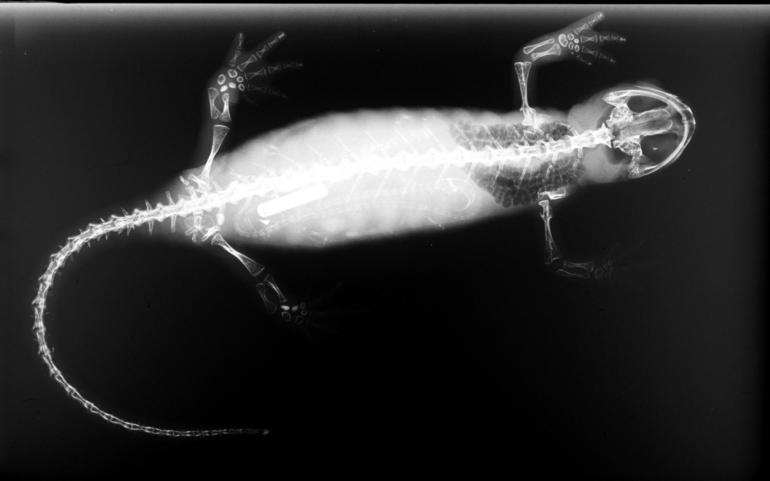
Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults.
This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost limbs as well as other damaged parts of their bodies. Researchers hope to reverse engineer the regenerative processes for potential human medical applications, such as brain and spinal cord injury treatment or preventing harmful scarring during heart surgery recovery.
Members of the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Salamandridae
Salamandridae is a family of salamanders consisting of true salamanders and newts. Salamandrids are distinguished from other salamanders by the lack of rib or costal grooves along the sides of their bodies and by their rough skin. Their skin is ...
are mostly known as newt
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aqua ...
s and lack the costal grooves along the sides of their bodies typical of other groups. The skin of some species contains the powerful poison tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovere ...
; these salamanders tend to be slow-moving and have bright warning coloration
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste ...
to advertise their toxicity. Salamanders typically lay eggs in water and have aquatic larvae, but great variation occurs in their lifecycles. Some species in harsh environments reproduce while still in the larval state.
Description
 The skin lacks scales and is moist and smooth to the touch, except in
The skin lacks scales and is moist and smooth to the touch, except in newt
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aqua ...
s of the Salamandridae, which may have velvety or warty skin, wet to the touch. The skin may be drab or brightly colored, exhibiting various patterns of stripes, bars, spots, blotches, or dots. Male newts become dramatically colored during the breeding season. Cave species dwelling in darkness lack pigmentation and have a translucent pink or pearlescent appearance.
Salamanders range in size from the minute salamanders, with a total length of , including the tail, to the Chinese giant salamander which reaches and weighs up to . Most, however, are between in length.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) p. 3
Trunk, limbs and tail
An adult salamander generally resembles a small lizard, having a basaltetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
body form with a cylindrical trunk, four limbs, and a long tail. Except in the family Salamandridae, the head, body, and tail have a number of vertical depressions in the surface which run from the mid-dorsal region to the ventral area and are known as costal grooves. Their function seems to be to help keep the skin moist by channeling water over the surface of the body.
 Some aquatic species, such as sirens and
Some aquatic species, such as sirens and amphiuma
''Amphiuma'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders from the United States, the only extant genus within the family Amphiumidae . They are colloquially known as amphiumas. They are also known to fishermen as "conger eels" or "Congo snakes", which are ...
s, have reduced or absent hind limbs, giving them an eel-like appearance, but in most species, the front and rear limbs are about the same length and project sidewards, barely raising the trunk off the ground. The feet are broad with short digits, usually four on the front feet and five on the rear. Salamanders do not have claws, and the shape of the foot varies according to the animal's habitat. Climbing species have elongated, square-tipped toes, while rock-dwellers have larger feet with short, blunt toes. The tree-climbing salamander (''Bolitoglossa'' sp.) has plate-like webbed feet which adhere to smooth surfaces by suction, while the rock-climbing '' Hydromantes'' species from California have feet with fleshy webs and short digits and use their tails as an extra limb. When ascending, the tail props up the rear of the body, while one hind foot moves forward and then swings to the other side to provide support as the other hind foot advances.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 26–30
In larvae and aquatic salamanders, the tail is laterally flattened, has dorsal and ventral fins, and undulates from side to side to propel the animal through the water. In the families Ambystomatidae and Salamandridae, the male's tail, which is larger than that of the female, is used during the amplexus embrace to propel the mating couple to a secluded location. In terrestrial species, the tail moves to counterbalance the animal as it runs, while in the arboreal salamander and other tree-climbing species, it is prehensile
Prehensility is the quality of an appendage or organ that has adapted for grasping or holding. The word is derived from the Latin term ''prehendere'', meaning "to grasp". The ability to grasp is likely derived from a number of different orig ...
. The tail is also used by certain plethodontid salamanders that can jump, to help launch themselves into the air. The tail is used in courtship
Courtship is the period wherein some couples get to know each other prior to a possible marriage. Courtship traditionally may begin after a betrothal and may conclude with the celebration of marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private m ...
and as a storage organ for proteins and lipids. It also functions as a defense against predation, when it may be lashed at the attacker or autotomised when grabbed. Unlike frogs, an adult salamander is able to regenerate limbs and its tail when these are lost.
Skin
pituitary
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypoph ...
and thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The ...
glands. During moulting, the skin initially breaks around the mouth, and the animal moves forwards through the gap to shed the skin. When the front limbs have been worked clear, a series of body ripples pushes the skin towards the rear. The hind limbs are extracted and push the skin farther back, before it is eventually freed by friction as the salamander moves forward with the tail pressed against the ground.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 10–16 The animal often then eats the resulting sloughed skin.
Glands
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream ( endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ( exocrine gland).
Structure
...
in the skin discharge mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
which keeps the skin moist, an important factor in skin respiration and thermoregulation. The sticky layer helps protect against bacterial infections and molds, reduces friction when swimming, and makes the animal slippery and more difficult for predators to catch. Granular glands scattered on the upper surface, particularly the head, back, and tail, produce repellent or toxic secretions. Some salamander toxins are particularly potent. The rough-skinned newt
The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt (''Taricha granulosa'') is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.
