Rocket Artillery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
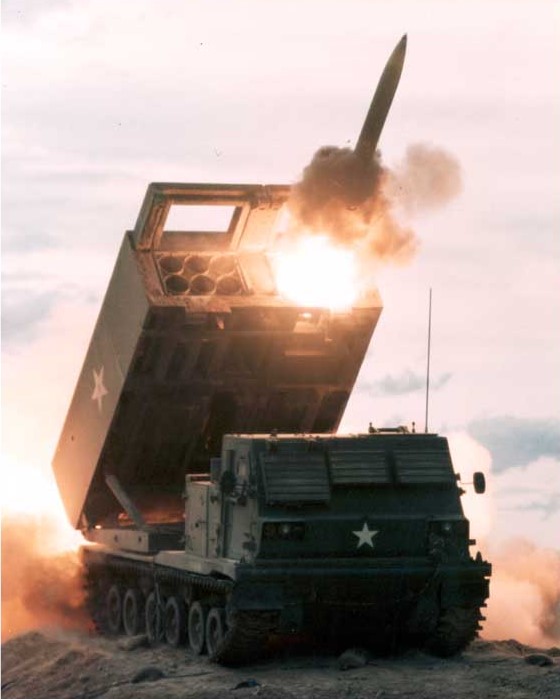 Rocket artillery is
Rocket artillery is
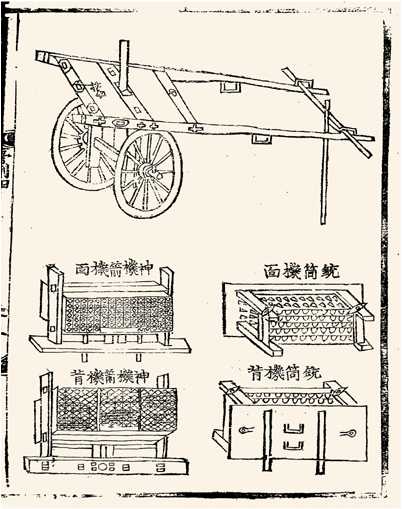 The use of
The use of

 Although the rockets were quite primitive, they had a demoralizing effect on the enemy due to the noise and bursting light. The rockets could be of various sizes but usually consisted of a tube of soft hammered iron about 8 inches (20 cm) long and 1.5 to 3 inches (3.8 to 7.6 cm) in diameter, closed at one end and strapped to a shaft of bamboo about 4 ft (1 m) long. The iron tube acted as a combustion chamber and contained well-packed black powder propellant. A rocket carrying about one pound (~500 gm) of powder could travel almost 1,000 yards (~900 m).
According to Stephen Oliver Fought and John F. Guilmartin, Jr. in ''
Although the rockets were quite primitive, they had a demoralizing effect on the enemy due to the noise and bursting light. The rockets could be of various sizes but usually consisted of a tube of soft hammered iron about 8 inches (20 cm) long and 1.5 to 3 inches (3.8 to 7.6 cm) in diameter, closed at one end and strapped to a shaft of bamboo about 4 ft (1 m) long. The iron tube acted as a combustion chamber and contained well-packed black powder propellant. A rocket carrying about one pound (~500 gm) of powder could travel almost 1,000 yards (~900 m).
According to Stephen Oliver Fought and John F. Guilmartin, Jr. in ''
 The Indian
The Indian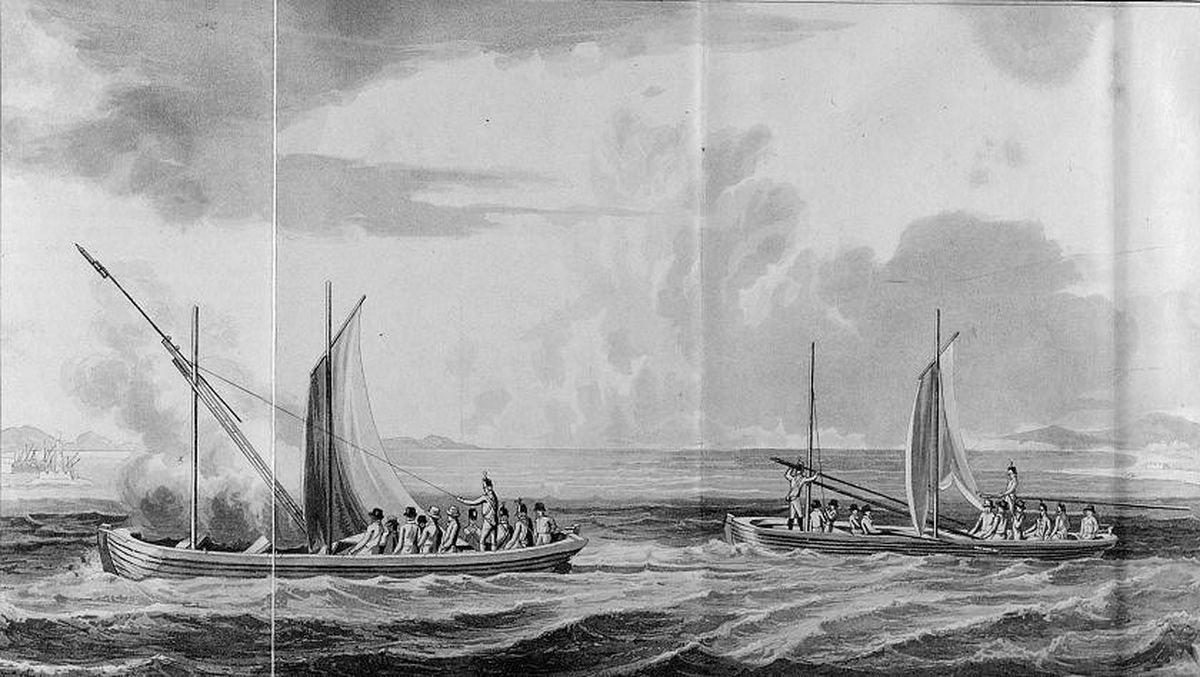  These rockets were used during the
These rockets were used during the  After the rockets were successfully used during Napoleon's defeat at the
After the rockets were successfully used during Napoleon's defeat at the
 Modern rocket artillery was first employed during
Modern rocket artillery was first employed during

 *Rockets produce no or little recoil, while conventional gun artillery systems produce significant recoil. Unless firing within a very small arc with the possibility of wrecking a
*Rockets produce no or little recoil, while conventional gun artillery systems produce significant recoil. Unless firing within a very small arc with the possibility of wrecking a
 Rocket artillery is
Rocket artillery is artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
that uses rocket explosives as the projectile. The use of rocket artillery dates back to medieval China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
where devices such as fire arrows were used (albeit mostly as a psychological weapon). Fire arrows were also used in multiple launch systems and transported via carts. First true rocket artillery was developed in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
by the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
. In the late nineteenth century, due to improvements in the power and range of conventional artillery, the use of early military rockets declined; they were finally used on a small scale by both sides during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
. Modern rocket artillery was first employed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, in the form of the German Nebelwerfer family of rocket ordnance designs, Soviet Katyusha-series and numerous other systems employed on a smaller scale by the Western allies and Japan. In modern use, the rockets are often guided by an internal guiding system or GPS in order to maintain accuracy.
History
Early history
 The use of
The use of rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entir ...
s as some form of artillery dates back to medieval China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
where devices such as fire arrows were used (albeit mostly as a psychological weapon). Fire arrows were also used in multiple launch systems and transported via carts. Devices such as the Korean hwacha
The ''hwacha'' or ''hwach'a'' ( ko, 화차; Hanja: ; literally "fire cart") was a multiple rocket launcher and an organ gun of similar design which were developed in fifteenth century Korea. The former variant fired one or two hundred rocket- ...
were able to fire hundreds of fire arrows simultaneously. The use of medieval rocket artillery was picked up by the invading Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
s and spread to the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
who in turn used them on the European battlefield.
The use of war-rockets is well documented in Medieval Europe. In 1408 Duke John the Fearless of Burgundy used 300 incendiary rockets in the Battle of Othée. The city dwellers coped with this tactic by covering their roofs with dirt.
Metal-cylinder rocket artillery
The earliest successful utilization of metal-cylinder rocket artillery is associated withKingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary allia ...
, South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union terr ...
. Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
's father Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali ( حیدر علی, ''Haidarālī''; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the att ...
successfully established the powerful Sultanate of Mysore and introduced the first iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
-cased metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
-cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an ...
rocket. The Mysorean rockets
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon, the iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. The Mysorean army, under Hyder Ali and his son Tipu Sultan, used the rockets effectively against the British East India Compa ...
of this period were innovative, chiefly because of the use of iron tubes that tightly packed the gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). T ...
propellant; this enabled higher thrust and longer range for the missile (up to 2 km range).
Tipu Sultan used them against the larger forces of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sou ...
during the Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pres ...
, especially during the Battle of Pollilur
The Battle of Pollilur (a.k.a. Pullalur), also known as the Battle of Polilore or Battle of Perambakam, took place on 10 September 1780 at Pollilur near Conjeevaram, the city of Kanchipuram in present-day Tamil Nadu state, India, as part of th ...
. Another battle where these missiles were deployed was the Battle of Sultanpet Tope, where Colonel Arthur Wellesley, later famous as the First Duke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister ...
, was almost defeated by Tipu's Diwan Purnaiah.

 Although the rockets were quite primitive, they had a demoralizing effect on the enemy due to the noise and bursting light. The rockets could be of various sizes but usually consisted of a tube of soft hammered iron about 8 inches (20 cm) long and 1.5 to 3 inches (3.8 to 7.6 cm) in diameter, closed at one end and strapped to a shaft of bamboo about 4 ft (1 m) long. The iron tube acted as a combustion chamber and contained well-packed black powder propellant. A rocket carrying about one pound (~500 gm) of powder could travel almost 1,000 yards (~900 m).
According to Stephen Oliver Fought and John F. Guilmartin, Jr. in ''
Although the rockets were quite primitive, they had a demoralizing effect on the enemy due to the noise and bursting light. The rockets could be of various sizes but usually consisted of a tube of soft hammered iron about 8 inches (20 cm) long and 1.5 to 3 inches (3.8 to 7.6 cm) in diameter, closed at one end and strapped to a shaft of bamboo about 4 ft (1 m) long. The iron tube acted as a combustion chamber and contained well-packed black powder propellant. A rocket carrying about one pound (~500 gm) of powder could travel almost 1,000 yards (~900 m).
According to Stephen Oliver Fought and John F. Guilmartin, Jr. in ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
'' (2008):
Congreve rockets
 The Indian
The Indian Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan (born Sultan Fateh Ali Sahab Tipu, 1 December 1751 – 4 May 1799), also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore based in South India. He was a pioneer of rocket artillery.Dalrymple, p. 243 He i ...
's rocket experiences, including Munro's book of 1789, eventually led to the Royal Arsenal
The Royal Arsenal, Woolwich is an establishment on the south bank of the River Thames in Woolwich in south-east London, England, that was used for the manufacture of armaments and ammunition, proofing, and explosives research for the Britis ...
beginning a military rocket R&D program in 1801. Several rocket cases were collected from Mysore and sent to Britain for analysis. The development was chiefly the work of Col. (later Sir) William Congreve, son of the Comptroller of the Royal Arsenal
The Royal Arsenal, Woolwich is an establishment on the south bank of the River Thames in Woolwich in south-east London, England, that was used for the manufacture of armaments and ammunition, proofing, and explosives research for the Britis ...
, Woolwich
Woolwich () is a district in southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich.
The district's location on the River Thames led to its status as an important naval, military and industrial area; a role that was maintained thr ...
, London, who set on a vigorous research and development programme at the Arsenal's laboratory; after development work was complete, the rockets were manufactured in quantity further north, near Waltham Abbey, Essex. He was told that "the British at Seringapatam had suffered more from the rockets than from the shells or any other weapon used by the enemy". "In at least one instance", an eyewitness told Congreve, "a single rocket had killed three men and badly wounded others".
It has been suggested that Congreve may have adapted iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
-cased gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). T ...
rockets for use by the British military from prototypes created by the Irish nationalist Robert Emmet during Emmet's Rebellion in 1803. But this seems far less likely given the fact that the British had been exposed to Indian rockets since 1780 at the latest, and that a vast quantity of unused rockets and their construction equipment fell into British hands at the end of the Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company (represented chiefly by the neighbouring Madras Pres ...
in 1799, at least 4 years before Emmet's rockets.
Congreve introduced a standardised formula for the making of gunpowder at Woolwich and introduced mechanical grinding mills to produce powder of uniform size and consistency. Machines were also employed to ensure the packing of the powder was perfectly uniform. His rockets were more elongated, had a much larger payload, and were mounted on sticks; this allowed them to be launched from the sea at a greater range. He also introduced shot into the payload, which added shrapnel damage to the incendiary capability of the rocket. By 1805 he was able to introduce a comprehensive weapons system to the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
.
