Roseola on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Roseola, also known as sixth disease, is an
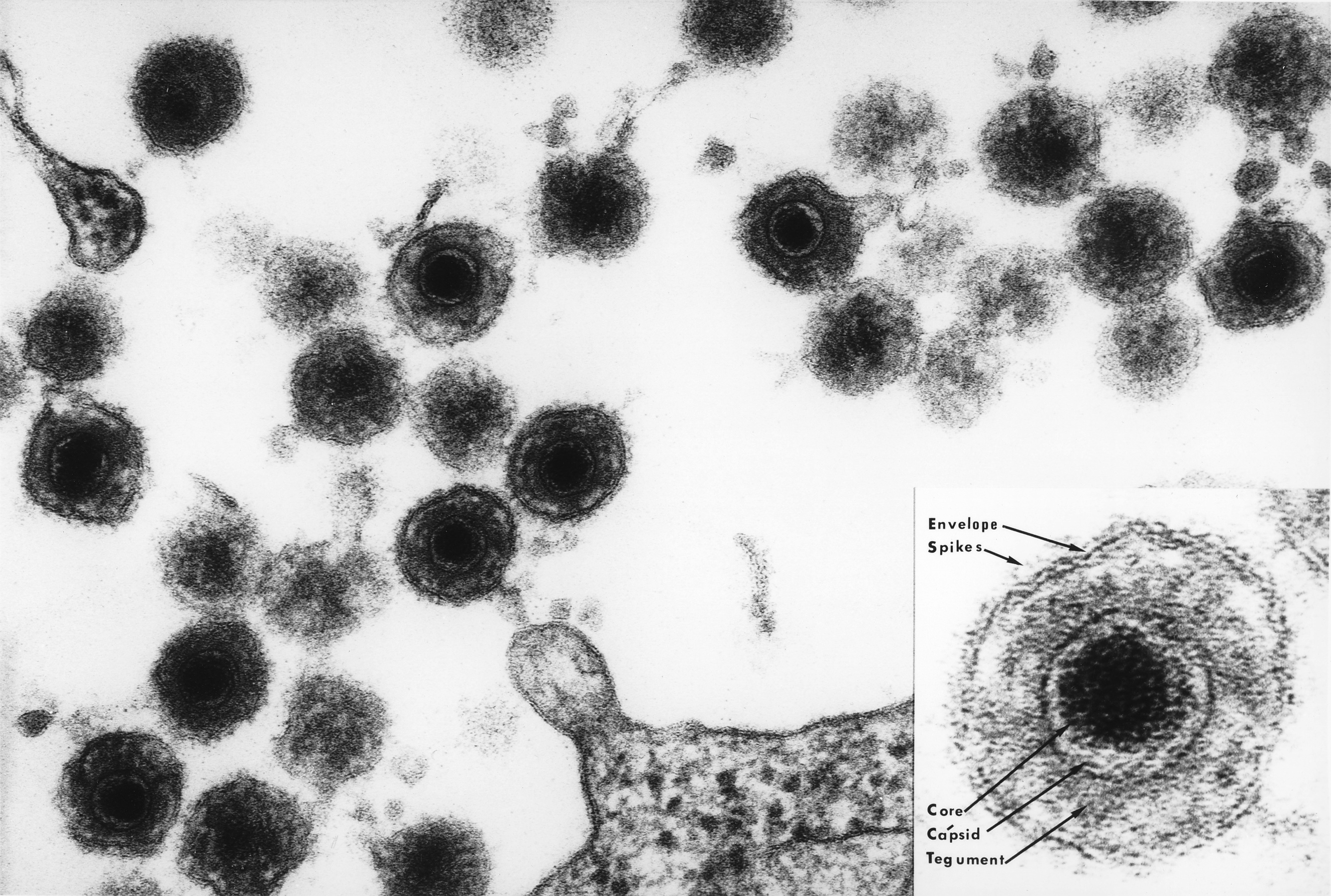 There are nine known human herpesviruses. Of these, roseola has been linked to two: '' human herpesvirus 6'' (HHV-6) and ''
There are nine known human herpesviruses. Of these, roseola has been linked to two: '' human herpesvirus 6'' (HHV-6) and ''
infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
caused by certain types of human herpes viruses. Most infections occur before the age of three. Symptoms vary from absent to the classic presentation of a fever of rapid onset followed by a rash. The fever generally lasts for three to five days, while the rash is generally pink and lasts for less than three days. Complications may include febrile seizures
A febrile seizure, also known as a fever fit or febrile convulsion, is a seizure associated with an increased body temperature but without any intracranial infection. Febrile seizures affect 2–7% of children and are more common in boys than gi ...