Appearance
A stocky newt with rounded snout, it ranges from light brown to olive or brownish-black on ...
(''Taricha granulosa'') produces the neurotoxin tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovere ...
, the most toxic nonprotein substance known. Handling the newts does no harm, but ingestion of even a minute fragment of skin is deadly. In feeding trials, fish, frogs, reptiles, birds, and mammals were all found to be susceptible.
Mature adults of some salamander species have "nuptial" glandular tissue in their cloacae, at the base of their tails, on their heads or under their chins. Some females release chemical substances, possibly from the ventral cloacal gland, to attract males, but males do not seem to use pheromones for this purpose. In some plethodonts, males have conspicuous mental glands on the chin which are pressed against the females' nostrils during the courtship ritual. They may function to speed up the mating process, reducing the risk of its being disrupted by a predator or rival male. The gland at the base of the tail in ''Plethodon cinereus
The red-backed salamander (''Plethodon cinereus'') is a small, hardy woodland salamander species in the family Plethodontidae. It is also known as the redback salamander, eastern red-backed salamander,Integrated Taxonomic Information System nter ...
'' is used to mark fecal pellets
Feces ( or faeces), known colloquially and in slang as poo and poop, are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relati ...
to proclaim territorial ownership.
Senses


Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, ...
in salamanders plays a role in territory maintenance, the recognition of predators, and courtship rituals, but is probably secondary to sight during prey selection and feeding. Salamanders have two types of sensory areas that respond to the chemistry of the environment. Olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity picks up airborne and aquatic odors, while adjoining vomeronasal organ
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapo ...
s detect nonvolatile chemical cues, such as tastes in the mouth. In plethodonts, the sensory epithelium of the vomeronasal organs extends to the nasolabial grooves, which stretch from the nostrils to the corners of the mouth. These extended areas seem to be associated with the identification of prey items, the recognition of conspecifics, and the identification of individuals.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 37–40
The eyes of most salamanders are adapted primarily for vision at night. In some permanently aquatic species, they are reduced in size and have a simplified retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which the ...
l structure, and in cave dwellers such as the Georgia blind salamander
The Georgia blind salamander (''Eurycea wallacei'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae (the "lungless salamanders"). It is endemic to the south-eastern United States where its natural habitats are inland karsts, caves and su ...
, they are absent or covered with a layer of skin. In amphibious species, the eyes are a compromise and are nearsighted in air and farsighted in water. Fully terrestrial species such as the fire salamander have a flatter lens which can focus over a much wider range of distances.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 42–44
To find their prey, salamanders use trichromatic color vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of ...
extending into the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
range, based on three photoreceptor types that are maximally sensitive around 450, 500, and 570 nm. The larvae, and the adults of some highly aquatic species, also have a lateral line
The lateral line, also called the lateral line organ (LLO), is a system of sensory organs found in fish, used to detect movement, vibration, and pressure gradients in the surrounding water. The sensory ability is achieved via modified epithelial ...
organ, similar to that of fish, which can detect changes in water pressure.
All salamanders lack middle ear cavity, eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the ...
and eustachian tube
In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in d ...
, but have an opercularis system like frogs, and are still able to detect airborne sound. The opercularis system consists of two ossicles: the columella (equivalent to the stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other animals which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the foo ...
of higher vertebrates) which is fused to the skull, and the operculum. An opercularis muscle connects the latter to the pectoral girdle, and is kept under tension when the animal is alert. The system seems able to detect low-frequency vibrations (500–600 Hz), which may be picked up from the ground by the fore limbs and transmitted to the inner ear. These may serve to warn the animal of an approaching predator.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 69–72
Salamanders are usually considered to have no voice and do not use sound for communication in the way that frogs do; however, in mating system they communicate by pheromone signaling; some species can make quiet ticking or popping noises, perhaps by the opening and closing of valves in the nose. The California giant salamander
The California giant salamander (''Dicamptodon ensatus'') is a species of salamander in the family Ambystomatidae. ''Dicamptodon ensatus'' is endemic to California, in the western United States. The species once additionally included individual ...
can produce a bark or rattle, and a few species can squeak by contracting muscles in the throat. The arboreal salamander can squeak using a different mechanism; it retracts its eyes into its head, forcing air out of its mouth. The ensatina salamander occasionally makes a hissing sound, while the sirens sometimes produce quiet clicks, and can resort to faint shrieks if attacked. Similar clicking behaviour was observed in two European newts '' Lissotriton vulgaris'' and '' Ichthyosaura alpestris'' in their aquatic phase. Vocalization in salamanders has been little studied and the purpose of these sounds is presumed to be the startling of predators.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 76–77
Respiration
Respiration differs among the different species of salamanders, and can involve gills, lungs, skin, and the membranes of mouth and throat. Larval salamanders breathe primarily by means ofgill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s, which are usually external and feathery in appearance. Water is drawn in through the mouth and flows out through the gill slits. Some neotenic
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compare ...
species such as the mudpuppy (''Necturus maculosus'') retain their gills throughout their lives, but most species lose them at metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
. The embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
s of some terrestrial lungless salamanders, such as ''Ensatina'', that undergo direct development, have large gills that lie close to the egg's surface.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 17–25
When present in adult salamanders, lungs vary greatly among different species in size and structure. In aquatic, cold-water species like the southern torrent salamander
The southern torrent salamander (''Rhyacotriton variegatus'') is a member of the salamander family Rhyacotritonidae. This species of torrent salamander is found the farthest south in the region. It is a small salamander endemic to the Pacific N ...
(''Rhyacotriton variegatus''), the lungs are very small with smooth walls, while species living in warm water with little dissolved oxygen, such as the lesser siren (''Siren intermedia''), have large lungs with convoluted surfaces. In the terrestrial lungless salamanders (family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Plethodontidae
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil, although a few species are found in Sardinia, Europe south of the Alps, and South Korea. In ...
), no lungs or gills are present, and gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
mostly takes place through the skin, supplemented by the tissues lining the mouth. To facilitate this, these salamanders have a dense network of blood vessels just under the skin and in the mouth.