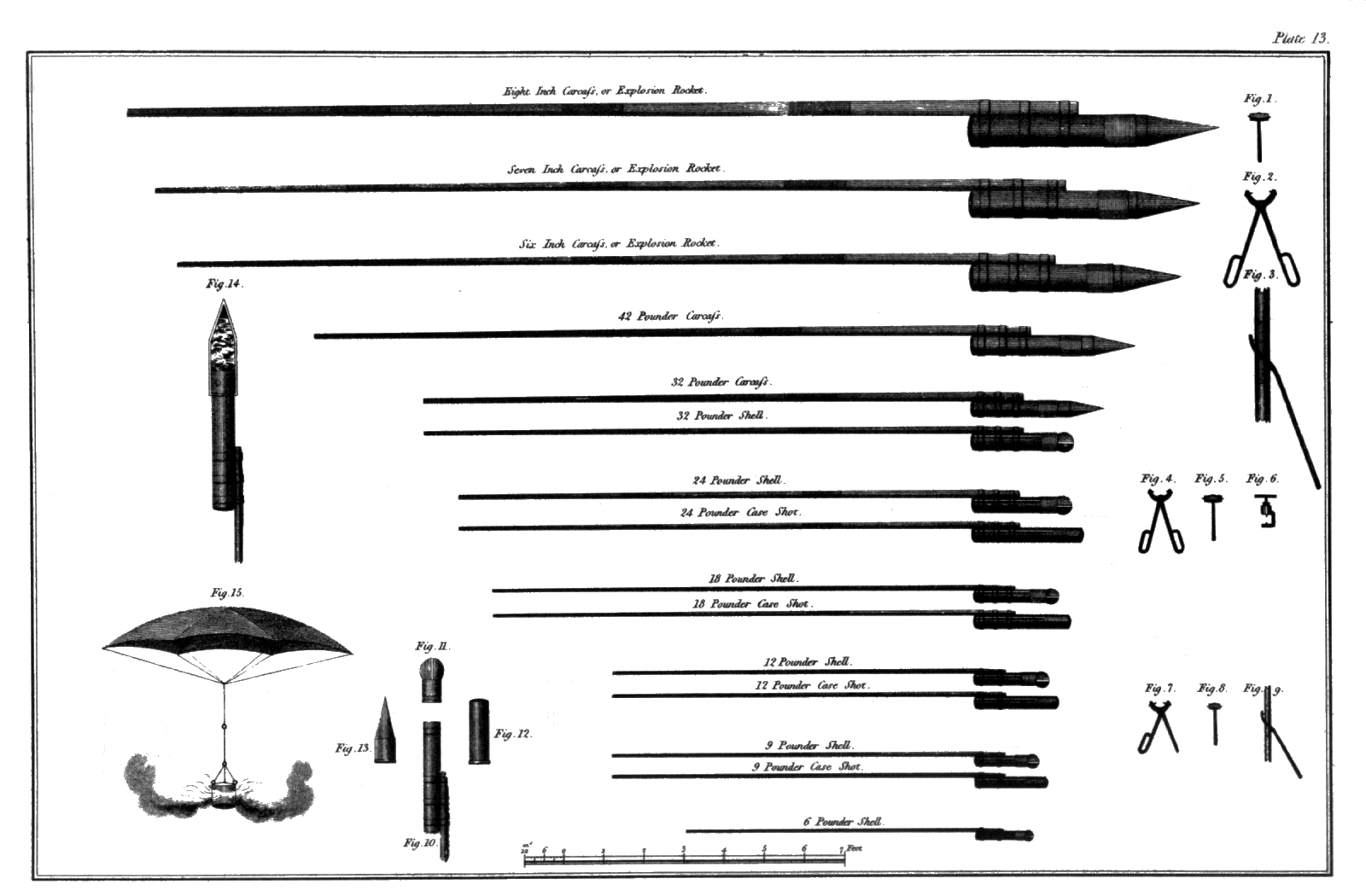
The rocket had a "cylindro-conoidal" warhead and was launched in pairs from half troughs on simple metal A-frames. The original rocket design had the guide pole side-mounted on the warhead, this was improved in 1815 with a base plate with a threaded hole. They could be fired up to two miles, the range being set by the degree of elevation of the launching frame, although at any range they were fairly inaccurate and had a tendency for premature explosion. They were as much a psychological weapon as a physical one, and they were rarely or never used except alongside other types of artillery. Congreve designed several different warhead sizes from . The type with a guide pole was the most widely used variant. Different warheads were used, including explosive, shrapnel and incendiary. They were manufactured at a special facility near the Waltham Abbey Royal Gunpowder Mills beside the River Lea
The River Lea ( ) is in South East England. It originates in Bedfordshire, in the Chiltern Hills, and flows southeast through Hertfordshire, along the Essex border and into Greater London, to meet the River Thames at Bow Creek. It is one of ...
in Essex
Essex () is a Ceremonial counties of England, county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the Riv ...
.
 These rockets were used during the
These rockets were used during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
against the city of Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
, and during the naval bombardment of Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, where over 25,000 rockets were launched, causing severe incendiary damage to the city. The rockets were also adapted for the purpose of flares for signalling and battlefield illumination. Henry Trengrouse utilized the rocket in his life-saving apparatus, in which the rocket was launched at a shipwreck with an attached line to help rescue the victims.
The Congreve rockets are also famous for inspiring the lawyer Francis Scott Key
Francis Scott Key (August 1, 1779January 11, 1843) was an American lawyer, author, and amateur poet from Frederick, Maryland, who wrote the lyrics for the American national anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner". Key observed the British bombardment ...
to pen the words the "rockets' red glare" in what became the US National Anthem during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
.
 After the rockets were successfully used during Napoleon's defeat at the
After the rockets were successfully used during Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Sevent ...
, various countries were quick to adopt the weapon and establish special rocket brigades. The British created the British Army Rocket Brigade in 1818, followed by the Austrian Army
The Austrian Armed Forces (german: Bundesheer, lit=Federal Army) are the combined military forces of the Republic of Austria.
The military consists of 22,050 active-duty personnel and 125,600 reservists. The military budget is 0.74% of nat ...
and the Russian Army.
One persistent problem with the rockets was their lack of aerodynamic stability. The British engineer William Hale designed a rocket with a combination of tail fins and directed nozzles for the exhaust. This imparted a spin to the rocket during flight, which stabilized its trajectory and greatly improved its accuracy, although it did sacrifice somewhat of the maximum range. Hale rockets were enthusiastically adopted by the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and during the Mexican War in 1846 a volunteer brigade of rocketeers was pivotal in the surrender of Mexican forces at the Siege of Veracruz
The Battle of Veracruz was a 20-day siege of the key Mexican beachhead seaport of Veracruz during the Mexican–American War. Lasting from March 9–29, 1847, it began with the first large-scale amphibious assault conducted by United States ...
.
By the late nineteenth century, due to improvements in the power and range of conventional artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
, the use of military rockets declined; they were finally used on a small scale by both sides during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
.
World War II
 Modern rocket artillery was first employed during
Modern rocket artillery was first employed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, in the form of the German Nebelwerfer family of rocket ordnance designs, and Soviet Katyusha-series. The Soviet Katyushas, nicknamed by German troops ''Stalin's Organ'' because of their visual resemblance to a church musical organ and alluding to the sound of the weapon's rockets, were mounted on trucks or light tanks, while the early German Nebelwerfer ordnance pieces were mounted on a small wheeled carriage which was light enough to be moved by several men and could easily be deployed nearly anywhere, while also being towed by most vehicles. The Germans also had self-propelled rocket artillery in the form of the Panzerwerfer and Wurfrahmen 40 which equipped half-track
A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with regular wheels at the front for steering and continuous tracks at the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. The purpose of this combination is to produce a vehicle with the cro ...
armoured fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle (AFV) is an armed combat vehicle protected by armour, generally combining operational mobility with offensive and defensive capabilities. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked. Examples of AFVs are tanks, armoured cars, ...
s. An oddity in the subject of rocket artillery during this time was the German " Sturmtiger", a vehicle based on the Tiger I
The Tiger I () was a German heavy tank of World War II that operated beginning in 1942 in Africa and in the Soviet Union, usually in independent heavy tank battalions. It gave the German Army its first armoured fighting vehicle that mounted ...
heavy tank chassis that was armed with a 380 mm rocket mortar.
The Western Allies of World War II employed little rocket artillery. During later periods of the war, British and Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
troops used the Land Mattress, a towed rocket launcher. The United States Army built and deployed a small number of turret-mounted T34 Calliope
The Rocket Launcher T34 (Calliope) was a tank-mounted multiple rocket launcher used by the United States Army during World War II. The launcher was placed atop the M4 Sherman, with its prominent vertical side frames anchored to the turret's si ...
and T40 Whizbang rocket artillery tanks (converted from M4 Sherman medium tanks) in France and Italy. In 1945, the British Army also fitted some M4 Shermans with two 60 lb RP3 rockets, the same as used on ground attack aircraft and known as "''Tulip''".
In the Pacific, however, the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
made heavy use of rocket artillery on their LSM(R) transports, adding to the already intense bombardment by the guns of heavy warships to soften up Japanese-held islands before the US Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through comb ...
would land. On Iwo Jima
Iwo Jima (, also ), known in Japan as , is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands and lies south of the Bonin Islands. Together with other islands, they form the Ogasawara Archipelago. The highest point of Iwo Jima is Mount Suribachi at high.
...
, the Marines made use of rocket artillery trucks in a similar fashion as the Soviet Katyusha, but on a smaller scale.
The Japanese Imperial Army deployed the naval Type 4 20 cm (8 in) Rocket Launcher and army Type 4 40 cm (16 in) Rocket Launcher against the United States Marines and Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
troops at Iwo Jima and Okinawa
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan. Okinawa Prefecture is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan, has a population of 1,457,162 (as of 2 February 2020) and a geographic area of 2,281 Square kilometre, km2 (880 sq mi).
...
, and United States Army troops during the Battle of Luzon
The Battle of Luzon ( tl, Labanan sa Luzon; ja, ルソン島の戦い; es, Batalla de Luzón) was a land battle of the Pacific Theater of Operations of World War II by the Allied forces of the U.S., its colony the Philippines, and allies agai ...
, as well Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
troops during Manchuria Campaign, South Sakhalin
Karafuto Prefecture ( ja, 樺太庁, ''Karafuto-chō''; russian: Префектура Карафуто, Prefektura Karafuto), commonly known as South Sakhalin, was a prefecture of Japan located in Sakhalin from 1907 to 1949.
Karafuto became ter ...
and Kuril Island Campaign. Their deployment was limited relative to other mortar types and the projectiles on the 40 cm launcher were so large and heavy that they had to be loaded using small hand-operated cranes
Crane or cranes may refer to:
Common meanings
* Crane (bird), a large, long-necked bird
* Crane (machine), industrial machinery for lifting
** Crane (rail), a crane suited for use on railroads
People and fictional characters
* Crane (surname ...
, but they were extremely accurate and had a pronounced psychological effect on opposing troops, who called them "Screaming Mimis", a nickname originally applied to the German Nebelwerfer tube-launched rocket mortar series in the European Theater of Operations
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) was a Theater of Operations responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the European theatre of World War II, from 1942 to 1945. It commanded Army Ground For ...
. They were often used at night to conceal their launching sites and increase their disruptiveness and psychological effectiveness. The Japanese 20 cm rockets were launched from tubes or launching troughs, while the larger rockets were launched from steel ramps reinforced with wooden monopods.
The Japanese also deployed a limited number of 447mm rocket launchers, termed 45 cm Rocket Mortars by United States personnel who test-fired them at the close of the war. Their projectiles consisted of a 1,500 lb cylinder filled with propellant and ballistite
Ballistite is a smokeless propellant made from two high explosives, nitrocellulose and nitroglycerine. It was developed and patented by Alfred Nobel in the late 19th century.
Military adoption
Alfred Nobel patented https://www.nobelprize.org/alfr ...
sticks detonated by black powder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). T ...
, which produced a blast crater approximately the size of an American 1,000 lb bomb. In effect, this made the 447mm projectile a type of surface-to-surface barrel bomb
A barrel bomb is an improvised unguided bomb, sometimes described as a flying IED (improvised explosive device). They are typically made from a large barrel-shaped metal container that has been filled with high explosives, possibly shrapnel, oi ...
. While these latter weapons were captured at Luzon and proved effective in subsequent testing, it is not clear that they were ever used against American troops, in contrast to the more common 20 and 40 cm types, which clearly contributed to the 37,870 American casualties sustained at Luzon.