, with serious complications being rare.
It is caused by '' human herpesvirus 6'' (HHV-6A, HHV-6B) or ''human herpesvirus 7
''Human betaherpesvirus 7'' (HHV-7) is one of nine known members of the ''Herpesviridae'' family that infects humans. HHV-7 is a member of ''Betaherpesvirinae'', a subfamily of the ''Herpesviridae'' that also includes HHV-6 and '' Cytomegaloviru ...
'' (HHV-7). Spread is usually through the saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can ...
of those who are otherwise healthy. However, it may also spread from the mother to baby during pregnancy. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and does not need to be confirmed with blood tests (PCR or antigen). Low numbers of white blood cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
s may also be present.
Treatment includes sufficient fluids and medications to treat the fever. Nearly all people are infected at some point in time. Males and females are affected equally often. The disease may reactivate in those with a weakened immune system and may result in significant health problems.
The disease was first described in 1910 while the causal virus was determined in 1988. The name "sixth disease" comes from its place on the standard list of rash-causing childhood diseases, which also includes measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
(first), scarlet fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects chi ...
(second), rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
(third), Dukes' disease
Dukes' disease, named after Clement Dukes, also known as fourth disease or Filatov-Dukes' disease (after Nil Filatov), is an exanthem. It is distinguished from measles or forms of rubella, though it was considered as a form of viral rash. Althou ...
(fourth, but is no longer widely accepted as distinct from scarlet fever), and erythema infectiosum
Erythema infectiosum, fifth disease, or slapped cheek syndrome is one of several possible manifestations of infection by parvovirus B19. Fifth disease typically presents as a rash and is more common in children. While parvovirus B19 can affect hu ...
(fifth).
Signs and symptoms
Fever
Symptoms begin with a three to six day febrile illness. During this time, temperatures can peak above 40 °C and children can experience increased irritability with general malaise. However, many children in the febrile phase feel well, engaged, and alert. For these patients, fever is usually diagnosed incidentally. The most common complication (10-15% of children between 6 and 18 months) and most common cause of hospitalization in children with primary infection of HHV-6B isfebrile seizure
A febrile seizure, also known as a fever fit or febrile convulsion, is a seizure associated with an increased body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even whe ...
s which can precipitate status epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes or 2 or more seizures within a 5-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The s ...
due to the sudden rise in body temperature.
Rash
Once the febrile phase subsides, a rash develops. In some cases, the rash can present after one or two days after the fever resolves. The rash is classically described as an erythematous morbilliform exanthem and presents as a distribution of soft pink, discrete, and slightly raised lesions each with a 2-5mm diameter. It classically begins on the trunk (torso) and spreads outward to the neck, extremities, and face. This pattern is referred to as a centrifugal spread. Usually, peeling and itching are not characteristic of this rash. This phase can last anywhere from several hours to 2 days.Other symptoms
A small percentage of children acquire HHV-6 with few signs or symptoms of the disease. Children with HHV-6 infection can also present with myringitis (inflammation of the tympanic membranes), upper respiratory symptoms, diarrhea, and a bulging fontanelle. In addition, children can experience pharyngitis with lymphoid hyperplasia seen on the soft palate and swelling of the eyelids. These symptoms usually present during the febrile phase of roseola. Cervical and postocciptallymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In cl ...
can also be seen, but this generally presents 2–4 days after the onset of the febrile phase.
In rare cases, HHV-6 can become active in an adult previously infected during childhood and can show signs of mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adult ...
.
Cause
 There are nine known human herpesviruses. Of these, roseola has been linked to two: '' human herpesvirus 6'' (HHV-6) and ''
There are nine known human herpesviruses. Of these, roseola has been linked to two: '' human herpesvirus 6'' (HHV-6) and ''human herpesvirus 7
''Human betaherpesvirus 7'' (HHV-7) is one of nine known members of the ''Herpesviridae'' family that infects humans. HHV-7 is a member of ''Betaherpesvirinae'', a subfamily of the ''Herpesviridae'' that also includes HHV-6 and '' Cytomegaloviru ...
'' (HHV-7), which are sometimes referred to collectively as Roseolovirus
''Roseolovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Betaherpesvirinae''. There are currently six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: HHV-6: si ...
. These viruses are of the Herpesviridae
''Herpesviridae'' is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''ἕρπει� ...
family and the ''Betaherpesvirinae
''Betaherpesvirinae'' is a subfamily of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'' and in the family ''Herpesviridae''. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are 26 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera. Diseases associated with this sub ...
'' subfamily, underwhich Cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betah ...
is also classified. HHV-6 has been further classified into HHV-6A and HHV-6B, two ''distinct'' viruses which share 88% of the same DNA makeup, with HHV-6B the most common cause of roseola.