In the amphiuma
''Amphiuma'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders from the United States, the only extant genus within the family Amphiumidae . They are colloquially known as amphiumas. They are also known to fishermen as "conger eels" or "Congo snakes", which are ...
s, metamorphosis is incomplete, and they retain one pair of gill slit
Gill slits are individual openings to gills, i.e., multiple gill arches, which lack a single outer cover. Such gills are characteristic of cartilaginous fish such as sharks and rays, as well as deep-branching vertebrates such as lampreys. In co ...
s as adults, with fully functioning internal lungs. Some species that lack lungs respire through gills. In most cases, these are external gills, visible as tufts on either side of the head. Some terrestrial salamanders have lungs used in respiration, although these are simple and sac-like, unlike the more complex organs found in mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s. Many species, such as the olm, have both lungs and gills as adults.
 In the ''Necturus'', external gills begin to form as a means of combating hypoxia in the egg as egg yolk is converted into metabolically active tissue. However, molecular changes in the mudpuppy during post-embryonic development primarily due to the
In the ''Necturus'', external gills begin to form as a means of combating hypoxia in the egg as egg yolk is converted into metabolically active tissue. However, molecular changes in the mudpuppy during post-embryonic development primarily due to the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
prevent the internalization of the external gills as seen in most salamanders that undergo metamorphosis. The external gills seen in salamanders differs greatly from that of amphibians with internalized gills. Unlike amphibians with internalized gills which typically rely on the changing of pressures within the buccal and pharyngeal cavities to ensure diffusion of oxygen onto the gill curtain, neotenic salamanders such as Necturus use specified musculature, such as the levatores arcuum, to move external gills to keep the respiratory surfaces constantly in contact with new oxygenated water.
Feeding and diet
Salamanders are opportunistic predators. They are generally not restricted to specific foods, but feed on almost any organism of a reasonable size. Large species such as the Japanese giant salamander (''Andrias japonicus'') eat crabs, fish, small mammals, amphibians, and aquatic insects. In a study of smaller dusky salamanders (''Desmognathus'') in theAppalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
, their diet includes earthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. T ...
s, flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced m ...
, beetles
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describe ...
, beetle larvae, leafhopper
A leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family Cicadellidae. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and ...
s, springtail
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called ...
s, moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s, spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species ...
s, grasshopper
Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are among what is possibly the most ancient living group of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.
Grasshopp ...
s, and mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear e ...
s. Cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
sometimes takes place, especially when resources are short or time is limited. Tiger salamander tadpoles in ephemeral pools sometimes resort to eating each other, and are seemingly able to target unrelated individuals. Adult blackbelly salamander
The blackbelly salamander (''Desmognathus quadramaculatus'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to the United States. Its natural habitats are rivers, intermittent rivers, and freshwater springs. It is threaten ...
s (''Desmognathus quadramaculatus'') prey on adults and young of other species of salamanders, while their larvae sometimes cannibalise smaller larvae.
 Most species of salamander have small teeth in both their upper and lower jaws. Unlike
Most species of salamander have small teeth in both their upper and lower jaws. Unlike frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s, even the larvae of salamanders possess these teeth. Although larval teeth are shaped like pointed cones, the teeth of adults are adapted to enable them to readily grasp prey. The crown, which has two cusps (bicuspid), is attached to a pedicel by collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
ous fibers. The joint formed between the bicuspid and the pedicel is partially flexible, as it can bend inward, but not outward. When struggling prey is advanced into the salamander's mouth, the teeth tips relax and bend in the same direction, encouraging movement toward the throat, and resisting the prey's escape. Many salamanders have patches of teeth attached to the vomer
The vomer (; lat, vomer, lit=ploughshare) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right max ...
and the palatine bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ...
s in the roof of the mouth, and these help to retain prey. All types of teeth are resorbed and replaced at intervals throughout the animal's life.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 57–58
A terrestrial salamander catches its prey by flicking out its sticky tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
in an action that takes less than half a second. In some species, the tongue is attached anteriorly to the floor of the mouth, while in others, it is mounted on a pedicel. It is rendered sticky by secretions of mucus from glands in its tip and on the roof of the mouth.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 58–60 High-speed cinematography
Cinematography (from ancient Greek κίνημα, ''kìnema'' "movement" and γράφειν, ''gràphein'' "to write") is the art of motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography.
Cinematographers use a lens to focu ...
shows how the tiger salamander
The tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') is a species of mole salamander and one of the largest terrestrial salamanders in North America.
Description
These salamanders usually grow to a length of with a lifespan of around 12–15 years. ...
(''Ambystoma tigrinum'') positions itself with its snout close to its prey. Its mouth then gapes widely, the lower jaw remains stationary, and the tongue bulges and changes shape as it shoots forward. The protruded tongue has a central depression, and the rim of this collapses inward as the target is struck, trapping the prey in a mucus-laden trough. Here it is held while the animal's neck is flexed, the tongue retracted and jaws closed. Large or resistant prey is retained by the teeth while repeated protrusions and retractions of the tongue draw it in. Swallowing involves alternate contraction and relaxation of muscles in the throat, assisted by depression of the eyeballs into the roof of the mouth. Many lungless salamanders of the family Plethodontidae have more elaborate feeding methods. Muscles surrounding the hyoid bone
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verteb ...
contract to store elastic energy in springy connective tissue, and actually "shoot" the hyoid bone out of the mouth, thus elongating the tongue. Muscles that originate in the pelvic region and insert in the tongue are used to reel the tongue and the hyoid back to their original positions.
An aquatic salamander lacks muscles in the tongue, and captures its prey in an entirely different manner. It grabs the food item, grasps it with its teeth, and adopts a kind of inertial feeding. This involves tossing its head about, drawing water sharply in and out of its mouth, and snapping its jaws, all of which tend to tear and macerate the prey, which is then swallowed.
Though frequently feeding on slow-moving animals like snails, shrimps
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referre ...
and worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete wor ...
s, sirenids are unique among salamanders for having developed speciations towards herbivory, such as beak-like jaw ends and extensive intestines. They feed on algae and other soft-plants in the wild, and easily eat offered lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable, but sometimes for its stem and seeds. Lettuce is most often used for salads, although it is also seen in other kinds of food, ...
.
