rasterizer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
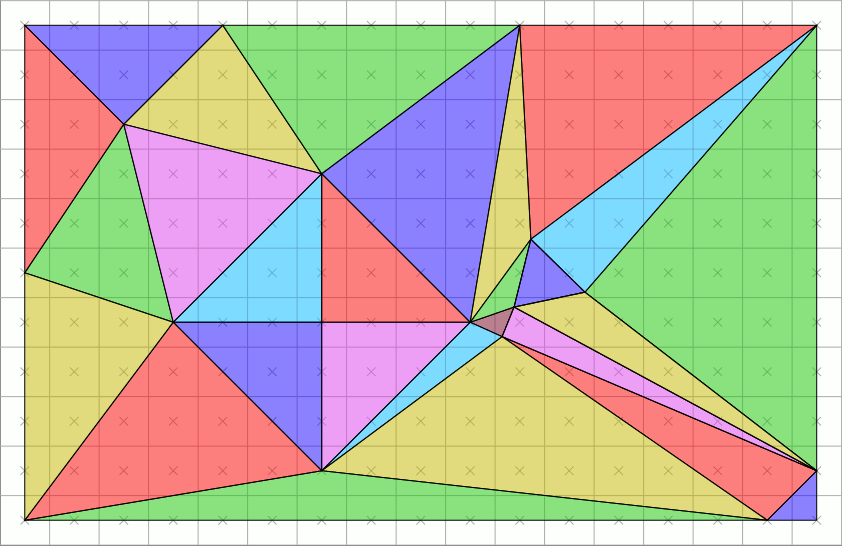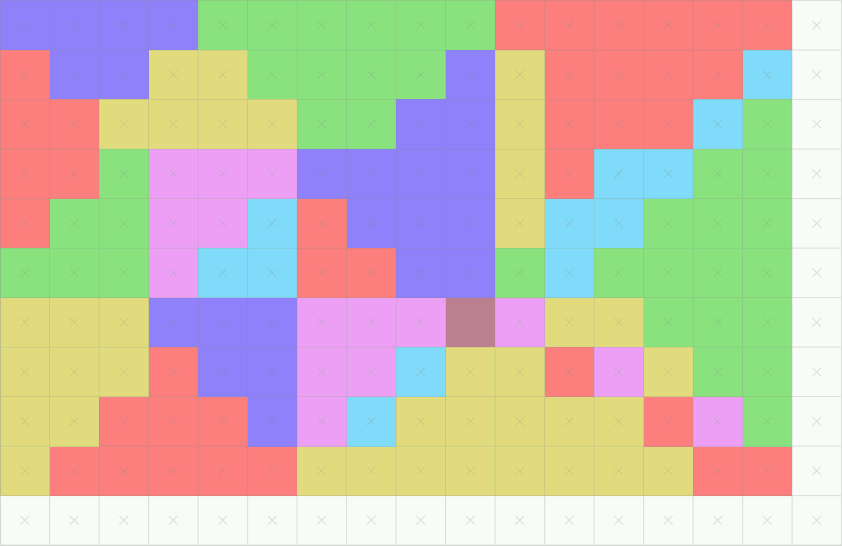 A common representation of digital 3D models is polygonal. Before rasterization, individual polygons are broken down into triangles, therefore a typical problem to solve in 3D rasterization is rasterization of a triangle. Properties that are usually required from triangle rasterization algorithms are that rasterizing two adjacent triangles (i.e. those that share an edge)
# leaves no holes (non-rasterized pixels) between the triangles, so that the rasterized area is completely filled (just as the surface of adjacent triangles). And
# no pixel is rasterized more than once, i.e. the rasterized triangles don't overlap. This is to guarantee that the result doesn't depend on the order in which the triangles are rasterized. Overdrawing pixels can also mean wasting computing power on pixels that would be overwritten.
This leads to establishing rasterization rules to guarantee the above conditions. One set of such rules is called a top-left rule, which states that a pixel is rasterized if and only if
# its center lies completely inside the triangle. Or
# its center lies exactly on the triangle edge (or multiple edges in case of corners) that is (or, in case of corners, all are) either ''top'' or ''left'' edge.
A ''top'' edge is an edge that is exactly horizontal and lies above other edges, and a ''left'' edge is a non-horizontal edge that is on the left side of the triangle.
This rule is implemented e.g. by
A common representation of digital 3D models is polygonal. Before rasterization, individual polygons are broken down into triangles, therefore a typical problem to solve in 3D rasterization is rasterization of a triangle. Properties that are usually required from triangle rasterization algorithms are that rasterizing two adjacent triangles (i.e. those that share an edge)
# leaves no holes (non-rasterized pixels) between the triangles, so that the rasterized area is completely filled (just as the surface of adjacent triangles). And
# no pixel is rasterized more than once, i.e. the rasterized triangles don't overlap. This is to guarantee that the result doesn't depend on the order in which the triangles are rasterized. Overdrawing pixels can also mean wasting computing power on pixels that would be overwritten.
This leads to establishing rasterization rules to guarantee the above conditions. One set of such rules is called a top-left rule, which states that a pixel is rasterized if and only if
# its center lies completely inside the triangle. Or
# its center lies exactly on the triangle edge (or multiple edges in case of corners) that is (or, in case of corners, all are) either ''top'' or ''left'' edge.
A ''top'' edge is an edge that is exactly horizontal and lies above other edges, and a ''left'' edge is a non-horizontal edge that is on the left side of the triangle.
This rule is implemented e.g. by
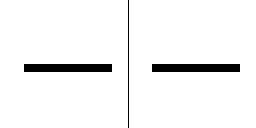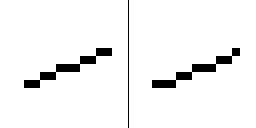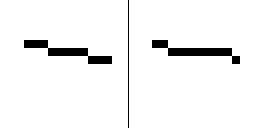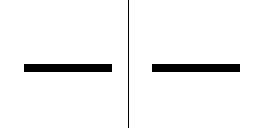 The quality of rasterization can be improved by antialiasing, which creates "smooth" edges. Sub-pixel precision is a method which takes into account positions on a finer scale than the pixel grid and can produce different results even if the endpoints of a primitive fall into same pixel coordinates, producing smoother movement animations. Simple or older hardware, such as PlayStation 1, lacked sub-pixel precision in 3D rasterization.
The quality of rasterization can be improved by antialiasing, which creates "smooth" edges. Sub-pixel precision is a method which takes into account positions on a finer scale than the pixel grid and can produce different results even if the endpoints of a primitive fall into same pixel coordinates, producing smoother movement animations. Simple or older hardware, such as PlayStation 1, lacked sub-pixel precision in 3D rasterization.
Michael Abrash’s articles on computer graphicsMicrosoft’s DirectX APIOpenGL APIRasterization, a Practical Implementation
{{Graphics Processing Unit Shading Computer graphics 3D computer graphics Television terminology Video Video signal
 In
In computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great de ...
, rasterisation (British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadl ...
) or rasterization (American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances ...
) is the task of taking an image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensio ...
described in a vector graphics
Vector graphics is a form of computer graphics in which visual images are created directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves and polygons. The associated mechanisms may include vector display ...
format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (a series of pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes). The rasterized image may then be displayed on a computer display
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.
The ...
, video display or printer, or stored in a bitmap file format. Rasterization may refer to the technique of drawing 3D model
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of any surface of an object (inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, an ...
s, or the conversion of 2D rendering primitives such as polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed '' polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two ...
s, line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between i ...
s into a rasterized format.
Etymology
The term "rasterisation" comes .2D Images
Line primitives
Bresenham's line algorithm
Bresenham's line algorithm is a line drawing algorithm that determines the points of an ''n''-dimensional raster that should be selected in order to form a close approximation to a straight line between two points. It is commonly used to draw li ...
is an example of algorithm used to render a line.
Circle primitives
Algorithms such as Midpoint circle algorithm are used to render circle onto a pixelated canvas.3D images
Rasterization is one of the typical techniques of rendering 3D models. Compared with other rendering techniques such as ray tracing, rasterization is extremely fast and therefore used in most realtime 3D engines. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. The specific color of each pixel is assigned by a pixel shader (which in modern GPUs is completely programmable). Shading may take into account physical effects such as light position, their approximations or purely artistic intent. The process of rasterizing 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen (" screen space") is often carried out by fixed function (non-programmable) hardware within thegraphics pipeline
In computer graphics, a computer graphics pipeline, rendering pipeline or simply graphics pipeline, is a conceptual model that describes what steps a graphics system needs to perform to render a 3D scene to a 2D screen. Once ...
. This is because there is no motivation for modifying the techniques for rasterization used at render time and a special-purpose system allows for high efficiency.