After infection, these viruses enter a latent phase. Roseola caused by HHV-7 has been linked to the ability of HHV-7 infection to reactivate latent HHV-6.
Spread
After exposure to roseola, the causative virus becomes latent in its host but is still present in saliva, skin, and lungs. HHV-6 is thought to be transmitted from previously exposed or infected adults to young children by the shedding of virus through saliva. Even so, most cases of roseola are transmitted without known exposure.Diagnosis
The diagnosis of roseola is made clinically based on the presence of the two phases: fever and rash. Laboratory testing is seldom used as the results do not alter management of the disease. An exception is in people who are immunocompromised in who serologic tests with viral identification can be used to confirm the diagnosis. Roseola should be differentiated from other similar-appearing illnesses, such asrubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
, measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, fifth disease
Erythema infectiosum, fifth disease, or slapped cheek syndrome is one of several possible manifestations of infection by parvovirus B19. Fifth disease typically presents as a rash and is more common in children. While parvovirus B19 can affect hu ...
, scarlet fever
Scarlet fever, also known as Scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection (Group A strep). It most commonly affects chi ...
, and drug reactions. This differentiation may be determined based on symptoms.
Prevention
Many viruses can cause Roseola and are shed by carriers without symptoms. Because of this and the fact that most children with the disease are not seriously ill, there is no particular method of prevention. Proper hygienic measures, like regular handwashing, can be implemented as a routine method of prevention. Those who have been exposed or infected have been shown to shed the virus for the rest of their lives. Because of this, there are no current guidelines regarding children staying home or away from child-care when infected.Treatment
Most cases of HHV-6 infection improve on their own. Because of this, supportive care is the mainstay treatment. The febrile phase can be managed using acetaminophen to control fever and prevent spikes in temperature which can lead to febrile seizures. In the case of febrile seizures, medical advice should be sought, and treatment aggressively pursued. Antiepileptic drugs are not recommended for patients who develop seizures from Roseola. Once children have entered the rash phase, reassurance is important as this indicates resolution of the infection. Ifencephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations ...
occurs in immunocompromised children, ganciclovir
Ganciclovir, sold under the brand name Cytovene among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections.
Ganciclovir was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1988.
Medical use
Ganciclovir is indicated ...
or foscarnet have inconsistently shown usefulness in treatment. Treatment of children who are immunocompromised centers around decreasing their levels of immunosuppression as much as possible.
Prognosis
Children infected with roseola generally have a good prognosis. Most recover without intervention and without long-term effects.Epidemiology
Between the two types of human herpesvirus 6, HHV-6B has been detected much more frequently in hosts. HHV-6B has been shown to affect about 90% of children before the age of 3. Out of these, 20% develop symptoms of roseola, also known as exanthem subitum. Roseola affects girls and boys equally worldwide year-round. Roseola typically affects children between six months and two years of age, with peak prevalence in children between 7 and 13 months old. This correlates with the decrease in maternal antibodies, thus virus protection, that occurs at the age of 6 months. Out of all emergency department visits for children between the ages of 6 months and 12 months who have fever, twenty percent of these are due to HHV-6. Many children who have been exposed and infected can present without symptoms, which makes determining the incidence within the population difficult.History
John Zahorsky MD wrote extensively on this disease in the early 20th century, his first formal presentation was to the St Louis Pediatric society in 1909 where he described 15 young children with the illness. In a JAMA article published on Oct 18, 1913 he noted that "the name 'Roseola infantilis' had an important place in the medical terminology of writers on skin diseases" but that descriptions of the disease by previous writers tended to confuse it with many other diseases that produce febrile rashes. In this JAMA article Zahorsky reports on 29 more children with Roseola and notes that the only condition that should seriously be considered in the differential diagnosis is German Measles (rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and ...
) but notes that the fever of rubella only lasts a few hours whereas the prodromal fever of Roseola lasts three to five days and disappears with the formation of a morbilliform The term morbilliform refers to a rash that looks like measles. The rash consists of macular lesions that are red and usually 2–10 mm in diameter but may be confluent in places. A morbilliform rash is a rose-red flat ( macular) or slightly ...
rash.
Names
Research
HHV-6 has been tentatively linked withneurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophi ...
s.
See also
*Fifth disease
Erythema infectiosum, fifth disease, or slapped cheek syndrome is one of several possible manifestations of infection by parvovirus B19. Fifth disease typically presents as a rash and is more common in children. While parvovirus B19 can affect hu ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Exanthema Subitum Virus-related cutaneous conditions Pediatrics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate