resolution (chromatography) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
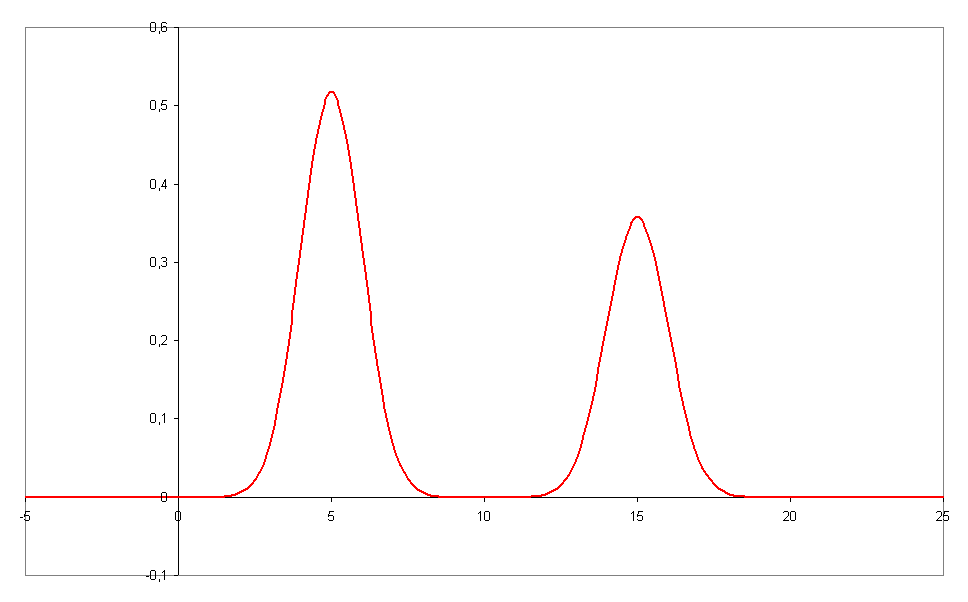 The
The
IUPAC Nomenclature for Chromatography
{{chromatography,
chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
, resolution is a measure of the separation of two peak Peak or The Peak may refer to:
Basic meanings Geology
* Mountain peak
** Pyramidal peak, a mountaintop that has been sculpted by erosion to form a point Mathematics
* Peak hour or rush hour, in traffic congestion
* Peak (geometry), an (''n''-3)-d ...
s of different retention time ''t'' in a chromatogram
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
.
Expression
Chromatographic peak resolution is given by : where tR is the retention time and wb is the peak width at baseline. The bigger the time-difference and/or the smaller the bandwidths, the better the resolution of the compounds. Here compound 1 elutes before compound 2. If the peaks have the same width :.Plate number
 The
The theoretical plate
A theoretical plate in many separation processes is a hypothetical zone or stage in which two phases, such as the liquid and vapor phases of a substance, establish an equilibrium with each other. Such equilibrium stages may also be referred to as ...
height is given by
:
where L is the column length and N the number of theoretical plates. The relation between plate number and peak width at the base is given by
:.See also
*Image resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ...
*Resolution (mass spectrometry)
In mass spectrometry, resolution is a measure of the ability to distinguish two peaks of slightly different mass-to-charge ratios ''ΔM'', in a mass spectrum.
Resolution and resolving power
There are two different definitions of resolution and ...
*Van Deemter equation
The van Deemter equation in chromatography, named for Jan van Deemter, relates the variance per unit length of a separation column to the linear mobile phase velocity by considering physical, kinetic, and thermodynamic properties of a separation. ...
References
External links
IUPAC Nomenclature for Chromatography
{{chromatography,