Defense
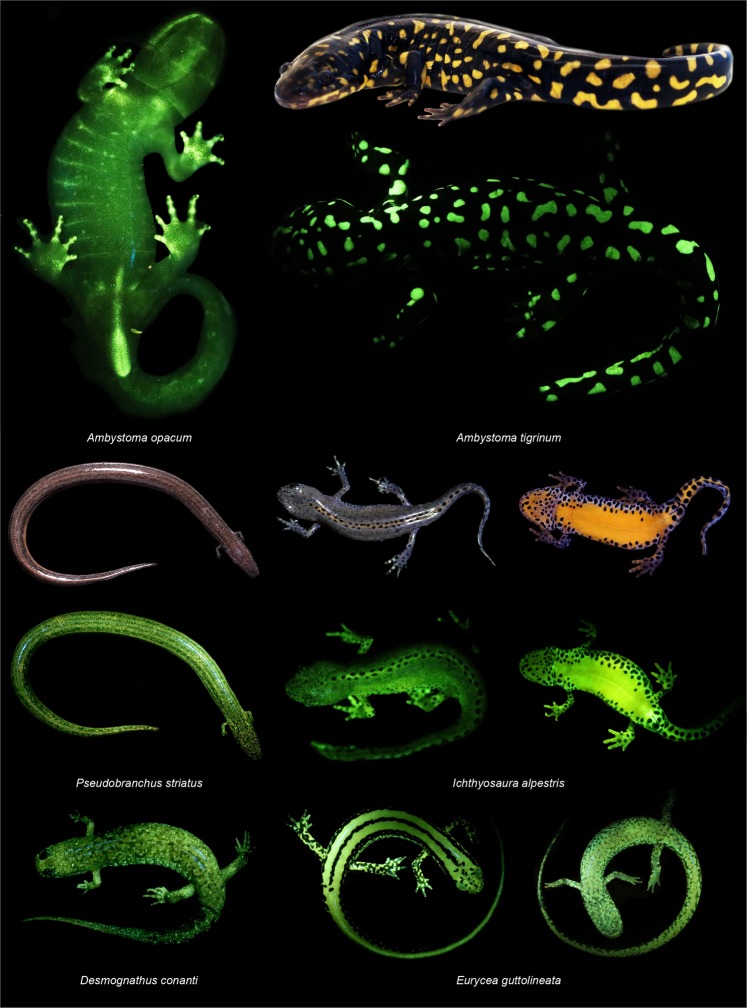
Salamanders have thin skins and soft bodies, and move rather slowly, and at first sight might appear to be vulnerable to opportunistic predation. However, they have several effective lines of defense. Mucus coating on damp skin makes them difficult to grasp, and the slimy coating may have an offensive taste or be toxic. When attacked by a predator, a salamander may position itself to make the main poison glands face the aggressor. Often, these are on the tail, which may be waggled or turned up and arched over the animal's back. The sacrifice of the tail may be a worthwhile strategy, if the salamander escapes with its life and the predator learns to avoid that species of salamander in the future.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 110–120Aposematism
 Skin secretions of the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') fed to rats have been shown to produce aversion to the flavor, and the rats avoided the presentational medium when it was offered to them again. The fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra'') has a ridge of large granular glands down its spine which are able to squirt a fine jet of toxic fluid at its attacker. By angling its body appropriately, it can accurately direct the spray for a distance of up to .
The
Skin secretions of the tiger salamander (''Ambystoma tigrinum'') fed to rats have been shown to produce aversion to the flavor, and the rats avoided the presentational medium when it was offered to them again. The fire salamander (''Salamandra salamandra'') has a ridge of large granular glands down its spine which are able to squirt a fine jet of toxic fluid at its attacker. By angling its body appropriately, it can accurately direct the spray for a distance of up to .
The Iberian ribbed newt
The Iberian ribbed newt, gallipato or Spanish ribbed newt (''Pleurodeles waltl'') is a newt endemic to the central and southern Iberian Peninsula and Morocco. It is the largest European newt species and it is also known for its sharp ribs whi ...
(''Pleurodeles waltl'') has another method of deterring aggressors. Its skin exudes a poisonous, viscous fluid and at the same time, the newt rotates its sharply pointed ribs through an angle between 27 and 92°, and adopts an inflated posture. This action causes the ribs to puncture the body wall, each rib protruding through an orange wart arranged in a lateral row. This may provide an aposematic signal that makes the spines more visible. When the danger has passed, the ribs retract and the skin heals.
Camouflage and mimicry
Although many salamanders havecryptic
Cryptic may refer to:
In science:
* Cryptic species complex, a group of species that are very difficult to distinguish from one another
* Crypsis, the ability of animals to blend in to avoid observation
* Cryptic era, earliest period of the Earth ...
colors so as to be unnoticeable, others signal their toxicity by their vivid coloring. Yellow, orange, and red are the colors generally used, often with black for greater contrast. Sometimes, the animal postures if attacked, revealing a flash of warning hue on its underside. The red eft, the brightly colored terrestrial juvenile form of the eastern newt (''Notophthalmus viridescens''), is highly poisonous. It is avoided by birds and snakes, and can survive for up to 30 minutes after being swallowed (later being regurgitated). The red salamander
The red salamander (''Pseudotriton ruber'') is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae endemic to the eastern United States. Its skin is orange/red with random black spots.
Its habitats are temperate forests, small creeks, ponds, ...
(''Pseudotriton ruber'') is a palatable species with a similar coloring to the red eft. Predators that previously fed on it have been shown to avoid it after encountering red efts, an example of Batesian mimicry
Batesian mimicry is a form of mimicry where a harmless species has evolved to imitate the warning signals of a harmful species directed at a predator of them both. It is named after the English naturalist Henry Walter Bates, after his work on ...
. Other species exhibit similar mimicry. In California, the palatable yellow-eyed salamander (''Ensatina eschscholtzii'') closely resembles the toxic California newt
The California newt or orange-bellied newt (''Taricha torosa''), is a species of newt endemic to California, in the Western United States. Its adult length can range from . Its skin produces the potent toxin tetrodotoxin.
Subspecies
''Taricha ...
