psychoactive plant on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactivity may include
Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactivity may include
Erowid – Psychoactive Plants & Fungi
{{Authority control Herbal and fungal hallucinogens
 Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactivity may include
Psychoactive plants are plants, or preparations thereof, that upon ingestion induce psychotropic effects. As stated in a reference work:
Psychoactivity may include sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but ...
, stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
, euphoric, deliriant, and hallucinogenic effects.
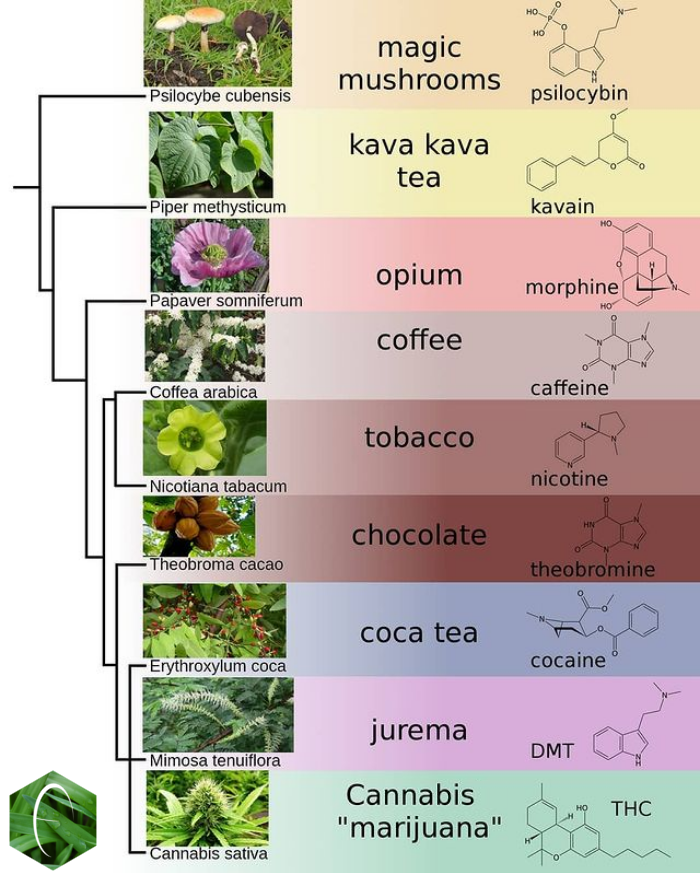
Several hundred psychoactive plants are known.
Some popular examples of psychoactive plants include ''Coffea arabica
''Coffea arabica'' (), also known as the Arabic coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is believed to be the first species of coffee to have been cultivated and is currently the dominant cultivar, ...
'' (coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world.
Seeds of ...
), ''Camellia sinensis
''Camellia sinensis'' is a species of evergreen shrub or small tree in the flowering plant family Theaceae. Its leaves and leaf buds are used to produce the popular beverage, tea. Common names include tea plant, tea shrub, and tea tree (not t ...
'' ( tea), ''Nicotiana tabacum
''Nicotiana tabacum'', or cultivated tobacco, is an annually grown herbaceous plant of the ''Nicotiana'' genus. The plant is tropical in origin, is commonly grown throughout the world, and is often found in cultivation. It grows to heights be ...
'' (tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
), and ''Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
'' (including hashish
Hashish ( ar, حشيش, ()), also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds (female flowers) containing the most trichomes. European Monitoring ...
).
Psychoactive plants have been used ritually (''e.g.'', peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains Psychoactive cactus, psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar Pupa#Cocoo ...
as an entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoac ...
), medicinally (''e.g.'', opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy '' Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which ...
as an analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
), and therapeutically (''e.g.'', cannabis as a drug) for thousands of years. Hence, the sociocultural and economic significance of psychoactive plants is enormous.
Examples of psychoactive plants
In the table below, a few examples of significant psychoactive plants and their effects are shown. For further examples, see List of psychoactive plants.Botanical taxonomy
Botanical taxonomy delimits groups of plants and describes and names taxa based on these groups to identify other members of the same taxa. The circumscription of taxa is directed by the principles of classification, and the name assigned is governed by a code of nomenclature. In the plant kingdom ( Plantae), almost all psychoactive plants are found within theflowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants t ...
s (angiosperms).
There are many examples of psychoactive fungi
This is a list of psychoactive plants, fungi, and animals.
Plants
Psychoactive plants include, but are not limited to, the following examples:
* ''Cannabis'': cannabinoids
* Tobacco: nicotine and beta-carboline alkaloids
* Coca: cocaine
* O ...
, but fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately fr ...
are not part of the plant kingdom.
Some important plant families containing psychoactive species are listed below. The listed species are examples only, and a family may contain more psychoactive species than listed.
Phytochemistry
Phytochemistry
Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human an ...
is the study of phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are chemical compounds produced by plants, generally to help them resist fungi, bacteria and plant virus infections, and also consumption by insects and other animals. The name comes . Some phytochemicals have been used as pois ...
, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeably with "terpenes" ...
. Active constituents of the majority of psychoactive plants fall within the alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar ...
(''e.g.'', nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
, morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
, mescaline
Mescaline or mescalin (3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine) is a naturally occurring psychedelic protoalkaloid of the substituted phenethylamine class, known for its hallucinogenic effects comparable to those of LSD and psilocybin.
Biological ...
, caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
, ephedrine), a class of nitrogen-containing natural products. Examples of psychoactive compounds of plant origin that do not contain nitrogen are tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC' ...
(a phytocannabinoid from '' Cannabis sativa'') and salvinorin A (a diterpenoid from ''Salvia divinorum
''Salvia divinorum'' (Latin: "sage of the diviners"; also called ska maría pastora, seer's sage, yerba de la pastora, magic mint or simply salvia) is a plant species with transient psychoactive properties when its leaves are consumed by che ...
'').
See also
References
External links
Erowid – Psychoactive Plants & Fungi
{{Authority control Herbal and fungal hallucinogens