Post-World War II

Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
fitted some of their Sherman tanks with different rocket artillery. An unconventional Sherman conversion was the turretless Kilshon ("Trident") that launched an AGM-45 Shrike anti-radiation missile.
The Soviet Union continued its development of the Katyusha during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, and also exported them widely.
Modern rocket artillery such as the US M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System is highly mobile and are used in similar fashion to other self-propelled artillery
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled ...
. Global Positioning and Inertial Navigation terminal guidance systems have been introduced.
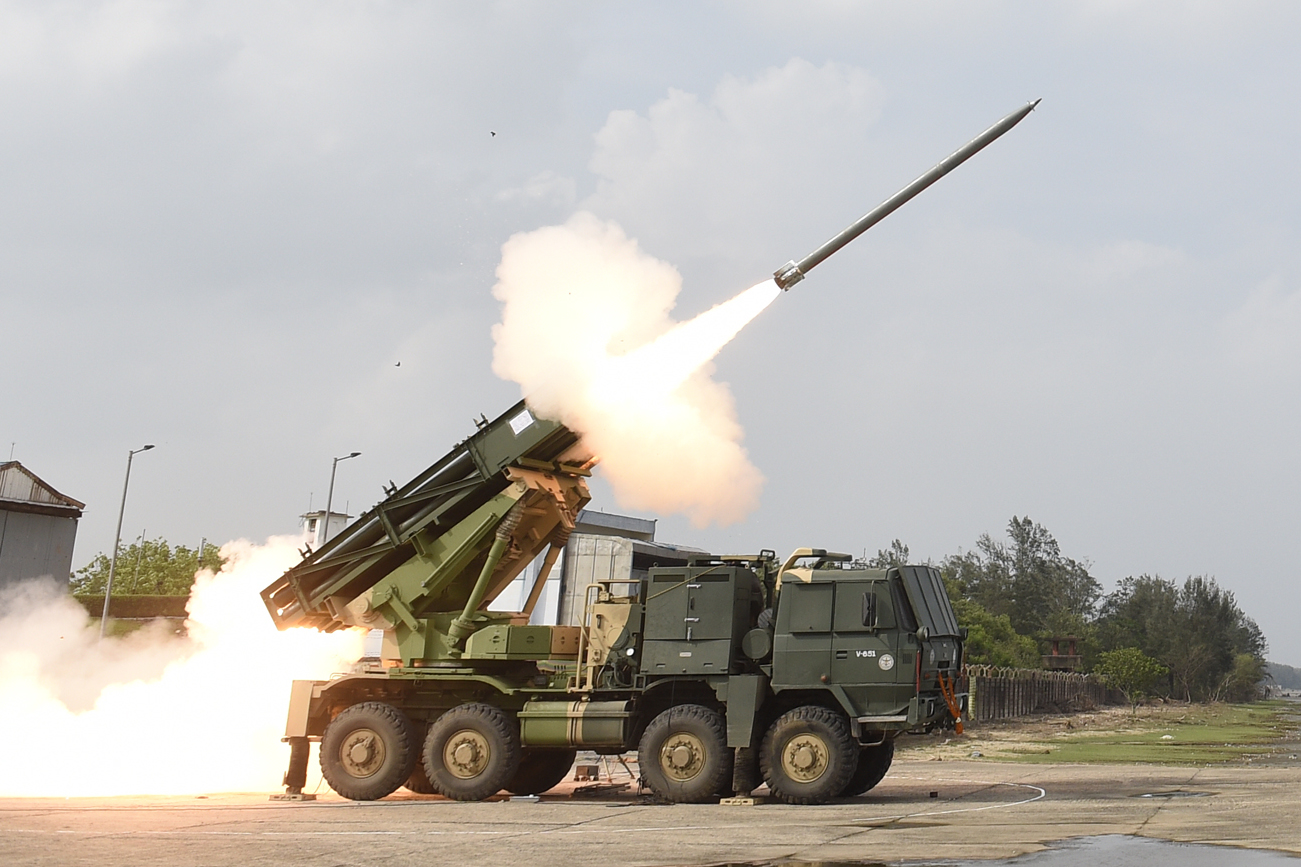
During the Kargil war of 1999, the Indian army
The Indian Army is the Land warfare, land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Arm ...
pressed into service the Pinaka MBRL against Pakistani forces. Despite the system still being under development, it was still able to perform successfully, after which the Indian Army showed interest in inducting the system into service.