(''Taricha torosa'') and the rough-skinned newt (''Taricha granulosa''), whereas in other parts of its range, it is cryptically colored. A correlation exists between the toxicity of Californian salamander species and diurnal habits: relatively harmless species like the California slender salamander
The California slender salamander (''Batrachoseps attenuatus'') is a lungless salamander Stebbins, Robert C. (2003). ''A Field Guide to Western Reptiles and Amphibians'', 3rd Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company, that is found primarily in coastal ...
(''Batrachoseps attenuatus'') are nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
and are eaten by snakes, while the California newt has many large poison glands in its skin, is diurnal, and is avoided by snakes.
Autotomy
Some salamander species use tail autotomy to escape predators. The tail drops off and wriggles around for a while after an attack, and the salamander either runs away or stays still enough not to be noticed while the predator is distracted. The tail regrows with time, and salamanders routinely regenerate other complex tissues, including thelens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
or retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which the ...
of the eye. Within only a few weeks of losing a piece of a limb, a salamander perfectly reforms the missing structure.
Distribution and habitat
Salamanders split off from the other amphibians during the mid- to late Permian, and initially were similar to modern members of the Cryptobranchoidea. Their resemblance tolizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia altho ...
s is the result of symplesiomorphy, their common retention of the primitive tetrapod body plan, but they are no more closely related to lizards than they are to mammals. Their nearest relatives are the frogs and toads, within Batrachia
The Batrachia are a clade of amphibians that includes frogs and salamanders, but not caecilians nor the extinct allocaudates. The name Batrachia was first used by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1800 to refer to frogs, but has more ...
. The earliest known salamander fossils have been found in geological deposits in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, dated to the middle Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period around 164 million years ago.
Salamanders are found only in the Holarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical reg ...
and Neotropical
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In bioge ...
regions, not reaching south of the Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and wa ...
, the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, or in South America the Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Boli ...
. They do not extend north of the Arctic tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snow ...
, with the northernmost Asian species, ''Salamandrella keyserlingii
''Salamandrella keyserlingii'', the Siberian salamander, is a species of salamander found in Northeast Asia. It lives in wet woods and riparian groves.
Distribution
It is found primarily in Siberia east of the Sosva River and the Urals, in ...
'' occurring in the Siberian larch
''Larix sibirica'', the Siberian larch or Russian larch, is a frost-hardy tree native to western Russia, from close to the Finnish border east to the Yenisei valley in central Siberia, where it hybridises with the Dahurian larch ''L. gmelinii' ...
forests of Sakha
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far ...
and the most northerly species in North America, '' Ambystoma laterale'', reaching no farther north than Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
and ''Taricha granulosa
The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt (''Taricha granulosa'') is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.
Appearance
A stocky newt with rounded snout, it ranges from light brown to olive or brownish-black on t ...
'' not beyond the Alaska Panhandle
Southeast Alaska, colloquially referred to as the Alaska(n) Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia (and a small part ...
. They had an exclusively Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
n distribution until '' Bolitoglossa'' invaded South America from Central America, probably by the start of the Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages: the Aquitanian age, Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages.
The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 annum, Ma to ...
, about 23 million years ago. They also lived on the Caribbean Islands
Almost all of the Caribbean islands are in the Caribbean Sea, with only a few in inland lakes. The largest island is Cuba. Other sizable islands include Hispaniola, Jamaica, Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago. Some of the smaller islands a ...
during the early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
epoch, confirmed by the discovery of '' Palaeoplethodon hispaniolae'', found trapped in amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
in the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
. However, possible salamander fossils have been found in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
at the Murgon fossil site
The Murgon fossil site is a paleontological site of early Eocene age in south-eastern Queensland, Australia. It lies near the town of Murgon, some 270 km north-west of Brisbane. The Murgon site is important as the only site on the contine ...
, representing the only known salamanders known from the continent.
There are about 760 living species of salamander. One-third of the known salamander species are found in North America. The highest concentration of these is found in the Appalachian Mountains region, where the Plethodontidae are thought to have originated in mountain streams. Here, vegetation zones and proximity to water are of greater importance than altitude. Only species that adopted a more terrestrial mode of life have been able to disperse to other localities. The northern slimy salamander (''Plethodon glutinosus'') has a wide range and occupies a habitat similar to that of the southern gray-cheeked salamander (''Plethodon metcalfi''). The latter is restricted to the slightly cooler and wetter conditions in north-facing cove forests in the southern Appalachians, and to higher elevations above 900 m (3,000 ft), while the former is more adaptable, and would be perfectly able to inhabit these locations, but some unknown factor seems to prevent the two species from co-existing.
One species, the Anderson's salamander, is one of the few species of living amphibians to occur in brackish or salt water.
Reproduction and development
 Many salamanders do not use vocalisations, and in most species the sexes look alike, so they use olfactory and tactile cues to identify potential mates, and
Many salamanders do not use vocalisations, and in most species the sexes look alike, so they use olfactory and tactile cues to identify potential mates, and sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex (in ...
occurs. Pheromones play an important part in the process and may be produced by the abdominal gland in males and by the cloacal glands and skin in both sexes. Males are sometimes to be seen investigating potential mates with their snouts. In Old World newts, '' Triturus'' spp., the males are sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
and display in front of the females. Visual cues are also thought to be important in some '' Plethodont'' species.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 143–154
In about 90% of all species, fertilisation is internal. The male typically deposits a spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophore ...
on the ground or in the water according to species, and the female picks this up with her vent. The spermatophore has a packet of sperm supported on a conical gelatinous base, and often an elaborate courtship behavior is involved in its deposition and collection. Once inside the cloaca, the spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromos ...
move to the spermatheca, one or more chambers in the roof of the cloaca, where they are stored for sometimes lengthy periods until the eggs are laid. In the most primitive salamanders, such as the Asiatic salamander
The Asiatic salamanders (family Hynobiidae) are primitive salamanders found all over Asia, and in European Russia. They are closely related to the giant salamanders (family Cryptobranchidae), with which they form the suborder Cryptobranchoidea. A ...
s and the giant salamander
The Cryptobranchidae are a family of fully aquatic salamanders commonly known as the giant salamanders. They include the largest living amphibians. The family is native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. They constitute one of two ...
s, external fertilization occurs, instead. In these species, the male releases sperm onto the egg mass in a reproductive process similar to that of typical frogs.