Triangle rasterization
 A common representation of digital 3D models is polygonal. Before rasterization, individual polygons are broken down into triangles, therefore a typical problem to solve in 3D rasterization is rasterization of a triangle. Properties that are usually required from triangle rasterization algorithms are that rasterizing two adjacent triangles (i.e. those that share an edge)
# leaves no holes (non-rasterized pixels) between the triangles, so that the rasterized area is completely filled (just as the surface of adjacent triangles). And
# no pixel is rasterized more than once, i.e. the rasterized triangles don't overlap. This is to guarantee that the result doesn't depend on the order in which the triangles are rasterized. Overdrawing pixels can also mean wasting computing power on pixels that would be overwritten.
This leads to establishing rasterization rules to guarantee the above conditions. One set of such rules is called a top-left rule, which states that a pixel is rasterized if and only if
# its center lies completely inside the triangle. Or
# its center lies exactly on the triangle edge (or multiple edges in case of corners) that is (or, in case of corners, all are) either ''top'' or ''left'' edge.
A ''top'' edge is an edge that is exactly horizontal and lies above other edges, and a ''left'' edge is a non-horizontal edge that is on the left side of the triangle.
This rule is implemented e.g. by
A common representation of digital 3D models is polygonal. Before rasterization, individual polygons are broken down into triangles, therefore a typical problem to solve in 3D rasterization is rasterization of a triangle. Properties that are usually required from triangle rasterization algorithms are that rasterizing two adjacent triangles (i.e. those that share an edge)
# leaves no holes (non-rasterized pixels) between the triangles, so that the rasterized area is completely filled (just as the surface of adjacent triangles). And
# no pixel is rasterized more than once, i.e. the rasterized triangles don't overlap. This is to guarantee that the result doesn't depend on the order in which the triangles are rasterized. Overdrawing pixels can also mean wasting computing power on pixels that would be overwritten.
This leads to establishing rasterization rules to guarantee the above conditions. One set of such rules is called a top-left rule, which states that a pixel is rasterized if and only if
# its center lies completely inside the triangle. Or
# its center lies exactly on the triangle edge (or multiple edges in case of corners) that is (or, in case of corners, all are) either ''top'' or ''left'' edge.
A ''top'' edge is an edge that is exactly horizontal and lies above other edges, and a ''left'' edge is a non-horizontal edge that is on the left side of the triangle.
This rule is implemented e.g. by Direct3D
Direct3D is a graphics application programming interface (API) for Microsoft Windows. Part of DirectX, Direct3D is used to render three-dimensional graphics in applications where performance is important, such as games. Direct3D uses hardware ...
and many OpenGL implementations (even though the specification doesn't define it and only requires a consistent rule).
Quality
See also
* Font rasterization * Sub-pixel resolution * Image tracing * Hidden surface determination *Bresenham's line algorithm
Bresenham's line algorithm is a line drawing algorithm that determines the points of an ''n''-dimensional raster that should be selected in order to form a close approximation to a straight line between two points. It is commonly used to draw li ...
for a typical method in rasterization
* Scanline rendering for line-by-line rasterization
* Rendering (computer graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined ...
for more general information
* Graphics pipeline
In computer graphics, a computer graphics pipeline, rendering pipeline or simply graphics pipeline, is a conceptual model that describes what steps a graphics system needs to perform to render a 3D scene to a 2D screen. Once ...
for rasterization in commodity graphics hardware
* Raster image processor
A raster image processor (RIP) is a component used in a printing system which produces a raster image also known as a bitmap. Such a bitmap is used by a later stage of the printing system to produce the printed output. The input may be a page d ...
for 2D rasterization in printing systems
* Vector graphics
Vector graphics is a form of computer graphics in which visual images are created directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves and polygons. The associated mechanisms may include vector display ...
for the source art
* Raster graphics
upright=1, The Smiley, smiley face in the top left corner is a raster image. When enlarged, individual pixels appear as squares. Enlarging further, each pixel can be analyzed, with their colors constructed through combination of the values for ...
for the result
* Raster to vector for conversion in the opposite direction
* Triangulated irregular network
In computer graphics, a triangulated irregular network (TIN) is a representation of a continuous surface consisting entirely of triangular facets (a triangle mesh), used mainly as Discrete Global Grid in primary elevation modeling.
The ve ...
, a vector source for topography data, often rasterized as a (raster) digital elevation model.
* Display list
References
External links
Michael Abrash’s articles on computer graphics
{{Graphics Processing Unit Shading Computer graphics 3D computer graphics Television terminology Video Video signal