Rocket artillery vs gun artillery
 *Rockets produce no or little recoil, while conventional gun artillery systems produce significant recoil. Unless firing within a very small arc with the possibility of wrecking a
*Rockets produce no or little recoil, while conventional gun artillery systems produce significant recoil. Unless firing within a very small arc with the possibility of wrecking a self-propelled artillery
Self-propelled artillery (also called locomotive artillery) is artillery equipped with its own propulsion system to move toward its firing position. Within the terminology are the self-propelled gun, self-propelled howitzer, self-propelled ...
system's vehicle suspension, gun artillery must usually be braced against recoil. In this state they are immobile, and cannot change position easily. Rocket artillery is much more mobile and can change position easily. This "shoot-and-scoot
Shoot-and-scoot (alternatively, fire-and-displace or fire-and-move) is an artillery tactic of firing at a target and then immediately moving away from the location from where the shots were fired to avoid counter-battery fire (e.g. from enemy a ...
" ability makes the platform difficult to target. A rocket artillery piece could, conceivably, fire on the move. Rocket systems produce a significant amount of backblast, however, which imposes its own restrictions. Launchers may be sighted by the firing arcs of the rockets, and their fire can damage themselves or neighbouring vehicles.
*Rocket artillery cannot usually match the accuracy and sustained rate of fire of conventional gun artillery. They may be capable of very destructive strikes by delivering a large mass of explosives simultaneously, thus increasing the shock effect and giving the target less time to take cover. Modern computer-controlled conventional artillery have recently begun to acquire the possibility to do something similar through MRSI but it is an open question if MRSI is really practical in a combat situation. On the other hand, precision-guided rocket artillery demonstrates extreme accuracy, comparable with the best guided gun artillery systems.
*Rocket artillery typically has a very large fire signature
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are pr ...
, leaving a clear smoke trail showing exactly where the barrage came from. Since the barrage does not take much time to execute, however, the rocket artillery can move away quickly.
*Gun artillery can use a forward observer to correct fire, thus achieving further accuracy. This is usually not practical with rocket artillery.
*Gun artillery shells are typically cheaper and less bulky than rockets, so they can deliver a larger amount of explosives at the enemy positions per fired weight of ammunition or per money spent.
*While gun artillery shells are smaller than rockets, the gun itself must be very large to match the range of rockets. Therefore, rockets typically have longer range while the rocket launchers remain small enough to mount on mobile vehicles. Extremely large guns like the Paris Gun
The Paris Gun (german: Paris-Geschütz / Pariser Kanone) was the name given to a type of German long-range siege gun, several of which were used to bombard Paris during World War I. They were in service from March to August 1918. When the guns w ...
and the Schwerer Gustav have been rendered obsolete by long range missiles.
*Rate of fire
Rate of fire is the frequency at which a specific weapon can fire or launch its projectiles. This can be influenced by several factors, including operator training level, mechanical limitations, ammunition availability, and weapon condition. In m ...
: If the artillery barrage was intended as a preparation for an attack, and it usually is, a short but intense barrage will give the enemy less time to prepare by, for instance, dispersing or entering prepared fortifications such as trenches and bunkers.
*The higher accuracy of gun artillery means that it can be used to attack an enemy close to a friendly force. This, combined with the higher capacity for sustained fire, makes gun artillery more suitable than rocket artillery for defensive fire.
*The accuracy of gun artillery and its ability to be rapidly laid to engage targets makes it the system of choice for the engagement of moving targets and to deliver counter-battery fire
Counter-battery fire (sometimes called counter-fire) is a battlefield tactic employed to defeat the enemy's indirect fire elements (multiple rocket launchers, artillery and mortars), including their target acquisition, as well as their command ...
.
*Many multiple rocket launcher
A multiple rocket launcher (MRL) or multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) is a type of rocket artillery system that contains multiple launchers which are fixed to a single platform, and shoots its rocket ordnance in a fashion similar to a vo ...
vehicles now have the capability to fire guided rockets, eliminating the accuracy disadvantage.
See also
* List of rocket artillery * Rocket-assisted projectile * Tactical ballistic missileReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rocket Artillery Rocket weapons Missile types