Three different types of egg deposition occur. '' Ambystoma'' and ''Taricha
The genus ''Taricha'' consists of four species of highly toxic newts in the family Salamandridae. Their common name is Pacific newts, sometimes also western newts or roughskin newts. The four species within this genus are the California newt, ...
'' spp. spawn large numbers of small eggs in quiet ponds where many large predators are unlikely. Most dusky salamanders (''Desmognathus'') and Pacific giant salamander
The Pacific giant salamanders (frequently stylized as Giant Pacific Salamanders or GPS) are members of the genus ''Dicamptodon''. They are large salamanders endemic to the Pacific Northwest in North America. They are included in the family Ambyst ...
s (''Dicamptodon'') lay smaller batches of medium-sized eggs in a concealed site in flowing water, and these are usually guarded by an adult, normally the female. Many of the tropical climbing salamanders (''Bolitoglossa'') and lungless salamanders (Plethodontinae) lay a small number of large eggs on land in a well-hidden spot, where they are also guarded by the mother. Some species such as the fire salamanders (''Salamandra'') are ovoviviparous, with the female retaining the eggs inside her body until they hatch, either into larvae to be deposited in a water body, or into fully formed juveniles.
In temperate regions, reproduction is usually seasonal and salamanders may migrate to breeding grounds. Males usually arrive first and in some instances set up territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
. Typically, a larval stage follows in which the organism is fully aquatic. The tadpole has three pairs of external gills, no eyelids, a long body, a laterally flattened tail with dorsal and ventral fins and in some species limb-buds or limbs. Pond-type larvae may have a pair of rod-like balancers on either side of the head, long gill filaments and broad fins. Stream-type larvae are more slender with short gill filaments, narrower fins and no balancers, but instead have hind limbs already developed when they hatch.Stebbins & Cohen (1995) pp. 175–179 The tadpoles are carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
and the larval stage may last from days to years, depending on species. Sometimes this stage is completely bypassed, and the eggs of most lungless salamanders (Plethodontidae) develop directly into miniature versions of the adult without an intervening larval stage.
By the end of the larval stage, the tadpoles already have limbs and metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
takes place normally. In salamanders, this occurs over a short period of time and involves the closing of the gill slits and the loss of structures such as gills and tail fins that are not required as adults. At the same time, eyelids develop, the mouth becomes wider, a tongue appears, and teeth are formed. The aqueous larva emerges onto land as a terrestrial adult.
 Not all species of salamanders follow this path.
Not all species of salamanders follow this path. Neoteny
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the physiological, or somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny is found in modern humans compare ...
, also known as paedomorphosis, has been observed in all salamander families, and may be universally possible in all salamander species. In this state, an individual may retain gills or other juvenile features while attaining reproductive maturity. The changes that take place at metamorphosis are under the control of thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
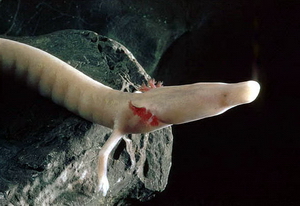
s and in obligate neotenes such as the axolotl
The axolotl (; from nci, āxōlōtl ), ''Ambystoma mexicanum'', is a paedomorphic salamander closely related to the tiger salamander. Axolotls are unusual among amphibians in that they reach adulthood without undergoing metamorphosis. I ...
(''Ambystoma mexicanum''), the tissues are seemingly unresponsive to the hormones. In other species, the changes may not be triggered because of underactivity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid mechanism which may occur when conditions in the terrestrial environment are too inhospitable. This may be due to cold or wildly fluctuating temperatures, aridity, lack of food, lack of cover, or insufficient iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
for the formation of thyroid hormones. Genetics may also play a part. The larvae of tiger salamanders (''Ambystoma tigrinum''), for example, develop limbs soon after hatching and in seasonal pools promptly undergo metamorphosis. Other larvae, especially in permanent pools and warmer climates, may not undergo metamorphosis until fully adult in size. Other populations in colder climates may not metamorphose at all, and become sexually mature while in their larval forms. Neoteny allows the species to survive even when the terrestrial environment is too harsh for the adults to thrive on land.
Conservation
 A general decline in living amphibian species has been linked with the fungal disease
A general decline in living amphibian species has been linked with the fungal disease chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and '' Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or extinc ...
. A higher proportion of salamander species than of frogs or caecilians are in one of the at-risk categories established by the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
. Salamanders showed a significant diminution in numbers in the last few decades of the 20th century, although no direct link between the fungus and the population decline has yet been found. The IUCN made further efforts in 2005 as they established the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan (ACAP), which was subsequently followed by Amphibian Ark (AArk), Amphibian Specialist Group (ASG), and finally the umbrella organization known as the Amphibian Survival Alliance (ASA). Researchers also cite deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
, resulting in fragmentation of suitable habitats, and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
as possible contributory factors. Species such as '' Pseudoeurycea brunnata'' and '' Pseudoeurycea goebeli'' that had been abundant in the cloud forest
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud ...
s of Guatemala and Mexico during the 1970s were found by 2009 to be rare. However, few data have been gathered on population sizes over the years, and by intensive surveying of historic and suitable new locations, it has been possible to locate individuals of other species such as '' Parvimolge townsendi'', which had been thought to be extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
. Currently, the major lines of defense for the conservation of Salamanders includes both in situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
and ex situ conservation methods. There are efforts in place for certain members of the Salamander family to be conserved under a conservation breeding program (CBP) but it is important to note that there should be research done ahead of time to determine if the Salamander species is actually going to value from the CBP, as researchers have noted that some species of amphibians completely fail in this environment.
Various conservation initiatives are being attempted around the world. The Chinese giant salamander, at 1.8 m (6 ft) the largest amphibian in the world, is critically endangered, as it is collected for food and for use in traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of acti ...
. An environmental education programme is being undertaken to encourage sustainable management of wild populations in the Qinling Mountains and captive breeding programmes have been set up. The hellbender is another large, long-lived species with dwindling numbers and fewer juveniles reaching maturity than previously. Another alarming finding is the increase in abnormalities in up to 90% of the hellbender population in the Spring River watershed in Arkansas. Habitat loss, silting of streams, pollution and disease have all been implicated in the decline and a captive breeding programme at Saint Louis Zoo
The Saint Louis Zoo, officially known as the Saint Louis Zoological Park, is a zoo in Forest Park, St. Louis, Missouri. It is recognized as a leading zoo in animal management, research, conservation, and education. The zoo is accredited by the ...
has been successfully established. Of the 20 species of minute salamanders (''Thorius'' spp.) in Mexico, half are believed to have become extinct and most of the others are critically endangered. Specific reasons for the decline may include climate change, chytridiomycosis, or volcanic activity, but the main threat is habitat destruction as logging, agricultural activities, and human settlement reduce their often tiny, fragmented ranges. Survey work is being undertaken to assess the status of these salamanders, and to better understand the factors involved in their population declines, with a view to taking action.
'' Ambystoma mexicanum'', an aquatic salamander, is a species protected under the Mexican UMA (Unit for Management and conservation of wildlife) as of April 1994. Another detrimental factor is that the axolotl lost their role as a top predator since the introduction of locally exotic species such as Nile tilapia and carp. Tilapia and carp directly compete with axolotls by consuming their eggs, larvae, and juveniles. Climate change has also immensely affected axolotls and their populations throughout the southern Mexico area. Due to its proximity to Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
, officials are currently working on programs at Lake Xochimilco to bring in tourism and educate the local population on the restoration of the natural habitat of these creatures. This proximity is a large factor that has impacted the survival of the axolotl, as the city has expanded to take over the Xochimilco region in order to make use of its resources for water and provision and sewage. However, the axolotl has the benefit of being raised in farms for the purpose of research facilities. So there is still a chance that they may be able to return to their natural habitat. The recent decline in population has substantially impacted genetic diversity among populations of axolotl, making it difficult to further progress scientifically. It is important to note that although there is a level of limited genetic diversity due to ''Ambystoma'' populations, such as the axolotl, being paedeomorphic species, it does not account for the overall lack of diversity. There is evidence that points towards a historical bottlenecking of ''Ambystoma'' that contributes to the variation issues. Unfortunately, there is no large genetic pool for the species to pull from unlike in historical times. Thus there is severe concern for inbreeding due to lack of gene flow. One way researchers are looking into maintaining genetic diversity within the population is via cryopreservation of the spermatophores from the male axolotl. It is a safe and non-invasive method that requires the collection of the spermatophores and places them into a deep freeze for preservation. Most importantly, they have found that there is only limited damage done to the spermatophores upon thawing and thus it is a viable option. As of 2013, it is a method that is being used to save not only the axolotl but also numerous other members of the salamander family.
Research is being done on the environmental cues that have to be replicated before captive animals can be persuaded to breed. Common species such as the tiger salamander and the mudpuppy are being given hormones to stimulate the production of sperm and eggs, and the role of arginine vasotocin
Vasotocin is an oligopeptide homologous to oxytocin and vasopressin found in all non-mammalian vertebrates (including birds, fishes, and amphibians) and possibly in mammals during the fetal stage of development. Arginine vasotocin (AVT), a hormone ...
in courtship behaviour is being investigated. Another line of research is artificial insemination
Artificial insemination is the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female's cervix or uterine cavity for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse. It is a fertility treatment ...
, either ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology a ...
'' or by inserting spermatophores into the cloacae of females. The results of this research may be used in captive-breeding programmes for endangered species.
Taxonomy
Disagreement exists among different authorities as to the definition of the terms Caudata and Urodela. Some maintain that the Urodela should be restricted to thecrown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor ...
, with the Caudata being used for the total group. Others restrict the name Caudata to the crown group and use Urodela for the total group. The former approach seems to be most widely adopted and is used in this article.
The ten families belonging to Urodela are divided into three suborders. The clade Neocaudata is often used to separate the Cryptobranchoidea and Salamandroidea from the Sirenoidea.
Phylogeny and evolution
The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians (gymnophionans, urodeles and anurans) is a matter of debate. A 2005 molecular phylogeny, based on rDNA analysis, suggested that the first divergence between these three groups took place soon after they had branched from the lobe-finned fish in theDevonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
(around 360 million years ago), and before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. The briefness of this period, and the speed at which radiation took place, may help to account for the relative scarcity of amphibian fossils that appear to be closely related to lissamphibians. However, more recent studies have generally found more recent (Late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferou ...
to Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
) age for the basalmost divergence among lissamphibians.
Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period (geology), Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively ...
of Kyrgyzstan, two species of the apparently neotenic, aquatic ''Marmorerpeton
''Marmorerpeton'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem group-salamanders that lived in Britain during the Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic.
They are among the oldest known salamanders. Two species were named when the genus was first d ...
'' from the Middle Jurassic of England and Scotland, and ''Karaurus
''Karaurus'' (meaning ''head-tail'') is an extinct genus of stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle to Late Jurassic (Callovian–Kimmeridgian) Karabastau Formation of Kazakhstan. It is one of the oldest salamanders known.
''Karaurus'' ...
'' from the Middle-Late Jurassic of Kazakhstan, resembled modern mole salamander
The mole salamanders ( genus ''Ambystoma'') are a group of advanced salamanders endemic to North America. The group has become famous due to the presence of the axolotl (''A. mexicanum''), widely used in research due to its paedomorphosis, an ...
s in morphology and probably had a similar burrowing lifestyle. They looked like robust modern salamanders but lacked a number of anatomical features that characterise all modern salamanders.
The two groups of extant salamanders are the Cryptobranchoidea (which includes asiatic and giant salamanders) and the Salamandroidea
The Salamandroidea are a suborder of salamanders, referred to as advanced salamanders. The members of the suborder are found worldwide except for Antarctica, sub-Saharan Africa, and Oceania. They differ from suborder Cryptobranchoidea as the an ...
(which includes all other living salamanders), also known as Diadectosalamandroidei. Both groups are known from the Middle-Late Jurassic of China. the former being exemplified by ''Chunerpeton tianyiensis
''Chunerpeton tianyiensis'' is an extinct species of salamander from the Late Jurassic Daohugou Beds in Ningcheng County, Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia), China. It is the only species classified under the genus ''Chunerpeton''. It was a small anim ...
'', ''Pangerpeton sinensis
''Pangerpeton'' is an extinct genus of salamanders. Its monotypic species is ''Pangerpeton sinensis''.
''Pangerpeton'' is a metamorphosed, primitive salamander from the Late Jurassic Daohugou fossil bed near Wubaiding Village of Lingyuan City, ...
'', ''Jeholotriton paradoxus
''Jeholotriton'' is a genus of primitive salamander from the Daohugou Beds (possibly dating to the late Jurassic period) near Daohugou village of Inner Mongolia, China.
Wang Yuan from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthro ...
'', '' Regalerpeton weichangensis'', ''Liaoxitriton daohugouensis
''Liaoxitriton'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric cryptobranchoid salamanders from the Early Cretaceous of China. It contains one species, ''L. zhongjiani'', from the Aptian aged Yixian Formation. A second species, ''L. daohugouensis'' from ...
'' and '' Iridotriton hechti'', and the latter by '' Beiyanerpeton jianpingensis''. By the Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
, most or all of the living salamander families had probably appeared.
The following cladogram shows the relationships between salamander families based on the molecular analysis of Pyron and Wiens (2011). The position of the Sirenidae is disputed, but the position as sister to the Salamandroidea best fits with the molecular and fossil evidence.
Genome and genetics
Salamanders possess gigantic genomes, spanning the range from 14 Gb to 120 Gb (thehuman genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the ...
is 3.2 Gb long). The genomes of '' Pleurodeles waltl'' (20 Gb) and ''Ambystoma mexicanum'' (32 Gb) have been sequenced.
In human society
Myth and legend
 Legends have developed around the salamander over the centuries, many related to fire. This connection likely originates from the tendency of many salamanders to dwell inside rotting logs. When the log was placed into a fire, the salamander would attempt to escape, lending credence to the belief that salamanders were created from flames.
The association of the salamander with fire appeared first in ancient Rome, with
Legends have developed around the salamander over the centuries, many related to fire. This connection likely originates from the tendency of many salamanders to dwell inside rotting logs. When the log was placed into a fire, the salamander would attempt to escape, lending credence to the belief that salamanders were created from flames.
The association of the salamander with fire appeared first in ancient Rome, with Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
writing in his '' Natural History'' that "A salamander is so cold that it puts out fire on contact. It vomits from its mouth a milky liquid; if this liquid touches any part of the human body it causes all the hair to fall off, and the skin to change color and break out in a rash." The ability to put out fire is repeated by Saint Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; la, Aurelius Augustinus Hipponensis; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430), also known as Saint Augustine, was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Afr ...
in the fifth century and Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
in the seventh century.
 The mythical ruler Prester John supposedly had a robe made from salamander hair; the "Emperor of India" possessed a suit made from a thousand skins; Pope Alexander III had a tunic which he valued highly and William Caxton (1481) wrote: "This Salemandre berithe wulle, of which is made cloth and gyrdles that may not brenne in the fyre." The salamander was said to be so toxic that by twining around a tree, it could poison the fruit and so kill any who ate them and by falling into a well, could kill all who drank from it.
In his autobiography, Benvenuto Cellini relates:
The Japanese giant salamander has been the subject of legend and artwork in Japan, in the ''ukiyo-e'' work by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. The well-known Japanese mythological creature known as the Kappa (folklore), ''kappa'' may be inspired by this salamander.
The mythical ruler Prester John supposedly had a robe made from salamander hair; the "Emperor of India" possessed a suit made from a thousand skins; Pope Alexander III had a tunic which he valued highly and William Caxton (1481) wrote: "This Salemandre berithe wulle, of which is made cloth and gyrdles that may not brenne in the fyre." The salamander was said to be so toxic that by twining around a tree, it could poison the fruit and so kill any who ate them and by falling into a well, could kill all who drank from it.
In his autobiography, Benvenuto Cellini relates:
The Japanese giant salamander has been the subject of legend and artwork in Japan, in the ''ukiyo-e'' work by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. The well-known Japanese mythological creature known as the Kappa (folklore), ''kappa'' may be inspired by this salamander.
Limb regeneration as applied to humans
Salamanders' limb regeneration has long been the focus of interest among scientists. The first extensive cell-level study was by Vincenzo Colucci in 1886. Researchers have been trying to find out the conditions required for the growth of new limbs and hope that such Regenerative medicine, regeneration could be replicated in humans using stem cells. Axolotls have been used in research and have been genetically engineered so that a Fluorescence, fluorescent protein is present in cells in the leg, enabling the cell division process to be tracked under the microscope. It seems that after the loss of a limb, cells draw together to form a clump known as a blastema. This superficially appears undifferentiated, but cells that originated in the skin later develop into new skin, muscle cells into new muscle and cartilage cells into new cartilage. It is only the cells from just beneath the surface of the skin that are pluripotent and able to develop into any type of cell. Researchers from the Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute have found that when macrophages were removed, salamanders lost their ability to regenerate and instead formed scar tissue. If the processes involved in forming new tissue can be reverse engineered into humans, it may be possible to heal injuries of the spinal cord or brain, repair damaged organs and reduce scarring and fibrosis after surgery.Brandy
A 1995 article in the Slovenian weekly magazine ''Mladina'' publicized salamander brandy, a liquor supposedly indigenous to Slovenia. It was said to combine hallucinogenic with aphrodisiac effects and is made by putting several live salamanders in a barrel of fermenting fruit. Stimulated by the alcohol, they secrete toxic mucus in defense and eventually die. Besides causing hallucinations, the neurotoxins present in the brew were said to cause extreme sexual arousal. Later research by Slovenian anthropologist Miha Kozorog (University of Ljubljana) paints a very different picture—Salamander in brandy appears to have been traditionally seen as an adulterant, one which caused ill health. It was also used as a term of slander.References
Citations
Cited texts
* * * * *External links
Tree of Life: Caudata
Salamander Gallery
Caudata Culture
Critter Crossings: Salamander Tunnels
at U.S. Department of Transportation
ArchéoZooThèque : Urodele skeleton drawing
: available in vector, image and PDF formats {{Authority control Salamanders, Aposematic animals Articles containing video clips Extant Late Jurassic first appearances Taxa named by André Marie Constant Duméril